Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids
Hochgeladen von
Jonas GaleosOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids
Hochgeladen von
Jonas GaleosCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
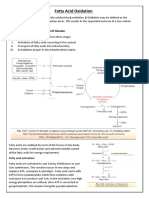
Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids An Overview Beta oxidation of fatty acids takes place in the mitochondrial matrix for
the most part. However, fatty acids have to be activated for degradation by coenzyme A by forming a fatty acyl-CoA thioester. For short and medium length fatty acids, they undergo this reaction in the mitochondria. The long chain fatty acids can't go through the membrane though, so this reaction occurs at the outer mitochondrial membrane and the product has to be carried by carnitine across the inner mitochondrial membrane. They are made into acylcarnitine derivatives by carnitine transferase I on the outer side of the inner membrane. These are then transported across the membrane by a translocaseand then they are passed to carnitine acyltransferase II on the matrix side which puts the fatty acyl group back on CoA leaving the original fatty acyl-CoA. Beta Oxidation of Unsaturated Fatty Acids Unsaturated fatty acids are catabolized by the beta oxidation pathway, but they require two additional enzymes to handle the cis-double bonds. These fatty acids (with one cis-double bond) go through the beta oxidation cycle as many times as they can before coming to the double bond. The Enoyl-CoA Isomerase makes the cis-double bond into a trans-double bond and moves it over one carbon. This product can
then continue through the beta oxidation pathway. For polyunsaturated fatty acids (with more than one cis-double bond) it goes through the same thing, but it only goes through one more round of beta oxidation because then you get to a fatty acid with a trans and a cis double bond. For this we use 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase to produce a trans-3-enoyl product which is converted by an enoyl-CoA isomerase to a trans-2-enoyl-CoA which then goes normally through the pathway. Beta Oxidation of Saturated Fatty Acids Each cycle of beta-oxidation of saturated fatty acid will release one molecule of acetyl CoA (2 carbon acid thioester). Let say there is a palmitic acid (containing 16 carbon) undergoing beta-oxidation, it requires 7 cycle to complete the beta-oxidation and 8 molecules of acetyl CoA will form. Each cycle release 2-carbon acid and palmitic acid is a 16-carbon acid, thus 1st cycle will prvide 14-carbon acid and acetyl CoA 2 nd cycle will prvide 12-carbon acid and acetyl CoA ...so on and so on 7th cycle will break down a butyryl acid (4carbon acid) to TWO molecules of acetyl CoA. From above observation, we can conclude that: (1) numbers of acetyl CoA will be provided by complete beta-oxidation are:
number of Carbon of that fatty acid divided by 2 (2) numbers of cycles of complete beta-oxidation will be required: number of Carbon of that fatty acid divided by 2 minus ONE
Biochemistry CHEM 123
Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids & Lipid Digestion and Absorption
Submitted by: Genesis Torres Shida Salikala Miel Atilano Jonas Rafael Galeos
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cellular Respiration Review WorksheetkeyDokument6 SeitenCellular Respiration Review WorksheetkeyMohammed AlMujainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tree NotesDokument67 SeitenTree NotesRahul RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Corinthians-Basic Christian LivingDokument50 Seiten1 Corinthians-Basic Christian LivingAndré HolandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem. Chapter 7 Notes. Myoglobin and Hemoglobin, Muscle Contraction, and AntibodiesDokument10 SeitenBiochem. Chapter 7 Notes. Myoglobin and Hemoglobin, Muscle Contraction, and AntibodiesOANoch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 4: Central Dogma of Biology: Protein SynthesisDokument32 SeitenScience: Quarter 3 - Module 4: Central Dogma of Biology: Protein SynthesisEricha Solomon56% (9)
- Beta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDokument34 SeitenBeta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsZelda LoverNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 5 Electrons in AtomsDokument28 SeitenCH 5 Electrons in Atomsapi-291289442Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure: Earning UtcomesDokument25 SeitenAtomic Structure: Earning Utcomessabrina_sarranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of A CellDokument4 SeitenParts of A CelltadashiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separation of Stable IsotopesDokument56 SeitenSeparation of Stable IsotopesKaranam.RamakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Configuration!Dokument19 SeitenElectron Configuration!joyyswainnNoch keine Bewertungen
- WWW Codechef Com Certification Data Structures and Algorithms Prepare FoundationDokument15 SeitenWWW Codechef Com Certification Data Structures and Algorithms Prepare FoundationCool KSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christian LivingDokument17 SeitenChristian LivingLance RonquilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Laws Review Sheet Answers RenoDokument2 SeitenGas Laws Review Sheet Answers RenoERICA BURNSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDokument27 SeitenOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYC100% (1)
- Alkenes and AlkynesDokument22 SeitenAlkenes and AlkynesAyodele AdeyonuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaDokument60 SeitenMetabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaAmanda PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- IsotopesDokument1 SeiteIsotopesShiela Marie ArrojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13-3 Global Warming PDFDokument15 Seiten13-3 Global Warming PDFRocío RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myoglobin & HemoglobinDokument53 SeitenMyoglobin & HemoglobinAgnetasia PriscilliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioenergetics How The Body Converts Food To EnergyDokument38 SeitenBioenergetics How The Body Converts Food To EnergyShereen AlobinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glyoxylate CycleDokument14 SeitenGlyoxylate CycleUtkarsh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life.: Key ConceptDokument16 SeitenCells Are The Basic Unit of Life.: Key ConceptCristopher Calhoun ImitolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron ConfigurationDokument9 SeitenElectron ConfigurationShuganthi MasilamanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological OxidationDokument42 SeitenBiological OxidationSapana Subedi100% (1)
- The Foundations of ChemistryDokument38 SeitenThe Foundations of ChemistryJesusBlasVitangcolNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOENERGETICS - How The Body Converts Food To Energy - Group 7 (MC 102 - Lecture) EDITEDDokument73 SeitenBIOENERGETICS - How The Body Converts Food To Energy - Group 7 (MC 102 - Lecture) EDITEDJowe VarnalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cofactor and CoenzymeDokument24 SeitenCofactor and CoenzymeBIDIN100% (1)
- Fatty Acid Synthesis 11.12.19Dokument18 SeitenFatty Acid Synthesis 11.12.19Sanreet Randhawa100% (1)
- Protein Biocatalyst (Enzyme)Dokument3 SeitenProtein Biocatalyst (Enzyme)Khairul RidwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument30 SeitenLecture 1حموده ابراهيم يونسNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism IIDokument3 Seiten4 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism IILinus LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reduction Potential - WikipediaDokument28 SeitenReduction Potential - WikipediaBabar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Origin and Chemistry of Life: Prepared By: Asst. Prof. Sheryl Santa Cruz-BiscochoDokument25 SeitenThe Origin and Chemistry of Life: Prepared By: Asst. Prof. Sheryl Santa Cruz-Biscochoirish x100% (1)
- Sugars Power PointDokument67 SeitenSugars Power PointCLEMENTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hexose Monophosphate ShuntDokument43 SeitenHexose Monophosphate ShuntSecret AgentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Configuration Fall 2016Dokument31 SeitenElectron Configuration Fall 2016Aviral TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Endocrine DiseasesDokument6 SeitenList of Endocrine DiseasesPreethiHonavarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterocyclic ChemistryDokument8 SeitenHeterocyclic ChemistryM FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment (Carbs&Lipids)Dokument4 SeitenAssignment (Carbs&Lipids)Jeon JungkayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional and Structural Properties of Natural BiomembranesDokument7 SeitenFunctional and Structural Properties of Natural BiomembranesAhsan RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hexose Mono Phosphate (HMP) ShuntDokument28 SeitenHexose Mono Phosphate (HMP) ShuntVishesh JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- B Y: - Idr. Megha Gaur BDS IDokument89 SeitenB Y: - Idr. Megha Gaur BDS IRishab GaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatty Acid OxidationDokument28 SeitenFatty Acid OxidationEmm NomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism of Ketone BodiesDokument38 SeitenMetabolism of Ketone BodiesJavedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino AcidsDokument32 SeitenAmino AcidsStephen Leonel100% (1)
- Browning Reactions in Foods: Food TechnologyDokument53 SeitenBrowning Reactions in Foods: Food Technologykasun HerathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 20 ETC and Oxidative PhosphDokument29 SeitenChapter 20 ETC and Oxidative PhosphSpencer ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholesterol - Synthesis, Metabolism, Regulation PDFDokument10 SeitenCholesterol - Synthesis, Metabolism, Regulation PDFAdreiTheTripleA100% (1)
- Lehninger PPT Ch13 2Dokument45 SeitenLehninger PPT Ch13 2송정근0% (2)
- Urea CycleDokument38 SeitenUrea CycleAbdimalik Ali100% (1)
- Absorption of LipidsDokument22 SeitenAbsorption of LipidsEmm Noman100% (1)
- Enzyme Catalysis-Chapter 7 (Part 1)Dokument22 SeitenEnzyme Catalysis-Chapter 7 (Part 1)OmSilence2651Noch keine Bewertungen
- Michaelis Menten EquationDokument9 SeitenMichaelis Menten Equationsadaf zaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- + F.R.Fatty Acid SynthesisDokument28 Seiten+ F.R.Fatty Acid SynthesisAmanuel MaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Aromatic Hydrocarbons BenzeneDokument116 Seiten01 Aromatic Hydrocarbons BenzeneHamid Hussain HamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism IDokument3 Seiten2 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism ILinus LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hybridization 1Dokument37 SeitenHybridization 1Anzari MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatty Acid Oxidation Stages and TissuesDokument3 SeitenFatty Acid Oxidation Stages and TissuesAhsan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beta-Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDokument6 SeitenBeta-Oxidation of Fatty AcidsBinku Dutta100% (1)
- Fast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportVon EverandFast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For PneumoniaDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For PneumoniaJonas Galeos100% (2)
- Chemically Impaired NursesDokument2 SeitenChemically Impaired NursesJonas GaleosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acquired Immune Deficiency SyndromeDokument14 SeitenAcquired Immune Deficiency SyndromeJonas GaleosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typhoid Feve1Dokument9 SeitenTyphoid Feve1Jonas Galeos100% (1)
- Passive and Active Transport-Igcse Biology Chapter 3Dokument3 SeitenPassive and Active Transport-Igcse Biology Chapter 3Jiya ChhugeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipotoxicidad Por Ceramidas CayetanoDokument13 SeitenLipotoxicidad Por Ceramidas CayetanoLuciana Taco MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separation and Characterization Techniques For Proteins and AminoDokument34 SeitenSeparation and Characterization Techniques For Proteins and AminoAnna Donato100% (2)
- A202001006 - PUTRI WAHYUNI - Primer3 Output (Primer3 - Results - Cgi Release 4.1.0)Dokument2 SeitenA202001006 - PUTRI WAHYUNI - Primer3 Output (Primer3 - Results - Cgi Release 4.1.0)sasyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pro Clot PCDokument3 SeitenPro Clot PCSmithesh TpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rational Drug DesignDokument25 SeitenRational Drug DesignWaseem KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Biotechnology Module 2Dokument18 SeitenBasic Biotechnology Module 2roger policarpioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cape Biology - Unit 1 - EnzymesDokument7 SeitenCape Biology - Unit 1 - EnzymesSteven IStudy Smith67% (3)
- PCGPV VectorDokument1 SeitePCGPV VectorAlleleBiotechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Dysregulation of Innate Immune Response Genes and Neuronal Activity Dependent Genes in AutismDokument8 SeitenTranscriptome Analysis Reveals Dysregulation of Innate Immune Response Genes and Neuronal Activity Dependent Genes in AutismKarim ElghachtoulNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 2.2 LAS General Biology 2 Ist QuarterDokument6 SeitenWEEK 2.2 LAS General Biology 2 Ist QuarterJoshua EsguerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementDokument2 SeitenCell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementJaniya KellyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - 2023 - DNA PolymerasesDokument53 SeitenLecture 2 - 2023 - DNA PolymerasesChen ZhonghaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription Factor - WikipediaDokument112 SeitenTranscription Factor - WikipediaBaikuntha SabarNoch keine Bewertungen
- LipidsDokument2 SeitenLipidsGianneCarloGomedNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOTECON Diagnostics Product Sheet RoboPrep32Dokument2 SeitenBIOTECON Diagnostics Product Sheet RoboPrep32anggialwieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell SurfaceDokument3 SeitenCell SurfaceNabindra RuwaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanger Troubleshooting Guide v1Dokument5 SeitenSanger Troubleshooting Guide v1yavuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- (VCE Biology) 2018 ACED Unit 3/4 ExamDokument28 Seiten(VCE Biology) 2018 ACED Unit 3/4 ExamAyesha RiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics MCQDokument3 SeitenGenetics MCQibdpNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 - Lecture 3-CanvasDokument42 Seiten2018 - Lecture 3-CanvasAdam Bryant PoonawalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA and RNA Are PolynucleotidesDokument35 SeitenDNA and RNA Are PolynucleotidesnaomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ap Biology Vocabulary ListDokument6 SeitenAp Biology Vocabulary Listapi-415920554Noch keine Bewertungen
- Espript/Endscript: Extracting and Rendering Sequence and 3D Information From Atomic Structures of ProteinsDokument4 SeitenEspript/Endscript: Extracting and Rendering Sequence and 3D Information From Atomic Structures of ProteinsRigers ZalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Beacons: A Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay For Detecting SalmonellaDokument7 SeitenMolecular Beacons: A Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay For Detecting Salmonellatvh122Noch keine Bewertungen
- Receptor TypesDokument3 SeitenReceptor TypesPardeep SonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q3 Week 5 Stem G11 General Biology 1Dokument23 SeitenQ3 Week 5 Stem G11 General Biology 1John Benedict MaurilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culture BacteriaDokument6 SeitenCulture BacteriaCelina PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anishnu Mukhopadhyay - Sec 1 Assignment - 704Dokument17 SeitenAnishnu Mukhopadhyay - Sec 1 Assignment - 704Anjishnu Mukhopadhyay BIOTECH SXCBNoch keine Bewertungen