Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Invertebrate Classification Key
Hochgeladen von
Heru Si HeroeOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Invertebrate Classification Key
Hochgeladen von
Heru Si HeroeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
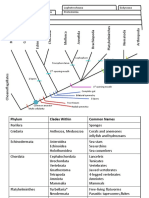
Classification Key
of common invertebrates of Australian freshwater bodies.
Sponges Hydras and Jellyfish
Phylum: Porifera Family: Spongillidae
Mat-like structure, spongy to touch, dull coloured. Very small or several metres long, depending on species, age and environment. Freshwater Mussels
Phylum: Cnidaria Order: Hydrozoa Kingdom: Animalia
May be free-floating or sessile, sexual or asexual, solitary or colonial, exhibit a range of body forms.
Primitive Worms
Class: Bivalvia
Shell consists of 2 separate valves hinged together. 3 families. Freshwater Snails
Phylum: Mollusca
Single large foot, hard calcareous resistant shell into which the animal may retreat.
Proboscis Worms
Phylum: Annelida
Elongate, segmented, lacking appendages, body wall soft and covered by thing cuticle.
Phylum: Nemertea
Horsehair Worms
Class: Gastropoda
A coiled or limpet-like shell from which a large foot protrudes. Creeps along substrate on surface of foot. 12 families. Water Mites
Phylum: Nematomorpha
Round Worms
Phylum: Nematoda Class: Polychaeta
Segmented Worms
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Bilateral symmetry, absence of distinct respiratory, circulatory and skeletal systems.
Phylum: Arthropoda
Possess an exoskeleton containing chitin, a segmented body and jointed appendages.
Class: Arachnida
Possess 4 pairs of legs, 2 feeding appendages, no antennae.
Class: Oligochaeta
Leeches
Class: Hirudinea Order: Acariformes
Mayflies
Class: Temnocephalidea
Flatworms
Crustaceans
Class: Crustacea
2 pairs of antennae, mandibles and 2 pairs of maxillae on the head, a pair of appendages on each body segment. Fairy Shrimps
No sign of external segmentation. Parasitic as larvae, free-living as nymphs and adults. Insects
Order: Ephemeroptera
Damsefliesl & Dragonflies
Class: Turbellaria
Damselfies
Order: Odonata
Labium extensible, often covering face. Beetles
Suborder: Zygoptera
Larvae usually slender with 3 large terminal gills. 11 Australian families, 107 species. Dragonflies
Class: Insecta
Usually possess defined head, thorax, abdomen, 1 or 2 pairs of wings, 3 pairs of jointed legs and a 1 pair of antennae. Larvae often have different habitat and structure to adults. Springtails
Order: Anostraca
Shield/Tadpole Shrimps
Order: Coleoptera
Caddislies
Suborder: Anisoptera
Larvae stout, without terminal gills but with anal pyramid. 6 Australian species, 198 species. Backswimmers
Order: Notostraca
Seed Shrimps
Order: Trichoptera
Aquatic Bugs
Subclass: Ostracoda Subclass: Copepoda
Cyclops
Class: Collembola
Wingless, possess abdomen with 6 segments. Up to 3mm in size. Habitats the surface film of still waters.
Order: Hemiptera
Mouth-parts consist of hinged stylets, mandibles and maxillae, resting in an anterior, grooved rostrumlike labium, generally 2 pairs of wings. 15 families and 222 species have aquatic stages. Moths
Family: Notonectidae
Large eyes, elongate body, swim with back downwards. 6 genera. Water Boatmen
Family: Corixidae
Fore-tarsi usually scoop-like with row of long hairs, head slightly overlapping the pronotum. 5 genera, 31 species recorded. Mosquitoes
Order: Cyclopoida
Information taken directly from: Hawking, John H. & Smith, Felicity J. Colour Guide to Invertebrates of Australian Inland Waters Co-operative Research Centre for Freshwater Ecology, NSW 1997. * This classification key only includes a selection of the known class, order, and family levels for each phylum.
Order: Lepidoptera
Two-winged Flies
Order: Diptera
Larvae do not have true legs.
Family: Culicidae
Prolegs absent, thoracic segments fused, mouth brushes present.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Phylum Annelida 4Dokument22 SeitenPhylum Annelida 4Ahmed OrabyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paleontology and Neontology of CephalopodsVon EverandPaleontology and Neontology of CephalopodsM. R. ClarkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduced Dung Beetles in Australia: A Pocket Field GuideVon EverandIntroduced Dung Beetles in Australia: A Pocket Field GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pismo Monarch Butterflies: Magic, Myths, & MysteriesVon EverandPismo Monarch Butterflies: Magic, Myths, & MysteriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Entomology: Third Semester Lamjung CampusDokument206 SeitenIntroductory Entomology: Third Semester Lamjung Campusnishan khatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zoo RevDokument18 SeitenZoo RevKenneth DayritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entomology: Naming of TaxaDokument19 SeitenEntomology: Naming of TaxaAliah Alleyne Canals - BSA - 1ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2. The Variety of Life PDFDokument7 SeitenUnit 2. The Variety of Life PDFIrenita gacha verseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Kingdom BiologyDokument8 SeitenAnimal Kingdom BiologyMary Ann SalvatierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arthropod Coloring SheetDokument9 SeitenArthropod Coloring Sheetkrupa4prezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entomology Lab HandoutsDokument13 SeitenEntomology Lab Handoutshumanupgrade100% (1)
- Group 3: Kingdom AnimaliaDokument23 SeitenGroup 3: Kingdom AnimaliabrettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal DiversityDokument3 SeitenAnimal DiversityChristian Dave Sanchez0% (1)
- Study Guide For Entomology 10Dokument9 SeitenStudy Guide For Entomology 10Alex TunqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classes of Vertebrates (Comparative Analysis)Dokument173 SeitenClasses of Vertebrates (Comparative Analysis)Vinci EbordeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animals NotesDokument25 SeitenAnimals NotesMyerza Syafiq'qahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Diversity 1 PDFDokument20 SeitenAnimal Diversity 1 PDFRica Jane Delan MapaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invertebrates ChartDokument1 SeiteInvertebrates ChartNicole K. DelizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thallophytes 2Dokument32 SeitenThallophytes 2Starnley TemboNoch keine Bewertungen
- CnidariaDokument12 SeitenCnidariaDave RapaconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invertebrates G7Dokument65 SeitenInvertebrates G7Julia MeirellesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of LarvaDokument12 SeitenTypes of LarvaFarrin Khanzlaluu Menunggunya100% (1)
- Insect MorphologyDokument10 SeitenInsect MorphologyDragan GrčakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of Living Organisms FinalDokument13 SeitenCharacteristics of Living Organisms FinalSunny x10Noch keine Bewertungen
- 15 January 2004 1st Lecture Herpetology ECOL 483/583 University of Arizona Spring 2004Dokument14 Seiten15 January 2004 1st Lecture Herpetology ECOL 483/583 University of Arizona Spring 2004andreaweiler1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chordate Origin and EvolutionDokument3 SeitenChordate Origin and Evolutionmonique100% (2)
- Invert Lab 2Dokument1 SeiteInvert Lab 2Beruk BerhaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Insect ClassificationDokument11 SeitenHistory of Insect Classificationapi-685744638Noch keine Bewertungen
- TOXONOMYDokument42 SeitenTOXONOMYNanami MumuzunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Respiratory SystemDokument80 SeitenHuman Respiratory SystemAj MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echinoderm Larvae PDFDokument15 SeitenEchinoderm Larvae PDFMadhav GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insects OrdersDokument1 SeiteInsects OrderssankaiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turtle Dissection PDFDokument7 SeitenTurtle Dissection PDFDemetra AlbescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Bio320 PDFDokument3 SeitenChapter 1 Bio320 PDFNurul Amirah HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phylum PoriferaDokument17 SeitenPhylum PoriferaRhiZhal SquDetto FrizTalNoch keine Bewertungen
- LamarckDokument1 SeiteLamarckGapmil Noziuc NylevujNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Polychaete Worms. Definitions and Keys To The Order, Families and GeneraDokument198 SeitenThe Polychaete Worms. Definitions and Keys To The Order, Families and Generalaandeer100% (1)
- Taxonomy and Classification....Dokument8 SeitenTaxonomy and Classification....Andrew MarariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- InvertebratesDokument8 SeitenInvertebratesDita SiagianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of PoriferaDokument14 SeitenClassification of PoriferaHastin Atas AsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arthropod Unit PlanDokument13 SeitenArthropod Unit PlanJonacyr BonoanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 6 Animalia (Invertebrate)Dokument17 SeitenCHAPTER 6 Animalia (Invertebrate)mottong100% (1)
- Animal DiversityDokument45 SeitenAnimal DiversitySafiqa Tasfia100% (1)
- 11.2 Domain Bacteria and ArchaeaDokument39 Seiten11.2 Domain Bacteria and ArchaeaZkdlin SpaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Type in SpongesDokument14 SeitenCell Type in SpongesMuhammad Asad FaroquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phylum MolluscaDokument10 SeitenPhylum MolluscaRenz GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Biology Notes Ch01 Reproductions in OrganismsDokument7 Seiten12 Biology Notes Ch01 Reproductions in Organismsarsalaan khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 2019 Herpetology PPTDokument45 Seiten1 2019 Herpetology PPTBryceNoch keine Bewertungen
- CnidariaDokument48 SeitenCnidariaMafe CabilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal DiversityDokument10 SeitenAnimal DiversityjenforrestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esquema FuncionesDokument1 SeiteEsquema FuncionesPaloma GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clasification of InsectsDokument68 SeitenClasification of InsectsMarie Serena McConnellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertebrates Birds, Reptiles, Amphibians, FishDokument17 SeitenVertebrates Birds, Reptiles, Amphibians, FishcarmenbtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protocols in Lichenology Culturing, Biochemistry, Ecophysiology andDokument585 SeitenProtocols in Lichenology Culturing, Biochemistry, Ecophysiology andRuben SierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter7-Cnidaria Notes2Dokument8 SeitenChapter7-Cnidaria Notes2api-195601294Noch keine Bewertungen
- Frog DissectDokument5 SeitenFrog DissectGeeklyGamer 02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Animal KingdomDokument22 SeitenAnimal KingdomdellfrogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Kingdom: Basis of ClassificationDokument15 SeitenAnimal Kingdom: Basis of ClassificationChaitali Deshmukh100% (1)
- Evolution of Amphibians PDFDokument2 SeitenEvolution of Amphibians PDFChadNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Dokument7 SeitenBIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Tonet LapeNoch keine Bewertungen
- How and Why Wonder Book of Sea ShellsDokument50 SeitenHow and Why Wonder Book of Sea Shellskett8233100% (2)
- Il Piano Ecoturistico Del FayoumDokument160 SeitenIl Piano Ecoturistico Del FayoumayepatagonikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Reading - History of ClassificationDokument3 Seiten05 Reading - History of Classificationapi-2597274820% (1)
- Department of The InteriorDokument63 SeitenDepartment of The InteriorSohini ChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Official Guide To The TOEFL Test - 2018 - Reading Practice Set 1Dokument5 SeitenThe Official Guide To The TOEFL Test - 2018 - Reading Practice Set 1Gonzalo QuiñonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer UCSPol PDFDokument3 SeitenReviewer UCSPol PDFLeila J Orosco50% (2)
- Annales Du Service Des Antiquites de LEgypte 1200021213Dokument300 SeitenAnnales Du Service Des Antiquites de LEgypte 1200021213Jordi Teixidor AbelendaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stratigraphic CorrelationDokument46 SeitenStratigraphic Correlationmemos2011100% (3)
- Ben Avraham and Emery 1973 - Structural Framework of Sunda ShelfDokument44 SeitenBen Avraham and Emery 1973 - Structural Framework of Sunda ShelfionizedxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambay 593Dokument6 SeitenCambay 593Sanjeev Singh NegiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newick Utilities TutorialDokument74 SeitenNewick Utilities TutorialCarlos GarcíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paläo-Art: Vom Jugendstil Bis in Die ModerneDokument3 SeitenPaläo-Art: Vom Jugendstil Bis in Die ModerneGianluca KlavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal SystemDokument25 SeitenSkeletal SystemLeonard Soria GuanzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 535 551 Hadi EtalDokument20 Seiten535 551 Hadi EtalPanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deuterostomia Protostomia Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa: Lophophore AcelomateDokument3 SeitenDeuterostomia Protostomia Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa: Lophophore AcelomateGiulia CostantiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wb95011vol1 PDFDokument154 SeitenWb95011vol1 PDFjhon berez223344Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biol 438Dokument43 SeitenBiol 438Xue CaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easters End DiscovermagazineDokument7 SeitenEasters End Discovermagazineapi-263638354Noch keine Bewertungen
- 174Dokument28 Seiten174Timon S. BullardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture#3 Kinematic AnalysisDokument8 SeitenLecture#3 Kinematic AnalysisRenuga Subramaniam100% (1)
- The Tectonic Evolution of Interior OmanDokument24 SeitenThe Tectonic Evolution of Interior OmanHumaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Lemigas 2009Dokument110 SeitenLaporan Lemigas 2009Lutfi SijeniusNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Proceedings BESA2012 Page1 84Dokument84 Seiten1 Proceedings BESA2012 Page1 84bayu sungkonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Interview GeologyDokument61 SeitenTest Interview GeologySikander MushtaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mesozoic EraDokument18 SeitenThe Mesozoic EraQueen Justine100% (1)
- Lebanese Amber, Oldest Insect Ecosystem in Fossilized Resin 2001Dokument97 SeitenLebanese Amber, Oldest Insect Ecosystem in Fossilized Resin 2001dgarcialopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fossil Collecting in PennsylvaniaDokument69 SeitenFossil Collecting in PennsylvaniacgermaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Anatomy - Respiratory SystemDokument13 SeitenComparative Anatomy - Respiratory SystemGeo ZahariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geologic Time Scale Glossary:: Uc-Shs 1Dokument43 SeitenGeologic Time Scale Glossary:: Uc-Shs 1John Denver AdaoagNoch keine Bewertungen