Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
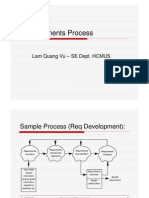
Requirements Elicitation
Hochgeladen von
Shephali TyagiOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Requirements Elicitation
Hochgeladen von
Shephali TyagiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
Requirements Determination Part 1
Elicitation, analysis and negotiating customer requirements
Requirements Determination
Requirements determination is the least technical but the most critical phase of the software development lifecycle
requires good social, communication and management skills service statements
The focus is on determining the stakeholder's requirements
functional requirements: what the system does, its functionality, data structures non-functional requirements: how well the system provides the functional requirements
constraint statements
usability, reusability, reliability, performance, efficiency, supportability
Requirements Examples
Functional requirements
the system should provide budget reports the user can select which pages to print operational constraints
Non-functional requirements
the system should be able to work on any Web browser any interaction between the user and the system should not exceed 2 seconds only direct managers can see personnel records of staff
performance constraints
security constraints
The Requirements Determination Process
Requirements elicitation
obtaining requirements from customers analyse requirements to eliminate duplication or contradictions
Requirements reviews and renegotiations
Classification and prioritisation Business modelling
system scope model, business use case model, business class model
Requirements document Requirements management
estimate the impact of a change on other requirements
Requirements Elicitation (1)
Domain Expert
Customer
Domain Knowledge Requirements
Business Analyst
Use Case Requirements
Business Model
Business Class Model
Business Use Case Model
Requirements Elicitation (2)
Traditional methods of requirements elicitation
interviewing customers and domain experts, questionnaires, observation, study of documents and software systems prototyping, brainstorming, JAD, RAD unclear objectives, undocumented procedures, unstable requirements, eroded user expertise, inexperienced developers, insufficient user commitment
Modern methods of requirements elicitation
High risk projects
Traditional techniques are usually used in low-risk projects, while modern techniques are usually used in high-risk projects
Requirements Elicitation: Interviews (1)
The target: customers and domain experts
use case requirements v. knowledge transfer may only have a vague picture of their requirements may be unwilling to cooperate may be unable to express their requirements in understandable terms may demand requirements that exceed the project budget the requirements of different customers may be in conflict
Difficulties with customers
Requirements Elicitation: Interviews (2)
Two kinds of interview
structured, unstructured open-ended, closed-ended, probing ensure that people at different levels of the organisation are interviewed provide a starting point and context for the discussion send a memo summarising the interview to the interviewee after the meeting good communication and interpersonal skills help
Different kinds of questions
Advice
Requirements Elicitation: Interviews (3)
The following categories of questions should be asked
questions about specific details questions about a vision for the future questions about alternative ideas questions about a minimally acceptable solution questions about other sources of information questions soliciting diagrams opinionated questions biased questions imposing questions
Three kinds of questions which should be avoided
10
Requirements Elicitation: Interviews (4)
Advantages
Disadvantages
provides high quality information can probe in greater depth if the interviewee has nothing to say, the interview can be terminated
time-consuming the analyst must work to obtain results after the interview the interviewer may be biased conflicting information from interviewees may be difficult to resolve
11
Requirements Elicitation: Questionnaires (1)
Questionnaires are an efficient way of gathering information and are normally used in addition to interviews Questionnaires are passive
respondent has time to consider their response respondent cannot clarify the question multiple-choice, rating questions, ranking questions a well-designed, easy-to-answer questionnaire gets a higher response rate need to consider distortions when evaluating the results
Closed-ended questions are emphasised
Advice
12
Requirements Elicitation: Questionnaires (2)
Advantages
Disadvantages
economical way of gathering data from large numbers of people in well-designed questionnaires, results are easy to analyse
good questionnaires can be difficult to construct it is difficult to follow up may suffer from low response rates
13
Requirements Elicitation: Observation (1)
A business analyst may find it difficult to obtain complete information through interviews and questionnaires
observation may be an effective fact-finding technique passive observation, active observation, explanatory observation observations should be carried out for a prolonged period of time, at different time intervals, and at different workloads be aware that people behave differently when observed
Three forms of observation
Advice
14
Requirements Elicitation: Observation (2)
Advantages
Disadvantages
provides first hand experience of the way people work data collected can have a high level of validity can be used to verify information or to examine exceptional procedures can provide data about the performance of the existing system and users
people do not like being observed requires a trained and skilled observer has serious logistical problems for the analyst there may be ethical problems
Requirements Elicitation: Studying Documents and Software Systems (1)
15
Useful for discovering both use case and domain knowledge requirements Potential sources of information
organisation documents
business forms, work procedures, job descriptions, policy manuals, business plans, organisational charts, correspondence, minutes, accounting records, external correspondence, customer complaints computer screens and reports, system operating manuals, user and technical documentation, system analysis and design models
system forms and reports
business domain journals and reference books software packages
Requirements Elicitation: Studying Documents and Software Systems (2)
16
Is it worth studying legacy systems?
if some of the functionality is required in the new system if some of the data must be migrated into the new system if the documentation provides algorithms that might be needed in the new system to make sure any defects are avoided in the new system may help to understand the organisation if parts of the existing system may be retained baseline information can be used to evaluate the new system's performance
Requirements Elicitation: Studying Documents and Software Systems (3)
17
Advantages
Disadvantages
helps in understanding the organisation helps in preparing other kinds of fact finding the existing system may provide formally defined requirements for the new system
written documents often do not match up to reality
out of date, differences between policy and practice
18
Requirements Elicitation: Prototyping (1)
Effective for eliciting requirements that are difficult to obtain from customers (especially concerning new systems) The most frequently used method of modern requirements elicitation
software prototypes are constructed to visualise parts of the system a quick and dirty working model of the solution
contains a GUI, and simulates the system behaviour
Two kinds of prototype
throw-away prototyping, evolutionary prototyping
19
Requirements Elicitation: Prototyping (2)
Advantages
Disadvantages
helps to assess the feasibility and usefulness of a system useful for clarifying requirements and resolving conflicts may speed up delivery
user may find it difficult to realise the complexity of the project quick and dirty solutions may end up in the final product too much emphasis may be placed on the user interface
20
Requirements Elicitation: Brainstorming (1)
Brainstorming is a technique for forming new ideas or for finding a solution to a specific problem
used because of the difficulty in reaching a consensus among stakeholders about the requirements a facilitator
Consists of
defines a probortunity statement consisting of trigger questions think of answers to trigger questions read out ideas vote to prioritise the ideas
12-20 people in a circle
21
Requirements Elicitation: Brainstorming (2)
Examples of trigger questions
what features should be supported by the system? what are the input data and outputs? what classes are needed in the business/domain object model? what questions should be raised in interviews/questionnaires? what issues need to be considered? what are the main risks? what trigger questions should be asked during this or future sessions?
22
Requirements Elicitation: JAD (1)
Joint Application Development (JAD)
one or more workshops that bring together all stakeholders a workshop can take a few hours to a couple of weeks leader
Participants (should not exceed 30)
conducts and moderates the meeting, is not a stakeholder records the session, must have touch-typing skills
scribe
customers (users and managers) developers
listen rather than speak
23
Requirements Elicitation: JAD (2)
Advantages
Disadvantages
group synergy is likely to produce better solutions to problems
problems during the sessions may be difficult to deal with
groups increase productivity, learn faster, make more educated judgements, eliminate more errors, take riskier decisions, focus attention on the most important issues, etc.
domination, noncontributors, side discussions, agenda merrygo-round, unresolved conflicts, etc.
design by committee can be bad
24
Requirements Elicitation: RAD (1)
An approach to software development emphasising speed of delivery over technical excellence
attractive for smaller projects evolutionary prototyping CASE tools with code generation specialists with advanced tools (SWAT) interactive JAD
RAD combines
replace the scribe with the SWAT team forbids scope creep by trimming down the solution
timeboxing
25
Requirements Elicitation: RAD (2)
Advantages
Disadvantages
good for smaller projects provides fast solutions
fast solutions are unlikely to be optimal or sustainable problems
inconsistent GUI designs specialised rather than generic solutions deficient documentation software that is difficult to scale up
26
Requirements Elicitation Planning (1)
Identify the stakeholders Evaluate the risk of the project Select the most appropriate requirements elicitation techniques for each stakeholder and the project as a whole Consider the implementation details for each selected technique
e.g. select people to interview, identify questions for interviews and questionnaires, decide how many interviews or questionnaires, organise JAD session, etc.
27
Requirements Elicitation Planning (2)
Criteria for selecting the most appropriate techniques (1)
analyst's experience
studying business documents requires little experience while participating in a JAD session requires a lot understanding the current system, identifying improvements, developing the new system how rich and detailed is the information produced? to what extent is the technique useful for obtaining and understanding facts and opinions?
type of information
depth of information
28
Requirements Elicitation Planning (3)
Criteria for selecting the most appropriate techniques (2)
breadth of information
the range of information and information sources that can be collected using a technique how easy is it to combine information from different sources and resolve differences in opinion or facts how much time and energy do the intended users devote to the analysis process? low cost or high cost?
integration of information
user involvement
cost
29
Requirements Elicitation Planning (4)
Requirements elicitation combines different techniques Example
to gain an understanding of the project and big picture
interviews with senior manager(s) analyse documents, interviews JAD sessions, questionnaires interviews with senior managers, JAD sessions for users at all levels
to understand the existing system
to identify improvements
to understand the new system requirements
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Letters and Sounds Parent LeafletDokument10 SeitenLetters and Sounds Parent Leafletابو مريمNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Analysis, System Development and System ModelsDokument56 SeitenSystem Analysis, System Development and System Modelsmaaya_ravindra100% (1)
- Brock2018 - The Development of Theory of MindDokument12 SeitenBrock2018 - The Development of Theory of MindTSG100% (1)
- Software Requirements SpecificationDokument9 SeitenSoftware Requirements Specificationjulija602Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Systems Analysis and DesignDokument47 SeitenModern Systems Analysis and DesignMhz RegNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Requirements ElicitationDokument9 SeitenSoftware Requirements ElicitationMarija SazdovskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Analyst Certificate Program: SUMMER 2006Dokument8 SeitenBusiness Analyst Certificate Program: SUMMER 2006fuzzy.logic.2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business Analyst in InterviewDokument3 SeitenBusiness Analyst in InterviewLakshmipathy VenusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive Health RightsDokument39 SeitenReproductive Health RightsMayom Mabuong75% (4)
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Dokument40 SeitenSoftware Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Anonymous aQxekTRNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Analysis and DesignDokument410 SeitenSystem Analysis and Designerangirifad92% (13)
- Servicenow Cis Questions: O O O O O O ODokument1 SeiteServicenow Cis Questions: O O O O O O ONani BuoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument29 SeitenChapter 4Prudhvinadh Kopparapu100% (1)
- ERP ModulesDokument10 SeitenERP ModulesSaravana VenkataramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asking Questions For BRDDokument5 SeitenAsking Questions For BRDNur SafiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Analysis and DesignDokument90 SeitenSystem Analysis and Designapi-371930380% (15)
- IT GovernanceDokument25 SeitenIT GovernanceBambang Puji Haryo WicaksonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Engineering - Lecture NotesDokument84 SeitenSoftware Engineering - Lecture Notesmutha12383% (6)
- Functional and Non-Functional RequirementsDokument7 SeitenFunctional and Non-Functional RequirementsChayt Kasote0% (2)
- International Institute of Business Analysis Standard RequirementsVon EverandInternational Institute of Business Analysis Standard RequirementsNoch keine Bewertungen
- En - requirements-ElicitationTechniques (Compatibility Mode)Dokument30 SeitenEn - requirements-ElicitationTechniques (Compatibility Mode)nmhuong90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Management ProcessDokument15 SeitenProblem Management ProcessVincenzo BasileNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is SDLCDokument18 SeitenWhat Is SDLCAmit Rathi100% (3)
- Making A Core Banking System DecisionDokument7 SeitenMaking A Core Banking System DecisionSteve Pitt100% (1)
- Questions-with-Answers: To Download Full Version of All The Questions - ClickDokument21 SeitenQuestions-with-Answers: To Download Full Version of All The Questions - ClickskumaritesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 Bar Examinations Frequently Asked Questions FAQs As of December 15 2022Dokument11 Seiten2023 Bar Examinations Frequently Asked Questions FAQs As of December 15 2022MD Lebria100% (1)
- Steps Involved in System Analysis and deDokument20 SeitenSteps Involved in System Analysis and deSurya Ghanathe100% (1)
- System Development Life Cycle PresentationDokument25 SeitenSystem Development Life Cycle Presentationsalim bba90% (10)
- Production Support ProcessDokument26 SeitenProduction Support ProcessMonikha100% (2)
- Non Functional RequirementsDokument7 SeitenNon Functional RequirementsSrinivasa GarlapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Requirement Analysis & NegotiationDokument32 SeitenRequirement Analysis & NegotiationNesrelah Mussa100% (1)
- Continuous Auditing A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandContinuous Auditing A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Plan Vs Test StrategyDokument11 SeitenTest Plan Vs Test StrategyArthy JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use Case DiagramDokument35 SeitenUse Case DiagramVaibhav Jain100% (1)
- Valerie Arraj, Managing Director, Compliance Process Partners, LLCDokument5 SeitenValerie Arraj, Managing Director, Compliance Process Partners, LLCmikeolmonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 - Requirements Elicitation 1-2 PDFDokument42 Seiten05 - Requirements Elicitation 1-2 PDFjayanthikrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA7205 Information ManagementDokument10 SeitenBA7205 Information ManagementshivacrazzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 - Requirements Elicitation 1-2Dokument42 Seiten05 - Requirements Elicitation 1-2mydin mamataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance Info - BADokument14 SeitenInsurance Info - BAHemi AngelicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Requirements SpecificationDokument26 SeitenSoftware Requirements SpecificationG.C.Reddy100% (1)
- Use CasesDokument8 SeitenUse CasesGwen HarrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2: Data Model: I-The Entity-Relationship ModelDokument48 SeitenChapter 2: Data Model: I-The Entity-Relationship ModelAWAHNJI JEAN100% (1)
- Chapter One Introduction To SADDokument26 SeitenChapter One Introduction To SADCali Cali100% (1)
- Technology Platforms A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionVon EverandTechnology Platforms A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certified International Payment Systems ProfessionalDokument4 SeitenCertified International Payment Systems ProfessionalMakarand Lonkar50% (2)
- IT Strategy ScopingDokument13 SeitenIT Strategy ScopingSteve Mclean100% (1)
- Mastering Software Project ManagementDokument189 SeitenMastering Software Project Managementhtyeh100% (2)
- Thus Core Banking Components IncludeDokument2 SeitenThus Core Banking Components IncludeMohit Agarwal50% (2)
- System Development Life CycleDokument8 SeitenSystem Development Life CycleKumar Abhishek100% (1)
- Bit4209 Distributed Systems ModuleDokument117 SeitenBit4209 Distributed Systems ModuleJames MuthuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Requirements ElicitationDokument5 SeitenRequirements ElicitationShivendra VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Systems and System Development: Understanding ComputersDokument74 SeitenInformation Systems and System Development: Understanding Computershussnain tararNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Engineering ProjectDokument27 SeitenSoftware Engineering Projectcharity diolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L9 - Logical Architecture and UML Package DiagramsDokument3 SeitenL9 - Logical Architecture and UML Package Diagramsryu447Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intranet Best Practices: What Are The Business Benefits?Dokument5 SeitenIntranet Best Practices: What Are The Business Benefits?maheshdbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Technology Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandInformation Technology Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBAP NotesDokument3 SeitenCBAP NotesAnubha JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Infrastructure Deployment A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandIT Infrastructure Deployment A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Requirement A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionVon EverandFunctional Requirement A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Support A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandApplication Support A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Consulting A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandInformation Consulting A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pde Sas Elments of A Story Lesson PlanDokument7 SeitenPde Sas Elments of A Story Lesson Planapi-278843253Noch keine Bewertungen
- WorksheetDokument6 SeitenWorksheetruffa mae enriquez100% (1)
- Class-record-Amy - Pansy (2nd Grading)Dokument48 SeitenClass-record-Amy - Pansy (2nd Grading)Amelita Benignos OsorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- CareerguideDokument97 SeitenCareerguidegrechenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Guidelines For ME261-2016: University Attendance PolicyDokument4 SeitenAssessment Guidelines For ME261-2016: University Attendance PolicyAnonymous 75V3NgrONoch keine Bewertungen
- RMK Versi Pelajar Edup3033 Learning and The Learner (BI)Dokument7 SeitenRMK Versi Pelajar Edup3033 Learning and The Learner (BI)Annette CaelyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal University DutsinDokument7 SeitenFederal University DutsinAbu elijahNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Rpms Portfolio (Design 1) 2023-2024 - DepedclickDokument51 SeitenE-Rpms Portfolio (Design 1) 2023-2024 - DepedclickFrinces Mae CristalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Definition of A ProfessionDokument5 SeitenThe Definition of A ProfessionPeter WdowiakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education: Crafting/Conference ON School Governance Council S.YDokument5 SeitenDepartment of Education: Crafting/Conference ON School Governance Council S.YRenalyn CuntapayNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Language Aqa Coursework IdeasDokument6 SeitenEnglish Language Aqa Coursework Ideasafiwgbuua100% (2)
- Jurimetrics 1Dokument24 SeitenJurimetrics 1Maiko Lesmana D0% (1)
- Phil HealthDokument92 SeitenPhil HealthJoshua LoyolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 - Mapeh 1ST QuarterDokument18 SeitenGrade 10 - Mapeh 1ST QuarterHero LaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- #ThisIsNotArt BlurbDokument7 Seiten#ThisIsNotArt BlurbcarolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group DiscussionDokument16 SeitenGroup DiscussionPooja KaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Furqan Ahmed: Personal DetailDokument4 SeitenFurqan Ahmed: Personal DetailFarooq Khurshid AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal ResearchDokument31 SeitenProposal ResearchYeccy AjjhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Best Strategies For Ensuring Quality in Hospitals?Dokument25 SeitenWhat Are The Best Strategies For Ensuring Quality in Hospitals?Chandranath ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription - M1S1Dokument37 SeitenTranscription - M1S1GrowUP. AINoch keine Bewertungen
- Bilingual Method MarielDokument15 SeitenBilingual Method MarielRave LegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Iancu Aurelia IonelaDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan Iancu Aurelia IonelaIancu AureliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV Index Short Biography 14.01.20 PDFDokument57 SeitenCV Index Short Biography 14.01.20 PDFtomalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument12 SeitenChapter 5ramana3339Noch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Governance: A Key Factor For Smart Cities ImplementationDokument6 SeitenSmart Governance: A Key Factor For Smart Cities ImplementationAtestate LiceuNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Thanksgiving LessonDokument3 SeitenFirst Thanksgiving Lessonapi-251387458Noch keine Bewertungen