Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
RACI
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous ocCa18ROriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
RACI
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous ocCa18RCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
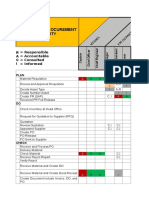
Responsibility assignment matrix
A Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM), also known as RACI matrix (pronounced /resi/) or Linear Responsibility Chart (LRC), describes the participation by various roles in completing tasks or deliverables for a project or business process. It is especially useful in clarifying roles and responsibilities in cross-functional/departmental projects and processes. RACI is an acronym derived from the four key responsibilities most typically used: Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed.
Key Responsibility Roles
Responsible Those who do the work to achieve the task. There is typically one role with a participation type of Responsible, although others can be delegated to assist in the work required (see also RASCI below for separately identifying those who participate in a supporting role). Accountable (also Approver or final Approving Authority) The one ultimately answerable for the correct and thorough completion of the deliverable or task, and the one from whom Responsible is delegated the work. In other words, an Accountable must sign off (Approve) on work that Responsible provides. There must be only one Accountable specified for each task or deliverable. Consulted (sometimes Counsel) Those whose opinions are sought, typically subject matter experts; and with whom there is twoway communication. Informed Those who are kept up-to-date on progress, often only on completion of the task or deliverable; and with whom there is just one-way communication. Very often the role that is Accountable for a task or deliverable may also be Responsible for completing it (indicated on the matrix by the task or deliverable having a role Accountable for it, but no role Responsible for its completion, i.e. it is implied). Outside of this exception, it is generally recommended that each role in the project or process for each task receive, at most, just one of the participation types. Where more than one participation type is shown, this generally implies that participation has not yet been fully resolved, which can impede the value of this technique in clarifying the participation of each role on each task. Role Distinction There is a distinction between a role and individually identified people: a role is a descriptor of an associated set of tasks; may be performed by many people; and one person can perform many roles. For example, an organization may have 10 people who can perform the role of project manager, although traditionally each project only has one project manager at any one time; and a person who is able to perform the role of project manager may also be able to perform the role of business analyst and tester. Matrix Format
The matrix is typically created with a vertical axis (left-hand column) of tasks (e.g., from a work breakdown structure WBS) or deliverables (e.g., from a product breakdown structure PBS), and a horizontal axis (top row) of roles (e.g., from an organizational chart) - as illustrated in the image of an example responsibility assignment (or RACI) matrix.
RASCI
This is an expanded version of the standard RACI, less frequently known as RASIC, breaking the Responsible participation into: Responsible Those who are responsible for the task, ensuring that it is done as per the Approver. Support Resources allocated to Responsible. Unlike Consulted, who may provide input to the task, Support will assist in completing the task. Typical steps in a RACI process: 1. 2. 3. 4. Identify all of the processes / activities involved and list them down the left hand side of the chart. Identify all of the roles and list them along the top of the chart. Complete the cells of the chart: identify who has the R, A, S, C, I for each process. Every process should preferably have one and only one R as a general principle. A gap occurs when a process exists with no R (no role is responsible), an overlap occurs when multiple roles exist that have an R for a given process. 5. Resolve Overlaps - Every process in a role responsibility map should contain one and only one R to indicate a unique process owner. In the case of multiple Rs, there is a need to zoom in and further detail the sub processes associated with obtain resource commitment to separate the individual responsibilities. 6. Resolve Gaps - The simpler case to address is the resolution of a gap. Where no role is identified that is responsible for a process, the individual with the authority for role definition must determine which existing role is responsible or new role that is required, update the RASCI map and clarify with the individual(s) that assume that role.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Governance Theory As A FrameworkDokument64 SeitenGovernance Theory As A FrameworkGuilherme RosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benefit Ion Management Ch4Dokument17 SeitenBenefit Ion Management Ch4jorge gomesNoch keine Bewertungen
- RACIDokument23 SeitenRACIchotumotu131111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Distributing Services Through Physical and Electronic ChannelsDokument39 SeitenDistributing Services Through Physical and Electronic Channelsscribdchakri100% (2)
- M - CPS - HCC - 0518 - Technical Proposal - Consultancy Services - People & Organizational - TransformationDokument82 SeitenM - CPS - HCC - 0518 - Technical Proposal - Consultancy Services - People & Organizational - TransformationHadeel Al-OtaibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Management IntroductionDokument40 SeitenSupply Chain Management IntroductionAwaneesh ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CII Bench Marking & MetricsDokument53 SeitenCII Bench Marking & MetricsjorgearangogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate in Management ConsultingDokument7 SeitenCertificate in Management ConsultingaliarabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project - Programme - Portfolio Management - View On ReportingDokument62 SeitenProject - Programme - Portfolio Management - View On ReportingjeffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Request and Approval Process.v1.6 Final 02202015Dokument22 SeitenProject Request and Approval Process.v1.6 Final 02202015Saud ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obashi Case Studies. 0 PDFDokument43 SeitenObashi Case Studies. 0 PDFPTINoch keine Bewertungen
- Organisational StructureDokument2 SeitenOrganisational StructureAkshat GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stakeholder Engagement EssentialsDokument21 SeitenStakeholder Engagement EssentialsdaohoaflowerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Brief TemplateDokument8 SeitenProject Brief TemplateYadinuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PM Raci MatrixDokument7 SeitenPM Raci MatrixLidiane CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- RACI - ChartDokument3 SeitenRACI - ChartFaraz MatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT G C U: Overnance at Arleton NiversityDokument12 SeitenIT G C U: Overnance at Arleton Niversityamjedns21531Noch keine Bewertungen
- Visual milestone planning methodDokument23 SeitenVisual milestone planning methodEsteban100% (1)
- Topics Covered Topics Covered: Portfolio Planning ToolsDokument18 SeitenTopics Covered Topics Covered: Portfolio Planning ToolsAMAYA.K.P 18BCO406Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Model Definition PDFDokument10 SeitenCost Model Definition PDFshule1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Annual business planning and budgeting processesDokument1 SeiteAnnual business planning and budgeting processesvivekcp87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stakeholder ManagementDokument9 SeitenStakeholder ManagementrussiatimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baseline Survey PDFDokument882 SeitenBaseline Survey PDFomkar100% (1)
- Supplier Relocation Project Plan Template Ver.3Dokument14 SeitenSupplier Relocation Project Plan Template Ver.3Gábor LantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Management Guidelines PPT Compatibility ModeDokument6 SeitenProject Management Guidelines PPT Compatibility Modemohanp716515Noch keine Bewertungen
- Setting Up A Pmo: Presented by - Group EDokument7 SeitenSetting Up A Pmo: Presented by - Group EYousuf KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01.15 Smart Cities in EuropeDokument40 Seiten01.15 Smart Cities in EuropeLjupco TrajkovskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beyond Portfolio ManagementDokument3 SeitenBeyond Portfolio ManagementfrankitectureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Change Control RegisterDokument12 SeitenChange Control RegisterSunil BenedictNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Project Name) Business Case (Phase #) : Date: Month Day, YearDokument13 Seiten(Project Name) Business Case (Phase #) : Date: Month Day, YearracringandhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing Business Case (Chapter-2)Dokument46 SeitenAnalyzing Business Case (Chapter-2)Ayisha ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agile Project Management in Construction IndustryDokument3 SeitenAgile Project Management in Construction IndustryJeeva VenkatramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Requirement Data CentreDokument12 SeitenDesign Requirement Data Centrekavya pushparajNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Growing Importance of Epmo in Todays OrganisationsDokument16 SeitenThe Growing Importance of Epmo in Todays OrganisationsGetuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ict Investment Approval 2nd Pass Business Case TemplateDokument12 SeitenIct Investment Approval 2nd Pass Business Case Templatebangun777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Whitepaper Future of Project ManagementDokument4 SeitenWhitepaper Future of Project Managementluis lopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itil 2011mind MapsDokument1 SeiteItil 2011mind MapsGabriel CamachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Sizing Analysis Grid: General Interpretation GuideDokument1 SeiteProject Sizing Analysis Grid: General Interpretation Guideanirban_surNoch keine Bewertungen
- RecordPoint Records Management With SharePointDokument17 SeitenRecordPoint Records Management With SharePointoptical420Noch keine Bewertungen
- RACI FinalDokument27 SeitenRACI Finalyogeshdhuri22Noch keine Bewertungen
- RACI Matriks ATR (Read Only)Dokument18 SeitenRACI Matriks ATR (Read Only)catrapalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business vs. IT: Solving The Communication GapDokument12 SeitenBusiness vs. IT: Solving The Communication GapiarnabNoch keine Bewertungen
- RACI ExampleDokument4 SeitenRACI ExampleSandeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stakeholder involvement classDokument6 SeitenStakeholder involvement classmorcamtecNoch keine Bewertungen
- TAM ManualDokument392 SeitenTAM ManualMaidan KimyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maturing PMO PDFDokument9 SeitenMaturing PMO PDFA ChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership AssignmentDokument15 SeitenLeadership AssignmentShelveyElmoDiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMC PM HandbookDokument25 SeitenCMC PM HandbookYusuf DemirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pmo CVDokument4 SeitenPmo CVprince2venkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architecture Governance Framework and ADM CycleDokument12 SeitenArchitecture Governance Framework and ADM Cyclemahesh881245Noch keine Bewertungen
- Governance - Strategy and PMDokument43 SeitenGovernance - Strategy and PMpadmanabhdixitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Rationalization - Torry Harris WhitepaperDokument7 SeitenApplication Rationalization - Torry Harris WhitepaperTorry Harris Business SolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PM GUIDE 03 End To End Project Delivery FrameworkDokument31 SeitenPM GUIDE 03 End To End Project Delivery Frameworktimur.bartashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prometric Test Center Advice for TOGAF 9 ExamsDokument2 SeitenPrometric Test Center Advice for TOGAF 9 ExamsSuneel BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Planning - NotesDokument32 SeitenProject Planning - NotesVikas Reddy MarepallyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apm in The Togaf EnvironmentDokument3 SeitenApm in The Togaf Environmentvenkat2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Choose One of The Following AnswersDokument24 SeitenChoose One of The Following AnswersfabianlaudNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 P3M3 Programme ModelDokument22 Seiten03 P3M3 Programme ModelSuhail IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- EA Roles and ResponsibilitiesDokument4 SeitenEA Roles and ResponsibilitiesccnewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redefining the Basics of Project Management: Filling the Practice Gaps by Integrating Pmbok® Guide with a Project Life Span Approach!Von EverandRedefining the Basics of Project Management: Filling the Practice Gaps by Integrating Pmbok® Guide with a Project Life Span Approach!Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bump Caps Vs Hard HatsDokument6 SeitenBump Caps Vs Hard HatsAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assesing The Need of PpeDokument57 SeitenAssesing The Need of PpeAli AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical HazardsDokument26 SeitenElectrical HazardsAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Cold Stress RiskDokument4 SeitenThermal Cold Stress Riskted_connellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solvent Recovery and VOC Emission Control SystemsDokument8 SeitenSolvent Recovery and VOC Emission Control SystemsAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSG 65 Guide To Measuring H&S Performance 2002Dokument30 SeitenHSG 65 Guide To Measuring H&S Performance 2002venapusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working at Heights GuidelineDokument13 SeitenWorking at Heights GuidelineKwang Sun100% (1)
- ANSI Emergency Eyewash StandardDokument28 SeitenANSI Emergency Eyewash StandardWilliam Condori Rafael100% (3)
- Contractor Job Safety PlanDokument15 SeitenContractor Job Safety PlanAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 10 Property Fire HazardsDokument4 SeitenTop 10 Property Fire HazardsAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8d Training 9-8-2008-Root Cause AnalysisDokument78 Seiten8d Training 9-8-2008-Root Cause AnalysisShashindra Dhopeshwar100% (1)
- Ageing Plant Summary GuideDokument53 SeitenAgeing Plant Summary GuideEyoma EtimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Egress Fire LPDokument4 SeitenEgress Fire LPRobert Paredes DimapilisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Managing Process ChangesDokument30 Seiten8 Managing Process ChangesAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ehs Guidance For Contractors: Wellesley CollegeDokument2 SeitenEhs Guidance For Contractors: Wellesley CollegeAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breaking Containment - Process Cleaning Operations PDFDokument4 SeitenBreaking Containment - Process Cleaning Operations PDFAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- (III) PSSR PROCEDURE (Rev00) PDFDokument17 Seiten(III) PSSR PROCEDURE (Rev00) PDFDen Bagus Blitar100% (5)
- Safety Audit in Developing CountriesDokument8 SeitenSafety Audit in Developing CountriesAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ageing Plant Summary GuideDokument53 SeitenAgeing Plant Summary GuideEyoma EtimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Safety Enhancement in Chemical Plant Design by Exploiting Accident KnowledgeDokument88 SeitenProcess Safety Enhancement in Chemical Plant Design by Exploiting Accident KnowledgeAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitrogen BlanketingDokument7 SeitenNitrogen Blanketing3bandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressed Air SafetyDokument9 SeitenCompressed Air SafetyAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behavior Based Safety ManagementDokument4 SeitenBehavior Based Safety ManagementAnonymous ocCa18R100% (1)
- Occupational Exposure AssessmentDokument59 SeitenOccupational Exposure AssessmentAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double Block and Bleed ValvesDokument1 SeiteDouble Block and Bleed ValvesAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMCO Induction and Training ProcedureDokument11 SeitenEMCO Induction and Training ProcedureAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Size of Access Openings in Boilers and Pressure VesselsDokument3 SeitenSize of Access Openings in Boilers and Pressure VesselsAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prohibiting Wooden Pallets For Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 DrumsDokument2 SeitenProhibiting Wooden Pallets For Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 DrumsAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Divinylbenzene Storage and HandlingDokument8 SeitenDivinylbenzene Storage and HandlingAnonymous ocCa18RNoch keine Bewertungen
- D BB Pipeline Isolation PaperDokument24 SeitenD BB Pipeline Isolation Paperhadi137Noch keine Bewertungen
- Junkspace: Hilary PowellDokument5 SeitenJunkspace: Hilary PowellPilar PinchartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graduation SpeechesDokument9 SeitenGraduation SpeechesSeun IsraelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PACIFICO B. ARCEO, JR, Jr. vs. People of The Philippines, G.R. No. 142641, 17 July 2006Dokument1 SeitePACIFICO B. ARCEO, JR, Jr. vs. People of The Philippines, G.R. No. 142641, 17 July 2006Sonson VelosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hughes explores loss of childhood faithDokument2 SeitenHughes explores loss of childhood faithFearless713Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gliding Birdflight Basis AviationDokument172 SeitenGliding Birdflight Basis AviationErnest DevensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSR 9278 - DLR1 - OtherlandsDokument106 SeitenTSR 9278 - DLR1 - OtherlandsDiego RB100% (5)
- LVMPD Use of Force PolicyDokument26 SeitenLVMPD Use of Force PolicyFOX5 VegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adverbs Further ReadingDokument17 SeitenAdverbs Further ReadingᅳNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Curse of MillhavenDokument2 SeitenThe Curse of MillhavenstipemogwaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sociology of Behavioral ScienceDokument164 SeitenSociology of Behavioral ScienceNAZMUSH SAKIBNoch keine Bewertungen
- NafsDokument3 SeitenNafsMabub_sddqNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSCC Great Expectations 09Dokument6 SeitenNSCC Great Expectations 09HDTT_09101199Noch keine Bewertungen
- PROACTIVITYDokument8 SeitenPROACTIVITYShikhaDabralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bail and Right To Bail in IndiaDokument43 SeitenBail and Right To Bail in IndiaAkshar Haritwal100% (3)
- No Going BackDokument39 SeitenNo Going BackandrophilemxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 2 AmberjordanDokument15 SeitenTask 2 Amberjordanapi-200086677100% (2)
- SecondaryDokument51 SeitenSecondarysnowden150% (2)
- Seminar Report on 21st Century TeachingDokument4 SeitenSeminar Report on 21st Century Teachingeunica_dolojanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biblical Interpretation in 1 Maccabees: The Anachronism of A "Bible" For The Second-Temple PeriodDokument26 SeitenBiblical Interpretation in 1 Maccabees: The Anachronism of A "Bible" For The Second-Temple PeriodshmareparksNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2125 Things We Can No Longer Do During An RPGDokument51 Seiten2125 Things We Can No Longer Do During An RPGPećanac Bogdan100% (2)
- Earnings Price Anomaly (Ray Ball, 1992)Dokument27 SeitenEarnings Price Anomaly (Ray Ball, 1992)jeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lit Exam 2nd QuarterDokument4 SeitenLit Exam 2nd Quarterjoel Torres100% (2)
- 2014 JC2 H2 Econs Prelim Paper 2Dokument3 Seiten2014 JC2 H2 Econs Prelim Paper 2Ezra Notsosure WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 1Dokument5 SeitenProblem Set 1sxmmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applying Evidence to Help High-Risk YouthDokument26 SeitenApplying Evidence to Help High-Risk YouthIvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Στιχοι απο εμεναDokument30 SeitenΣτιχοι απο εμεναVassos Serghiou SrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Leiomyomas After Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Report of Two CasesDokument5 SeitenMultiple Leiomyomas After Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Report of Two CasesYosef Dwi Cahyadi SalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Objectives: Checking of AttendanceDokument4 SeitenI. Objectives: Checking of AttendanceJoAnn MacalingaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marxist Approaches in AnthropologyDokument30 SeitenMarxist Approaches in AnthropologyLions_Read_Theory100% (1)
- Taxation of RFCs and NFCs in PHDokument4 SeitenTaxation of RFCs and NFCs in PHIris Grace Culata0% (1)