Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pile Foundation
Hochgeladen von
Engr Darlington ChukwurahOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pile Foundation
Hochgeladen von
Engr Darlington ChukwurahCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bored piles is a type of foundation structure made of reinforced concrete.
It is used to carry heavy loads by transmitting the load to a stable soil strata. As the name suggest, bored piles is constructed by first drilling a hole in the ground until a competent load bearing layer is reached. Once this achieved, a reinforcement steel cage is lowered into the drilled hole and the hole is filled with concrete. Thus due to the method of construction of bored piles, it is also known as cast in place piles. Bored piles varies in diameter and depth. The dimension can varies from 450mm to 2000mm. The diameter or depth of the bored piles are determined by the designers who will size the bored piles according to the load requirement and as well as the soil condition of the site. Bored piles is widely used and they can be constructed in most soil condition and over water. Due to their flexibility they are widely used in deep foundation for high rise buildings, jetties, bridge foundation and can even be used as vertical retaining structures like a retaining wall or sheet piles wall. In this case the bored piles is known as contiguous bored pile wall. Bored piles is designed either as a point bearing piles or friction piles. If competent load bearing layer like bed rock is present, then the bored piles will be designed as an end-bearing pile. This means that the load carrying capacity of the piles is mainly derived from the bearing capacity of the rock layer at the toe of the pile.
On the other hand bored piles which are designed as friction piles the load carrying capacity of the piles is derived mainly from the skin friction between the pile surface and the surrounding soil. The designers may some time design bored piles as a combination of skin friction and end-bearing piles. Bored piles can be constructed as a single pile or a in a pile groups. The can also be inclined to a certain angle. Angle bored piles also known as raked piles are found in structures that requires resistance to horizontal load like in a retaining wall or bridge and piers foundation. However the construction of angle bored piles poses some construction challenges. When bored piles are constructed close to one another or overlapping slightly, this is known as contiguous bored piles wall or secant piles wall. Below are some simplify diagrams of bored piles uses:-
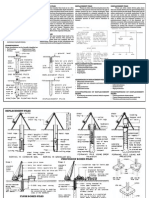
Single Bored Piles
Group of Bored Piles
Inclined or Raked Piles below Retaining Wall
Contiguous Bored Piles Wall
Concreting of bored piles marks the final stage of of the construction. Once the required depth or design depth is drilled the drilling stops. The drilling auger is then changed into a cleaning bucket to clean up any loose debris left at the bottom of the hole. This process will take place for a few times until the bottom is reasonable cleaned. Cleaning bucket can be used in both dry holes and holes under drilling fluid. In some instances, an inspection of the base will be required in large diameter dry holes. This will be done manually by lowering a competent inspector down the hole. This process can be dangerous and it would be better to send cameras down. In fluid filled hole, inspection will not be possible, but the drilling depth will be continued to be monitored for any soil collapse.
Lowering of Reinforcement cage When all is fine, the reinforcement cage is lowered into the drilled hole. Sometimes the cage does not go down all the way thus it will need to be suspended at the top. There are designs where the cage goes all the way, ie as in tension piles, thus there is a need to provide a clearance between the bottom of the cage and the bottom of the hole. Round spacers are used to spaced out the cage from the soil surface. When the reinforcement cage is in, the next phase is to lowered in the tremie pipe. In a wet hole the tremie pipe is installed all the way down. However if it is a dry hole, the tremie pipe will be install 1/3 to 1/2 of the drilled depth. A tremie pipe is used to allow concrete ( tremie mix) to be poured right to the bottom of the bored piles without segregation. This is it when the cement and stones separated during a free falling situation. By this time the concrete truck will have arrived at the site , once the cubes taken and slump test done and passed, the truck will then proceed to the respective bored piles and poured out the concrete. The concreting process duration is dependent on the size of the piles. After each pour, the depth of the concrete rise is determined by lowering a measuring tape. Every so and then, small sections of the tremie pipe is removed during the concreting process.
During concreting, the drilling fluid in the hole is also displaced, this fluid is pumped back to the storage silos for reuse or to be de-sanded when it becomes to contaminated with drilling debris of fine sand, silt, etc. Once the process of concreting is completed, any casing used is taken out by using a vibratory hammer and the area cordoned off to indicate a freshly concreted pile. The tremie pipes are cleaned and ready for another concreting session. During all this, a service crane is used with an excavator standing by for general light lifting.
Dry hole concreting of Bored Pile
Wet hole concreting of bored pile As can be noted from the above 2 photos, once can tell what types of concreting is being done. In the wet hole situation, drilling fluid is being displaced why none is observed in the dry hole situation. A sump pump is always used in wet hole situation as can be seen there is a
pump head next to the bored pile casing in the wet hole concreting. Judging from the picture, well a dry hole working environment is preferred as the work site will not be turning up messy.
Round Spacers used along the reinforcement cage And this is what I meant about using round plastic spacers. These are hardy, consistent and easily installed. It is sage too if anyone of the space is dislodged. Using this is preferred to own fabrications of concrete spacer cast on site.
Bored piles as mentioned in this post What is Bored Piles? are constructed following the sequence below. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The first step is to drill a hole of the require diameter into the ground. When the design depth or foundation bearing layer is reached, drilling stopped. The hole is then cleaned. Steel reinforcement cage is lowered into the hole. Concrete is then poured into the hole until the designed cut-off level of the pile. After Step5, the construction of bored pile is deem completed.
Thus it can be seen that bored piles are constructed by first drilling into ground. Drilling is one of the most important step in bored pile construction. Only successful drilling can the next construction step be carried out. Thus drilling requires experience and the use of the right tools and equipment. In this post we will take a look at the types of drilling machines used.
Bored piles can be drilled by using an auger ( see attached picture of an auger) that is powered mechanically. There will be an auger attached to a the tip of a telescopic Kellybar. Telescopic means the Kellybar is extensible, there by enabling drilling to greater depths. Drilling rigs can be crane mounted or as a single unit known as rotary drilling rig. Both of which is discussed in greater details below. Crane Mounted Drilling Rig The drilling rig is a power unit that rotates the Kellybar which in turn rotates the auger. The power unit is normally diesel powered. The Kellybar is slotted through the power unit at the front end known as the Table. Horizontal rotation of the diesel engine is converted to vertical rotation which rotates the Kellybar. There is also a pair hydraulic arms at the table. These arms can clamped to the Kellybar and are use to raise or lower the the it slowly over a short lenght. Rotation can be either anticlockwise or clockwise. The whole power unit, Kellybar and auger assembly is then mounted onto a base crane. Drilling starts by pressing and rotating the auger at the same time. Once the initial hole is formed and depending on the soil material, the weight of the Kellybar pushes the drilling deeper. The Kellybar is raised and lowered into the hole by a separate lifting cable of the base crane. This enables the Kellybar and auger to be lifted up quickly to the surface to dispose of the drilled material and later lowered back again to the hole to continue drilling. This processes is repeated until the desired depth is reached. Below is a picture of a crane mounted drilling rig.
Name of Parts 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. KellyBar Auger Diesel Powered Drilling Rig Base Crane Table Hydraulic arms
The drilling rig can also be mounted onto a heavy truck like what is shown in the picture below.
A Truck Mounted Drilling Rig Rotary Drilling Rigs
A Rotary Drilling Rig A compact design in which the drilling rig is permanently mounted onto a crawler unit. The drilling rig is hydraulic powered giving it a very powerful drilling capability. The drilling process is the same as what is mentioned above. However rotary drilling unit is easy to deploy. There is no setting up required compared to crane mounted drilling rig. A crane mounted rig requires assembly on site assembly and requires the help of another crane to mount and set up. As for for rotary drilling rigs, there is no such requirement. Once mobilized to site it is just a matter of raising up the leader , attached the auger and drilling can start. On the left is an example of a rotary drilling rig. Drilling By Using Continuous Flight Auger
Continuous Flight Auger Rig Drilling of bored piles can also be carried out by using continuous flight auger (CFA). CFA is used when bored piles depths are fixed and the diameter not larger than 1500mm. The construction of bored piles using CFA is different from the auger and Kellybar drilling. The major difference is this, when the bored pile desired depth is reached, the hole can be filled by injecting concrete down the hollow stem of the CFA. In this way the bored pile is concreted as the auger is slowly raised. After completing the concreting and the auger had been removed, a reinforcing cage is pushed down the shaft while the concrete has not set. It is not uncommon to push down cage length of 12m. Thus it can be seen that the final steps of bored piles construction by CFA is different from the Kellybar and auger process. However if the drilled hole depth is shallow and the ground stable ( the drilled hole does not collapse), the CFA can be completely removed. In this case, the concreting can be carried out like those of the Kellybar and auger method. On the left is a picture of a Continuous Flight Auger Rig. Modern drilling rigs can drill bored piles of diameters ranging from 600mm to 4000mm. Due to the convenience of the rotary drilling rigs, they have become more common nowadays as compared to the crane mounted drilling rigs. Rotary drilling rigs are self-mounting and also easily transportable. On the whole this capability which reduces cost of mobilization. In the next post we will look at the types of drilling tools used. <<< - Note: Pictures source, www.soilmec.co.uk and www.soilmec.it - >>>
In the bored piles construction we had looked at the method how bored piles are generally drilled. Continuing on the subject of drilling, this post we will look at the type of drilling tools used. There are a number of ways to drill or to form the required diameter and depth of the bored piles. In this post we will look at the rotary method. The rotary method is perhaps the most common method used. The circular action produced by the engine is used to remove or excavate away material from the ground to form the bored pile of the right diameter and depth. In normal dry ground situation, the most common tool used with the rotary method is the auger. There can be two types of auger, the short auger or the continuous flight auger.
Bored Pile Auger Both tools will be rotated into the ground and by the rotary action , soil is excavated in the process. This is repeated until the required design depth is achieved. The process of auguring can only be carry out when the drilled bore pile hole remains dry. That is the bored pile hole remains dry and stable ie without collapsing. Should the hole be unstable, it can be stabilized using casings.
Continuous Flight Auger On the other hand, if the ground water table is high and the drilled whole is wet or filled with water, casing can still be used with the hope that it sealed of the hole thus allowing dry condition drilling. If this is not possible than drilling had to be carried out in submerged condition ie under water. In this case the auger will need to be changed to a drilling or boring bucket.
Drilling or boring bucket Again in drilling under water, the bored hole has to be stabilize from collapsing during and after drilling. Most commonly casing is used and if this failed, than there is the option of using bentonite slurry or polymer fluids to stabilized the hole. Drilling will still make use of drilling bucket.
Cleaning Bucket When the founding depth is reached, the base of the bored pile will cleaned using a cleaning bucket before concreting. Thus far the drilling discussed in this blog is for soft to hard cohesive soil. However if boulder or drilling in rocks is required, than the drilling tools will be different.
Once hard rock formations are encountered or there is a need to socket the bored piles into rock foundations due to design requirement, than the drilling will need to use tools geared for rock drilling.
Rock Auger With Bullet Teeths As rocks have different hardness, thus drilling tools can be adapted to drill in different degree of hardness. As an example, the versatile auger can be modified and installed with bullet teeth with replaceable bullet style carbide teeth turning it into a rock auger.
Bullet Teeth with Holder Rock augers are used under dry drilling conditions when the drilled bored pile hole is dry. However there are times when the drilling is under fluid used to stabilization fluid. In this case, the drilling in rock will make use of rock boring bucket. The purpose of using bucket is to allow the drilled materials to be collected into the bucket and disposed off.
Rock Boring Bucket
When the drilling hits very hard rocks like granites, than the drilling tools are changed. There are 3 ways to drill in very hard rocks. In dry or semi-dry conditions the drilling can make use of down the hole hammers. DTHH comes in various sizes from 100mm to 600mm. For large diameter piles ie 1m and above, DTHH can be maneuver around to achieve the required diameter.
Chisel for Rocks When DTHH cant be used, then the piling contractor can have the options of using chisels or coring bucket. Chisels are large heavy rectangular object with a sharpened. The chisel is lifted above the rock level to a certain height and allows it to free fall thus slowly chiseling or pounding away at the rock level. Effectiveness of this method depends on the mass, cutting tip of the chisel. The rest is the job of gravity.
Coring Bucket The next tool is coring bucket.This tool has bullet teeth with replaceable bullet style carbide teeth arranged in a circular pattern in various diameters. Through the weight and circular action of the boring rig, the coring bucket slowly cored into the rocks. The working principle is like the cement coring. However the coring process may fractured the rock into pieces, these loose pieces are picked up using cleaning or boring bucket. As coring is under the stabilization fluid, the fluid acts as a coolant and lubricant during the coring process.
Coring Barell The availability of tools depends on the piling or foundation contractors. An experience and established foundation contractors will have all the above tools and more at their disposal to counter any types of geological conditions.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 2) Pile Execution MethodDokument34 Seiten2) Pile Execution Methodmehtabhumikaa50% (2)
- Chapter 2a) Drilled Shaft FoundationsDokument15 SeitenChapter 2a) Drilled Shaft FoundationsAngelaDeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Castinsituplace154 150108061806 Conversion Gate01Dokument6 SeitenCastinsituplace154 150108061806 Conversion Gate01Anjumara HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Piles and GroupsDokument36 SeitenBearing Piles and Groupsjologscresencia100% (1)
- Bored Piles - Production MethodDokument10 SeitenBored Piles - Production MethodroldskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sub Con Unit 1 NotesDokument16 SeitenSub Con Unit 1 NotesDarshan KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cassion FoundationsDokument32 SeitenCassion FoundationsAayushi PawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile Foundations Lecture Note 1 PDFDokument99 SeitenPile Foundations Lecture Note 1 PDFMalbattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNDERPINNING Text MaterialDokument14 SeitenUNDERPINNING Text MaterialYoga RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile Foundations Lecture Note 1 PDFDokument99 SeitenPile Foundations Lecture Note 1 PDFMohamedRaahim100% (3)
- KMC ReportDokument19 SeitenKMC ReportBijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constech 252 Ass1Dokument21 SeitenConstech 252 Ass1MAYVELLINE DVIONA GEORGENoch keine Bewertungen
- CMT Pile FoundationDokument9 SeitenCMT Pile Foundationkumar AbhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 103 Sce Module 3Dokument8 Seiten103 Sce Module 3Joab Gabriel Elegado CalumpianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft Well PileDokument42 SeitenDraft Well PileRavi VarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bored Piles - Production MethodDokument10 SeitenBored Piles - Production MethodFrank Stephens100% (1)
- Well Foundation PDFDokument41 SeitenWell Foundation PDFpeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- PierDokument52 SeitenPierEngdasew BirhaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well FoundationDokument26 SeitenWell FoundationMohit SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet PilingDokument12 SeitenSheet PilingTanvi Rane100% (1)
- Methods of Piles InstallationDokument5 SeitenMethods of Piles InstallationAsif KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep FoundationDokument74 SeitenDeep FoundationShantanu PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Driven Cast in Situ PilesDokument17 SeitenDriven Cast in Situ PilesSonu KumawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview On Bored Cast in Situ ConcreDokument12 SeitenAn Overview On Bored Cast in Situ ConcreElric TambilawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loh Jie Yao - Tutorial 3 SubmissionDokument6 SeitenLoh Jie Yao - Tutorial 3 SubmissionLOH JIE YAONoch keine Bewertungen
- Under Reamed Pile-5108Dokument12 SeitenUnder Reamed Pile-5108anku510880% (5)
- Cen-306: Foundation Engineering by Dr. Kaustav Chatterjee: Indian Institute of Technology RoorkeeDokument26 SeitenCen-306: Foundation Engineering by Dr. Kaustav Chatterjee: Indian Institute of Technology RoorkeeSiddhantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Uncased Cast-in-Situ Concrete PilesDokument4 SeitenTypes of Uncased Cast-in-Situ Concrete PilesPritha DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture (7) Foundation (Piles)Dokument19 SeitenLecture (7) Foundation (Piles)علي نصير أبراهيمNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnderpinningDokument66 SeitenUnderpinningvetrivelanpec100% (1)
- Types of Caissons:: (I) Single Wall Open Caisson (Ii) Cylindrical Open Caisson (Iii) Open Caisson With Dredging WellsDokument4 SeitenTypes of Caissons:: (I) Single Wall Open Caisson (Ii) Cylindrical Open Caisson (Iii) Open Caisson With Dredging WellsKeith GarridoNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Drill Bored PileDokument4 SeitenHow To Drill Bored Pileezdiani84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Construction EngDokument7 SeitenConstruction EngazieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Piles 2Dokument94 SeitenShort Piles 2vivek_gesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAISSON Discussion PaperDokument5 SeitenCAISSON Discussion PaperKeith GarridoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Sinking ProceduresDokument7 SeitenWell Sinking ProceduresAjit ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well FoundationDokument45 SeitenWell Foundationmonika chauhan100% (2)
- Training ReportDokument21 SeitenTraining ReportMonaliza SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Report SARNENDU (L-17)Dokument21 SeitenTraining Report SARNENDU (L-17)Monaliza SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well FoundationsDokument6 SeitenWell FoundationsNithin Sudersanan100% (1)
- What Is Well FoundationDokument7 SeitenWhat Is Well FoundationAble KuriakoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnderpinningDokument30 SeitenUnderpinningAimi Athirah ZahibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Components of FlyoverDokument3 SeitenMajor Components of FlyoverSaran KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Installing Pile FoundationsDokument5 SeitenMethods of Installing Pile FoundationslaikienfuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 09: Well FoundationsDokument77 SeitenChapter - 09: Well Foundationsdhedy husadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile FoundationDokument44 SeitenPile FoundationKasim MalekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Sinking ProceduresDokument8 SeitenWell Sinking ProceduresSaurabh TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PilesDokument47 SeitenPilesnurulselangorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.pile Foundation: Q1. Write Down Functions and Classification of Pile FoundationDokument9 Seiten1.pile Foundation: Q1. Write Down Functions and Classification of Pile FoundationSuhail AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionVon EverandReinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Von EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Steam Turbines A Book of Instruction for the Adjustment and Operation of the Principal Types of this Class of Prime MoversVon EverandSteam Turbines A Book of Instruction for the Adjustment and Operation of the Principal Types of this Class of Prime MoversBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Rock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesVon EverandRock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 312, December 24, 1881Von EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 312, December 24, 1881Noch keine Bewertungen
- How to Build a Global Model Earthship Operation I: Tire WorkVon EverandHow to Build a Global Model Earthship Operation I: Tire WorkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turf Wall Architecture and Turf Furniture Assembly GuideVon EverandTurf Wall Architecture and Turf Furniture Assembly GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- A0 - ReviewedDokument20 SeitenA0 - ReviewedJODIN MAKINDA -Noch keine Bewertungen
- InfraCo Review 2007Dokument63 SeitenInfraCo Review 2007m_edas4262Noch keine Bewertungen
- StratosDokument4 SeitenStratosCelith Rossy Inga PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExamDokument18 SeitenExamMark MamaradloNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Second Industrial Revolution 1850 - 1914 - 5 JULY 2022Dokument41 SeitenThe Second Industrial Revolution 1850 - 1914 - 5 JULY 2022Jason KDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bureau of Indian StandardsDokument147 SeitenBureau of Indian Standardsbalakarthickpbsm100% (2)
- 04 FORM Personal Daily Report HSEDokument4 Seiten04 FORM Personal Daily Report HSEArga Sakti YusnandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConclusionDokument2 SeitenConclusionKhairul AsyrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract CostingDokument36 SeitenContract CostingdivinamariageorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Searay 330 Sundancer-ReportDokument11 SeitenSearay 330 Sundancer-ReportAshok KamathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistivity Testing of SubstationDokument17 SeitenResistivity Testing of SubstationBernard Kipng'enoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hot CrackingDokument3 SeitenHot CrackingFsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.4 Ccontract ManagmentDokument27 Seiten2.4 Ccontract Managmentbereket gNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elmo 2bh1 Gas Ring Vacuum PumpsDokument11 SeitenElmo 2bh1 Gas Ring Vacuum PumpsAlberto Costilla GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pse 115a2512#dl PSDL D Com Proper 1 To 4Dokument4 SeitenPse 115a2512#dl PSDL D Com Proper 1 To 4Rinowan PanggoariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blueprint Project DilationsDokument2 SeitenBlueprint Project DilationsDatta KambleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permalok Steel Casing Pipe For Microtunneling and Other Jacking ApplicationsDokument36 SeitenPermalok Steel Casing Pipe For Microtunneling and Other Jacking Applicationsvmi_dude100% (2)
- Piled Foundation ReportDokument7 SeitenPiled Foundation ReportDijo Mathews100% (1)
- Paling BillDokument5 SeitenPaling Billanon_b186Noch keine Bewertungen
- Viking Manual 110Dokument90 SeitenViking Manual 110Marcelo RochaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sumit CV 2021 2Dokument3 SeitenSumit CV 2021 2Vimal TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Sizing Example #3Dokument26 Seiten6 Sizing Example #3BryanHarold BrooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installation Guidelines: 1. Preparing The SubgradeDokument3 SeitenInstallation Guidelines: 1. Preparing The SubgradeElard QANoch keine Bewertungen
- Union 18k Split With ImageDokument3 SeitenUnion 18k Split With Imageubaldoferns9357Noch keine Bewertungen
- Boq Package 4-Mep Rumus1Dokument413 SeitenBoq Package 4-Mep Rumus1Muhammad Iqbal ArdhiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressostat Steer - GeearDokument240 SeitenPressostat Steer - GeearПетр ШкильNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Training ReportDokument11 SeitenIndustrial Training ReportAashu MahlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course DescriptionsDokument28 SeitenCourse DescriptionsRoberto HoffmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LS Bridge-New Bridge Excel-For LL VehicleDokument39 SeitenLS Bridge-New Bridge Excel-For LL Vehiclesharath mathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constant Volume - Constant Speed. Chilled Water Systems. Chillers Pumps & PiDokument3 SeitenConstant Volume - Constant Speed. Chilled Water Systems. Chillers Pumps & PiMohamed AdelNoch keine Bewertungen