Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sin, Cos and Tan: Example
Hochgeladen von
Mani KandanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sin, Cos and Tan: Example
Hochgeladen von
Mani KandanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sin, Cos and Tan
Page 1 of 4
Sin, Cos and Tan
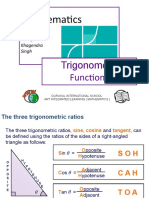
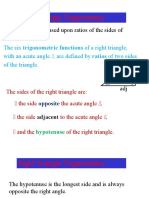
A right-angled triangle is a triangle in which one of the angles is a rightangle. The hypotenuse of a right angled triangle is the longest side, which is the one opposite the right angle. The adjacent side is the side which is between the angle in question and the right angle. The opposite side is opposite the angle in question. In any right angled triangle, for any angle: The sine of the angle = the length of the opposite side the length of the hypotenuse The cosine of the angle = the length of the adjacent side the length of the hypotenuse The tangent of the angle = the length of the opposite side the length of the adjacent side So in shorthand notation: sin = o/h cos = a/h tan = o/a Often remembered by: soh cah toa Example Find the length of side x in the diagram below:
http://www.mathsrevision.net/gcse/pages.php?page=39
17/12/2010
Sin, Cos and Tan
Page 2 of 4
The angle is 60 degrees. We are given the hypotenuse and need to find the adjacent side. This formula which connects these three is: cos(angle) = adjacent / hypotenuse therefore, cos60 = x / 13 therefore, x = 13 cos60 = 6.5 therefore the length of side x is 6.5cm.
The Graphs of Sin, Cos and Tan
The following graphs show the value of sin, cos and tan against ( represents an angle). From the sin graph we can see that sin = 0 when = 0 degrees, 180 degrees and 360 degrees.
http://www.mathsrevision.net/gcse/pages.php?page=39
17/12/2010
Sin, Cos and Tan
Page 3 of 4
Note that the graph of tan has asymptotes (lines which the graph gets close to, but never crosses). These are the red lines (they aren't actually part of the graph). Also notice that the graphs of sin, cos and tan are periodic. This means that they repeat themselves. Therefore sin() = sin(360 + ), for example.
http://www.mathsrevision.net/gcse/pages.php?page=39
17/12/2010
Sin, Cos and Tan
Page 4 of 4
Notice also the symmetry of the graphs. For example, cos is symmetrical in the y-axis, which means that cos = cos(-). So, for example, cos(30) = cos (-30). Also, sin x = sin (180 - x) because of the symmetry of sin in the line = 90.
Learn Maths VI to XII Resolve all NCERT Math Problems Concepts,Solutions,Tests videos
www.mathtopper.com
Free NCERT Solutions Math, Phy, Chem, Bio, English, SST CBSE, ICSE Class 4-12, Register Now
www.MeritNation.com
MathsRevision.Net Home;Revision World;
http://www.mathsrevision.net/gcse/pages.php?page=39
17/12/2010
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Trigonometric Functions 2Dokument34 SeitenTrigonometric Functions 2Sahil JindalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B-Spline & NURBS CurvesDokument94 SeitenB-Spline & NURBS CurvesMoustafa MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOHCAHTOADokument17 SeitenSOHCAHTOAYsa BurguillosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circumference and Are A of A CircleDokument2 SeitenCircumference and Are A of A Circleana kamariahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plane TrigonometryDokument3 SeitenPlane TrigonometrylolaceitunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument7 SeitenTrigonometryRagav VijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 2005Dokument12 SeitenSolution 2005BHAAJI0001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry: Made By:-Suyash Agarwal X I - BDokument47 SeitenTrigonometry: Made By:-Suyash Agarwal X I - BSuyash Agarwal100% (1)
- Trigonometry of Right TrianglesDokument9 SeitenTrigonometry of Right TrianglesKenneth D. Ligutom100% (1)
- Engineering Drawing Course Material PDFDokument113 SeitenEngineering Drawing Course Material PDFAisha NoureenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shinglee EmathTxt 6thedtDokument216 SeitenShinglee EmathTxt 6thedtMethodology OfStudies88% (8)
- Lesson Plan Trigo Class X by ManishaDokument20 SeitenLesson Plan Trigo Class X by Manishamansiha agrawal82% (17)
- Reviewer in Pre-Calculus 11Dokument18 SeitenReviewer in Pre-Calculus 11RJ Seva IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Cybernetics (Ashby)Dokument156 SeitenAn Introduction To Cybernetics (Ashby)telecult100% (2)
- RD Sharma Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 15 Properties of Triangles PDFDokument55 SeitenRD Sharma Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 15 Properties of Triangles PDFsamridh guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Six Trigonometric Ratios (Powerpoint Presentation) 2Dokument12 SeitenThe Six Trigonometric Ratios (Powerpoint Presentation) 2Francelle Zaira PimentelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 9-Q4-Module-1Dokument18 SeitenMath 9-Q4-Module-1An Neh Gyn100% (2)
- MATH 9 Q4 MELC 1 To 4Dokument27 SeitenMATH 9 Q4 MELC 1 To 4Ella de la Cruz Gulanes100% (1)
- TrigonometryDokument101 SeitenTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six TrigoDokument19 SeitenSix TrigoJLacissej 117Noch keine Bewertungen
- Space TrussDokument29 SeitenSpace TrussPrashant PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rev Math 1 Con 3Dokument3 SeitenRev Math 1 Con 3For NobellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Right Triangle DefinitionsDokument4 SeitenRight Triangle DefinitionsArki TektureNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument13 SeitenTrigonometryjobmajuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument36 SeitenTrigonometryYoshika GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry Part 1Dokument28 SeitenTrigonometry Part 1Annisa IstiqomahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 6 EDU 10 FCODokument6 SeitenGroup 6 EDU 10 FCOJaishenne CastuloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Random LecturesDokument30 SeitenRandom LecturesTrisha KayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Six Trigonometric RatiosDokument30 SeitenThe Six Trigonometric Ratiosmaligaya evelynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step Up Pakistan: Team Roshni: Mathematics 4024 Trigonometry: Sin, Cos, TanDokument6 SeitenStep Up Pakistan: Team Roshni: Mathematics 4024 Trigonometry: Sin, Cos, TannmarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Do Trigonometry Step by StepDokument4 SeitenHow To Do Trigonometry Step by Stepnishagoyal100% (1)
- 14-4 Trigonometry Ratios in Right TriangleDokument21 Seiten14-4 Trigonometry Ratios in Right Triangleapi-277585828Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometria N Virginia C CDokument14 SeitenTrigonometria N Virginia C CJavier MelesioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry Realms: Sin (X)Dokument28 SeitenTrigonometry Realms: Sin (X)amit34521Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Trigonometry IntroductionDokument4 SeitenMaths Trigonometry IntroductionDivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six Trigonometric Ratios and Special Right TrianglesDokument21 SeitenSix Trigonometric Ratios and Special Right TrianglesDiana Rose Bagui LatayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Right TrianglesDokument13 SeitenRight TrianglesMHARLOU TORINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Proper - TRIGONOMETRYDokument5 SeitenLesson Proper - TRIGONOMETRYMontenegro Roi Vincent100% (1)
- The Six Trigonometric RatiosDokument30 SeitenThe Six Trigonometric Ratiosmaligaya evelynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q4 MATH 9-WEEK 3-Solving Right Triangle Using Trigonometric RatiosDokument39 SeitenQ4 MATH 9-WEEK 3-Solving Right Triangle Using Trigonometric RatiosAngela Camille PaynanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Ratios (Definition, Formulas, ExampDokument2 SeitenTrigonometric Ratios (Definition, Formulas, Examp5kptyrh78bNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Find The Sides of A Right TriangleDokument5 SeitenHow To Find The Sides of A Right TriangleandsrbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pythagroas and SOHCAHTOADokument8 SeitenPythagroas and SOHCAHTOA姚凤娇Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 U4 ReadingDokument3 Seiten1 U4 Readingapi-292718088Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric FunctionsDokument6 SeitenTrigonometric FunctionsnathanalocilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4Dokument15 SeitenWeek 4lexmaster0224Noch keine Bewertungen
- q391 Assignment LawrenzaquinoDokument50 Seitenq391 Assignment LawrenzaquinoReuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Ail Name - Khagendra Singh Class XI-BDokument10 SeitenMaths Ail Name - Khagendra Singh Class XI-BJougan OtsusukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- E - ContentDokument8 SeitenE - ContentSomasundariNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument13 SeitenTrigonometryjohn_muellorNoch keine Bewertungen
- B2 Module 1 Lesson 2Dokument11 SeitenB2 Module 1 Lesson 2Kate RellitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 in MfeDokument9 SeitenModule 1 in Mfevantae SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 10 DLS 26-27Dokument6 SeitenMathematics 10 DLS 26-27Ivan Miguel MariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coc-Pen Math1 Study Guide of Trigonometry 01 Easy Way (How To Learn Trigonometry Faster)Dokument9 SeitenCoc-Pen Math1 Study Guide of Trigonometry 01 Easy Way (How To Learn Trigonometry Faster)Marlon AmpoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Trigonometry FormulasDokument29 SeitenBasic Trigonometry FormulasNina RicciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry Ratios in Right TriangleDokument19 SeitenTrigonometry Ratios in Right Trianglemicaela Jomil TizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To TrigonometryDokument9 SeitenIntroduction To TrigonometryPaula FanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Trigonometric FunctionsDokument26 Seiten3 - Trigonometric FunctionsZamanoden D. UndaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry WorkbookDokument20 SeitenTrigonometry WorkbookElaine zhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- (English) Basic Trigonometry - Sin Cos Tan (NancyPi) (DownSub - Com)Dokument6 Seiten(English) Basic Trigonometry - Sin Cos Tan (NancyPi) (DownSub - Com)Jisoo KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathway To Trigonometry: Grade 9Dokument9 SeitenPathway To Trigonometry: Grade 9Bernaliza CaserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Functions - WikipediaDokument14 SeitenTrigonometric Functions - WikipediaAlone EulerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Unit 7 MathDokument3 SeitenAssignment Unit 7 Mathstephen makoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRIGNOMETRYDokument6 SeitenTRIGNOMETRYABNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primer Trig PhysicsDokument13 SeitenPrimer Trig PhysicsjayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Functions and The Right TriangleDokument15 SeitenBasic Functions and The Right TriangleChetan Tolia100% (1)
- Trigonometry Test BasicDokument2 SeitenTrigonometry Test BasicAdesh Partap SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jonas NobilityOfSightDokument14 SeitenJonas NobilityOfSightThomas PfauNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1993 JoSG Strain Kinematic Analysis General Shear Zones PDFDokument20 Seiten1993 JoSG Strain Kinematic Analysis General Shear Zones PDFLalit JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review and Consolidate of Year 9 (Optional) : Skill Test Yourself Exercises/ Learning Resources Student Check AlgebraDokument14 SeitenReview and Consolidate of Year 9 (Optional) : Skill Test Yourself Exercises/ Learning Resources Student Check AlgebraSayed Qasim ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acta Astronautica: Anne W. JohnsonDokument7 SeitenActa Astronautica: Anne W. Johnsontotenkopf0424Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abelian Varieties, Theta Functions and The Fourier Transform PDFDokument307 SeitenAbelian Varieties, Theta Functions and The Fourier Transform PDFAmeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary - 02 PDFDokument4 SeitenSummary - 02 PDFImran MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Tensor Form of The Dirac EquationDokument28 SeitenA Tensor Form of The Dirac Equationapi-3773171Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperbola: Section - I: Straight Objective TypeDokument8 SeitenHyperbola: Section - I: Straight Objective TyperashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-Sss Sas Asa and Aas CongruenceDokument4 Seiten4-Sss Sas Asa and Aas CongruenceSohel MozidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euclidean Geometry and Transformations PDFDokument2 SeitenEuclidean Geometry and Transformations PDFHipolito25% (4)
- Dynamics - Chapter 11 (Beer7)Dokument49 SeitenDynamics - Chapter 11 (Beer7)api-370949667% (3)
- Kinematics FREE WORKSHEET/QUESTION BANK BY ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC)Dokument3 SeitenKinematics FREE WORKSHEET/QUESTION BANK BY ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES (ATC)ANURAG TYAGI100% (2)
- HelicalDokument3 SeitenHelicalsathiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT-III Straight Lines Inclined To Both The PlanesDokument13 SeitenUNIT-III Straight Lines Inclined To Both The PlanessainathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antonio Padilla, Paul M. Saffin and Shuang-Yong Zhou - Multi-Galileons, Solitons and Derrick's TheoremDokument12 SeitenAntonio Padilla, Paul M. Saffin and Shuang-Yong Zhou - Multi-Galileons, Solitons and Derrick's TheoremHuntsmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM F5 C8: Circular MeasureDokument4 SeitenSPM F5 C8: Circular MeasureAzfarina JaafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiential Learning Theory: A Dynamic, Holistic Approach To Management Learning, Education and DevelopmentDokument59 SeitenExperiential Learning Theory: A Dynamic, Holistic Approach To Management Learning, Education and DevelopmentamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tournament of Towns 2007Dokument10 SeitenTournament of Towns 2007OklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Angles 1Dokument2 SeitenTypes of Angles 1Abi PiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of A ForceDokument4 SeitenMoment of A ForceReeseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polytechnic, Department of Electrical Engineering,: The Maharaja Sayajirao University of BarodaDokument1 SeitePolytechnic, Department of Electrical Engineering,: The Maharaja Sayajirao University of BarodaRajeev Kumar AaryaNoch keine Bewertungen