Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Biology
Hochgeladen von
Piriya DharshiniOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Biology
Hochgeladen von
Piriya DharshiniCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 1 Biology : The study of life and living things and their interactions with one another and
the natural enviroment. Chapter 2 Both plant and animal cells have : nucleus, cytoplasm, plasma membrane Plasma Membrane - Seperates content of cell from external enviroment - Regulates the movement of substances leaving and entering cell - Exchange of nutrients, waste products, respiratory gases between cell and its enviroment Cytoplasm - Acts as a medium where bio-chemical reactions and living processes occur - Provides organelles with substances obtained from external enviroment Cell Wall - Maintains shape of plant cell - Provides mechnical strength and support to plant cell - Protects plant cell from bursting due to excess of water into cell Vacoules - Stores chemicals (organic acids, sugars, amino acids, mineral salts, oxygen, carbon dioxide, waste minerals, pigments, metabolic by products) - Contributes to plant elongation by absorbing water and causing plant to expand Nucleus - Controls all cellular activities - Contains DNA Mitochondria - Sites of cellular respiration (respiratory enzymes) - Releases energy in the form of ATP Ribosomes - Sites of protein synthesis Endoplasmic Reticulum - Rough ER : Transports protein made by ribosomes - Smooth ER : Synthesises lipids and carries out detoxification Golgi Apparatus - Processing, packaging and transport centre of carbohydrates, proteins and glyco-proteins
Lysosomes - Digestive compartment in a cell - Hydrolytic enzymes digest and break down complex organic molecules Centrioles - Form spindle fibres during cell division in animal cell Chloroplast - Contains green pigment, chlorophyll - Chlorophyll : Traps sunlight energy , converts light energy into chemical energy during photosynthesis - Green pigment : Gives plant their green colour ANIMAL CELLS AND PLANT CELLS Similarities - Both have nucleus, cytoplasm, plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, ER, ribosomes Differences Structure/ Characteristic Shape Cell Walls Chloroplasts Vacoules Food Storage (Carbohydrate in the form of) Centrioles Animal Cells No No No No, if present(small and numerous) Glycogen Yes Plant Cells Yes, fixed shape Yes Yes Yes Starch No
The Density of Organelles in Specific Cells Mitochondria (Energy in the form of ATP generated during celular respiration, instant source of energy to cell) Sperm Cell : Requires energy to propel through uterus towards the Fallopian tubes Muscle Cell : Contracts and relax to enable movement or flight Meristematic Cells : For cell division to produce new cells Chloroplasts Palisade Mesophyll Cell : Absorbs sunlight during photosynthesis Rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus Pancreatic Cells : Synthesise and secrete enzymes and hormones Salivary Gland Cells : Synthesise and secrete enzyme Intestinal and Stomach Epithelial : Secretes digestive enzymes
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Interstitial cells in testes and adrenal glands : Synthesise and secretes steroids and hormones Liver Cells : Carbohydrate metabolism and detoxification Golgi apparatus Goblet Cells : Secrete mucus Root cap Cells : Secrete slimy lubricant helps in the movement of root between soil particles Unicellular organism Single cell Feed, respire, excrete, move Responds to stimuli Reproduces and grows Amoeba s.p & Paramecium s.p Amoeba (key words) LOCOMOTION Pseudopodia / false feet Cytoplasmic projection (extending pseupodia) Cytoplasm into pseudopodia Locomotion : Ameboid Movement FEEDING Microscopic organisms (bacteria) Engulfing food Phagocytosis o Approach food o 2 Pseudopodia extends out and encloses food o Food particles packaged in food vacoule, fuses with lysosome (contains lysozyme) o Food particles digested by lysozyme o Nutrients diffuse into cytoplasm o Undigested material left behind RESPIRATION Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide through plasma membrane by simple diffusion
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Context: Lesson Author Date of DemonstrationDokument4 SeitenContext: Lesson Author Date of DemonstrationAR ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Boden 2015 Mass Media Playground of StereotypingDokument16 SeitenBoden 2015 Mass Media Playground of StereotypingMiguel CuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- 7 - LESSON PLAN CULTURAL HERITAGE AND CULTURAL DIVERSITY - Lesson PlanDokument4 Seiten7 - LESSON PLAN CULTURAL HERITAGE AND CULTURAL DIVERSITY - Lesson PlanRute SobralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Aìgas of Bhakti. at The End of The Last Chapter Uddhava Inquired AboutDokument28 SeitenAìgas of Bhakti. at The End of The Last Chapter Uddhava Inquired AboutDāmodar DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Determining Rounding Common CoreDokument2 SeitenDetermining Rounding Common Coreapi-3662903730% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- English Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenEnglish Lesson PlanJeremias MartirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- AS 1 Pretest TOS S.Y. 2018-2019Dokument2 SeitenAS 1 Pretest TOS S.Y. 2018-2019Whilmark Tican MucaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Mitochondrial Mechanisms of PhotobiomodulationDokument4 SeitenMitochondrial Mechanisms of PhotobiomodulationGabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Match The Animal With Its NameDokument4 SeitenMatch The Animal With Its Namekawa kawka kawuniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Improving Self-Esteem - 08 - Developing Balanced Core BeliefsDokument12 SeitenImproving Self-Esteem - 08 - Developing Balanced Core BeliefsJag KaleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hard Soft Acid Base TheoryDokument41 SeitenHard Soft Acid Base TheorythinhbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Oracle QuestDokument521 SeitenOracle Questprasanna ghareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- TOEIC® Practice OnlineDokument8 SeitenTOEIC® Practice OnlineCarlos Luis GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Plastique: Art and EducationDokument7 SeitenPlastique: Art and EducationJackStevensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ministry of Truth Big Brother Watch 290123Dokument106 SeitenMinistry of Truth Big Brother Watch 290123Valentin ChirilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- FreeMarkets: Procurement & Outsourcing StrategiesDokument44 SeitenFreeMarkets: Procurement & Outsourcing StrategiesFarhaad MohsinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To E-Business SystemsDokument19 SeitenIntroduction To E-Business SystemsArtur97% (79)
- Electronic Load FundamentalsDokument16 SeitenElectronic Load FundamentalsMiguel PenarandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Who, Summary NotesDokument12 SeitenWho, Summary NotesIvan Lohr100% (2)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Ccounting Basics and Interview Questions AnswersDokument18 SeitenCcounting Basics and Interview Questions AnswersAamir100% (1)
- Arif Dirlik - The Origins of Chinese Communism-Oxford University Press, USA (1989)Dokument335 SeitenArif Dirlik - The Origins of Chinese Communism-Oxford University Press, USA (1989)Denisa FeisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Fascinating Numbers: Some Numbers of 3 Digits or More Exhibit A Very Interesting PropertyDokument2 SeitenFascinating Numbers: Some Numbers of 3 Digits or More Exhibit A Very Interesting PropertyAnonymous JGW0KRl6Noch keine Bewertungen
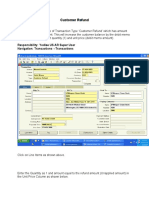
- Customer Refund: Responsibility: Yodlee US AR Super User Navigation: Transactions TransactionsDokument12 SeitenCustomer Refund: Responsibility: Yodlee US AR Super User Navigation: Transactions TransactionsAziz KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Villegas vs. Subido - Case DigestDokument5 SeitenVillegas vs. Subido - Case DigestLouvanne Jessa Orzales BesingaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rediscovering The True Self Through TheDokument20 SeitenRediscovering The True Self Through TheManuel Ortiz100% (1)
- Csm6 Ext1y11 BookDokument955 SeitenCsm6 Ext1y11 BookJesse Davis100% (12)
- Summarized ACLS ScriptDokument7 SeitenSummarized ACLS Scriptnc.angel.niceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bossa Nova Book PDFDokument5 SeitenBossa Nova Book PDFschmimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- (Kre?Imir Petkovi?) Discourses On Violence andDokument610 Seiten(Kre?Imir Petkovi?) Discourses On Violence andGelazul100% (1)
- Rectification or Correction of Sale DeedDokument4 SeitenRectification or Correction of Sale Deedsumanth_0678Noch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)