Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 3-The U.S. Constitution: I. Basic Principles
Hochgeladen von
albertmorales82Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 3-The U.S. Constitution: I. Basic Principles
Hochgeladen von
albertmorales82Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 3- The U.S.
Constitution
I. Basic Principles
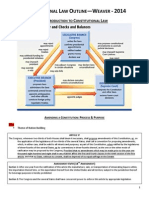
A. Popular Sovereignty 1. Framers wanted a nat'l govt to a. Serve the people b. Prevents the concentration & abuses of power c. Respects the rights of states 2. Govt. authority comes from the people B. Limited Govt 1. Constitution limits govt. by setting guidelines for how govt. may act. C. Separation of Powers 1. Article 1- responsibilities of Legislative Branch a. Many of Congress' powers are implied b. House of Representatives & Senate share responsibilities for passing laws c. Only Senate can approve presidential appointments & treaties w/foreign countries 2. Article 2 - duties of the Executive Branch 3. Article 3 - role of the Judicial Branch D. Checks & Balances 1. Constitution gives each branch power to check the powers of the other branches 2. Executive & Legislative Checks a. Veto = official rejection b. Congress may override a veto with 2/3 vote in the House & Senate
c. Only Congress can approve spending ('Power of the Purse') d. Treaties must be approved by a 2/3 majority in the Senate e. President must consider Congress when proposing legislation, making appointments, & negotiating treaties 3. Judicial Review = power to decide if laws & other govt. actions violate the US Constitution a. Not specifically mentioned in the Constitution b. Unconstitutional = law or govt. action that violates any part of the Constitution c. Section II of Article III implies that the courts have the power d. Marbury v. Madison in 1803 E. Federalism 1. Constitution protects states' rights, but saw need for national govt. to maintain order a. States cannot do certain things 1) Negotiate treaties 2) Minting money 3) Keeping troops or warships during peacetime 4) Engaging in war b. Supremacy Clause = The Constitution- together with US laws passed under the Constitution & treaties made by the national govt. - is the supreme law of the land
II. Amending the Constitution
A. Amendments = changes made to the Constitution 1. All amendments must proposed & ratified
B. Methods for Amending the Constitution 1. Proposing Amendments a. Vote in Congress 1) All amendments have been proposed by Congress 2) At least 2/3 of the House & Senate must approve an amendment before it can be sent to states for ratification b. National Convention - called by Congress at request of at least 2/3 of state legislatures 2. Ratifying Amendments a. Vote in state legislatures 1) Legislatures in at least of the states must approve an amendment before it becomes part of the Constitution b. Special conventions in at least of the states 1) Repeal = legislative reversal 2) 21st amendment was ratified this way 3) Repealed prohibition C. The 27 Amendments 1. Protecting Individual Freedoms a. Bill of Rights = 1st ten amendments 1) 1st amendment protects freedom of speech, religion, assembly, & press 2) 9th says that people have additional rights not specifically mentioned in the Constitution 3) 10th says that states & people have powers not specifically given to national govt.
2. Expanding Voting & Other Rights a. Times of social & political change b. 13th, 14th, & 15th - adopted after Civil War 1) African Americans - free, citizenship, vote c. 17th - popular election of senators d. 19th - female vote 3. Extending Govt. Powers a. 16th - national income tax b. 18th - prohibition = Production, sale & transportation of alcoholic beverages were outlawed (later repealed)
III. A Flexible Document
A. Govt. Actions 1. Court Decisions a. Wording can be vague b. Marbury v. Madison c. 4th - forbids unreasonable searches & seizures 2. Congressional Legislation a. Congress also interprets vague wording in Constitution b. Laws have been passed concerning labor 3. Executive Actions a. Executive agreements = arrangements that presidents make with foreign govts that do not require Senate approval
B. Political Parties 1. Political Party = an organized group that seeks to win elections and influence the activities of govt 2. Not mentioned in the Constitution C. Custom & Tradition 1. Informal & long-established ways of doing things 2. Cabinet = group of executive dept. heads who act as advisors to thePresident a. George Washington had the 1st cabinet 3. 22nd amendment a. Limits presidents to two terms of service b. Formalized custom started by Washington
IV. The Constitution & the Public Good
A. Preventing Control by Factions 1. Factions = groups of people motivated by self-interest 2. James Madison was concerned about factions a. Believed that the Constitution prevented factions in two ways 3. Size a. US was large and diverse b. Constitution gives everyone an equal voice 4. Checks & Balances a. If one branch were to be controlled by a particular faction, the other branches would keep it in check 5. Madison said that the Constitution formed a republic in which it is likelythat govt will serve the broader interests of society or public good
B. Effective Govt 1. Gridlock = Govt business comes to a standstill as political opponents block each other's efforts 2. Avoiding Responsibility a. Some say the Constitution makes it too easy for leaders to avoid responsibility for failed policies
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- AP US Government and Politics Midterm ReviewDokument17 SeitenAP US Government and Politics Midterm ReviewWarpaintItNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civics & Economics Notes 2.01-2.03Dokument5 SeitenCivics & Economics Notes 2.01-2.03Matt ByrneNoch keine Bewertungen
- American Government 10th Edition Ch. 2 OutlineDokument5 SeitenAmerican Government 10th Edition Ch. 2 Outlineliz92715100% (2)
- Mag CHP 03 OutlineDokument6 SeitenMag CHP 03 Outlineapi-267189291Noch keine Bewertungen
- Beck Outline 2007Dokument50 SeitenBeck Outline 2007christensen_a_gNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 4 Exam Us GovernmentDokument7 SeitenUnit 3 4 Exam Us Governmentapi-666230349Noch keine Bewertungen
- AbcdDokument15 SeitenAbcd=*=Noch keine Bewertungen
- Con Law Outline 1Dokument60 SeitenCon Law Outline 1Zachary SchmidtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Most Important Things About The ConstitutionDokument4 Seiten10 Most Important Things About The ConstitutionMaddie LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConLaw Gewirtzman ALL Class NOTES 2014Dokument170 SeitenConLaw Gewirtzman ALL Class NOTES 2014achrys13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Regents Prep 2Dokument8 SeitenRegents Prep 2api-242847854Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I - Constitutional Underpinnings of The United States Government AP Test Prep Quiz Mrs. ProbstDokument5 SeitenUnit I - Constitutional Underpinnings of The United States Government AP Test Prep Quiz Mrs. ProbstJack_Quincy_208Noch keine Bewertungen
- Con Law OutlineDokument15 SeitenCon Law OutlineDantel RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modified US ConstitutionDokument6 SeitenModified US ConstitutionMary FigNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Outline ConDokument38 SeitenMy Outline ConChristian EmsiekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Honors - Chapter 3 2015Dokument22 SeitenGovernment Honors - Chapter 3 2015cyndalea100% (1)
- Ap Gopo Final Review KeyDokument10 SeitenAp Gopo Final Review Keyapi-328296165Noch keine Bewertungen
- Constitutional Law I Outline - Final Exam OutlineDokument38 SeitenConstitutional Law I Outline - Final Exam OutlineJoseph KleinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Con Law 1L OutlineDokument23 SeitenCon Law 1L Outlinebethora100% (1)
- Spring 2023 3304 Exam 3Dokument28 SeitenSpring 2023 3304 Exam 3Stephanie AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constitutional Law I Funk 2006docDokument28 SeitenConstitutional Law I Funk 2006docLaura SkaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Con Law Outline - Rules and AnalysisDokument16 SeitenCon Law Outline - Rules and Analysischampion_egy325100% (4)
- AP Unit2 TestBankDokument19 SeitenAP Unit2 TestBankCasey HarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rodriguez Fall 05Dokument90 SeitenRodriguez Fall 05Vic ToranVictor WaitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Govt. Multiple Choice Question BankDokument40 SeitenAP Govt. Multiple Choice Question BankKavita KrishnamorthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Unit 4Dokument6 SeitenSummative Unit 4api-272836132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Constitution and Amendments Cheat SheetDokument7 SeitenConstitution and Amendments Cheat SheetPrice MarshallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Constitutional BarbriDokument9 SeitenShort Constitutional BarbriMichael FNoch keine Bewertungen
- Con Law Outline-29Dokument41 SeitenCon Law Outline-29Scott HymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TestDokument5 SeitenTestapi-355053390Noch keine Bewertungen
- Constituion LPDokument7 SeitenConstituion LPapi-264023680Noch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide Gov FinalDokument12 SeitenStudy Guide Gov Finalapi-280626818Noch keine Bewertungen
- Constitutional LawDokument41 SeitenConstitutional LawAnnie BerningNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP American Government: Chapter Two: The ConstitutionDokument7 SeitenAP American Government: Chapter Two: The Constitutionirregularflowers100% (1)
- Constitution MakingDokument5 SeitenConstitution MakingJawad AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Con Law Bible 1Dokument176 SeitenCon Law Bible 1Liam MurphyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constitution Law OUTLINEDokument28 SeitenConstitution Law OUTLINEchazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 Kreimer Good Outline!!Dokument114 Seiten2020 Kreimer Good Outline!!Gaelle Pierre-LouisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constitution of The USADokument30 SeitenConstitution of The USAAiman RashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constitutional Law OverviewDokument16 SeitenConstitutional Law OverviewStacy OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Con Law I Outline - WeaverDokument62 SeitenCon Law I Outline - WeaverJasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.6 Amsco APUSH OutlineDokument3 SeitenCh.6 Amsco APUSH OutlineJosh Morgan50% (6)
- Constitutional Law OutlineDokument86 SeitenConstitutional Law OutlineEvanKing100% (2)
- Con Law Outline (Adler)Dokument59 SeitenCon Law Outline (Adler)Alena Shautsova50% (2)
- ConLaw KaczorowskiDokument41 SeitenConLaw Kaczorowskitarap1230% (1)
- ConstitutionDokument4 SeitenConstitutionapi-726423851Noch keine Bewertungen
- Citizenship in The Nation: Merit Badge Counselor WorkbookDokument9 SeitenCitizenship in The Nation: Merit Badge Counselor Workbookygarcia3535Noch keine Bewertungen
- Powers of Congress: I. Expressed Powers: Definition & ExamplesDokument2 SeitenPowers of Congress: I. Expressed Powers: Definition & ExamplesJakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- American Government and Politics - 1/3 Term Exam: Sebastian BermudezDokument3 SeitenAmerican Government and Politics - 1/3 Term Exam: Sebastian Bermudezsebastian bermudezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 - Legislative Branch 3:1: I: An Outline of The ConstitutionDokument6 SeitenUnit 3 - Legislative Branch 3:1: I: An Outline of The ConstitutionMichael David SchadtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Executive Foreign DelegationDokument4 SeitenExecutive Foreign DelegationkoreanmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Con Law Young 08Dokument107 SeitenCon Law Young 08DavidFriedman100% (1)
- Constitutional Law - Long NotesDokument106 SeitenConstitutional Law - Long NotesstaceyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP American Government: Chapter Fourteen: The JudiciaryDokument6 SeitenAP American Government: Chapter Fourteen: The JudiciaryirregularflowersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Con Law Oultine-PersonalDokument5 SeitenCon Law Oultine-PersonalAshley DanielleNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSL Notes - Chapter 3Dokument9 SeitenNSL Notes - Chapter 3APNSL100% (1)
- United States Civics - Bill Of Rights for Kids | 1787 - 2016 incl Amendments | 4th Grade Social StudiesVon EverandUnited States Civics - Bill Of Rights for Kids | 1787 - 2016 incl Amendments | 4th Grade Social StudiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States Civics - The US Constitution for Kids | 1787 - 2016 with Amendments | 4th Grade Social StudiesVon EverandUnited States Civics - The US Constitution for Kids | 1787 - 2016 with Amendments | 4th Grade Social StudiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federalist and Jefferson Era Study GuideDokument3 SeitenFederalist and Jefferson Era Study Guidealbertmorales82Noch keine Bewertungen
- The American Revolution 1776Dokument10 SeitenThe American Revolution 1776albertmorales82Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Federalist Era1Dokument10 SeitenThe Federalist Era1albertmorales82Noch keine Bewertungen
- French and Indian War OutlineDokument5 SeitenFrench and Indian War Outlinealbertmorales82Noch keine Bewertungen
- French and Indian War OutlineDokument5 SeitenFrench and Indian War Outlinealbertmorales82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1,2,3 Study GuideDokument4 SeitenChapter 1,2,3 Study Guidealbertmorales82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Contact - New World Unit 1Dokument17 SeitenContact - New World Unit 1albertmorales82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1-The Role of GovernmentDokument5 SeitenChapter 1-The Role of Governmentalbertmorales82Noch keine Bewertungen
- SANNADKA XII. Muqdisho - 18 Maajo 1984 - L. 1 R. 5Dokument32 SeitenSANNADKA XII. Muqdisho - 18 Maajo 1984 - L. 1 R. 5Cumar MaxamuudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of LawDokument16 SeitenSources of LawJayananthini PushbahnathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karnataka Official Language Act, 1963Dokument5 SeitenKarnataka Official Language Act, 1963Latest Laws TeamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity: Comparison and Contrast of Philippine ConstitutionDokument3 SeitenActivity: Comparison and Contrast of Philippine Constitutionjustine key igot100% (2)
- Interpretation of StatutesDokument11 SeitenInterpretation of StatutespriyanandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occena Vs Comelec 104 Scra 1Dokument5 SeitenOccena Vs Comelec 104 Scra 1MykaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three Branches of GovernmentDokument17 SeitenThree Branches of GovernmentJhez Magno PelagioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 2 Gonzales vs. Comelec, 21 SCRA 774 (1968) - SummaryDokument3 SeitenCase 2 Gonzales vs. Comelec, 21 SCRA 774 (1968) - Summaryblude cosing100% (1)
- Equity and TrustDokument4 SeitenEquity and TrustXYZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Is Born Shorts 2Dokument1 SeiteGovernment Is Born Shorts 2Jorge A VillarrealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Sankari Prasad Singh Deo Vs Union of India and State of BiharDokument19 SeitenSri Sankari Prasad Singh Deo Vs Union of India and State of BiharRohit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiu Vs CA DigestDokument1 SeiteTiu Vs CA DigestLennart Reyes100% (2)
- Federalism (Part1)Dokument9 SeitenFederalism (Part1)Tapas BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article 370 of The Constitution of India - WikipediaDokument97 SeitenArticle 370 of The Constitution of India - WikipediaAswinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010-08 - Order Recalling Certain Writs of Bodily Attachment Over 5 Years OldDokument328 Seiten2010-08 - Order Recalling Certain Writs of Bodily Attachment Over 5 Years OldAnna MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salmonds Classification of LawDokument11 SeitenSalmonds Classification of LawStar BoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSE - Philippine Constitution Part 1Dokument7 SeitenCSE - Philippine Constitution Part 1Vienna Corrine Quijano AbucejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONSTILAW - Santiago Vs Comelec GR127325Dokument2 SeitenCONSTILAW - Santiago Vs Comelec GR127325Lu CasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Law Governing The Constitutional Commission of 1986Dokument13 SeitenThe Law Governing The Constitutional Commission of 1986Macafra LingatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABESTANODokument6 SeitenABESTANOLirpa Mae OtrofNoch keine Bewertungen
- Historic 8th Amendment Is Passed - Landmark in The Constitutional History of PakistanDokument2 SeitenHistoric 8th Amendment Is Passed - Landmark in The Constitutional History of PakistanHamza Azhar100% (1)
- Constitution (First Amendment) Act, 1974Dokument4 SeitenConstitution (First Amendment) Act, 1974bakhokharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stages in The Amendatory Process Part 1Dokument3 SeitenStages in The Amendatory Process Part 1mikhaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- STATUTORY CONSTRUCTION. Outline of Topics With Cases. 2021 2022Dokument6 SeitenSTATUTORY CONSTRUCTION. Outline of Topics With Cases. 2021 2022ben carlo ramos srNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agpalo Notes - Statutory Construction, CH 10Dokument2 SeitenAgpalo Notes - Statutory Construction, CH 10Chikoy Anonuevo100% (2)
- CustomDokument6 SeitenCustomRoshnee MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compare and Contras1Dokument2 SeitenCompare and Contras1Jessa Pascua Sumio50% (2)
- Legislative Power: What Is It?Dokument6 SeitenLegislative Power: What Is It?Sally FetouhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salient Features of British Constitution: I) UnwrittenDokument3 SeitenSalient Features of British Constitution: I) UnwrittenAnishfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - The Philippine ConstitutionDokument15 SeitenModule 1 - The Philippine ConstitutionRei Clarence De AsisNoch keine Bewertungen