Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Blood Vessels Lab F11
Hochgeladen von
Kelly TrainorOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Blood Vessels Lab F11
Hochgeladen von
Kelly TrainorCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
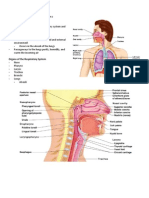
BIO 202 Blood Vessels Lab Goals for this activity: Identify the main arteries and veins of the body by locating them on diagrams or the cadaver Describe the route of blood flowing through vessels for various parts of the body Identify the primary histological structures of blood vessels Collect heart rate and blood pressure data during various activities and develop graphs showing the results Identify the Following: Great vessels of the heart Aorta o Big artery leaving the left side of the heart. Aortic Arch (3 arteries extending from the arch) o The three arteries are listed from proximal to distal in reference to the heart. Brachiocephalic artery going to the right side, will split and go to arm & head Left Common Carotid Artery going up to the head Left Subclavian Artery - going to the left arm Major veins of thorax Right / Left Brachiocephalic veins returning from head and arms Left Subclavian Vein coming from arm Superior Vena Cava Inferior Vena Cava Neck Arteries & Veins Common Carotid artery main artery going to skull and brain Bifurcation splits common carotid into internal & external carotid artery External & Internal Jugular vein located more superficially than carotid arteries. Upper Arm Arteries & Veins Axillary artery/vein armpit area Brachial artery/vein upper arm area (same artery as axillary, just more distal) Radial artery/vein along radius (thumb-side of the forearm) **pulse point Ulnar artery/vein along ulna (pinky-side of the forearm) Abdominal / Pelvic Arteries & Veins Descending Aorta Abdominal Aorta & Inferior Vena Cava Celiac trunk (3 arteries) hepatic (liver), left gastric (stomach), splenic (spleen) Hepatic portal vein going to liver Renal artery/vein going to kidneys Common Iliac artery/vein travels up / down each leg External/Internal iliac artery/vein Leg (Thigh) Arteries & Veins Femoral artery/vein thigh Popliteal artery/vein behind knee Great Saphenous vein main vein used for coronary bypass, located superficially Lower Leg Arteries & Veins Anterior & Posterior tibial artery/vein
Activity: Questions to Answer: The big arteries in the neck are called the: The big veins in the neck are called the: Where does the aorta end? What huge vein runs next to the aorta? Under each collar bone is an artery called the: In each armpit is an artery called the: In each upper arm is an artery called the: Parts of the great saphenous veins are cut out and used for cardiac bypass surgery. Where are the great saphenous veins? Circulatory Routes: Write the numbers 2-12 in the blanks to show the blood vessel route from the heart to one of the toes then back to the heart. __1_ heart's left side ____ femoral artery ____ external iliac artery ____ aorta ____ common iliac artery ____ anterior tibial artery __7_ toe's capillaries ____ inferior vena cava ____ femoral vein ____ anterior tibial vein ____ external iliac vein ____ common iliac vein _13_ heart's right side Follow the path a drop of blood would take, starting from the left ventricle to the site specified below, and back to the right ventricle. Stomach Right thumb Left toe Quadriceps Kidney
Vessel Histology: Artery - 3 layers tunica intima endothelium, one cell layer next to the lumen (space for blood), connective tissue and elastin tunica media smooth muscle with elastin fibers tunica adventitia outermost layer of artery made of connective tissue Nerve bundles next to artery Vein The veins are not usually round like the arteries as they are collapsed from the slide preparation. 3 layers (same as the artery but the layers are much thinner) Atherosclerosis This is the development of a mass under the endothelium that protrudes into the lumen and will eventually stop blood flow and result in a heart attack when it occurs in a coronary artery.
Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Determination: The heart rate is the number of times the heart beats per minute. You can do this by counting the number of beats in15 seconds and multiplying that number by 4 to get the number per minute. My heart rate is: Stethescope My blood pressure is: Systolic Diastolic Palpatation
Effect of Posture on Blood Pressure & Heart Rate: Lying down Measure the heart rate after lying down relaxed (not sleeping!); head lower than heart. Lying Down Heart Rate Lying Down Blood Pressure
Immediate Standing Have the subject hold onto something in case he/she gets dizzy! Standing Heart Rate Standing Blood Pressure
Effect of Exercise on Blood Pressure & Heart Rate: Static Exercise Do 10 squats (slow and deep) then measure the heart rate and blood pressure. Measure the heart rate and blood pressure every minute for 4 minutes after exercise Blood Pressure Pre-Exercise Post-Exercise 1-min Post-Ex 2-min Post-Ex 3-min Post-Ex 4-min Post-Ex Heart Rate Pre-Exercise Post-Exercise 1-min Post-Ex 2-min Post-Ex 3-min Post-Ex 4-min Post-Ex
Dynamic Exercise Walk briskly around the courtyard and up the stairs then around the courtyard again. This is to get your heart going and increase your blood flow in a different way than the static exercise of the squats. Measure the heart rate and blood pressure every minute for 4 minutes after exercise. Chart your heart rate and blood pressure changes on the graph shown. Blood Pressure Pre-Exercise Post-Exercise 1-min Post-Ex 2-min Post-Ex 3-min Post-Ex 4-min Post-Ex Heart Rate Pre-Exercise Post-Exercise 1-min Post-Ex 2-min Post-Ex 3-min Post-Ex 4-min Post-Ex
preexercise
postexercise
1-min after exercise
2-min after exercise
3-min after exercise
4-min after exercise
preexercise
postexercise
1-min after exercise
2-min after exercise
3-min after exercise
4-min after exercise
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Handouts Immune Defenses F11Dokument12 SeitenHandouts Immune Defenses F11Kelly Trainor100% (1)
- Cadaver Images For Exam IVDokument2 SeitenCadaver Images For Exam IVKelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fetal Pig DissectionDokument3 SeitenFetal Pig DissectionKelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts Lymphatic System F11Dokument7 SeitenHandouts Lymphatic System F11Kelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 201 Upper Limbs Muscles of The Upper Limbs Brachial PlexusDokument5 SeitenBIO 201 Upper Limbs Muscles of The Upper Limbs Brachial PlexusKelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts Upper Limbs Bones Sp11Dokument3 SeitenHandouts Upper Limbs Bones Sp11Kelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts - Urinary System Sp11 BIO 160Dokument7 SeitenHandouts - Urinary System Sp11 BIO 160Kelly Trainor100% (2)
- Lower Limb Lab SheetDokument3 SeitenLower Limb Lab SheetKelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts Upper Limbs Bones Sp11Dokument3 SeitenHandouts Upper Limbs Bones Sp11Kelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 201 Upper Limbs Muscles of The Upper Limbs Brachial PlexusDokument5 SeitenBIO 201 Upper Limbs Muscles of The Upper Limbs Brachial PlexusKelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 160 The Respiratory System - Part I ObjectivesDokument9 SeitenBIO 160 The Respiratory System - Part I ObjectivesKelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscles of The Head Neck and Trunk - HandoutsDokument5 SeitenMuscles of The Head Neck and Trunk - HandoutsKelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts - Digestive System Sp11Dokument6 SeitenHandouts - Digestive System Sp11Kelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Senses Lab SheetDokument3 SeitenSpecial Senses Lab SheetKelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory Receptors HandoutsDokument2 SeitenSensory Receptors HandoutsKelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Mastering Temporary Invasive Cardiac Pacing: ClinicalDokument8 SeitenMastering Temporary Invasive Cardiac Pacing: ClinicaldenokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sports Science and NutritionDokument40 SeitenSports Science and NutritionMuthu KumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 4 Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument4 SeitenActivity 4 Anatomy and PhysiologySarah Jane MaganteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checking Vital Sign: Group 4Dokument20 SeitenChecking Vital Sign: Group 4Dwi Dian NitamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of The Circulatory SystemDokument47 SeitenEvolution of The Circulatory SystemWwwanand111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science - YEAR 8Dokument56 SeitenScience - YEAR 8Soh Mei LingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaesthesia in First Degree Atrioventricular Block: 37, Pages 1190-1 194Dokument5 SeitenAnaesthesia in First Degree Atrioventricular Block: 37, Pages 1190-1 194achmad mustikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan For COT First QuarterDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan For COT First QuarterJunnel Maravilla100% (1)
- Echocardiography in Fontan PhysiologyDokument30 SeitenEchocardiography in Fontan PhysiologyNavojit ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angina PectorisDokument33 SeitenAngina PectorisRosse Del MundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 Learning Guide Name: Brandon Au-Young: InstructionsDokument31 SeitenUnit 6 Learning Guide Name: Brandon Au-Young: InstructionsBrandonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spesifikasi-Alat-UM-Prosim 8 User Manual + SPO2 Module + YSIDokument6 SeitenSpesifikasi-Alat-UM-Prosim 8 User Manual + SPO2 Module + YSIBayu FebriandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg Mcqs - Aippg ForumDokument19 SeitenEcg Mcqs - Aippg Forumbmhsh100% (1)
- Patofisiologi ACSDokument48 SeitenPatofisiologi ACSImelva GirsangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pig Heart Dissection Lab Write UpDokument5 SeitenPig Heart Dissection Lab Write Upapi-94693850Noch keine Bewertungen
- STEP 1 ChecklistDokument11 SeitenSTEP 1 ChecklistHasan Khan RoudbaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- VPB 111Dokument3 SeitenVPB 111Dr-Ashok KeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology On ArrhythmiaDokument34 SeitenPathophysiology On ArrhythmiaYhr Yh100% (1)
- Anatomy of Spleen: Research TitleDokument8 SeitenAnatomy of Spleen: Research TitleOmar MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of Erectile Dysfunction As Explained in AyurvedaDokument25 SeitenCauses of Erectile Dysfunction As Explained in Ayurvedacharanmann9165Noch keine Bewertungen
- Activity On Circulatory SystemDokument2 SeitenActivity On Circulatory SystemChin CustodioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aksesories Total BionetDokument4 SeitenAksesories Total Bionetcicik wijayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCLT?Dokument5 SeitenDCLT?My selfNoch keine Bewertungen
- PracticeDokument212 SeitenPracticeMallela Venkata RajendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echo GuideDokument35 SeitenEcho GuideAdriana VillarrealNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7th Grade Natural Science Reinforcement WorksheetDokument3 Seiten7th Grade Natural Science Reinforcement WorksheetnataliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wellen's Syndrome: Mohan GameshDokument28 SeitenWellen's Syndrome: Mohan Gameshmyolie wuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test & Measurment CH 6Dokument22 SeitenTest & Measurment CH 6Harkirat SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- PericarditisDokument19 SeitenPericarditisxmitchxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Test - QuestionsDokument5 SeitenAnatomy Test - QuestionsNom NomNoch keine Bewertungen