Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Skeletal System Questions
Hochgeladen von
Elsada LawrenceOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Skeletal System Questions
Hochgeladen von
Elsada LawrenceCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 7 Skeletal System
Review Questions
1. The five functions of skeletal system 1. SUPPORT : Provide internal framework that supports the body. 2. PROTECTION : Protects internal organs and helps fight disease by producing white blood cells. 3. MOVEMENT : Makes movement possible 4. STORAGE : Stores calcium 5. HEMATOPOIESIS : the process of blood cell formation
2. The structures of the osteon also know as the haversian system is constructed of cylindrical units forming the hard shell of the compact bone. Each circular and tube like osteon is composed of calcified matrix arranged in multiple layers resembling the rings of an onion. Each ring is called lamella and surrounds the central canal. 3. The structure of cartilage also called chrondrocytes lacunae are suspended in the cartilage matrix much like air bubbles in a block of firm gelatin, because there is no blood vessels in cartilage nutrients must diffuse through the matrix to reach the cells and cause it to rebuild itself slowly after an injury. 4. The process of endochondral ossification, including the function of the osteoblasts and osteoclasts is the process of constantly remodeling a growing bone as it changes from a small cartilage model to the characteristic shape and proportion of the adult . 5. The epiphyseal plate is important for growth continuation of bones. 6. The bones of the axial skeleton, and the appendicular skeleton the bone of the skull, spine,and chest and the hyoid bone in the neck are in the axial skeleton. The bone of the upper extrimities represent the appendicular skeleton( shoulder, pectorial girdles, arms, wrists, and hands)and lower extremities are( hip, pelvic girdles legs ankles and feet).
7.
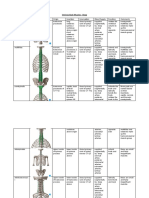
The vertebral column is divided into five sections 1. Cervical 7 vertebrae 2. Thoracic 12 vertebrae 3. Lumbar 5 vertebrae 4. Sacrum 1 vertebrae 5. Coccyx 1 vertebrae
8. The first seven pairs of ribs referred to as the true ribs are attached to the sternum The eight, ninth, and tenth pairs of ribs are sometimes called the false ribs. The last two ribs the eleventh and twelfth is not attached to any costal cartilage but float free in front which fit there names the floating ribs. 9. The synarthroses do not allow any significant movement , it is a joint in which fibrous connective tissue grows between the articulating bones holding them close together such as the joint between the cranial bones. 10.T he amphiarthrotic joint allow slight movement, it is a joint that cartilage connects the articulating bones such as the symphysis pubis the joint between the two pubic bones. 11.diarthrotic joint are vastly distributed in our bodies they allow considerable amount of movement they are made alike in many ways and they all have a joint capsule, joint cavity and a layer of cartilage over the end of two joining bones for example , the shoulder and hip joints, of all the joint in our bodies these permit the widest range of movement. 12.A joint capsule is made of the bodies strongest and toughest material ,fibrous tissue, and is lined with a smooth, slippery synovial membrane. 13.Open, closed and comminuted fractures , open fractures are fractures in which bone pierces the skin and invites the possibility of infection or osteomyelitis. Closed fractures are do not pierce the skin and so do not pose an immediate danger of bone infection. In comminuted fracture are breaks that produce many fragments. 14.Three types of arthritis . a. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that involves chronic inflammation of connective tissue, it begins in synovial membrane and spreads to cartilage and other tissue often causing severe crippling.
b. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease it is the most common noninflammatory disorder of moveable joints, abnormal formation of new bone spur at joint surfaces and degeneration of articular cartilage are characteristic features of osteoarthritis. c. Gouty arthritis is a metabolic condition in which uric acid, a nitrogenous waste increases in the blood. Excess uric is deposited as sodium urate crystals in distal joints and tissue.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- AANEM LEWorkbookDokument80 SeitenAANEM LEWorkbooknewguy927Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trauma Radiography EditdDokument107 SeitenTrauma Radiography Editdjustinjose08100% (2)
- Biomechanics of The Lumbar Spine: MalcolmDokument5 SeitenBiomechanics of The Lumbar Spine: MalcolmalbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSF AnalysisDokument12 SeitenCSF AnalysismedicoprakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNS Chaitow Book 2Dokument6 SeitenDNS Chaitow Book 2Milos DjuricNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banton BiomechanicsDokument9 SeitenBanton BiomechanicsIoan AndraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho Physiology of Spinal Cord InjuryDokument1 SeitePa Tho Physiology of Spinal Cord InjuryGenel Joseph Jacildo Peñaflor100% (2)
- Support and MovementDokument22 SeitenSupport and MovementAzrin MohayaddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap-21 Neural Control and CordinationDokument48 SeitenChap-21 Neural Control and CordinationMANIK CHHABRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Posterior Spinal Instrumentation: Presented By-Dr Prateek Randhawa (Resident) Guide - Dr. Mandar Borde (Asst. Prof)Dokument58 SeitenPosterior Spinal Instrumentation: Presented By-Dr Prateek Randhawa (Resident) Guide - Dr. Mandar Borde (Asst. Prof)chitturi yashwanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMS TensPainReliefGuide PDFDokument34 SeitenEMS TensPainReliefGuide PDFhola como estas100% (1)
- Identifying and Correcting Thoracic Spinal Flexion in The SquatDokument4 SeitenIdentifying and Correcting Thoracic Spinal Flexion in The SquatlangolierNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSC - RADIOLOGY Syllabus-7 ModulesDokument35 SeitenBSC - RADIOLOGY Syllabus-7 Modulesagoyal5145Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intrinsic Back Muscles - DeepDokument3 SeitenIntrinsic Back Muscles - DeepmkklmlkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Function of The BrainDokument16 SeitenFunction of The BrainJohn Matthew CrisostomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1351587407binder2Dokument34 Seiten1351587407binder2CoolerAdsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spinal Cord Injury: Causation & PathophysiologyDokument10 SeitenSpinal Cord Injury: Causation & Pathophysiologycpradheep100% (3)
- LuederActiveSittingProc NECE 2013Dokument5 SeitenLuederActiveSittingProc NECE 2013William VenegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maturation Manual Litopenaeus Vannamei (Aug2017)Dokument28 SeitenMaturation Manual Litopenaeus Vannamei (Aug2017)phymell vera100% (1)
- Sal or SarDokument5 SeitenSal or SarArgleydsson Mendes DurãesNoch keine Bewertungen
- IELTS Reading Practice Test 95 With Answers IELTS Training OnlineDokument1 SeiteIELTS Reading Practice Test 95 With Answers IELTS Training Onlineabdusalomova00Noch keine Bewertungen
- Porcine Meat StandardDokument27 SeitenPorcine Meat StandardoptimeatvaleriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Function of A Skeletal SystemDokument4 SeitenStructure and Function of A Skeletal Systemapi-280073172Noch keine Bewertungen
- Zen Intro To Buddhism & Practice of ZazenDokument33 SeitenZen Intro To Buddhism & Practice of ZazendudcomeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- lesson-PLAN of ScienceDokument5 Seitenlesson-PLAN of ScienceIrene Mae MosquedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retroperitoneal Approach To The Lumbar Spine UpdatedDokument14 SeitenRetroperitoneal Approach To The Lumbar Spine UpdatedAnonymous bUBXIFfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Various Physiological Changes Occur in The Pregnant WomanDokument2 SeitenVarious Physiological Changes Occur in The Pregnant WomanSharneel ShamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal System PDFDokument24 SeitenSkeletal System PDFJennifer LalondeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movement - Group 2 - BiologyDokument31 SeitenMovement - Group 2 - BiologyEjaz YusuffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaesthesia in The Prone PositionDokument19 SeitenAnaesthesia in The Prone Positionniketut tiniutamiNoch keine Bewertungen