Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Kaseya How To SNMP (Small)
Hochgeladen von
markdavidboydOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Kaseya How To SNMP (Small)
Hochgeladen von
markdavidboydCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Kaseya & Manual SNMP Identification
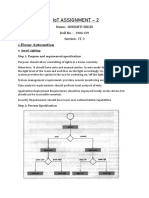
This document outlines step by step how to load an SNMP Object (MIB) into Kaseya, and turn it into an SNMP SET Tools Required Kaseya 6.0.0.0 or greater GetIF (Free download) Vendor Mibs of device you wish to monitor Assumptions You have the IP Address of the device you want to monitor You have SNMP Read access to the Device you wish to monitor For the purpose of this exercise, we will look at a HP Procurve 5308XL Core Series Switch You have GetIF Installed and familiar with the software Finding what to measure is a time consuming process per device Expect to spend at least an hour per device if you havent been exposed to SNMP / MIBS / GetIF Process Step 1: Get info about Device What Measurement Where Collect Mibs HP Procurve 5308XL Fan & PSU Failure On a customer site HP-ICF-OID.mib hpicfChassis.mib hpicfDcFan.mib hpicfDcPower.mib hpicfOid.mib RFC1155-SMI.txt RFC1213-MIB.txt RFC1271-MIB.txt rfc2578.mib rfc2579.mib rfc3411.mib The above mentioned MIBS are relevant for this device Other Devices have different MIBS, download other MIBS from Vendors
Note:
Step 2: Use GetIF, Analyse Results Copy Mibs to Run GetIF C:\Program Files\GetIF 2.3.1\Mibs Parameters tab > Enter IP Address > Click Start MBrowser tab > Search for values to measure In this case Iso.org.dod.internet. enterprise.hp.nm.icf. hpicfobjects.hpicfcommon.hpicfchassis. hpicfsensortable.hpicfsensorentry.hpicfsensorstatus Note OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.11.2.14.11.1.2.6.1.4
1. Fully qualified SNMP Object Name, Fully qualified SNMP Number 2. Select this to evaluate the mib 3. Note the three values inside the object Each value will be represent by another oid IE: Sensor status: 1.3.6.1.4.1.11.2.14.11.1.2.6.1.4 Sensor status 1 : 1.3.6.1.4.1.11.2.14.11.1.2.6.1.4.1 Sensor status 2 : 1.3.6.1.4.1.11.2.14.11.1.2.6.1.4.2 Sensor status 3 : 1.3.6.1.4.1.11.2.14.11.1.2.6.1.4.3 4. Note: i(integer) is the SYNTAX field used in step 3 What this means Sensor Status is what we are measuring; this is the object we need to import in Kaseya The sub values, that is, .1,.2,.3, are each individual sensor detected inside the unit. IMPORTANT: Note how many SUB VALUES Exist, this is the SNMP Instance number in Kaseya
Step 3: Import into Kaseya Follow these steps to import Mib Objects into Kaseya In Kaseya > Monitor Monitor > Edit > Add SNMP Object > Load Mib > Browse Mibs Load Mibs into Kaseya from Step 2 HP-ICF-OID.mib hpicfChassis.mib hpicfDcFan.mib hpicfDcPower.mib hpicfOid.mib RFC1155-SMI.txt RFC1213-MIB.txt RFC1271-MIB.txt rfc2578.mib rfc2579.mib rfc3411.mib Monitor > Edit > Monitor Lists > Counter Objects Browse counter objects to see if your object already exists Monitor > Edit > Monitor Lists > CMIB OIDs > ADD Display Name: HpICFSensorStatus Name: HpICFSensorStatus Numbered OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.11.2.14.11.1.2.6.1.4 Char OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.11.2.14.11.1.2.6.1.4 Syntax integer Access: Read-only Description HP Sensor Status.
In Kaseya > Monitor In Kaseya > Monitor
Step 4: Create SNMP Set In Kaseya > Monitor Monitor > Edit > Monitor Lists > SNMP Sets Shared Folder > Add Folder > New SNMP SET > SNMP Sets > ADD (Data) Mib Object: HpICFSensorStatus SNMP Version: 1 SNMP Instance: 1-3 (Remember, in this device we have 3 sensors) Value Returned as: _total Name: HpICFSensorStatus Description: HpICFSensorStatus Collection: -1 SNMP Timeout: 2 Seconds Alarm Operator: Under Alarm Threshold: 3 Duration: 30 Seconds Ignore Additional Alarm 1 Hours <<NEED TO CHECK LOGIC DOES ALARM UNDER 4 IMPLY SENSOR FAILURE?>> Step 5: Assign SNMP to device: I will assume the user will know how to do his step Step 6: Conclusion: If MIB Import is successful the Manual creation, and application SNMP set should be successful
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A), The Grep Commandis Case Sensitive, Use The I Parameterto Make ItDokument8 SeitenA), The Grep Commandis Case Sensitive, Use The I Parameterto Make ItRenato Franchesco Valega GamarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1.2.9 Lab - Web Application VulnerabilityDokument13 Seiten5.1.2.9 Lab - Web Application Vulnerabilityacostlow2422Noch keine Bewertungen
- InfoBlox SNMP Enterprise MIBDokument20 SeitenInfoBlox SNMP Enterprise MIBKali PsyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Device Sensor: Finding Feature InformationDokument28 SeitenDevice Sensor: Finding Feature Informationkarthong4057Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab1i Externaldatacollectors SNMP v3 - Tdeleon PDFDokument38 SeitenLab1i Externaldatacollectors SNMP v3 - Tdeleon PDFckent2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Walkthrough 2114Dokument61 SeitenWalkthrough 2114Mohd JadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP Security Secure Lab GuideDokument150 SeitenCCNP Security Secure Lab Guidebkaraqa67% (3)
- SECURE10LGDokument150 SeitenSECURE10LGAzzafirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Answer Key - Module 2 - Working With The PipelineDokument19 SeitenLab Answer Key - Module 2 - Working With The PipelinefigoenNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRTG Using Snmp-2022 60minDokument26 SeitenPRTG Using Snmp-2022 60minAdekusile John OluwaseunNoch keine Bewertungen
- F5 Ltm-140130073252-PhpappDokument149 SeitenF5 Ltm-140130073252-Phpappakino johnkennedyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Client Server Programming With WinsockDokument4 SeitenClient Server Programming With WinsockJack AzarconNoch keine Bewertungen
- CISA Class Notes 15 and 16 October 2022Dokument7 SeitenCISA Class Notes 15 and 16 October 2022Chitij ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceh v12 Lesson 3 - Netbios, SNMP & Ldap NetworDokument89 SeitenCeh v12 Lesson 3 - Netbios, SNMP & Ldap NetworUddesh WaghNoch keine Bewertungen
- QTP Elite)Dokument101 SeitenQTP Elite)Preetesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qradar Support 101: Wincollect TroubleshootingDokument38 SeitenQradar Support 101: Wincollect TroubleshootingSarwat TauqeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taking a BIGIP Backup and Creating Support FilesDokument11 SeitenTaking a BIGIP Backup and Creating Support FilesGurdarshan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- GestioIP 3.0 Installation GuideDokument17 SeitenGestioIP 3.0 Installation GuidepiterasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Realtime Temp Monitoring with BeagleBone Black and MQTTDokument4 SeitenRealtime Temp Monitoring with BeagleBone Black and MQTTEverton Klinger Sousa SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1: Finger Print Enrollment (38Dokument17 SeitenLab 1: Finger Print Enrollment (38morylexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devices 6212 Reference GuideDokument128 SeitenDevices 6212 Reference GuideMohamed El-TokhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SNMP Exercis1Dokument5 SeitenSNMP Exercis1Sulltana ShaqiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.4.1.2 Alt Lab - Isolate Compromised Host Using 5-TupleDokument10 Seiten12.4.1.2 Alt Lab - Isolate Compromised Host Using 5-Tuplec583706Noch keine Bewertungen
- Footprinting, Reconnaissance, Scanning and Enumeration Techniques of Computer NetworksVon EverandFootprinting, Reconnaissance, Scanning and Enumeration Techniques of Computer NetworksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nmap + OpenfismaDokument3 SeitenNmap + OpenfismaAlvaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC-Hardware & Networking Troubleshooting CommandsDokument3 SeitenPC-Hardware & Networking Troubleshooting Commandsdivakara sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backdooring PracticalDokument4 SeitenBackdooring PracticalSimo ErrafiyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLI Cheat Sheet: Device ManagementDokument7 SeitenCLI Cheat Sheet: Device ManagementMayur Kakadiya100% (2)
- FogBus End User TutorialDokument15 SeitenFogBus End User TutorialpashascribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 44 - SNMP ManagerDokument34 SeitenModule 44 - SNMP ManagerRafaael CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- PES2UG22CS397CNLABWEEK1Dokument15 SeitenPES2UG22CS397CNLABWEEK1Ashish GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zabbix Otrs enDokument4 SeitenZabbix Otrs enAlex JuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPnP Device Architecture Generic 20000710Dokument40 SeitenUPnP Device Architecture Generic 20000710bharathkumar363Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trend Micro Tipping Point IPS - LSM Deployment GuideDokument13 SeitenTrend Micro Tipping Point IPS - LSM Deployment Guidemodather nadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Snort RuleDokument22 SeitenSnort RuleQuang NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programmer's Guide For Fingerprint's SDKDokument18 SeitenProgrammer's Guide For Fingerprint's SDKguidoska88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practicals 3Dokument5 SeitenPracticals 3Tarik AmezianeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AKCP SNMP OID ManualDokument27 SeitenAKCP SNMP OID Manualadesedas2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- CLMGRDokument12 SeitenCLMGRAnvesh ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- F5 BIG-IP Configuration Guide - APM, LTM, GTM, Security, and High AvailabilityDokument11 SeitenF5 BIG-IP Configuration Guide - APM, LTM, GTM, Security, and High AvailabilityManjunath Shekar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- IoT Assignment - Smart Home and City ApplicationsDokument29 SeitenIoT Assignment - Smart Home and City ApplicationsIpsy NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functionality Test CasesDokument20 SeitenFunctionality Test CasesNitin PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Command Injection Lab GuideDokument16 SeitenCommand Injection Lab Guidehuynhphuc112Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1 SNMP-Wireshark BasicsDokument13 SeitenLab 1 SNMP-Wireshark BasicsMary Amirtha Sagayee. GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report on Hacking Victim WorkstationDokument9 SeitenLab Report on Hacking Victim Workstationlee leeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edge Service DocumentationDokument15 SeitenEdge Service DocumentationArjun GhoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malware AnalysisDokument21 SeitenMalware AnalysisAyush rawal100% (1)
- Network Management Installation and Configuration GuideDokument14 SeitenNetwork Management Installation and Configuration GuideERICK_GIL4369Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network Management Installation and Configuration GuideDokument14 SeitenNetwork Management Installation and Configuration GuideERICK_GIL4369Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pes1ug22cs363 Lab 1Dokument18 SeitenPes1ug22cs363 Lab 1Ashish GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Check Point Endpoint Connect R73Dokument9 SeitenCheck Point Endpoint Connect R73Farhat BajryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Android Native SDK Documentation 2020091800Dokument17 SeitenAndroid Native SDK Documentation 2020091800Toan Luong NhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to respond to a web security incidentDokument38 SeitenHow to respond to a web security incidentzain jamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to respond to a web security incidentDokument38 SeitenHow to respond to a web security incidentArkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkVon EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastering Unix Shell Scripting: Bash, Bourne, and Korn Shell Scripting for Programmers, System Administrators, and UNIX GurusVon EverandMastering Unix Shell Scripting: Bash, Bourne, and Korn Shell Scripting for Programmers, System Administrators, and UNIX GurusBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- SNMP and GetifDokument9 SeitenSNMP and GetifmarkdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaseya How To Large)Dokument13 SeitenKaseya How To Large)markdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- SNMP Without MIBS - Point Paper Rev 1Dokument6 SeitenSNMP Without MIBS - Point Paper Rev 1markdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaseya Patch ManagementDokument10 SeitenKaseya Patch ManagementmarkdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking FundamentalsDokument4 SeitenNetworking FundamentalsmarkdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaseya How To SNMP (Small)Dokument3 SeitenKaseya How To SNMP (Small)markdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaseya Patch ManagementDokument10 SeitenKaseya Patch ManagementmarkdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaseya Patch ManagementDokument10 SeitenKaseya Patch ManagementmarkdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaseya How To Large)Dokument13 SeitenKaseya How To Large)markdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security PracticesDokument3 SeitenSecurity PracticesmarkdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaseya Performance and Best Practices Guide: Authors: Jacques Eagle Date: Thursday, April 29, 2010Dokument34 SeitenKaseya Performance and Best Practices Guide: Authors: Jacques Eagle Date: Thursday, April 29, 2010markdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Firewall RulesDokument1 SeiteFirewall RulesmarkdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top Tools For Top Administrators 2Dokument9 SeitenTop Tools For Top Administrators 2markdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top Tools For Top AdministratorsDokument7 SeitenTop Tools For Top AdministratorsmarkdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Wireshark For Traffic AnalysisDokument2 SeitenUsing Wireshark For Traffic AnalysismarkdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel and SQLDokument6 SeitenExcel and SQLmarkdavidboydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Highlights: 7010X Series Data Center SwitchesDokument9 SeitenProduct Highlights: 7010X Series Data Center Switchesjun chanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify and Resolve Network ProblemsDokument76 SeitenIdentify and Resolve Network ProblemsBiniyam Efrem100% (2)
- Hexicom AR74 EoC Master User ManualDokument53 SeitenHexicom AR74 EoC Master User Manualthanhnam2624Noch keine Bewertungen
- VM Ware SystemDokument113 SeitenVM Ware SystemhassaanpashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brocade MIB ReferenceDokument1.212 SeitenBrocade MIB ReferencejessiwattsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broadworks Access Mediation Server Ems Configuration Management GuideDokument118 SeitenBroadworks Access Mediation Server Ems Configuration Management GuideLazaro BalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardware Installation Guide: D-Link™ DGS-3100 SERIES Gigabit Stackable Managed SwitchDokument74 SeitenHardware Installation Guide: D-Link™ DGS-3100 SERIES Gigabit Stackable Managed SwitchAlfred PskNoch keine Bewertungen
- IManager U2000 V100R001C00 Product Documentation Bookshelf (V1.09) enDokument36 SeitenIManager U2000 V100R001C00 Product Documentation Bookshelf (V1.09) enGaurav AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0day SecurityDokument30 Seiten0day SecurityRoberto RaimondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EasyPath EPON Operation ManualV3.30-GWD-320130520Dokument333 SeitenEasyPath EPON Operation ManualV3.30-GWD-320130520Guss SarangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Utilizare Network Video Recorder Dahua EZ-IP NVR1B04 4 Canale 8 MP 80 Mbps 4 PoEDokument229 SeitenManual de Utilizare Network Video Recorder Dahua EZ-IP NVR1B04 4 Canale 8 MP 80 Mbps 4 PoEDaniel RoșuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure DFX1000 2010Dokument2 SeitenBrochure DFX1000 2010johnnykentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switch Al Cat ElDokument8 SeitenSwitch Al Cat ElAgus YulfizarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProVision Plus Rel 2.13 GA Customer Release Notes 2022-AUG-31Dokument72 SeitenProVision Plus Rel 2.13 GA Customer Release Notes 2022-AUG-31Mohamed Saber MokdafNoch keine Bewertungen
- (July-2022-Updated) PassLeader 2020 CCNA 200-301 Exam DumpsDokument7 Seiten(July-2022-Updated) PassLeader 2020 CCNA 200-301 Exam Dumpstest accountNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teldat Bintec w2003n Ext 5510000325 Manual de UsuarioDokument9 SeitenTeldat Bintec w2003n Ext 5510000325 Manual de UsuarioHiderandRosario Pimentel TaipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automation Server Specification Sheet - SmartStruxure SolutionDokument6 SeitenAutomation Server Specification Sheet - SmartStruxure SolutionGutus NirwantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Com Ip DslamDokument226 SeitenC Com Ip DslamGiang VuNoch keine Bewertungen
- TL-SG3216 V2 DatasheetDokument5 SeitenTL-SG3216 V2 DatasheetMiguel Angel Gutierrez PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVP Security User Guide v9 - 41Dokument20 SeitenAVP Security User Guide v9 - 41Minh TuấnNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Simulate Network DevicesDokument12 SeitenHow To Simulate Network DevicesVerax Systems Corp.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network Programming and Management - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDokument3 SeitenNetwork Programming and Management - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TV100% (1)
- S2350 - S5300 - S6300 V200R003C00 Upgrade GuideDokument59 SeitenS2350 - S5300 - S6300 V200R003C00 Upgrade GuideMartin PelusoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobatime: NMS Overview and DSS OverviewDokument21 SeitenMobatime: NMS Overview and DSS OverviewShanavasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 12: Network Troubleshooting: Telecom AcademyDokument47 SeitenModule 12: Network Troubleshooting: Telecom AcademyCalin CojocaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Netway Vision 3.8 .X: Software SolutionsDokument89 SeitenNetway Vision 3.8 .X: Software Solutionstdurrer5Noch keine Bewertungen
- FortiManager-7 4 0-Administration - GuideDokument937 SeitenFortiManager-7 4 0-Administration - GuideJosé PabloNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT&T NetGate DataSheet - 8200 PDFDokument5 SeitenAT&T NetGate DataSheet - 8200 PDFShawn AmeliNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Use This TemplateDokument91 SeitenHow To Use This TemplateYeixon AmayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3COM OS Switch 4500 V3 (1) .03.02p21 Release Notes PDFDokument95 Seiten3COM OS Switch 4500 V3 (1) .03.02p21 Release Notes PDFRafael MineoNoch keine Bewertungen