Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
GR 10 Physics Exam Review
Hochgeladen von
Chris Merhai BaliOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GR 10 Physics Exam Review
Hochgeladen von
Chris Merhai BaliCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PHYSICS REVIEW Precision: Accuracy: Significant Digits (Sig Figs): S.D Rule for and S.
S.D Rule for + and Examples of Sig Figs: 1600 3.3 = 2.312 + 3.4510 = (5.03 103) 2 = km/h m/s Ex: Hannah runs at a Ex: Steven jogs around the block at a speed of 30km/h. What speed of 5.5m/s. What is that speed in speed is that in m/s? km/h?
m/s km/h
1km = 1m = 1cm =
m cm mm
Motion occurs if:
Scalar Quantity:
Position: Distance (d):
Vector Quantity: Displacement (d): Ref. Point: Time (t): Speed (v): Average Speed (3 formulas):
Velocity (v): Average Velocity (vav):
Instantaneous Speed: Constant Speed: The flight to Mexico is 4.5hrs with the vav being 650km/h. How far is it to Mexico. Show speed and velocity.
It takes 50 minutes to travel Biking 4km takes how long 34km from home to school. if you average 16km/h? Calculate vav in km/h and Show your answer in mins. m/s.
Distance-Time Graphs:
Slope of a D-T Graph:
Acceleration (5 formulas):
Area under the line shows: -constant fast speed
Acceleration: -constant slow speed aav = +ve value means:
It takes 10s for a car to stop while travelling 120km/h. What is the aav in km/h? How fast is this in m/s?
aav = -ve value means: -standing still (vav = 0)
A snowmobile reaches a final velocity 22.5m/s after accelerating at 1.2m/s/s for 17s. What was the intial speed? Convert to km/h.
Biking downhill your aav is 4km/h/s. How much faster will you be going in 12s? If you started at 10km/h what will be your final speed?
Brad is travelling at 1.50m/s [N] on his bike and then accelerates at 0.50m/s2 [N] for 15s. What is Brads displacement while he is accelerating down the path in the park near his home?
Velocity-Time Graphs:
Slope of V-T Graph:
Find the total distance travelled from each graph displayed below:
-constant fast acceleration
Area under the line shows:
-constant slow acceleration Formulas for these shapes:
-constant speed (aav = 0)
-fast negative acceleration
Compass:
Acceleration Due to Gravity:
Vector Diagrams: Thea walks 250m [W] and then 200m [W]. Use a scale diagram to show how far she walked.
Alison walks 350m [W] and then 200m [E]. Use a scale diagram to show how far she walked.
What angle is this:
What angle is this:
What angle is this:
What angle is this:
Sarah drives 50km [N] 30 [E] and 20km [E] 20 [N]. Find d and d.
Mike drives 4km [N] 30 [E], 4km [W] and [S] 30 [E]. Find d and d.
Universal Wave Equation: Speed of Light: The Ray Model of Light:
What is Light? Electromagnetic Spectrum: Converging Mirror: Diverging Mirror:
Forces: Newtons First Law: Newtons Second Law: Newtons Third Law:
Example
Example
Example
Forces as Vectors:
During a soccer game, three boys simultaneously kick the ball. Jeff exerts a force of 30N [E]. Chris exerts a force of 20N [N 30 E] and Tom exerts a force of 40N [W]. Find the resultant force acting on the ball.
Free Body Diagrams:
Frictional Forces:
A horizontal force of 20N is applied to a mass of 5.0kg which is at rest on a horizontal surface. The acceleration of the mass is 1.5m/s2. What is the force of friction on the mass?
The Coefficient of Friction: A 10kg mass is pushed across a wooden floor by a horizontal force of 75N. The coefficient of friction is = 0.40. (a) What is the force of friction? (b) What is the acceleration of the mass?
Consider the following system and find (a) the acceleration and (b) the tension in both strings. B
A
10kg = 0.4
10kg
5kg
Fa= 200N = 0.2
Newtons Law of Universal Gravitation:
Work:
Power:
Energy:
Kinetic Energy:
Gravitational Potential Energy:
The Law of Conservation of Energy:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Lecture 3Dokument10 SeitenLecture 3Darryl LazagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed and AccelerationDokument17 SeitenSpeed and AccelerationDan Warren Loyola NuestroNoch keine Bewertungen
- College Physics and Intefral Calculus ProblemsDokument125 SeitenCollege Physics and Intefral Calculus ProblemsLes Narciso PamintuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Forces and EnergyDokument47 SeitenUnit 3 Forces and Energy4w7b9kkyp8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science 20 Unit B 08Dokument133 SeitenScience 20 Unit B 08api-207957230100% (1)
- Motion 1Dokument24 SeitenMotion 1ManishNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS101 Egypt AssignmentDokument16 SeitenMS101 Egypt Assignmentrofaman100% (5)
- Scalar vs Vector Quantities ExplainedDokument15 SeitenScalar vs Vector Quantities Explainedanwar9602020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Exam Review 2014Dokument7 SeitenPhysics Exam Review 2014Salix MattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear MotionDokument59 SeitenLinear MotionAnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FizikDokument11 SeitenFizikorangramaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Linear MotionDokument8 SeitenLesson 1 Linear MotionAbul CepolNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW - Apb - C02Dokument6 SeitenHW - Apb - C02Ngoclinh Vo100% (1)
- Physics BenDokument32 SeitenPhysics BenAngeline NgouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4-5-2022Dokument18 SeitenLecture 4-5-2022Karar Haidar AltalibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOLITON TECHNOLOGIES APTITUDE QUESTION BANK TOPICSDokument18 SeitenSOLITON TECHNOLOGIES APTITUDE QUESTION BANK TOPICSVeeraragavan Subramaniam79% (14)
- LESSON 1 LINEAR MOTIONDokument14 SeitenLESSON 1 LINEAR MOTIONIzawati AmatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys11 C01 HomeworkDokument4 SeitenPhys11 C01 HomeworkAynaticNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Motion LessonDokument6 SeitenLinear Motion LessonSalmizam IzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS MOCK EX-WPS OfficeDokument26 SeitenPHYSICS MOCK EX-WPS OfficeAmunnadi Victor chinazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - MotionDokument140 SeitenChapter 2 - MotionBhargs VenkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-IGCSE Problem Set 1Dokument6 SeitenPre-IGCSE Problem Set 1Anas ElgaudNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 1 KinematicsDokument62 SeitenGeneral Physics 1 KinematicsPortia Egken100% (1)
- Dwnload Full Fundamentals of Physics Extended 10th Edition Halliday Solutions Manual PDFDokument35 SeitenDwnload Full Fundamentals of Physics Extended 10th Edition Halliday Solutions Manual PDFarrangernervousmi03o100% (9)
- Preparatory Guide Physics PDFDokument260 SeitenPreparatory Guide Physics PDFHasan NawazNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH1Dokument34 SeitenCH1none5402Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics: The Study of MotionDokument13 SeitenKinematics: The Study of MotioniskenderbeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces and Motionless on Booklet 2020 AnswersDokument35 SeitenForces and Motionless on Booklet 2020 Answersbininbiju09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Form 3 Physics NotesDokument100 SeitenForm 3 Physics NotesOdero BravinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yr 11 Physics Half Yearly 2011Dokument13 SeitenYr 11 Physics Half Yearly 2011David FengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regent Physics by Abhishek JaguessarDokument343 SeitenRegent Physics by Abhishek Jaguessarreedoye21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics ReviewDokument8 SeitenPhysics ReviewThomas HendersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinema TicsDokument18 SeitenKinema TicsElias MwapeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Midterm 1Dokument7 SeitenPractice Midterm 1Chetanya SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Allowed 3:00 Hrs Artist Hacalu Hundesa Memorial Gimbi Special Secondary School Physics Model Examination For Grade 11 in 2015Dokument14 SeitenTime Allowed 3:00 Hrs Artist Hacalu Hundesa Memorial Gimbi Special Secondary School Physics Model Examination For Grade 11 in 2015Habtamuu TamasgenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roll Number 124Dokument6 SeitenRoll Number 124ahmadrafaqat351Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 8Dokument11 SeitenNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 8shahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igcse 11 Movement&PositionDokument36 SeitenIgcse 11 Movement&PositionHany ElGezawy100% (1)
- Applied Mathematics April-1Dokument60 SeitenApplied Mathematics April-1EVANS KIPNGETICH0% (1)
- Physics Pre-Test ReviewDokument10 SeitenPhysics Pre-Test Reviewcarol janeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centripetal Force and Uniform Circular Motion ProblemsDokument6 SeitenCentripetal Force and Uniform Circular Motion Problemsnanio_7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion Quiz 4 (40 Points) : 500 (KM/H) 800 (KM) 20.0 2.00 (H)Dokument4 SeitenDiscussion Quiz 4 (40 Points) : 500 (KM/H) 800 (KM) 20.0 2.00 (H)Jan Adrian Galang FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - MotionDokument8 SeitenChapter 2 - MotionDani PrimantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics 02.06.17Dokument77 SeitenKinematics 02.06.17Murughesh Murughesan100% (1)
- Vectors vs. Scalars: Scalar QuantitiesDokument45 SeitenVectors vs. Scalars: Scalar Quantitieslala2398Noch keine Bewertungen
- PHY101 Mega File MidtermDokument63 SeitenPHY101 Mega File MidtermHumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen. Physics 1 Unit 1 Lesson 3 Kinematic QuantitiesDokument5 SeitenGen. Physics 1 Unit 1 Lesson 3 Kinematic QuantitiesMary Love JuanicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical: ClassworkDokument6 SeitenPhysical: ClassworkDianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument33 SeitenPhysicsMark Wael Karam GergasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1120 Newtons Laws Solutions - CompressDokument32 SeitenPhysics 1120 Newtons Laws Solutions - CompressTITO FAUZAN ADHIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSEP Solved Paper 2007Dokument10 SeitenNSEP Solved Paper 2007ShubhamKhannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idebe P-3-1Dokument156 SeitenIdebe P-3-1Charles Ghati100% (3)
- Kinematics EquationsDokument33 SeitenKinematics EquationsJoseph ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Test Physics (Questions and Answers) : Calculated by Adding or Subtracting Two Measured ValuesDokument10 SeitenPre-Test Physics (Questions and Answers) : Calculated by Adding or Subtracting Two Measured ValuesDaisy GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion 220729 031748Dokument29 SeitenMotion 220729 031748Imam Akbar RamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion Problems: Read From Lesson 6 of The 1-D Kinematics Chapter at The Physics ClassroomDokument2 SeitenMotion Problems: Read From Lesson 6 of The 1-D Kinematics Chapter at The Physics ClassroomPatrick AlimuinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MotionDokument60 SeitenMotionjoshua cerialesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics VectorsDokument24 SeitenPhysics VectorsNirvaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1.b MOTIONDokument8 Seiten2.1.b MOTIONduru selNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud ChartsDokument17 SeitenCloud ChartsEmilio Elb56% (9)
- PROBLEM SET 1 Work, Power, and EnergyDokument5 SeitenPROBLEM SET 1 Work, Power, and EnergyHan HanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics IAL Assignment 01 SolutionsDokument8 SeitenPhysics IAL Assignment 01 SolutionspastpaperscollectorNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBPS PO Previous Year Question Paper 2016: Quantitative Aptitude (Questions & Solutions)Dokument22 SeitenIBPS PO Previous Year Question Paper 2016: Quantitative Aptitude (Questions & Solutions)Raksha JagatapNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Physics1 Student Workbook SEDokument264 SeitenAP Physics1 Student Workbook SEAbeer ElayyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics HW2Dokument12 SeitenDynamics HW2Ddsaasdh Dhaka100% (1)
- Coding Aptitude (Company)Dokument24 SeitenCoding Aptitude (Company)velmurugan13777100% (1)
- Algebra1 Dist Rate TimeDokument2 SeitenAlgebra1 Dist Rate TimeWongsphat AmnuayphanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics ProblemsDokument2 SeitenKinematics Problemsbu20200% (1)
- Math Word Problems Extension 33 16Dokument2 SeitenMath Word Problems Extension 33 16woof1800Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class-13th DPP: Presented by Kailash SharmaDokument9 SeitenClass-13th DPP: Presented by Kailash SharmaSwatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces and Motion P2 Set-ADokument21 SeitenForces and Motion P2 Set-AAnonymous jwdY0VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Car deceleration and cyclist speed problemDokument4 SeitenCar deceleration and cyclist speed problemJason OrquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT Exam Paper IVDokument20 SeitenCAT Exam Paper IVapi-3708715Noch keine Bewertungen
- Balloon Rocket Lab ReportDokument11 SeitenBalloon Rocket Lab Reportapi-410426030Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sinjoe Tech Awc708c Lite Controller User Manual SJ 7.10L PDFDokument26 SeitenSinjoe Tech Awc708c Lite Controller User Manual SJ 7.10L PDFVelkov OrceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics Speed and Velocity TestDokument5 SeitenKinematics Speed and Velocity TestMahika PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Runner's Speed and Graph AnalysisDokument8 SeitenRunner's Speed and Graph AnalysisMunavi Bin Zaman Mbz100% (1)
- Day 21Dokument44 SeitenDay 21BT21EE017 Gulshan RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed Velocity Accel QuizDokument3 SeitenSpeed Velocity Accel QuizMolly AllenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Average PDFDokument8 SeitenAverage PDFNaresh JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11th Half Book TestDokument6 Seiten11th Half Book TestAhsan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gizmo Sled WarsDokument5 SeitenGizmo Sled WarsNephtalie CharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Participant Test DetailsDokument46 SeitenParticipant Test DetailsIshant RatheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- VEICHI - VC3M Flying Shears Chasing Shears User Manual V1.0.000Dokument28 SeitenVEICHI - VC3M Flying Shears Chasing Shears User Manual V1.0.000Leo MedvederNoch keine Bewertungen
- S2 PHYSICS Unit-3 & 6 Revision NoteDokument16 SeitenS2 PHYSICS Unit-3 & 6 Revision Noterayofthelight777100% (1)
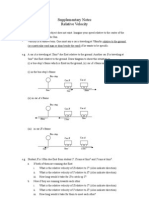
- Chapter 01-3 Relative VelocityDokument2 SeitenChapter 01-3 Relative VelocityalvinhimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Display "Jack Shepard" Display "123 Lost Lane" Display "Boston, MA 99999" Display "704-555-1212" Display "Computer Science"Dokument7 SeitenDisplay "Jack Shepard" Display "123 Lost Lane" Display "Boston, MA 99999" Display "704-555-1212" Display "Computer Science"Angel Perez HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AptiDokument50 SeitenAptilokeshNoch keine Bewertungen