Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Spectroscopy: Analysis of Light Emitted or Absorbed by Substances
Hochgeladen von
Pearl LawrenceOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Spectroscopy: Analysis of Light Emitted or Absorbed by Substances
Hochgeladen von
Pearl LawrenceCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Spectroscopy: analysis of light emitted or absorbed by substances. An atomic spectrum is formed when electromagnetic radiation is absorbed or emitted by an element.
. Light travels in packets or quanta of electromagnetic energy. Electromagnetic radiation can be viewed as a stream of photons, which are particles with no mass each travelling in a wave-like pattern and moving at the speed of light. Each photon contains a certain quantum of energy.
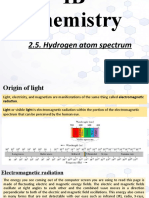
In the light the greater number of photons, the greater the intensity. Planks equation indicates that the energy contained in a photon is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. A quantum of energy absorbed or emitted by an atom can be detected by measuring the frequency or wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation absorbed or emitted. The whole range of frequencies of the electromagnetic radiation is called the electromagnetic spectrum.
The absorption or emission of energy by an element corresponds to specific points on the electromagnetic spectrum and produces a unique spectrum which may be used to identify the element. The quantum theory explains the properties of emission absorption process. Atoms, ions and molecules exist in a discrete state characterized by definite amounts of energy. When a species changes state it absorbs or emits energy exactly equal to the energy difference between the two states.
When a species absorbs or emits energy in making a transition from one energy state to another, the frequency or wavelength of radiation is released to the energy difference between the two states. Electrons moving in an orbit can only have certain amounts of energy, this energy is quantized. The energy needed for an electron to move in a particular orbit depends on the radius of the orbit. An electron moving in an orbit does not emit energy.
A continuous spectrum If a beam of white light is passed through a prism on to a serene, a spectrum of colours made up of all wavelengths of visible light is seen like in a rainbow. This is called a continuous spectrum. There are no distinct division between the colours as they blend in from one to another.
An absorption spectrum If white light passes through a substance, the atoms can absorb light of certain wavelength and dark lines appear in the spectrum. A line spectrum is formed which appears as distinct lines and not bands of colours. It is called a discontinuous spectrum. The wavelengths of the dark lines in the spectrum are the wavelengths of the light absorbed by the atoms. This line spectrum is an absorption spectrum.
This absorption spectrum of energy by an element corresponds to specific wavelengths on the electromagnetic spectrum and produces a unique spectrum.
An emission spectrum If atoms are supplied with heat or electrical energy to high enough temperatures, they emit energies of certain wavelengths as the excited atoms return to their ground state (stable orbit). An emission spectrum is produced which shows coloured lines on a dark background. The emission of energy by an element also corresponds to specific wavelengths on the electromagnetic spectrum and produces a unique spectrum.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Thermodynamic FormulasDokument17 SeitenThermodynamic Formulasdaniebenade86% (28)
- 1-Introduction To Spectrochemical MethodsDokument36 Seiten1-Introduction To Spectrochemical MethodsWahyuni EkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXPERIMENT 2 Colloids and Their Properties - Odango - BSN1bDokument4 SeitenEXPERIMENT 2 Colloids and Their Properties - Odango - BSN1bclint xavier odangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 247 0 Coating Brochure Web-EnDokument36 Seiten247 0 Coating Brochure Web-EnjorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endothermic and Exothermic Reaction Worksheet AnswersDokument5 SeitenEndothermic and Exothermic Reaction Worksheet AnswersAyesha NoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpectrosDokument15 SeitenSpectrosNarmada BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-1Principles of SpectrosDokument9 SeitenModule-1Principles of SpectrosveronislisteningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line Spectra-G13Dokument7 SeitenLine Spectra-G13Rushita LingiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 DP Hydrogen SpectrumDokument21 Seiten4 DP Hydrogen SpectrumVaida MatulevičiūtėNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic SpectrumDokument4 SeitenAtomic SpectrumIzuku MidoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectroscopy: Electromagnetic RadiationDokument19 SeitenSpectroscopy: Electromagnetic RadiationPriyanka SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line SpectrumDokument2 SeitenLine Spectrum27yuvrajsoni10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: TheoryDokument5 SeitenPhysics: TheoryIrshad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- By: Virwane Rose P. Abellera Hanz Raymond B. Consumo Bill Ervein P. RamientosDokument10 SeitenBy: Virwane Rose P. Abellera Hanz Raymond B. Consumo Bill Ervein P. RamientosMareld Dyzelle EcijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How The Position of Hydrogen Is Decided in Modern Periodic Table: Some Basic Concepts: Atomic SpectraDokument3 SeitenHow The Position of Hydrogen Is Decided in Modern Periodic Table: Some Basic Concepts: Atomic SpectramandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Photoelectric Effect and Atomic Spectra: Dreanzel Corbin Pascua:P Mark John ReyesDokument41 SeitenThe Photoelectric Effect and Atomic Spectra: Dreanzel Corbin Pascua:P Mark John ReyesRandy GasalaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nano TechDokument21 SeitenNano Techmandakini baskeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To SpectrosDokument10 SeitenIntroduction To SpectroskdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emission and Absorption SpectraDokument26 SeitenEmission and Absorption SpectraRiriii67% (3)
- Description: Electromagnetic Radiation Charged ParticlesDokument8 SeitenDescription: Electromagnetic Radiation Charged ParticlesfaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em Radiation and Matter-UpdatedDokument32 SeitenEm Radiation and Matter-Updatedb00100817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emission and Absorption SpectraDokument2 SeitenEmission and Absorption SpectraHossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line SpectraDokument1 SeiteLine Spectranwzd09Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Development of A New Atomic ModelDokument40 SeitenThe Development of A New Atomic Modelahmad batataNoch keine Bewertungen
- AtomsStarLight 01Dokument18 SeitenAtomsStarLight 01LukeMontanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpectrosDokument35 SeitenSpectrosLoren Victoria AgbayNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpectrosDokument21 SeitenSpectrosAman Rathore100% (1)
- ProjectDokument11 SeitenProjectMehak Parvez HamdaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectral Lines: Existence of Discrete Energy Levels Emission and Absorption SpectraDokument69 SeitenSpectral Lines: Existence of Discrete Energy Levels Emission and Absorption SpectraACSVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Structure 3Dokument41 SeitenElectronic Structure 3Victoria VirgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Notes ShortXDokument46 SeitenChapter 5 Notes ShortXdsckln/cmakNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nature of Light: Does It Behave? These Questions May Seem Simple To You, But They Have PresentedDokument5 SeitenThe Nature of Light: Does It Behave? These Questions May Seem Simple To You, But They Have PresentedAbdul QuadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Radiation Observations: Electromagnetic Radiation (EM Radiation or EMR) Refers To The Waves (OrDokument10 SeitenElectromagnetic Radiation Observations: Electromagnetic Radiation (EM Radiation or EMR) Refers To The Waves (OrYancy MiclatNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpectrosDokument2 SeitenSpectrosaijaz100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure Atomic Spectra and ElectronDokument11 SeitenAtomic Structure Atomic Spectra and Electrontechibu252Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 UvDokument24 Seiten12 UvMohit KambojNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemDokument15 SeitenChemSachin RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is SpectrosDokument4 SeitenWhat Is SpectrosCarlton GrantNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 LightDokument31 Seiten2 Lighthou1212!Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE XII Chemistry/Physics Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsDokument21 SeitenCBSE XII Chemistry/Physics Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsshantanurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2 Electron ConfigurationDokument2 Seiten2.2 Electron ConfigurationlauraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joseph Von Fraunhofer Lines Spectroscopy Collimator Prism Lens InfiniteDokument6 SeitenJoseph Von Fraunhofer Lines Spectroscopy Collimator Prism Lens InfiniteYousra OsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Notes Chap 2 Structure of An AtomDokument15 SeitenChemistry Notes Chap 2 Structure of An AtomJo ParkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 4 CDokument13 SeitenWEEK 4 CeodurotwumNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiophysicsDokument2 SeitenBiophysicsKristina Casandra PavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectrometry FinalDokument57 SeitenSpectrometry FinalAastha SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Source of ColorDokument6 SeitenSource of ColoryemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L2 Che101Dokument16 SeitenL2 Che101Musa Ahammed MahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Spectroscope Determination of Emission and Absorption SpectrumDokument1 SeiteThe Spectroscope Determination of Emission and Absorption SpectrumAlexandru DamocNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.6 Atomic Structur Notes 1 Revision Past PapersDokument12 SeitenS.6 Atomic Structur Notes 1 Revision Past PapersMaama PhionaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afs Ojhar: Project Submitted By: Sumit Anand Class: XII-ADokument17 SeitenAfs Ojhar: Project Submitted By: Sumit Anand Class: XII-ASumit AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Development of A New Atomic ModelDokument4 SeitenThe Development of A New Atomic ModelanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Work 7Dokument9 SeitenPractical Work 7Achraf RabadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - IntroductionDokument12 SeitenChapter 5 - IntroductionGeleta BekeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of Food AnalysisDokument60 SeitenPrinciple of Food AnalysisMuzahid IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- LASER07022023Dokument39 SeitenLASER07022023Akhyaya PattanaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilrds 1Dokument49 SeitenIlrds 1ELLAINE MAE FLORESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spektroskopi: Nadhifah Al Indis, S.Si., M.SiDokument28 SeitenSpektroskopi: Nadhifah Al Indis, S.Si., M.SiNadhifah Al IndisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light and Atomic Spectra Summary by Cristina ZelayaDokument1 SeiteLight and Atomic Spectra Summary by Cristina ZelayaCristina ZelayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Von EverandA New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unified Field Theory in a Nutshell1: The Quest for the Theory of EverythingVon EverandUnified Field Theory in a Nutshell1: The Quest for the Theory of EverythingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Theory of Light: Unsolved Mysteries Finally RevealedVon EverandFinal Theory of Light: Unsolved Mysteries Finally RevealedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 1005 Tutorial Sheet 1 2013-2014Dokument1 SeiteEcon 1005 Tutorial Sheet 1 2013-2014Pearl LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bishop Anstey High School Unit 2 Organic Chemistry: DUE: Friday 2 December, 2011. at The Start of ClassDokument1 SeiteBishop Anstey High School Unit 2 Organic Chemistry: DUE: Friday 2 December, 2011. at The Start of ClassPearl LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- May 2007 Physics CXC Multiple ChoiceDokument12 SeitenMay 2007 Physics CXC Multiple ChoicePearl LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uses of The Components of Crude Oil As FuelsDokument6 SeitenUses of The Components of Crude Oil As FuelsPearl LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microeconomics Chapter 7Dokument10 SeitenMicroeconomics Chapter 7Pearl LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructions:: Introduction To Financial Accounting B.Sc. 2 HrsDokument4 SeitenInstructions:: Introduction To Financial Accounting B.Sc. 2 HrsPearl LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Paper 2Dokument14 SeitenUnit Paper 2Pearl LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnergiticsDokument1 SeiteEnergiticsPearl LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmospheric Temperature, Pressure and Density As Function of The Height Above Sea LevelDokument53 SeitenAtmospheric Temperature, Pressure and Density As Function of The Height Above Sea LevelMustafa TıraşNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ in General Chemistry Part 1 - AnswersDokument3 SeitenMCQ in General Chemistry Part 1 - Answerssam labineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Component 1 MA 06 (MC)Dokument6 SeitenComponent 1 MA 06 (MC)Zareen KidwaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 PDFDokument3 SeitenExperiment 1 PDFShahbazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patente Saponificacion Oleorresina de Marigold 3Dokument6 SeitenPatente Saponificacion Oleorresina de Marigold 3Harry CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChE Reviewer 2014 (PART I)Dokument7 SeitenChE Reviewer 2014 (PART I)jantskieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 - Thermochemistry Font 11Dokument8 SeitenModule 5 - Thermochemistry Font 11Ruth AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 120 Exer 4Dokument2 Seiten120 Exer 4Anne OhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyanate Ester Resin5Dokument26 SeitenCyanate Ester Resin5rkkumarcpriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulsed Laser Ablation and Micromachining of 4H and 6H SiC Wafers PDFDokument113 SeitenPulsed Laser Ablation and Micromachining of 4H and 6H SiC Wafers PDFagiles6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes 1 - Fluid MechanicsDokument9 SeitenLecture Notes 1 - Fluid MechanicsJane AndaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics 2Dokument8 SeitenThermodynamics 2BINITHA MPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMDokument8 SeitenScreenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMAnushka ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEA Messo BrochureDokument16 SeitenGEA Messo Brochuredow2008100% (1)
- 9 Science Structure of AtomDokument8 Seiten9 Science Structure of AtomAjay AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Polymer BlendsDokument612 SeitenHandbook of Polymer BlendsKaihuanZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCSE Practical Guide Chemistry ElectrolysisDokument12 SeitenGCSE Practical Guide Chemistry Electrolysisr aNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proton Exchange MembraneDokument22 SeitenProton Exchange MembraneHanifan Lidinillah100% (1)
- PolymerDokument24 SeitenPolymerLakshya wardhan singh ShekhawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nov 24th 2014 Monday: Products DetailsDokument1 SeiteNov 24th 2014 Monday: Products DetailsXuân Giang NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Check List of Organic Chemistry Topics For B17CA and B17CB AppendedDokument6 SeitenCheck List of Organic Chemistry Topics For B17CA and B17CB AppendedSarah FeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5007Dokument427 Seiten5007dt5632Noch keine Bewertungen
- CalorimetryDokument54 SeitenCalorimetryTrixsha TapsirulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Lithography PDFDokument16 SeitenOptical Lithography PDFprashn80Noch keine Bewertungen
- t1-p1-2 Spectra-Structure Correlations in The Mid and Far InfraredDokument34 Seitent1-p1-2 Spectra-Structure Correlations in The Mid and Far InfraredCorvusdav EspinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 6 Entropy and The Second Law of ThermodynamicsDokument77 SeitenLec 6 Entropy and The Second Law of ThermodynamicsACCOUNT ONENoch keine Bewertungen