Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Theory of Structure 1
Hochgeladen von
Anil ThapaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Theory of Structure 1
Hochgeladen von
Anil ThapaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np what is the corresponding stress and the value of the unknown weight.
Take E = 2105 N/mm2. [12] [a] Explain about non-linearity in structural behavior. [4] [b] Determine the common equation for slope and deflection of simply supported beam loaded as show in Fig [2]. Calculate the slope at C and deflection at D of the beam. [12]
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY
IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002
LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG257CI,Theory of Structure-I TIME: 03:00 hrs Full Marks: 80 Pass marks: 32
Q.
[3]
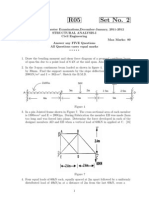
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks. Attempt any FIVE questions. Q. [1] Determine the vertical deflection of point 3 if (a) truss is loaded as shown in Fig[1](b) member 2.4 is subjected to temperature 20oC more than other member (c) find the total required adjustment of member 1-3 and 3-5 to get zero deflection at point 3. Area of members are A = 500mm2 , E = 2105 N/mm2 and = 1210-6 per oC. [16]
Q.
[4]
By using the ILD find the maximum SF and BM at 5m right point of beam along which three loads are moving shown in Fig. [3] [16]
Q.
[2]
[a] Explain difference between real and virtual work with sketches. [4] [b] An unknown weight falls through 100mm on a collar rigidly attached to the lower end of a vertical bar 3 meters long and 100 mm2 in cross-section. If the maximum instantaneous extension is known to be 4mm,
Q.
[5]
[a] Draw the influence lines for the bars 2-3, 3-7 and 8-7 of truss as shown in Fig. [4]. [16]
1 Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Q.
[6]
Find horizontal reaction, normal thrust, radial shear and bending moment at a section 15m form a left hand support of three hinged parabolic arch loaded as shown in Fig. [5] [16]
Q.
[7]
A suspension bridge with a three hinged stiffening girder has a span of 100m, a central dip of 5m and total dead weight 2000kN. It has to carry a live load of 40kN/m. Calculate the maximum tension and sectional area of cables required if the permissible stress is 120N/mm2. The live load covers half of right span. [16]
2 Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np [b] A beam AB is shown in fig 2[b]. Determine the deflection of beam at mid point by using Macaulays method. [8]
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY
IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2003
LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG257CI,Theory of Structure-I TIME: 03:00 hrs Full Marks: 80 Pass marks: 32
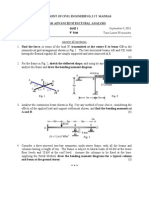
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks. The marks allotted for each sub-question is specified along its side. Attempt any FIVE questions. Q. Q. [1] [a] Determine the vertical deflection of the joint E of the truss shown in Fig. [1]. Area of each member is 1000 mm2 youngs modulus E = 200KN/m2 if the temperature of bottom chord members AE and EF goes up by 20oC, what will be the additional deflection of joint E? Given = 1210-6 /oC. If the diagonal members are 5mm to short before fabrication what will the deflection of joint E due to lack of fit? [16] [3] [a] Draw the I.L.D for shear force and bending moment at a distance 7m form left support for panel loading shown in fig. 3[a]. [8]
Q.
[2]
[a] Find the central deflection at D of the uniform bend shown in Fig. 2[a] using strain energy method. [Take E [8] = 200kN/mm2 and I = 30105 mm4]
3 Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np [b] An uniformly distributed load of span 3m shown in Fig. 3[b] roll along beam of span 10m. Find the maximum bending moment which can occurs at a section 6 meter form left support. [8]
Fig. 5[b]
Q. [a] Draw influence lien diagram for a force in the member u3, u4, u3 L3, L3 L4 and u3 L3 of the truss shown in Fig. [4]. [16]
[6]
Q.
[4]
A cord ACDEFB is supported at the ends of A and B. Support B is 6.5m high form level of A and point D is 8m below the level of A. The loads of 40KN, 20KN, 30kN, 10kN are acting at C, D, E and F as shown in Fig. [6] Determine: [i] reaction at the supports, [ii] The tension in different parts of the cord and [iii] the total length of the cord. [16]
Q.
[5]
[a] What is difference between arch and cable?
[4]
[b] A three hinged arch consisting of two quadrantal parts; AC and CB of radii 2m and 4m respectively. For the load system acting on the arch calculate the reactions at the supports and the bending moment under load at D and E. [12] 4 Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY
IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2004
LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG257CI,Theory of Structure-I TIME: 03:00 hrs Full Marks: 80 Pass marks: 32
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks. The marks allotted for each sub-question is specified along its side. Attempt any FIVE questions. Q. [1] Find the downward deflection of the end C due to bending of beam ABC and axial tension of wire BD. The applied force of 25KN in the structure shown in fig. [1]. ABC is the RCC beam of 200mm width and 400mm depth in section. BD is a steel wire of 10mm in diameter. Neglect the deflection caused by shear. Take modulus of elasticity E =7107 KN/m2. [16] [a] An unknown weight falls through 15mm on a collar rigidity attached to the lower end of a vertical bar 4 meter long and 800mm2 in section. If the maximum extension of the rod is to be 2mm, what is the corresponding stress and magnitude of unknown weight? [8] [b] A moving load of 20kN/m, 8 meter long moves on a simply supported girder of span 15 meter form left end to right end. Find the maximum shear forces and maximum bending moment which can occur at a section 5 meter form left end. [8]
Q.
[3]
Q.
[4]
[a] What is the main advantage of three hinged arch compare with a beam of the same span and carrying the same load system? [4] [b] For a beam of length 6 meter simply supported at ends and carrying a UDL of 5KN/m, find the slope at left support and mid span deflection if right end of the beam sinks by 5mm relative to left end. Take E =2104N/mm2 and I = 1.07109 mm4. (Use integration method). [12] Draw influence line diagram for the given members U2U3, L1L2 and U3L2 of deck type truss given in Fig.[4]. [16]
Q.
[2]
L3 L4
Q. [5] [a] How can you convert a conjugate beam from a real beam? Explain with an example. [4] [b] A three hinged parabolic arch of span 32m and central rise 6m. It carries a uniformly distributed load 30KN/m over the left half of the span together with a concentrated load of 80KN at 8m from the right end. Find the bending moment, normal thrust and shear at 5
Figure
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np section X 8 from the left support.
30 30
[12]
Fig. 5[b]
Q.
[6]
[a] Discuss about linear and non-linear design of a structure. [4] [b] A three hinged stiffened girder of suspension bridge of span 300 is subjected to two point loads of 300KN and 500KN acting at 60m and 120m respectively form left end support. The supporting cable has a central deep of 30m. Analyze and draws the bending moment diagram for the girder. [12]
6 Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np Compare the strain energy when the beam is loaded axially by load W. If the ration of length of the beam to depth is 6. [b] Explain real work and virtual work with example. [4] [a] Write the two theorem of conjugate beam method. [4] [b] For the beam shown in figure below, determine midspan and maximum deflection. [12]
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY
IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2005
LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG257CI,Theory of Structure-I TIME: 03:00 hrs Full Marks: 80 Pass marks: 32
Q.
[3]
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. Assume necessary data if required. The figure in the margin indicates full marks. The marks allotted for each sub-question is specified along its side. Attempt any FIVE questions. Q. [1] A truss as shown below is hinged at support A and placed on rollers at support C. The plane of the roller bed is inclined at 450 to the horizontal and the end C can only move in the plane of the roller bed. The truss is loaded at joint B with a load of 5000N. The truss is loaded at joint B with a load of 5000 N. The cross sectional area of all members is 90cm2 each and the value of E is 2105 N/cm2. Calculate the vertical deflection of joint B and the movement of joint C along the roller bed.
Q.
[4]
The structure shown in figure consists of two simply supported girders AB and BC, of effective spans of 20m each, and two supporting members DB and BE pinned at D, B and E. Draw the influence line of S.F and B.M at the quarter point of span AB and stress in the support DB. Calculate the maximum values for the above when the live load shown crosses the span AC. The load is reversible. [16]
Q.
[2]
[a] Show the strain energy U due to bending of beam of a rectangular section simply supported of the ends with a concentrated load W at the centre can be expressed as U = /..volume of beam. Where is the bending stress in the beam and E is the youngs modulus.
Q.
[5]
[a] What is the advantage of using an..simple 7
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np beam? [b] A three hinged parabolic arch has span of ..m and a central rise of 4m. Five wheel load3 and 2.5 KN spaced 1,1.5,1 and 1.5m in order , cross the arch form left to right with the 2KN load leading. When the leading load is 12.5m from the left hand hinge, calculate the horizontal thrust in the arch. Calculate the bending moments, normal thrust and shear force at the section under the tail load. [12] [a] Define and classify non-linearity in structural analysis and explain it briefly. [4] [b] A cable is used to support five equl and equidistant loads over a spa of 60m. Find the length of cable required and its sectional area if the safe tensile stress si 140N/mm2. The central dip of the cable is 5m and the loads are 10KN each. [12]
Q.
[6]
8 Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY
IV SEMESTER BACK-PAPER EXAMINATION-2005
LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG257CI,Theory of Structure-I TIME: 03:00 hrs Full Marks: 80 Pass marks: 32
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks. The marks allotted for each sub-question is specified along its side. Attempt any FIVE questions. Q. [1] Find the vertical displacement of joint H of pin-jointed H of pin-jointed truss loaded as shown in fig.[1]. Bottom boom member has decrease of temperature 20oC with compare to others. Find the adjustment at top boom member if to make vertical deflection at H =0. [Take A =600mm2, E = 2105 N/mm2, = 10.8106 o / C] [16] Q. [3] [a] Explain the difference between the arch and simple beam. [4] [b] Find the slope at support A and deflection at B beam as shown in Fig. 3[b] using Moment Area OR Conjugate Beam method. [12] [b] Using the influence line diagram find the maximum S.E and at point C as shown in Fig. 2[b]. [3]
Q.
[2]
[a] Find the instantaneous maximum deflection and bending stress for 100mm100mm steel beam shown in fig 2[a] struck by a 500N load falling form height 300mm above the top beam if [a] beam is on supports and [b] the beam is supported at each end spring. [Take k of spring = 350000 N/mm and E = 2105 N/mm2] [8] 9 Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np Q. [4] Draw the influence line diagram of member U3-U4, L3 U3 and L4-L5 of the truss as shown in fig. [4]. [16]
Q.
[5]
[a] Explain the integration method of finding the deflection. [4] [b] Find the normal thrust, radial shear and bending moment at point k of parabolic arch loaded as shown in Fig. 5[b]. [12]
Q.
[6]
[a] Explain principal and method of virtual work. [4] [b] A suspension bridge with a three-hinged stiffening girder has a span of 120m with a central deep 10m. It has to carry 30K/m dead load and 50kN/m live load. Calculate the maximum tension of cable, its crosssectional area if the permissible stresses of cable is 120N/mm2. [12]
10 Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- University of ZimbabweDokument6 SeitenUniversity of ZimbabweTynash NyakatsapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination SEMESTER 1 2014 / 2015Dokument8 SeitenCollege of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination SEMESTER 1 2014 / 2015Muhd Aidil ZuhairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerospace Vehicle Structures AnalysisDokument8 SeitenAerospace Vehicle Structures AnalysisYsharath ChandramouliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis Exam PapersDokument3 SeitenStructural Analysis Exam Papersfesada1100% (1)
- TCW1101200904 Engineering Mechanics I StaticsDokument6 SeitenTCW1101200904 Engineering Mechanics I StaticsTanaka MurekachiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Tech (Civil) - 1-CV4009 (2020-21)Dokument3 SeitenB.Tech (Civil) - 1-CV4009 (2020-21)Himanshu BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEMB123 Final Examination Paper Sem 2-09-10 FinalDokument6 SeitenMEMB123 Final Examination Paper Sem 2-09-10 FinalMei QiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mace 60035Dokument7 SeitenMace 60035eng_ayman_H_MNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUS Faculty of Engineering Exam for Precast Concrete TechnologyDokument11 SeitenNUS Faculty of Engineering Exam for Precast Concrete TechnologyYu Tian LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVEN3302 - Final Examination 2009Dokument5 SeitenCVEN3302 - Final Examination 2009fflegendsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics 2078Dokument2 SeitenApplied Mechanics 2078RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis 1Dokument7 SeitenStructural Analysis 1devarani93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ahmedabad Center-9Dokument3 SeitenAhmedabad Center-9RenieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bhm1123-Mechanics of Materials 11415Dokument7 SeitenBhm1123-Mechanics of Materials 11415MysteryNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAA 2113 - Theory of Structure Final Exam PaperDokument7 SeitenBAA 2113 - Theory of Structure Final Exam PaperAzil14100% (1)
- Advanced Structural AnalysisDokument24 SeitenAdvanced Structural Analysisbhkedar0% (1)
- JNTUH B.Tech II Year I Semester Mechanics of Solids Exam QuestionsDokument3 SeitenJNTUH B.Tech II Year I Semester Mechanics of Solids Exam Questionsmahendra babu mekalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce 1303 & Structural Analysis - IDokument14 SeitenCe 1303 & Structural Analysis - Ibaratkumr100% (1)
- ENGM031Dokument5 SeitenENGM031YHTRTRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis Shear Force and Bending Moment DiagramsDokument29 SeitenStructural Analysis Shear Force and Bending Moment DiagramsCt Kamariah Md SaatNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVEN3302 Final Exam S2 2012Dokument5 SeitenCVEN3302 Final Exam S2 2012Avinash SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADS Super Important Tie (1) PDFDokument6 SeitenADS Super Important Tie (1) PDFHêmãñth RâkåràddîNoch keine Bewertungen
- JNTU BTech Civil Engineering Advanced Structural Analysis Exam QuestionsDokument19 SeitenJNTU BTech Civil Engineering Advanced Structural Analysis Exam QuestionsMohammed AbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS MODEL QUESTION PAPERDokument7 SeitenSTRUCTURAL ANALYSIS MODEL QUESTION PAPERreynanbelendhran23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological University: Subject Code: 130604 Subject Name: Structural Analysis-1Dokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological University: Subject Code: 130604 Subject Name: Structural Analysis-1harnishtanna21285Noch keine Bewertungen
- IES Civil Engineering Conventional Paper 2014Dokument27 SeitenIES Civil Engineering Conventional Paper 2014mantuiitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Define Factor of SafetyDokument3 SeitenDefine Factor of SafetySunil AdhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MayJune - 2019Dokument3 SeitenMayJune - 2019AYRUSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3804Dokument8 Seiten3804Mukesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDokument7 SeitenDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sa-I QP PDFDokument19 SeitenSa-I QP PDFmythilispd_355305156Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mech2610 Lab Guidance - 2022 orDokument5 SeitenMech2610 Lab Guidance - 2022 orpofessor HammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT Madras Civil Engineering Quiz on Advanced Structural AnalysisDokument1 SeiteIIT Madras Civil Engineering Quiz on Advanced Structural AnalysisRK MEHTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Steel Structures and ComponentsDokument3 SeitenDesign of Steel Structures and ComponentsManish Shashikant DharekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 ME Som Model Examination 2013Dokument3 Seiten4 ME Som Model Examination 2013BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Structures PDFDokument4 SeitenTheory of Structures PDFfrancis dimakilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Memb243 Mom Final Semi 15-16Dokument7 SeitenMemb243 Mom Final Semi 15-16Malik Ismail100% (1)
- 9A01709 Advanced Structural AnalysisDokument8 Seiten9A01709 Advanced Structural AnalysissivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Exam-Ii Question BankDokument3 SeitenMid Exam-Ii Question BankKrishna Murthy100% (1)
- Strength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDokument2 SeitenStrength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartnvnrevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of SolidsDokument8 SeitenMechanics of SolidsKhaista RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce2302 QBDokument17 SeitenCe2302 QBRamesh Thangamani100% (1)
- Advanced Structural AnalysisDokument9 SeitenAdvanced Structural AnalysisYeswanth RaghavendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis-I-Summer-13Dokument2 SeitenStructural Analysis-I-Summer-13harnishtanna21285Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9A 01403 Structural Analysis - IDokument8 Seiten9A 01403 Structural Analysis - Isivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- MechanicsDokument9 SeitenMechanicsHarshal Dengle100% (1)
- Beams in bending: Tension cracks and stress diagramsDokument23 SeitenBeams in bending: Tension cracks and stress diagramsHarold Jackson MtyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of SolidsDokument9 SeitenMechanics of SolidsSrikanth GogineniNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOS I Schem Model Answer PaperDokument6 SeitenTOS I Schem Model Answer Paperirshadmirza753Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 6 BendingDokument4 SeitenTutorial 6 BendingKishenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDokument8 SeitenDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sab 3233Dokument13 SeitenSab 3233xperia30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of MaterialsDokument3 SeitenStrength of MaterialsPujan NeupaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDokument8 SeitenDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument2 SeitenAssignmentAthiyo MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Principles and Variational Methods in Applied MechanicsVon EverandEnergy Principles and Variational Methods in Applied MechanicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Designer JobDokument1 SeiteStructural Designer JobDina AvdićNoch keine Bewertungen
- (18044824 - Transactions of The VŠB - Technical University of Ostrava, Civil Engineering Series.) NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF CASTELLATED BEAMDokument7 Seiten(18044824 - Transactions of The VŠB - Technical University of Ostrava, Civil Engineering Series.) NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF CASTELLATED BEAMShinichi KudoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creep of ConcreteDokument2 SeitenCreep of ConcreteAnjali AnjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Assessment of Steel Railway Bridges PDFDokument15 SeitenEngineering Assessment of Steel Railway Bridges PDFNguyen Viet KhoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minutes of Special Meeting No 5 - 5 October 2019Dokument5 SeitenMinutes of Special Meeting No 5 - 5 October 2019Bianca SamaleaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Beams With Web OpeningsDokument17 SeitenSteel Beams With Web OpeningspestfariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Bridges NicholsonDokument94 SeitenSimple Bridges Nicholsonfarhaad shaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 2.5m Thick Cement Concrete 1:1/1.5:3 Damp Proof Course (DPC)Dokument7 Seiten3 2.5m Thick Cement Concrete 1:1/1.5:3 Damp Proof Course (DPC)NATIONAL XEROXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Superstructure Slab BeamDokument33 SeitenSuperstructure Slab BeamVenkata MayurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade beam design calculation summaryDokument3 SeitenGrade beam design calculation summaryArnold VercelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Basements & Cut & Cover - 2Dokument113 SeitenDeep Basements & Cut & Cover - 2bsitler100% (2)
- Cofraje PT Stalpi PDFDokument16 SeitenCofraje PT Stalpi PDFSerban MihaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimate PDFDokument3 SeitenEstimate PDFAnu PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IUST v9n4p611 en PDFDokument18 SeitenIUST v9n4p611 en PDFmehdi taheriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slump TestDokument6 SeitenSlump TestAngel MouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Public Works and Highways: Region VDokument11 SeitenDepartment of Public Works and Highways: Region VMarianne Jocel CostacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composition Book: Edificio Polifunzionale. Studio Passarelli.Dokument29 SeitenComposition Book: Edificio Polifunzionale. Studio Passarelli.Maria Camila Rodriguez0% (1)
- Details - WF Wall Footing Masonry Details: CHB To Slab-On-Grade End DetailsDokument1 SeiteDetails - WF Wall Footing Masonry Details: CHB To Slab-On-Grade End Detailsacurvz2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8th DH Errata PDFDokument10 Seiten8th DH Errata PDFClaudioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparitive Design Study BS8110 Vs EC2Dokument127 SeitenComparitive Design Study BS8110 Vs EC2DaGoose81100% (1)
- Intro Well FoundationDokument23 SeitenIntro Well FoundationgoutammandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Flat Slab with Reinforcement DetailsDokument8 SeitenDesign of Flat Slab with Reinforcement DetailsMeganathan Mega100% (1)
- Teaching Reinforced Concrete Design With Mathcad ApplicationDokument18 SeitenTeaching Reinforced Concrete Design With Mathcad ApplicationJames100% (1)
- BLDG-section Chua 02Dokument1 SeiteBLDG-section Chua 02leslieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typ. Ductile Moment Frame Girder Detail 4: Schedule of Footing BeamDokument1 SeiteTyp. Ductile Moment Frame Girder Detail 4: Schedule of Footing Beammichael saycoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trade License - DubaiDokument4 SeitenTrade License - DubaiArhaan shakilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Tension MemberDokument37 SeitenDesign of Tension MemberTariq HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Introduction To Prestressed ConcreteDokument19 SeitenModule 1 Introduction To Prestressed ConcreteDastardly HeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrusSteel - Truss Design Manual (2017) PDFDokument78 SeitenTrusSteel - Truss Design Manual (2017) PDFgrahambrasicNoch keine Bewertungen