Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
PCI Compliance Overview
Hochgeladen von
Online Tech0%(1)0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
67 Ansichten13 SeitenPCI-DSS stands for the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. PCI applies to every organization that receives, stores, processes or transmits cardholder data, from the large ecommerce style companies through the single pizza shop. The intent of this standard is to protect cardholder data (CHD) through an approach that covers every aspect of a technology based solution from policies through infrastructure and everything in between.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenPCI-DSS stands for the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. PCI applies to every organization that receives, stores, processes or transmits cardholder data, from the large ecommerce style companies through the single pizza shop. The intent of this standard is to protect cardholder data (CHD) through an approach that covers every aspect of a technology based solution from policies through infrastructure and everything in between.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0%(1)0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
67 Ansichten13 SeitenPCI Compliance Overview
Hochgeladen von
Online TechPCI-DSS stands for the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. PCI applies to every organization that receives, stores, processes or transmits cardholder data, from the large ecommerce style companies through the single pizza shop. The intent of this standard is to protect cardholder data (CHD) through an approach that covers every aspect of a technology based solution from policies through infrastructure and everything in between.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 13
PCI-DSS Overview
Adam Goslin, Co-Founder High Bit Security April 26, 2011
About High Bit Security
High Bit helps companies obtain or maintain their PCI compliance (Level 1 through Level 4 compliance) High Bit will identify where your organization stands against the PCI-DSS standards (GAP analysis), provide remediation advice, coordinate with security assessors High Bit provides cost effective Penetration Testing for either internal or external testing against the network and/or application layers High Bits manual Penetration Testing is performed by security engineers that hold industry recognized certifications
PCI Compliance Overview
PCI-DSS = Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard
PCI DSS stands for the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, and is a compliance standard founded in 2004 as a result of the combination of 5 different security programs in operation at the time by Visa, MasterCard, Discover, JCB and American Express. The intent of this standard is to protect cardholder data (CHD) through an approach that covers every aspect of a technology based solution from policies through infrastructure and everything in between.
Implemented through core payment processors, and disseminated through the industry from there starting with largest organizations through smaller organizations.
PCI Compliance Who Is Impacted?
Common misconception: PCI only applies to the large ecommerce style companies PCI applies to EVERY organization that receives, stores, processes or transmits cardholder data, from the large ecommerce online retailers through the single pizza shop PCI breaks out compliance into Levels, which for simplicity well separate into two groups
Level 1 = 6 million + annual transactions Levels 2-4 = < 6 million annual transactions
PCI Compliance Levels of Compliance
The levels (1-4) are broken out by quantity of annual transactions Level 1 = 6 million + annual transactions
Annual Report on Compliance (ROC) must be filed by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) Quarterly network scans by an Approved Scan Vendor (ASV) Completion of an Attestation of Compliance (AOC)
Levels 2-4 = < 6 million annual transactions
Annual Self Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) Quarterly network scans by an Approved Scan Vendor (ASV)
Level 4 - only if applicable
Completion of an Attestation of Compliance (AOC)
Level 4 - compliance validation requirements set by acquirer
PCI Compliance SAQs
SAQ A Card-not-present Merchants, All Cardholder Data Functions Outsourced SAQ B Merchants with Only Imprint Machines or Only Standalone, DialOut Terminals. No Electronic Cardholder Data Storage. SAQ C-VT Merchants with Web-Based Virtual Terminals, No Electronic Cardholder Data Storage. SAQ C Merchants with Payment Application Systems Connected to the Internet, No Electronic Cardholder Data Storage. SAQ D All Other Merchants and All Service Providers Defined by a Payment Brand as Eligible to Complete an SAQ
PCI Compliance First Steps
Untold benefits leveraging assistance from resources that have been through PCI compliance before
Quickly gain understanding of where your organization stands against the PCI DSS standards Mitigate the amount of time (cost) required by internal IT resources Streamline the process of getting to solution discussions, whether internal resources, external software; hardware; services Guidance for mitigating the breadth of the cardholder data environment
PCI Compliance First Steps Continued
PCI Compliance contains over 260 different individual requirements ranging from HR hiring / firing policies and procedures to the lockdown of services on each individual machine in the Card Holder Environment (CHE) Planning for your move to PCI compliance is essential, whether leveraging physical or virtual infrastructure
PCI Compliance Infrastructure Factors
Costs of becoming PCI compliant are directly proportional to the breadth of your Card Holder Environment (CHE) In many cases, companies will opt to migrate from one platform to another when performing their PCI compliance for several reasons infrastructure age; need to segregate CHE from existing non CHE functionality; ability to keep present systems avail
PCI Compliance Physical vs Cloud
If your environment is very small, physical infrastructure may make the most sense If your environment is comprised of several devices, a cloud architecture (Private Cloud) becomes more appealing In both cases, they must meet all requirements of PCI-DSS Cloud architecture allows staging of mostly compliant VMs as a base With cloud architecture, special considerations for the hypervisor (virtual environment management)
PCI Compliance Impact Areas
PCI DSS Requirements
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Install and maintain a firewall configuration to protect cardholder data Do not use vendor-supplied defaults for system passwords and other security parameters Protect stored cardholder data Encrypt transmission of cardholder data across open, public networks Use and regularly update anti-virus software on all systems commonly affected by malware Develop and maintain secure systems and applications Restrict access to cardholder data by business need-to-know Assign a unique ID to each person with computer access Restrict physical access to cardholder data Track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data Regularly test security systems and processes Maintain a policy that addresses information security
PCI Compliance Upcoming Webinars
Tuesday 5.03.11 @ 2pm - PCI Compliance: Detailed Requirements Walkthrough Tuesday 5.10.11 @ 2pm - PCI Compliance: Penetration Testing and Enhancing Security for Network and Applications
PCI Compliance Q&A
Free consultations for PCI DSS compliance Free consultations for Penetration Testing High Bit Security Cell: Email: Adam Goslin - Founder 248-388-4328 agoslin@HighBitSecurity.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- AG188-How To Update The Firmware On Post Mode-En-V1.0-090404Dokument6 SeitenAG188-How To Update The Firmware On Post Mode-En-V1.0-090404joro_sandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hho Dry Cell 21plates InfoDokument8 SeitenHho Dry Cell 21plates Infoz987456321100% (1)
- Layover Inspection Schedule Issue 09 (A320-232)Dokument19 SeitenLayover Inspection Schedule Issue 09 (A320-232)pankaj0% (1)
- IT Task Technology in Military: Muhammad Athallah 107 Ricky Adrianto 114 Dessyana Damayanti 161 Daffa Ramadhan S 293Dokument9 SeitenIT Task Technology in Military: Muhammad Athallah 107 Ricky Adrianto 114 Dessyana Damayanti 161 Daffa Ramadhan S 293LaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lcd2s SPI ExamplesDokument2 SeitenLcd2s SPI ExamplesJarfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- N5200 N5200pro FW 2.01.09 FWRNDokument8 SeitenN5200 N5200pro FW 2.01.09 FWRNIlham ASNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATC-277MM User's ManualDokument0 SeitenATC-277MM User's ManualMaitry ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bill of Quantity: Baner Lifespaces LLPDokument7 SeitenBill of Quantity: Baner Lifespaces LLPSales AlufacadesNoch keine Bewertungen
- N Tata Fir PDFDokument2 SeitenN Tata Fir PDFBranza GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- F 90Dokument35 SeitenF 90ulises100% (1)
- Grounding and Electromagnetic Compatibility of PLC Systems Basic Principles and Measures User ManualDokument344 SeitenGrounding and Electromagnetic Compatibility of PLC Systems Basic Principles and Measures User ManualSampath DayarathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inductive Sensor BI1.5-EG08K-Y1: Type DesignationDokument5 SeitenInductive Sensor BI1.5-EG08K-Y1: Type DesignationpinkpanterNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Build A Payment Integration With ATG CommerceDokument5 SeitenHow To Build A Payment Integration With ATG CommerceVishnu Vardhan100% (1)
- Toshiba Satellite C660 Compal LA-7202P PWWHA Delphi 10R Rev1.0 SchematicDokument43 SeitenToshiba Satellite C660 Compal LA-7202P PWWHA Delphi 10R Rev1.0 Schematicpcs prasannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pub002 003 00 - 1011Dokument88 SeitenPub002 003 00 - 1011jones0055Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Core Java With Android: An Industrial Training ReportDokument29 SeitenOn Core Java With Android: An Industrial Training ReportPt Kamal SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Excel Shortcuts For MAC PDFDokument6 SeitenMicrosoft Excel Shortcuts For MAC PDFJASMER SINGH 1611118Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bodas Rexroth Service Re95086 - 2018-04Dokument10 SeitenBodas Rexroth Service Re95086 - 2018-04harry programmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- NickN FSX BibleDokument176 SeitenNickN FSX BibleDimitris Phanos100% (1)
- Dell S718QL Laser 4k UST ProjectorDokument4 SeitenDell S718QL Laser 4k UST Projectordfsgsdf df3tegdfgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labview Programming, Part IvDokument27 SeitenLabview Programming, Part IvDImNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apxvbll15xt CDokument2 SeitenApxvbll15xt CSvetovidPerunsinNoch keine Bewertungen
- KLC M1 ManualDokument87 SeitenKLC M1 ManualCaroozoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spice Model of DiodeDokument20 SeitenSpice Model of DiodeharizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual SM17 - 002 - 083.00: Latching Boom Mechanism RetrofitDokument24 SeitenService Manual SM17 - 002 - 083.00: Latching Boom Mechanism RetrofitErissonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Codigo TunstallDokument5 SeitenCodigo TunstallLidia LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- (2-2.b) - As-Built For Metal BuildingDokument482 Seiten(2-2.b) - As-Built For Metal BuildingAbdul Wadood GharsheenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB Price Book 216Dokument1 SeiteABB Price Book 216EliasNoch keine Bewertungen
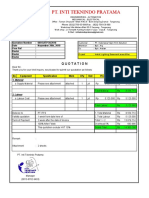
- 181128-Quotation Install Lighting at Basement Area PDFDokument3 Seiten181128-Quotation Install Lighting at Basement Area PDFAlex AlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Computer SoftwareDokument23 SeitenTypes of Computer SoftwareRachel FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen