Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Vitamin K (Phytonadione)
Hochgeladen von
EOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Vitamin K (Phytonadione)
Hochgeladen von
ECopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
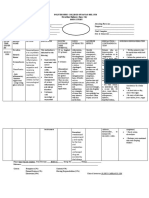
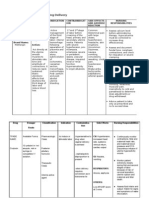
Clinical Medications Worksheets
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
phytonadione Vitamin K fat-soluble vitamins, 10mg SQ daily
Antifibrinolytic Agents
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
3-6 hr 1-2 hr 12-14 hr 10 mg daily
Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or solutions
Hypoprothrombinemia due to Vitamin K Deficiency N/A
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Required for hepatic synthesis of blood coagulation factors II Hypersensitivity, Hypersensitivity or intolerance to benzyl alcohol
(prothrombin), VII, IX, and X (injection only), use cautiously in impaired liver function
Common side effects
No known common side effects for this drug
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal Lab value alterations caused by medicine
medicines (ask patient specifically) Prothrombin time (PT) should be monitored prior to and throughout
No known interactions for this patient vitamin K therapy to determine response to and need for further
therapy
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication
Instruct patient to take this medication as ordered. If a dose is missed,
take as soon as remembered unless almost time for next dose. Notify
health care professional of missed doses. Cooking does not destroy
substantial amounts of vitamin K. Patient should not drastically alter
diet while taking vitamin K. Caution patient to avoid IM injections
and activities leading to injury. Use a soft toothbrush, do not floss, and
shave with an electric razor until coagulation defect is corrected.
Advise patient to report any symptoms of unusual bleeding or bruising
(bleeding gums; nosebleed; black, tarry stools; hematuria). Patients
receiving vitamin K therapy should be cautioned not to take OTC
medications without advice of health care professional. Advise patient
to inform health care professional of medication regimen prior to
treatment or surgery. Advise patient to carry identification at all times
describing disease process. Emphasize the importance of frequent lab
tests to monitor coagulation factors.
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this med? Check after giving
Monitor for frank and occult bleeding (guaiac Toxicity (hemolytic anemia, brain damage), Prevention of spontaneous
stools, Hematest urine, and emesis). Monitor pulse clot formation (e.g., DVT, pulmonary emboli) bleeding or cessation of bleeding
and blood pressure frequently; notify physician in patients with
immediately if symptoms of internal bleeding or hypoprothrombinemia secondary
hypovolemic shock develop. Inform all personnel to impaired intestinal absorption
of patient's bleeding tendency to prevent further or oral anticoagulant, salicylate,
trauma. Apply pressure to all venipuncture sites or anti-infective therapy.
for at least 5 min; avoid unnecessary IM injections
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Dexamethasone and MgSO4Dokument2 SeitenDexamethasone and MgSO4Nasriah MacadatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin KDokument2 SeitenVitamin KMuvs RazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeDokument5 SeitenDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - DelanDokument3 SeitenDrug Study - DelanJuliana Sophia DelanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cefotaxime Drug Class, Uses, Side EffectsDokument3 SeitenCefotaxime Drug Class, Uses, Side EffectsKristi WrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing-Care-Plan 4Dokument4 SeitenNursing-Care-Plan 4Christine CornagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteDrug StudycliffordbuenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG STUDY CLOBETASOL CREAMrevisedDokument2 SeitenDRUG STUDY CLOBETASOL CREAMrevisedswitchlers anneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)Dokument2 SeitenSenokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)E100% (1)
- Dexamethasone Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDexamethasone Drug StudyVIDMENTON PHNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINAL Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenFINAL Drug StudycasedraftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FADokument3 SeitenDrug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FAKristine ChampnessNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilDokument5 SeitenA Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilAlexis Khalyl Y. MontejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugstudy OrsdDokument10 SeitenDrugstudy OrsdRafmar A. SalundaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG-STUDY-Lidocaine RyreyDokument1 SeiteDRUG-STUDY-Lidocaine RyreyJanelle Cabida SupnadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxacillin Nursing ConsiderationsDokument1 SeiteOxacillin Nursing Considerationsnerissa_villanueva3523Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDokument2 SeitenName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationNicole CalpoturaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLDokument6 SeitenA Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLAlexandrea MayNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN Dog Bite InjuryDokument3 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN Dog Bite Injurykarrey danielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Vitamin C + ZincDokument2 SeitenDrug Study Vitamin C + ZincKrizzia FosterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug NystatinDokument1 SeiteDrug NystatinSrkocherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ascorbic AcidDokument2 SeitenAscorbic AcidJaymark Lambino100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenDrug StudyKristine Joy A. AniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationDokument2 SeitenDrug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationart_mutantNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG STUDY OXYTOCIN, METHERGINE EtcDokument9 SeitenDRUG STUDY OXYTOCIN, METHERGINE EtcPatricia Reese YutiamcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal PediaDokument2 SeitenJournal PediapeteiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Azithromycin Nursing ConsiderationsDokument2 SeitenAzithromycin Nursing ConsiderationsKristine YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- DocetaxelDokument4 SeitenDocetaxelfnurdiansah002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsDokument7 SeitenVirtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsEdgie FabreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study InsulinDokument2 SeitenDrug Study InsulinGrant Kenneth Dumo AmigableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manangan, Eugene B. - FDAR Boggy UterusDokument2 SeitenManangan, Eugene B. - FDAR Boggy UterusGin MananganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnesium Oxide (Antacid, Anti-Convulsant, Electrolyte, Laxative)Dokument1 SeiteMagnesium Oxide (Antacid, Anti-Convulsant, Electrolyte, Laxative)Danielle Marie SamblacenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Deficit: Presence of PediculosisDokument2 SeitenHealth Deficit: Presence of PediculosisMariecel GazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CetirizineDokument1 SeiteCetirizineGabby Robles PajeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)Dokument3 SeitenNursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)joyrena ochondraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyJonica CamposNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tramadol Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenTramadol Drug StudyJust A Nsg StudentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug AnalysisDokument3 SeitenDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solu CortefDokument1 SeiteSolu CortefKristine YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- F. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Dokument5 SeitenF. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Lopirts NiganiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMARYL 1mg, 2mg, 3mg, 4mg: 1 Indications and UsageDokument16 SeitenAMARYL 1mg, 2mg, 3mg, 4mg: 1 Indications and Usageddandan_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lowering Cholesterol with EzetimibeDokument2 SeitenLowering Cholesterol with EzetimibeFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VACCINES Hepatitis B and Tetanus Vaccine StudyDokument2 SeitenVACCINES Hepatitis B and Tetanus Vaccine StudyCarlo AniagNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEFOXITINDokument30 SeitenCEFOXITINJaessa FelicianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB DrugsDokument14 SeitenTB DrugsLexy CadigalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study FDokument3 SeitenDrug Study FFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Silver SulfadiazineDokument1 SeiteDrug Study Silver SulfadiazineMaica Lectana100% (1)
- JM DrugDokument3 SeitenJM DrugVerdie B. NgayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrioritizationDokument1 SeitePrioritizationJLAZRONoch keine Bewertungen
- Glipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardDokument1 SeiteGlipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardSheri490Noch keine Bewertungen
- 66 Drug AnaDokument3 Seiten66 Drug AnaAlexa RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coumadin WarfarinDokument1 SeiteCoumadin WarfarinSheri490100% (1)
- 使ってもらえるだけで嬉しいそれだけで十分ですDokument11 Seiten使ってもらえるだけで嬉しいそれだけで十分ですLANCE CHRISTIAN CUENCANoch keine Bewertungen
- Dilantin PhenytoinDokument2 SeitenDilantin PhenytoinCassieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tamoxifen NolvadexDokument1 SeiteTamoxifen NolvadexAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Ranitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenRanitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug StudyMarco MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument13 SeitenDrug StudyGi Ey ElNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predacot PrednisoneDokument1 SeitePredacot PrednisoneAdrianne BazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predacot PrednisoneDokument1 SeitePredacot PrednisoneAdrianne BazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron Deficiency Anemia PathoDokument6 SeitenIron Deficiency Anemia PathoENoch keine Bewertungen
- Left-Side CHF PathoDokument5 SeitenLeft-Side CHF PathoENoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISDokument4 SeitenPyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISENoch keine Bewertungen
- Bowel Resection PathoDokument7 SeitenBowel Resection PathoENoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperparathyroidism PathoDokument2 SeitenHyperparathyroidism PathoENoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyponatremic Dehydration PathoDokument4 SeitenHyponatremic Dehydration PathoENoch keine Bewertungen
- Influenza B PathoDokument4 SeitenInfluenza B PathoENoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart Failure-ABDokument3 SeitenCongestive Heart Failure-ABENoch keine Bewertungen
- Subluxation c6c7 Short PathoDokument1 SeiteSubluxation c6c7 Short PathoENoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumonia Short PathoDokument2 SeitenPneumonia Short PathoENoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pancreatitis PathoDokument5 SeitenAcute Pancreatitis PathoENoch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomic DysreflexiaDokument2 SeitenAutonomic DysreflexiaENoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Burns PathoDokument2 SeitenChemical Burns PathoENoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart FailureDokument4 SeitenCongestive Heart FailureENoch keine Bewertungen
- Pancreatitis Short PathoDokument2 SeitenPancreatitis Short PathoENoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDokument1 SeiteClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENoch keine Bewertungen
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Dokument1 SeiteFiberCon (Polycarbophil)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- ZofranDokument1 SeiteZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- Buspar (Buspirone)Dokument1 SeiteBuspar (Buspirone)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)Dokument2 SeitenGeodon (Ziprasidone)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Reglan (Metoclopramide)Dokument3 SeitenReglan (Metoclopramide)E100% (1)
- Zosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)Dokument2 SeitenZosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)E67% (3)
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Dokument1 SeiteSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Dokument1 SeiteCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDokument1 SeiteProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgENoch keine Bewertungen
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Dokument2 SeitenLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Dokument3 SeitenFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Dokument2 SeitenKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- Darvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)Dokument1 SeiteDarvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Dokument3 SeitenTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Instant Download Macroeconomics 4th Edition Hubbard Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDokument32 SeitenInstant Download Macroeconomics 4th Edition Hubbard Test Bank PDF Full ChapterHowardZunigaxgqt100% (5)
- Family Health Programs: Immunization, Maternal Care & Family PlanningDokument24 SeitenFamily Health Programs: Immunization, Maternal Care & Family Planningmirai desuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourth Stage of LaborDokument13 SeitenFourth Stage of LaborLindsay Ann Garcia Mariaca0% (1)
- Asthma & COPD Medication List PDFDokument11 SeitenAsthma & COPD Medication List PDFabdullah992011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Buttocks Lift For Tight ThighsDokument17 SeitenButtocks Lift For Tight ThighsLink ZeldaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diuretics: Generic and Brand NamesDokument22 SeitenDiuretics: Generic and Brand NamesKish GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Foundations of Addictions Counseling 4th Edition David Capuzzi Mark D StaufferDokument8 SeitenTest Bank For Foundations of Addictions Counseling 4th Edition David Capuzzi Mark D StaufferLucille Alexander100% (35)
- Validity Importance: Patients' Expected Event Rate (PEER) Menggambarkan Kemungkinan Pasien MengalamiDokument3 SeitenValidity Importance: Patients' Expected Event Rate (PEER) Menggambarkan Kemungkinan Pasien MengalamiDella Puspita SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood-Based Protein Changes in Childhood Are Associated With Increased Risk For Later Psychotic DisorderDokument34 SeitenBlood-Based Protein Changes in Childhood Are Associated With Increased Risk For Later Psychotic DisorderFelicia SaraswatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Renal Failure Guide for VeterinariansDokument12 SeitenAcute Renal Failure Guide for VeterinariansElsa SimangunsongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 60 Most Common DrugsDokument1 Seite60 Most Common DrugsNikkaLim100% (1)
- High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin at Presentation To Rule Out Myocardial Infarction (Historic)Dokument20 SeitenHigh-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin at Presentation To Rule Out Myocardial Infarction (Historic)DenisseRangelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profile For Females: Conners' Parent Rating Scale-Revised (S)Dokument2 SeitenProfile For Females: Conners' Parent Rating Scale-Revised (S)Claudya Abarca50% (8)
- IntroductionDokument5 SeitenIntroductionDivyansh GolyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HUNNER LESION DIAGNOSISDokument4 SeitenHUNNER LESION DIAGNOSISVasishta NadellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Rehabilitation Patient InjuriesDokument7 SeitenOral Rehabilitation Patient InjuriesAlexandru Codrin-IonutNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7457 Uslugi I Cenovnik Na Erdem Klinka IstanbulDokument3 Seiten7457 Uslugi I Cenovnik Na Erdem Klinka Istanbuljove11Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Links Between Obesity and Mental Health: Health Services and Programs (SFL Kirk, Section Editor)Dokument8 SeitenAn Overview of Links Between Obesity and Mental Health: Health Services and Programs (SFL Kirk, Section Editor)HugoNogueiraPereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myringotomy & MyringoplastyDokument35 SeitenMyringotomy & MyringoplastypriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minutes of 285th Meeting of Registration BoardDokument819 SeitenMinutes of 285th Meeting of Registration BoardSaheefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aq - Minimal Stok ApotekDokument30 SeitenAq - Minimal Stok ApotekSifa Septiani PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDHDokument47 SeitenCDHSameeta PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDokument9 SeitenHyperemesis GravidarumChyank Qu SaddamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System QuizDokument3 SeitenDigestive System Quizapi-709247070Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abnormal Psychology V2Dokument343 SeitenAbnormal Psychology V2Bianca Dennise Villar Guingab100% (2)
- Dr. M.S. Shamol Fcps (Medicine) : C O T S N I P A T I O NDokument20 SeitenDr. M.S. Shamol Fcps (Medicine) : C O T S N I P A T I O NiwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Supportive Supervision ChecklistDokument13 SeitenIntegrated Supportive Supervision ChecklistAbdiresak AbdusemedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echocardiogram (Echo) ExplainedDokument3 SeitenEchocardiogram (Echo) ExplainedSamantha CheskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Choking: What To Do If A Child Is Choking?Dokument3 SeitenChoking: What To Do If A Child Is Choking?Jamieson TobeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continue Renal Replacement Therapy: 1. CVVH 2. CVVHD 3. CVVHDFDokument21 SeitenContinue Renal Replacement Therapy: 1. CVVH 2. CVVHD 3. CVVHDFhengki jokteryNoch keine Bewertungen