Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Features and Structure of NSK Ball Screws
Hochgeladen von
Thanh Dat TranOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Features and Structure of NSK Ball Screws
Hochgeladen von
Thanh Dat TranCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
B-1 Selection Guide to NSK Ball Screw
B-1-1 Features of NSK Ball Screws
1 Quick delivery
Standard ball screws are in stock for short lead time. Precision ball screws with finished shaft end PSS Type, MA Type, FA Type, SA Type, KA Type Precision ball screws with blank shaft end MS Type, FS Type, SS Type Ball screws for transfer equipment are also available in stock. Finished shaft end VFA Type, RMA Type Blank shaft end RMS Type, R Series
6 Smooth movement assures high efficiency
NSK uses the Gothic arc design for the ball grooves. This design prevents the balls from slightly wedding into the groove of the ball nut and screw shaft and causing minute vibration. This phenomenon is common with the circular-arc design used by other manufacturers. The Gothic arc, along with the low friction inherent in a ball screw, results in a smooth and highly efficient conversion of motion as shown in Fig. 1.2.
7 Optimal units available
Utilizing bearing technology, NSK produces high quality support units ( for light load type to be used for small equipment and heavy load type to be used for machine tools ) which are exclusive for ball screws. These units are standardized and always in stock. NSK also offers quality-assured accessories such as lock nuts to tighten bearings, travel stoppers to prevent overrun, and sealing units to cool hollow shaft ball screws.
3 Unparalleled accuracy
NSK utilizes its unique grinding technique and measuring equipment for topnotch precision.
4 Superb durability
NSK uses thoroughly purified alloy steel for superb durability.
5 No backlash, and unparalleled rigidity
NSK ball screws use Gothic arch grooves as shown in Fig. 1.1. The Gothic arch has no clearance between the balls and grooves with applying preload, and no backlash can be obtained. As providing controlled rigidity is easy, appropriate rigidity is obtained. As the Gothic arch also minimizes the clearance between the balls and the grooves, the backlash is minimized without applying preload.
100 90 80 70 Efficiency 1 (%) 60 50 40 30 20 10
2 Competitive prices
NSK reduces cost by well-planned mass production of standardized items. We rank the best in the world production of ordered items. We are able to offer our products at competitive prices by producing similar items in the same production group.
03 0.0 = 5 .00 =0
100
1 =0.0
Back drive efficiency 2 (%)
90 80 70 60 50 40
0.0 =
03
Ball screw
5 .00 =0
B 2
Ball screw
=0. 01
0.1
Acme screw
20 10
Acme screw
Fig. 1.1 Ball groove profile of NSK ball screw
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Lead angle (degree) Lead angle (degree) Back drive efficiency Efficiency of normal operation (Converting rotary motion to linear motion) (Converting linear motion to rotary motion) : Friction coefficient : Friction coefficient
Fig. 1.2 Mechanical efficiency of ball screws
B1
0.1
0.2
30
B2
B-1-2 Structure of a Ball Screw
Balls are placed between the screw shaft and nut, and roll. This system is called a "ball screw." To keep the balls recirculating continually, this system requires a screw shaft, a nut, balls, and recirculation components as basic items. A ball screw has the following functions. 1 Converting motion: C h a n g i n g r o t a r y m o t i o n to linear motion (normal operation); Changing linear motion to rotary motion efficiently (back-drive operation). 2 Increasing power: A small torque is converted to a large thrust force. 3 Positioning: Sets accurate position in linear motion.
B-1-2.1 Ball Recirculation System
A ball recirculation system is categorically most important, as well as the preload system, to classify the structure of ball screw. As shown in Table 2.1, four types of ball recirculation system are used for NSK ball screw.
Table 2.1 Ball screw recirculation system
End deflector type
Ball nut End deflector Ball recirculation hole
Ball return tube type
Deflector type
End cap type
Ball recirculation hole Ball nut End cap End cap
Return tube
Screw shaft
Ball nut Deflector
B 4
Screw shaft
Screw shaft
Screw shaft
[Structure] Balls are smoothly picked up in tangential direction at the end of nut, and recirculated via hole in the nut. If the ball is picked up at the middle of the nut, it is called middle deflector type. [Features] Small nut O.D., allows compact design. Low noise, High speed.
[Structure] Balls are recalculated through pipe of optimized size, bridging the start and end of recirculation.
[Structure] Balls are recirculated by horseshoe shaped deflector bridging the pitch groove. [Features]
[Structure] Balls are picked up by cap placed at both ends of the nut, and recirculated via hole in the nut. [Features] Suitable for large lead ball screws. Not universal due to complex recirculation structure.
[Features] Adapt to various specifications. (screw shaft diameter, lead)
Suitable for fine lead ball screws. Small nut O.D., allows compact design.
B3
B4
B-1-2.2 Preload system
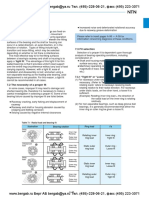
There are four systems to apply preload to NSK ball screws depending on the application. Table 2.2 Preload system for ball screw
Preload system Double nut preload (D Preload) Offset preload (Z Preload) Oversize ball preload (P Preload)
Ball nut
Spring preloaded double nut (J Preload)
Ball nut A Spring Ball nut B
Ball nut A Spacer Ball nut B
Ball nut
Main external load
Tension
Tension Spring
Tension
Structure
Spacer
Tension
Lead Lead+ Ball nut Lead
Lead Ball nut
Lead
Ball nut A
Ball nut B
Ball nut A
Ball nut B
B 6
Screw shaft
Screw shaft
Screw shaft
Ball nut Spacer ball
Screw shaft
Screw shaft
Load ball
Uses two nuts, and inserts a spacer between them to apply preload. In general, a spacer is thicker (by the Description deformation equivalent to the preload) than the actual space between two nuts. On the contrary, a thin spacer is inserted in some cases. Nut length
Torque characteristics
To apply preload, the lead near the center of the nut is enlarged by the volume equivalent to preload (). Uses a single nut to create a preload similar to D preload. Not using spacer enables compact nut design. Medium Fair Excellent
Balls slightly larger than the space of the ball groove (over-size balls) are inserted to apply preload by balls' four-point contact. Provide better torque characteristics in the low torque range.
A spring is used as a spacer of D Preload. Must be used with discretion in its varied rigidity by load direction.
Long Fair Excellent
Short Fair Fair
Long Excellent Poor
Rigidity
B5
B6
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Bearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsVon EverandBearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Ball Screw TutorialDokument73 SeitenBall Screw TutorialIvan Aryo ZaoldyeckNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSK - Drawn Cup Needle Roller ClutchesDokument11 SeitenNSK - Drawn Cup Needle Roller ClutchesWillian MoreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSK HB Ball ScrewsDokument289 SeitenNSK HB Ball ScrewsRani TaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Band Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsVon EverandBand Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Design of Mechanical Systems: 5th Term Electromechanical Eng. Program (Fall 2017) Lecture Four Ball ScrewsDokument49 SeitenDesign of Mechanical Systems: 5th Term Electromechanical Eng. Program (Fall 2017) Lecture Four Ball ScrewsMohamed MoatazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metalwork and Machining Hints and Tips for Home Machinists: 101 Plans and DrawingsVon EverandMetalwork and Machining Hints and Tips for Home Machinists: 101 Plans and DrawingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- BearingsDokument4 SeitenBearingsmimNoch keine Bewertungen
- En A15 174Dokument76 SeitenEn A15 174Ilija BozovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precision Ball Screw: Models Bif, Dik, BNFN, DKN, BLW, BNF, DK, MDK, BLK/WGF and BNTDokument44 SeitenPrecision Ball Screw: Models Bif, Dik, BNFN, DKN, BLW, BNF, DK, MDK, BLK/WGF and BNTclaudiu feierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Cross Reference PDFDokument21 SeitenBearing Cross Reference PDFGia Minh Tieu Tu100% (1)
- Bearing Number Code ReferenceDokument6 SeitenBearing Number Code ReferenceIbraheem KhressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Axial Needle Cage Assemblies: Double Row Self-Aligning Ball BearingsDokument6 SeitenAxial Needle Cage Assemblies: Double Row Self-Aligning Ball BearingsФилип ЃоргиевскиNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prefixes Suffixes SKFDokument9 SeitenPrefixes Suffixes SKFPatrick Baridon100% (1)
- Ball BearingsDokument6 SeitenBall Bearingsbranik100% (1)
- Bang Catalog Bac Dan NSKDokument0 SeitenBang Catalog Bac Dan NSKsariobaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rolling Bearings Handbook, by NTN Corporation JapanDokument84 SeitenRolling Bearings Handbook, by NTN Corporation JapanTheRFCBlueBearNoch keine Bewertungen
- SKF Cylindircal Roller BearingsDokument36 SeitenSKF Cylindircal Roller Bearingskvramanan_1100% (1)
- NTN Roller Bearing HandbookDokument84 SeitenNTN Roller Bearing HandbookKok Toong FattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uft 100 eDokument47 SeitenUft 100 ea04205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument12 SeitenChapter 5Fadhiran Yahya0% (1)
- INA Ball ScrewsDokument16 SeitenINA Ball ScrewsRuben PauwelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Rolling Contact BearingsDokument86 Seiten3 Rolling Contact BearingsMehmetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Niraj CRBDokument98 SeitenNiraj CRBnirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Motion Technology-Screw DriveDokument50 SeitenLinear Motion Technology-Screw DriveHossein GhazinezhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing With Rolling Bearings:part1Dokument52 SeitenDesigning With Rolling Bearings:part1Vanessa GomesNoch keine Bewertungen
- BearingsDokument30 SeitenBearingsIhsan AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing FitsDokument9 SeitenBearing FitsPPMNoch keine Bewertungen
- 309-8e SKR PDFDokument56 Seiten309-8e SKR PDFabs0001100% (1)
- CombinepdfDokument400 SeitenCombinepdfStar Moonlight21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo SKFDokument165 SeitenCatalogo SKFanon_769144622Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ball Bearing Cross ReferencesDokument5 SeitenBall Bearing Cross Referencesryasa1100% (1)
- Tapered+Roller+Bearing Detail SuffixDokument20 SeitenTapered+Roller+Bearing Detail SuffixDeni SuhayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing FitsDokument9 SeitenBearing Fitsm2110Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings For The Backing Shafts of Cluster MillsDokument10 SeitenCylindrical Roller Bearings For The Backing Shafts of Cluster Millsrochim_putech_126885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marwan Hesham 19104305 Ball Screw ReportDokument10 SeitenMarwan Hesham 19104305 Ball Screw ReportMarwan HeshamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be RingsDokument10 SeitenBe RingsdreamroseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thrust BearingsDokument9 SeitenThrust BearingsRakan Al-NaamnehNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Casquillos de Agujas Sin Fondo Clutch SimilarDokument98 Seiten06 Casquillos de Agujas Sin Fondo Clutch SimilarSara Sarmiento EcheverryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Cross Reference - Gregory BenderDokument16 SeitenBearing Cross Reference - Gregory BenderJenrry GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super Smart Ball Bushing Bearings BrenDokument8 SeitenSuper Smart Ball Bushing Bearings BrenAchim OvidiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suffix of BearingDokument14 SeitenSuffix of BearingPirnandoTariganNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNC PDFDokument455 SeitenCNC PDFbhuvneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- BoosDokument20 SeitenBooshollabackcockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reliable Bearing Solutions For Corrosive Environments: Stainless Steel Deep Groove Ball BearingsDokument8 SeitenReliable Bearing Solutions For Corrosive Environments: Stainless Steel Deep Groove Ball BearingsРуслан ПерцевNoch keine Bewertungen
- KWGDL KWGDLS AgdlDokument8 SeitenKWGDL KWGDLS Agdlalin.butunoi865Noch keine Bewertungen
- NSK CAT E1102m A7-141Dokument0 SeitenNSK CAT E1102m A7-141Kishor Kumar VishwakarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic of BearingDokument16 SeitenBasic of BearingSNEHAL PATEL100% (1)
- SKF Roller Bearing Handbook PDFDokument42 SeitenSKF Roller Bearing Handbook PDFsureshnfclNoch keine Bewertungen
- NBC (NEI) : National Engineering Industries LimitedDokument9 SeitenNBC (NEI) : National Engineering Industries LimitedAnupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Pipe Bending MachineDokument27 SeitenFinal Pipe Bending MachineVitthal GawhaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- SKF Thrust Ball BearingDokument28 SeitenSKF Thrust Ball Bearingsalmonsilalahi100% (1)
- Bearings Engle ZaDokument22 SeitenBearings Engle ZaAndreea Iuliana DrăgușNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4rCRB Mounting and Maintenance InstructionsDokument21 Seiten4rCRB Mounting and Maintenance InstructionsNishant JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Main Prefix and Suffix System PDFDokument9 SeitenBearing Main Prefix and Suffix System PDFNandu ThulasidharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bower 25 106Dokument82 SeitenBower 25 106victoryanezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SKF Cylindircal Roller Bearings PDFDokument36 SeitenSKF Cylindircal Roller Bearings PDFurp30234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Suruburi Cu Bile Si Role SKFDokument72 SeitenSuruburi Cu Bile Si Role SKF周小安Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modeling of Grain-Water Suspensions in TubeDokument15 SeitenComputational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modeling of Grain-Water Suspensions in TubebhuniakanishkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deformation ProcessDokument25 SeitenDeformation Processutpal singhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Injection Mold Maintenance Program LinkedInDokument11 SeitenPlastic Injection Mold Maintenance Program LinkedInMBRNoch keine Bewertungen
- CatalogoDokument18 SeitenCatalogocarlosorizabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTA-59 Procedures and Relevant Information For RTA Engines To Comply With The Annex VI NOx LimitDokument7 SeitenRTA-59 Procedures and Relevant Information For RTA Engines To Comply With The Annex VI NOx LimitCatalin CataNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC331 - Revision Gear FinalDokument9 SeitenMEC331 - Revision Gear FinalDiana PinkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torque Values RTJ (B16.5)Dokument3 SeitenTorque Values RTJ (B16.5)Dave Donohue100% (9)
- ROHR2fesu FeaturelistDokument20 SeitenROHR2fesu FeaturelistJohan ConradieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cavallini 2013Dokument14 SeitenCavallini 2013Satheesh Kumar SNoch keine Bewertungen
- TANCO 1400EH-2014-EnglishDokument116 SeitenTANCO 1400EH-2014-EnglishErwin GerdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil and Gas ProcessingDokument3 SeitenOil and Gas ProcessingRaghav AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Model of Systems:: Rotational Mechanical System Transfer FunctionDokument11 SeitenMathematical Model of Systems:: Rotational Mechanical System Transfer Functionchardo santosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tech Spec For Centrifugal PumpDokument5 SeitenTech Spec For Centrifugal PumpRoby Mirza100% (1)
- S.P.Catalog TNT600I600GS-3 2020-Ver 200908Dokument97 SeitenS.P.Catalog TNT600I600GS-3 2020-Ver 200908Rjay HayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motorcycle CatalogDokument24 SeitenMotorcycle CatalogCarsten JakobsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSS Hardware SectionDokument72 SeitenOSS Hardware SectionglobalindosparepartsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retentor Din 3760Dokument13 SeitenRetentor Din 3760Marcelo Godinho BatistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201104-Hopper Inserts For Improved Solids FlowDokument1 SeiteFacts at Your Fingertips-201104-Hopper Inserts For Improved Solids Flowonizuka-t2263Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sandvik DD321Dokument4 SeitenSandvik DD321Anonymous Dm7iMmt0% (2)
- EN 288-3xDokument38 SeitenEN 288-3xSyah Reza Maulana0% (1)
- Fusheng AD Series Pumps Parts CatalogueDokument48 SeitenFusheng AD Series Pumps Parts CatalogueTrunghieutc Hieu50% (2)
- Bomba A2fo Bosch RexrothDokument3 SeitenBomba A2fo Bosch RexrothHIDRAFLUIDNoch keine Bewertungen
- D4B8046FF18-Suspension Wheels SteeringDokument469 SeitenD4B8046FF18-Suspension Wheels SteeringDaniel CharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop 2 DaumDokument25 SeitenWorkshop 2 DaumAqsha QNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Flow Through Randomly Packed Columns and Fluidized BedsDokument6 SeitenFluid Flow Through Randomly Packed Columns and Fluidized BedsalexramquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geared Motor: Product ManualDokument178 SeitenGeared Motor: Product Manualsanjibkrjana100% (1)
- 29 V3800dit 26Dokument2 Seiten29 V3800dit 26Hector Dongo ArrayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Fundamentals of Creep in MaterialsDokument6 Seiten1-Fundamentals of Creep in MaterialsLucianoBorasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronic Converters For Ship PropulsionDokument6 SeitenPower Electronic Converters For Ship Propulsionq_man2512Noch keine Bewertungen
- AWQ5522EGEDokument2 SeitenAWQ5522EGEpant.vk8514Noch keine Bewertungen