Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Biology Scheme Pertgh Penggal 2
Hochgeladen von
Faida HamidOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Biology Scheme Pertgh Penggal 2
Hochgeladen von
Faida HamidCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1.
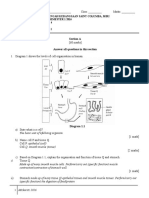
Diagram 1 shows the different stages which take place during cell division.
Diagram 1
(a) Name the cell division shown in Diagram 1. Mitosis [1 mark] (b) Arrange the stages in Diagram 1 according to the correct sequence of events during cell division L,N,K,M [1 mark] (c) Name the stages labelled K and N? K N : Anaphase (early ) : Metaphase [2 marks] (d) Explain the behaviour of chromosomes during stages K and N. K N : Sister chromatids separate and move towards to the opposite poles of the cell : Chromosomes align/lined up at the metaphase plate // 2 sister chromatids are attached to the spindle fibre by their centromeres [2 marks]
Diagram 2 shows an experiment carried out on animal cloning by using two different species of frog
Species X
Ovum Ovum without nucleus A
Species Y
C UV light
Intestine is removed from the tadpole
B D
Nucleus is sucked out from the intestine
Nucleated egg cell fused with the nucleus of intestinal cell E F (e) Based on Diagram 2, state the meaning of cloning. Cloning is a process to produce a new frog which is identical to its parent by mitosis [1 mark] (f) Name the type of reproduction shown in Diagram 2. Give a reason for your answer. Asexual reproduction (1 m). The production of offspring is not involving the process of fertilization (1 m) [2 marks] (g) Describe why a mature intestinal cell is used in this experiment. Give two reasons. Mature intestinal cells are able to undergo mitosis /cell division by mitosis. Have all the necessary factors required for a complete cell division [2 marks] (h) (i) Based on Diagram 2, name the species of frog that will be produced at the end of the experiment. Species Y [1 mark] (ii) Explain your answer in (h) (i). Nucleus of the frog is obtained from species Y [1 mark]
Diagram 2
2.
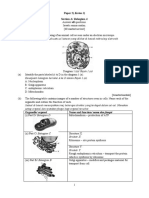
Diagram 3 shows the levels of cell organisation in human.
Cell
m u s cl Tissue c e ll Cell P Smooth muscle cell
Tissue P
Tissue Q
Diagram 3
Stomach
Level R
Gastric gland
(a) State what a cell is. Is a basic unit of life / living organism [1 mark] (b) Name Cell P and Tissue Q Cell P : Epithelial cell Tissue Q : Smooth muscle tissue [2 marks] (c) Based on Diagram 3, explain the organisation and function of Tissue Q and stomach. Tissue Q : Made up of many smooth muscle cells . Perform / carry out (specific function) muscle contraction /contraction of stomach wall Stomach : Made of many Tissue Q / epithelial tissues and smooth muscle tissues Perform / carry out (specific function) the digestion of food / protein [4 mark] (d) State the Level R of cell organisation. Organ [1 mark]
(e) (i)
Name the food molecules that are digested in the stomach and the enzyme for this reaction. Food molecules : protein //caseinogens (soluble milk protein) Enzyme : pepsin // rennin [2 marks]
(ii)
Describe how the hydrochloric acid produced by the gastric glands help in the digestion of food molecules in the stomach. Provide acidic medium for the optimum reaction of enzymepepsin in stomach / stop the activity of salivary amylase / helps to kill bacteria in food [2 marks]
3.
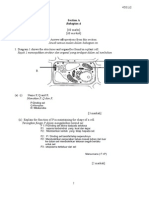
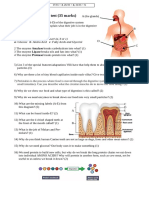
Diagram 4(a) shows the human digestive system.
Diagram 4(a)
(a) (i)
State the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion. Mechanical digestion breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces with aid of teeth. Chemical digestion breakdown of complex food into simple soluble substances / molecules. Process requires digestive enzymes. [2 marks]
(b) (ii) State the difference between absorption and assimilation. Absorption movement of simple soluble molecules/ substances across intestinal wall of the alimentary canal into the bloodstream Assimilation utilisation of absorbed food by body cells for energy , growth, reproduction , repair [2 marks] (c) Name the structures P and Q. P : Deodenum Q : Pancreas [2 marks] (d) Describe how Q is involved in the digestion of fats and starch in P Pancreatic juices containing lipase and pancreatic amylase transported from Q to P. Lipase hydrolyse tiny droplets of fats to fatty acids and glycerol . Pancreatic amylase hydrolyses starch to maltose [2 marks] (f) Diagram 4(b) shows two types of fats
Diagram 4(b)
(i)
State the type of fats shown in Diagram 4(b) R : Saturated fat S: Unsaturated fat [2 marks]
(ii) A girl takes food from group R continuously for a long period of time. Explain the consequences to the health of her heart. Able to explain the consequences of taking food from group P for a long period time
Sample answer: Food from group P contains high level of cholesterol (1m) Cholesterol//fatty deposits tend to accumulate on the inner wall of arteries (1m) Causes the narrowing of the blood vessels/ coronary arteries are blocked by the built-up of fatty tissues (1m) Reduces the flow of blood (1m) The heart muscles become starved of oxygen and dies (1m) The girl might get heart attack (1m) MAX: 3 marks [3 marks] 4. Diagram 5 represents the structures of four organic compounds which are found in living cells.
Diagram 5
(a) (i) Name the compounds of X and Z X : polypeptides / protein Z : lipid / fat [2 marks] (ii) State the monomer of X and Y X : amino acid Y : glucose / fructose / galactose [2 marks] Monomer X can be divided into 2 groups, which is essential and non-essential of monomer X. State the difference between these two groups.
(b) (i)
Essential amino acids cannot be synthesised by the body while non essential amino acids can be synthesised by the body [1 mark] (ii) State the reaction that leads to synthesis of compound Z. 1 molecule of glycerol + 3 molecules of fatty acids [1 mark] (c) What would happen if pancreatic cells are unable to synthesis compound X? Enzymes / any pancreatic enzymes / hormones cannot be synthesised [1 mark] (d) (i) In the space below draw and label the structure of the basic unit of organic compound W.
[2 mark] (ii) Name two type of organic compound W. RNA and DNA [1 mark] (iii) State 2 differences between the organic compounds you have named in (d)(ii) RNA Found in cytoplasm , ribosomes , and nucleus Consists of one strand of polynucleotide Strand of polynucleotide is linear DNA Found in nucleus , chloroplast , mitochondria Consists of double strands polynucleotide Strands of polynucleotide are twisted each other / double helix
[2 marks]
5.
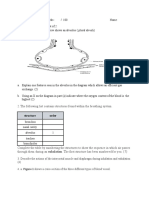
Diagram 6 shows three organisms P , Q and R.
Diagram 6
(a) (i) (ii)
Describe the type of nutrition in P and Q.
[4 marks]
Explain one similarity and four differences for the alimentary canals and types of nutrition between Q and R. [10 marks]
Poor eating habits result in health problems such as obesity, anaemia and constipation (b) Based on the statement above, state the causes and suggest ways on how to overcome the health problems mentioned in the statement. [6 marks]
7 (a) (i) Organism P shows autotrophic nutrition. Able to synthesis their own food / complex organic substances. Eg : green plant synthesise carbohydrates from inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide and water (2m) Organism Q shows heterotropic nutrition. Unable to synthesis its own food. Feed on food substances from other organisms (2m) 7 (a) (ii) Similarity : Both have alimentary canals which are unable to secrete enzyme cellulase to digest cellulose Differences: Organism Q Ruminant Made up of 4 chambers Rodent Has one stomach only with no division of chamber No caecum and appendix Food digested twice by regurgirating and rechewing before being swallowed again Has large caecum Faeces are eaten twice for a secong round of digestion Organism R
Cellulose is digested in the stomach
Cellulose is digested in the caecum and appendix
Microorganisms are found in rumen and reticulum
Microorganisms are found in caecum and appendix
7 (b)
Obesity Obesity is often caused by consumption of excess carbohydrates and fats and lack of exercise. People who are obese should reduce intake of fats and carbohydrates and carry out more exercise. Anaemia Anaemia may be due to insufficient red blood cells or the available red blood cells do not contain sufficient haemoglobin to transport oxygen Anaemia often results from a deficiency of nutritional factors (eg: iron , vitamin B12) required to synthesis haemoglobin or RBC. It may also be caused by excessive loss of blood or destruction of the cells There should be an increase in the intake of iron and vitamin B12 if anaemia is caused by the deficiency of these factors Constipation Constipation is the difficulty elimination of faeces from the body Eating more food high in dietary fibre and drink more fluid/water to prevent constipation
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cell Structure and OrganisationDokument15 SeitenCell Structure and Organisationzulkarnain100% (4)
- Bab 2 Kertas 2Dokument8 SeitenBab 2 Kertas 2Wan RoziahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and IonDokument14 SeitenCell Structure and IonNur NaNa100% (1)
- Biology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNDokument15 SeitenBiology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNMiz KarstzNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB QBANK 6.1 - p1-p2Dokument35 SeitenIB QBANK 6.1 - p1-p2Naz Gümüşlüoğlu100% (1)
- Biology F4 Chapter 2 (Exercise)Dokument11 SeitenBiology F4 Chapter 2 (Exercise)Nadiah Murad60% (5)
- Human Nutrition PDFDokument4 SeitenHuman Nutrition PDFaanyaverma267Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2122 Level M Biology IGCSE Top QuestionsDokument40 Seiten2122 Level M Biology IGCSE Top Questions-Bleh- WalkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 06Dokument19 SeitenCH 06cyberyeung0% (1)
- CT Bio 8-1 (21-22) - DraftDokument7 SeitenCT Bio 8-1 (21-22) - Draftmega.sukmadi44Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Bio SBP 2011 AnsDokument23 SeitenModul Bio SBP 2011 AnsAlan WangNoch keine Bewertungen
- HL Paper3Dokument29 SeitenHL Paper3RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: - Class: - Exercise Chapter 6.4 & 6.5 6.4 (Food Digestion) 6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested FoodDokument4 SeitenName: - Class: - Exercise Chapter 6.4 & 6.5 6.4 (Food Digestion) 6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested Foodsylent gohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module SBP Perfect Score SPM 2011 BiologyDokument102 SeitenModule SBP Perfect Score SPM 2011 BiologyKen Yew PiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student's Copy Chapter2Dokument11 SeitenStudent's Copy Chapter2Evilz DevilzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Figure 1 (I) Figure 1 (Ii)Dokument37 SeitenChapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Figure 1 (I) Figure 1 (Ii)Jonathan LingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Markscheme: (125 Marks)Dokument33 SeitenMarkscheme: (125 Marks)Naz GümüşlüoğluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Institute of Technology Tralee: Semester 1 Examinations A/Y 2009/2010 Biology 1 BIOL 61000 (CRN 45419) (CRN 43186)Dokument4 SeitenInstitute of Technology Tralee: Semester 1 Examinations A/Y 2009/2010 Biology 1 BIOL 61000 (CRN 45419) (CRN 43186)Mohmmad Alhazmi AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Bio Prelim P2 2009Dokument16 SeitenH2 Bio Prelim P2 2009Tan Eng BoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio SPM Intervensi m1Dokument10 SeitenBio SPM Intervensi m1teahockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 8 Biology (Chapter 1-3) RETESTDokument8 SeitenYear 8 Biology (Chapter 1-3) RETESTPiiNkiE Chong100% (1)
- Modul SC Chapter 2 - f1Dokument14 SeitenModul SC Chapter 2 - f1Raja InaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Dokument0 SeitenAnswer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Thuran NathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAME: PDG: : AnswersDokument16 SeitenNAME: PDG: : AnswersPollyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect Score Biology: Module Form 5Dokument15 SeitenPerfect Score Biology: Module Form 5Farhanah AlawdeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 4.4Dokument8 SeitenBio 4.4zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jawab Semua Soalan Dalam Bahagian Ini: Section ADokument34 SeitenJawab Semua Soalan Dalam Bahagian Ini: Section AArleenaAmnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2 (Kertas 2) Section A/ Bahagian ADokument22 SeitenPaper 2 (Kertas 2) Section A/ Bahagian ANgu Toh OnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- KERTAS 2 Ting 5Dokument23 SeitenKERTAS 2 Ting 5Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsDokument59 Seiten2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsVan halenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade: Viii Subject: General Biology Total Marks: 70 Time Duration: 2 HoursDokument2 SeitenGrade: Viii Subject: General Biology Total Marks: 70 Time Duration: 2 HoursHasna Hena SarkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology: The EssentialsVon EverandGastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology: The EssentialsJohn F. ReinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acjc H2 Bio P2Dokument16 SeitenAcjc H2 Bio P2DD97Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio WorkDokument7 SeitenBio WorkRiddhi TullooNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB 1A ch06 e SampleDokument10 SeitenQB 1A ch06 e Sampleteresa tsoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System. Paper. 1. Name-Nikol Surname - Kokhiya /14 1Dokument7 SeitenDigestive System. Paper. 1. Name-Nikol Surname - Kokhiya /14 1Giorgi JincharadzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise PDFDokument12 SeitenExercise PDFAmsyidi Asmida100% (1)
- Biology NameDokument8 SeitenBiology NameAnika AroviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Science Form 2Dokument36 SeitenModul Science Form 2AJ MukunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Unt 2-3 Feeding and NutritionDokument2 SeitenActivity Unt 2-3 Feeding and NutritionIES ConsaburumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution.: Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument11 SeitenSolution.: Multiple Choice QuestionsSiddhi KankaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Koleksi Esei Ting 5Dokument74 SeitenKoleksi Esei Ting 5Nurul AzuwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 62 F 5 B 6 B 93 e 3 F 3Dokument3 Seiten62 F 5 B 6 B 93 e 3 F 3HC GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 6.1: Digestion and AbsorptionDokument6 SeitenTopic 6.1: Digestion and AbsorptionJenna BarnesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Dec - AS BioDokument6 Seiten9th Dec - AS Bioshreyas niranjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gr. 10 Bio Semester 2 Revision Sheet Answer Key (2023-2024)Dokument13 SeitenGr. 10 Bio Semester 2 Revision Sheet Answer Key (2023-2024)8fr4xqpcb8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam BioDokument10 SeitenFinal Exam BiocomputeroboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Nutrition C.T.Dokument8 SeitenAnimal Nutrition C.T.Gaming TriadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Jawapan Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2012 BioDokument9 SeitenSkema Jawapan Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2012 Biogomathi24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Bio Answer KeyDokument10 SeitenFinal Exam Bio Answer KeycomputeroboNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper Set 4Dokument3 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper Set 4Unique InstituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Level LIP Course QuestionsDokument47 SeitenBiology Level LIP Course Questions2anasnegNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit TestDokument2 SeitenUnit TestNikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsDokument12 SeitenThis Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsKhusyairy Daeng Sailendra0% (1)
- 10-Biology-Monthly Test-1 (June 2021) QPDokument3 Seiten10-Biology-Monthly Test-1 (June 2021) QPDeepanKarthikA MTPNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationDokument6 SeitenAQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationJoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Question CompilationDokument18 SeitenBio Question CompilationGranpaXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huraian Sukatan Pelajaran Science Tingkatan 3Dokument65 SeitenHuraian Sukatan Pelajaran Science Tingkatan 3Radzuan Mokhtar RuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 7 RespirationDokument11 SeitenChap 7 RespirationAthirah MaestroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 001-027-SPS Bio - F5 - Chap 1-H.p1Dokument1 Seite001-027-SPS Bio - F5 - Chap 1-H.p1Athirah MaestroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refresh Refresh (Dynamic - Bypass - Reload) Click Here If You Are Not Automatically Redirected. For Assistance, Contact Your Network Support Team.Dokument1 SeiteRefresh Refresh (Dynamic - Bypass - Reload) Click Here If You Are Not Automatically Redirected. For Assistance, Contact Your Network Support Team.Athirah MaestroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Module: Coordination and ResponseDokument77 SeitenForm 5 Module: Coordination and ResponseAthirah MaestroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine A PDF Writer That Produces Quality PDF Files With Ease!Dokument18 SeitenMachine A PDF Writer That Produces Quality PDF Files With Ease!soonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13: Reproduction and Growth A: Formation of SpermsDokument4 SeitenChapter 13: Reproduction and Growth A: Formation of SpermsAthirah MaestroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine A PDF Writer That Produces Quality PDF Files With Ease!Dokument18 SeitenMachine A PDF Writer That Produces Quality PDF Files With Ease!soonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.PHOTOSYNTESIS Light IntensityDokument1 Seite1.PHOTOSYNTESIS Light IntensityJagung ManisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intervensi - Bio Chap 15Dokument3 SeitenIntervensi - Bio Chap 15Athirah MaestroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intervensi - Bio Chap 15Dokument3 SeitenIntervensi - Bio Chap 15Athirah MaestroNoch keine Bewertungen