Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Portal Hypertension Features
Hochgeladen von
Maha MukhtarOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Portal Hypertension Features
Hochgeladen von
Maha MukhtarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
17 September 2011 20:21
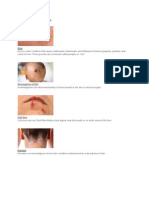
Portal hypertension: features ABCDE: Ascites Bleeding (haematemesis, piles) Caput medusae Diminished liver Enlarged spleen
WBC Count:
"Nobody Likes My Educational Background" "60, 30, 6, 3, 1" Neutrophils 60% Lymphocytes 30%Monocytes 6% Eosinophils 3% Basophils 1% Diabetic ketoacidosis: I vs. II ketONE bodies are seen in type ONE diabetes. MHC I and MHC II: T cell type 'MHC x T cell=8' MHC II goes with CD4 (2x4=8) MHC I goes with CD8 (1x8=8)
Renal failure (chronic): consequences ABCDEFG: Anemia -due to less EPO Bone alterations -osteomalacia -osteoporosis -von Recklinghausen Cardiopulmonary -atherosclerosis -CHF -hypertension -pericarditis D vitamin loss Electrolyte imbalance -sodium loss/gain -metabolic acidosis -hyperkalemia Feverous infections -due to leukocyte abnormalities and dialysis hazards GI disturbances -haemorrhagic gastritis -peptic ulcer disease
New Section 2 Page 1
-peptic ulcer disease -intractable hiccups Hypertension: secondary hypertension causes CHAPS: Cushing's syndrome Hyperaldosteronism [aka Conn's syndrome] Aorta coarctation Phaeochromocytoma Stenosis of renal arteries Note: only 5% of hypertension cases are secondary, rest are primary Hypercalcemia: symptoms of elevated serum levels "Bones, Stones, Groans, Moans": Bones: pain in bones Stones: renal Groans: pain Psychic moans/ Psychological overtones: confused state Acute ischemia: signs [especially limbs] 6 P's: Pain Pallor Pulselessness Paralysis Paraesthesia Perishingly cold Heart failure causes "HEART MAy DIE": Hypertension Embolism Anemia Rheumatic heart disease Thyrotoxicosis (incl. pregnancy) Myocardial infarct Arrythmia Y Diet & lifestyle Infection Endocarditis Liver failure (chronic): signs found on the arms CLAPS: Clubbing Leukonychia Asterixis Palmar erythema Scratch marks Constipation: causes DOPED: Drugs (eg opiates) Obstruction (eg IBD, cancer) Pain Endocrine (eg hypothyroid) Depression
New Section 2 Page 2
Splenomegaly: causes CHIMP: Cysts Haematological ( eg CML, myelofibrosis) Infective (eg viral (IM), bacterial) Metabolic/ Misc (eg amyloid, Gauchers) Portal hypertension Leukemias: acute vs. chronic rules of thumb ABCDE: Acute is: Blasts predominate Children Drastic course Elderly Few WBC's (so Fevers) Chronic is all the opposites: Mature cells predominate Middle aged Less debilitating course Elevated WBC's, so not a history of fevers and infections Gout: factors that can precipitate an attack of acute gouty arthritis DARK: Diuretics Alcohol Renal disease Kicked (trauma) And, the attack occurs most often at night *thus "dark"+. Causes of membrane over tonsils (shared by Taishan Medical University) I L(ove) MADAM TV I- Infectious Mononucleosis L(ove)- Leukemias M- Malignancy A- Agranulocytosis D- Diphtheria A- Aphthous ulcers M- Membranous tonsillitis T- Trauma V- Vincents angina Parkinson's disease: symptoms PQRST: Paucity of expression parQinson Rigidity (cogwheel) Stooped posture Tremor at rest
New Section 2 Page 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Mini BooksDokument28 SeitenMini BooksNina HaryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Medical Mnemonics: FOR Medicine & SurgeryDokument62 SeitenMedical Mnemonics: FOR Medicine & SurgeryShailen ShakyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Robbins Pathology - Chapter 6 TransDokument31 SeitenRobbins Pathology - Chapter 6 Transnath nathNoch keine Bewertungen
- d100 Appearance/touch Taste/scent Effect MiscibilityDokument5 Seitend100 Appearance/touch Taste/scent Effect MiscibilityFoxtrot OscarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLAB 2 ExaminationDokument9 SeitenPLAB 2 Examinationryanychu100% (1)
- Common Skin DisordersDokument10 SeitenCommon Skin DisordersPaul Vincent Alfonso100% (1)
- CT Mbbs by DR ShamolDokument197 SeitenCT Mbbs by DR ShamolSiva Sandeep Chennimalai50% (2)
- Endometrial Carcinoma: Tamoxifen Is An Estrogen Receptor AntagonistDokument1 SeiteEndometrial Carcinoma: Tamoxifen Is An Estrogen Receptor AntagonistMaha Mukhtar0% (1)
- ENTDokument8 SeitenENTapi-19863548Noch keine Bewertungen
- Histology SyllabusDokument32 SeitenHistology SyllabusAdrianAddieNovioDeJesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathognomonic Signs of DiseasesDokument4 SeitenPathognomonic Signs of DiseasesmydewyboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electroacupuctura VollDokument32 SeitenElectroacupuctura Vollminunat50% (2)
- Checklist For Steam Inhalation Using A Nelson'S Inhaler: S.No Content Demo Return Demo Practice 1 Practice 2 PurposeDokument5 SeitenChecklist For Steam Inhalation Using A Nelson'S Inhaler: S.No Content Demo Return Demo Practice 1 Practice 2 PurposeNeelofur Ibran Ali50% (2)
- PuerperiumDokument85 SeitenPuerperiumHema MaliniNoch keine Bewertungen
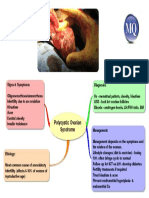
- Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeDokument1 SeitePolycystic Ovarian SyndromeMaha MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics and Mnemonics PDFDokument8 SeitenAntibiotics and Mnemonics PDFMaha MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem NotesDokument4 SeitenBiochem NotesMaha MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Random Mbbs PointsDokument1 SeiteRandom Mbbs PointsMaha MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step 1 BiochemistryDokument93 SeitenStep 1 BiochemistryAnnie AnnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forrester Classification, Nyha ClassificationDokument9 SeitenForrester Classification, Nyha ClassificationMaha MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead PoisoningDokument1 SeiteLead PoisoningMaha MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apex Beat..how To LocateDokument20 SeitenApex Beat..how To LocateMaha MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- JVPDokument1 SeiteJVPMaha MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- JVPDokument1 SeiteJVPMaha MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iqbal AsrareKhudiDokument8 SeitenIqbal AsrareKhudisadafrizviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ig Imp PointsDokument1 SeiteIg Imp PointsMaha MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ig Imp PointsDokument1 SeiteIg Imp PointsMaha MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care of A Child With Immune DisordersDokument4 SeitenNursing Care of A Child With Immune DisordersChin T. OndongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annotated - Exam Key - First Aid C - 10 28 2014 PDFDokument5 SeitenAnnotated - Exam Key - First Aid C - 10 28 2014 PDFSuliemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Can Oral Sex Transmit HIV?Dokument52 SeitenCan Oral Sex Transmit HIV?Leo LamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes 02 Clinical Chemistry 2Dokument6 SeitenNotes 02 Clinical Chemistry 2Brent LagartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Condition of Dairy Cows PDFDokument44 SeitenBody Condition of Dairy Cows PDFfranky100% (1)
- Silabus HistoDokument7 SeitenSilabus HistoamytenzerNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCG Vaccine EDokument17 SeitenBCG Vaccine Edr.kendrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolutionary History, Molecular Systematics and Evolutionary Ecology of Canidae (Wang Et Al., 2006) PDFDokument18 SeitenEvolutionary History, Molecular Systematics and Evolutionary Ecology of Canidae (Wang Et Al., 2006) PDFFrancisco J. OvalleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Meat Industry: Opportunities and Challenges: January 2011Dokument7 SeitenIndian Meat Industry: Opportunities and Challenges: January 2011satyajitNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHD Research ProposalDokument8 SeitenPHD Research ProposalMalik Ijaz Khan100% (1)
- Trial Spm-Bio k2 SkemaDokument14 SeitenTrial Spm-Bio k2 SkemaFarah Shafiqah AmiruddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Obstetric Blood Loss EstimationDokument5 SeitenVisual Obstetric Blood Loss Estimationrenia gustinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPK ParuDokument64 SeitenPPK Parusri wahyuniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sjavs 24a270 281Dokument12 SeitenSjavs 24a270 281Ramesh BeniwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contaminación de Los Suelos Con Huevos de Toxocara Canis en ParquesDokument12 SeitenContaminación de Los Suelos Con Huevos de Toxocara Canis en ParquesJahir QHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Friends Humane Society Complaint, Affidavits and ExhibitsDokument178 SeitenAnimal Friends Humane Society Complaint, Affidavits and ExhibitsAmanda EvrardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Ocular Dermoid Cyst A ReviewDokument12 SeitenCongenital Ocular Dermoid Cyst A ReviewSudhakar UtkNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThlasmiaDokument7 SeitenThlasmiaSonia AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Muscular System 4Dokument4 SeitenSummary of Muscular System 4api-253866502100% (1)
- Berkeley Science Review - Fall 2011Dokument60 SeitenBerkeley Science Review - Fall 2011The Berkeley Science Review100% (3)