Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Breech
Hochgeladen von
sss121qOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Breech
Hochgeladen von
sss121qCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
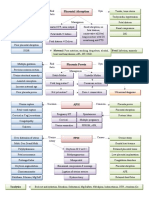
Frank/Extended (65%) Complete/Flexed (25%) Incomplete/Footling (10%) Fibroids or pelvic tumors Uterine Surgery Oligo/Polyhydramnios Uterine anomalies (bicornuate
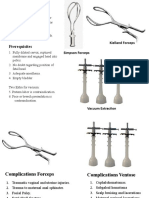
or septate) Multiple gestation Prematurity Placenta previa Structural anomaly (hydrocephalus, anencephaly) Forceps Method
Performed at 36-37 weeks Done under US guidance Fetal HR trace done before & after Tocolytics may help (ritodrine, salbutamol, nifedipine or GTN) Mauriceau-SmellieVeit maneuver
Types
Breech Presentation
The major factor predisposing to breech presentation is prematurity
Incidence
3% at term
Incidence falls as pregnancy advances
40% at 26 weeks, 25% before 28 w, 20% at 30 weeks
Uterine
Management includes exclusion of fetal and uterine anomalies after 34 weeks
Predisposing factors
Become a problem if baby isnt cephalic by 37 weeks
No controlled trials compare Vag vs c/s, the two small studies that do exist show vaginal safer for mother with increase morbidity for fetus and vice versa.
Complications Cord Prolapse (footling) Difficulty in delivering shoulders Head entrapment (asphyxia)
Fetal
The incidence of structural anomalies is > 6% (2 to 3 times vertex)
Diagnosis
Leopold Maneuver Vaginal Examination Confirmed by US Maternal (5 Ps) Vaginal Delivery
Post (Advanced) age Poor Obstetric history Primigravida
Discouraged
ECV (success )
Only 2% of successful term versions revert o breech Previous cesarean
Unstable Lie
Def: alternating btw trans, oblique, & long.
Pelvis narrow/small
Contraindications Placenta previa Oligo/Polyhydramnios History of APH Previous cesarean Previous uterine surgery Multiple gestation Preeclampsia/HT IUGR Placental abruption PROM Cord prolapse Fetal bradycardia
Transplacental hemorrhage (remember anti-D to Rh ve) Dx: asymmetrical abdomen, symphysis-fundal height less than expected, palpate buttocks or fetal head in iliac fossa, & empty pelvis. Management: Admit and perform cesarean. Gestation less than 36 w Premature breech fetuses are preferentially delivered by cesarean birth because of the head-abdominal size disparity. Risk: Cord prolapsed after SROM, and prolapsed of hand/shoulder/foot in labor
Fetal
Footling presentation Weight < 2.5 kg or > 3.5 kg Extended neck
Complications
Hx: Multiparous woman, lax uterus and abdominal muscles
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Complications During Labor and DeliveryDokument27 SeitenComplications During Labor and DeliveryMA. JYRELL BONITONoch keine Bewertungen
- USMLE Step 2 CK 6 Months Study Plan For 240Dokument1 SeiteUSMLE Step 2 CK 6 Months Study Plan For 240DhritisdiaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helminth ChartsDokument4 SeitenHelminth ChartsDrbee10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amboss Hemolytic AnemiaDokument16 SeitenAmboss Hemolytic AnemiaAhmed Ali100% (2)
- Gyne ReflectionDokument18 SeitenGyne ReflectionKC Dela RosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Factors - Step 2 PDFDokument5 SeitenRisk Factors - Step 2 PDFAmberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquifer Case - Summary - FamilyMedicine21 - 12-YDokument10 SeitenAquifer Case - Summary - FamilyMedicine21 - 12-YHyunsoo EllisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicowesome - AnatomyDokument19 SeitenMedicowesome - AnatomySubhashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Compatible ModeDokument93 SeitenChapter 1 Compatible ModeJyha KhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Failure - Notes From "Cardiology" (Timmis Et Al) : Main CausesDokument3 SeitenHeart Failure - Notes From "Cardiology" (Timmis Et Al) : Main CausesPrarthana Thiagarajan100% (3)
- Medstar ObGyn 2nd EditionDokument570 SeitenMedstar ObGyn 2nd EditionMerahit Abera100% (2)
- Cervix Cancer Power Point With SlidesDokument41 SeitenCervix Cancer Power Point With SlidesAmín JiménezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FHSIS Form TCL Pre NatalDokument11 SeitenFHSIS Form TCL Pre NatalEden Vblagasy100% (5)
- Vasa PraeviaDokument3 SeitenVasa PraeviaAngelica CabututanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EndometriosisDokument1 SeiteEndometriosisZiyad100% (1)
- Anomalies of the placenta and cord: risks and diagnosisDokument52 SeitenAnomalies of the placenta and cord: risks and diagnosisDaniel Andre S. Somoray100% (1)
- Ninja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT2 SLAY Most UpdatedDokument56 SeitenNinja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT2 SLAY Most UpdatedyenniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic LecturesDokument35 SeitenGenetic Lecturesميمونه عبدالرحيم مصطفىNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bilateral Peritonsillar Abscess Case ReportDokument2 SeitenBilateral Peritonsillar Abscess Case ReportshashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetics Simplified El-MowafiDokument515 SeitenObstetics Simplified El-Mowafiapi-370504650% (2)
- A Simple Guide to Adrenal Cancer, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to Adrenal Cancer, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sudden Maternal Collapse: Max Brinsmead MB Bs PHD May 2015Dokument23 SeitenSudden Maternal Collapse: Max Brinsmead MB Bs PHD May 2015DrChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary IncontinenceDokument1 SeiteUrinary IncontinenceZiyad100% (1)
- Urinary IncontinenceDokument1 SeiteUrinary IncontinenceZiyad100% (1)
- Antepartum HemorrhageDokument3 SeitenAntepartum Hemorrhagenur1146Noch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Diagnosis of The Adnexal Mass 2020Dokument38 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis of The Adnexal Mass 2020Sonia MVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 20 - Conditions Occurring During PregnancyDokument5 SeitenChapter 20 - Conditions Occurring During PregnancyEunice CortésNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deconstructing The ECG Curve - The Components of The Tracing: Key ConceptsDokument117 SeitenDeconstructing The ECG Curve - The Components of The Tracing: Key ConceptsdrynwhylNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment Algorithm for Severe Morning SicknessDokument2 SeitenTreatment Algorithm for Severe Morning Sicknessrayyanzubaidi100% (1)
- BIOL 215 - CWRU Final Exam Learning GoalsDokument32 SeitenBIOL 215 - CWRU Final Exam Learning GoalsKesharaSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Divine Intervention Episode 12 Bacteria Cases ADokument18 SeitenDivine Intervention Episode 12 Bacteria Cases ASwisskelly1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoulder dystocia management and PPH treatmentDokument9 SeitenShoulder dystocia management and PPH treatmentJeffrey HingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid & Electrolite Management in Surgical WardsDokument97 SeitenFluid & Electrolite Management in Surgical WardsBishwanath PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- USMLE Step 1 Review in BiochemistryDokument18 SeitenUSMLE Step 1 Review in BiochemistryDevindra 2k17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Councelling and History TakingDokument5 SeitenCouncelling and History TakingbashingarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Objectives - ACOGDokument164 SeitenStudent Objectives - ACOGmango91286100% (1)
- Clinical Key Master - Content - List - 14 Jun 2019Dokument49 SeitenClinical Key Master - Content - List - 14 Jun 2019Axevim GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biliary DisoderDokument50 SeitenBiliary DisoderZanida ZainonNoch keine Bewertungen
- HistCellBioUSMLEDokument25 SeitenHistCellBioUSMLERushi ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Vaccine Schedule Eng PDFDokument2 SeitenAdult Vaccine Schedule Eng PDFAbdur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Physio UsmleDokument61 SeitenRespiratory Physio UsmleDr.G.Bhanu Prakash100% (2)
- HHHHDokument36 SeitenHHHHdger11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biliary Disorders and Pancreatic Conditions ExplainedDokument59 SeitenBiliary Disorders and Pancreatic Conditions ExplainedErick Sioco InsertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Divine Intervention Episode 13 Step 1 Metabolism Review A: Some MS4Dokument11 SeitenDivine Intervention Episode 13 Step 1 Metabolism Review A: Some MS4Swisskelly1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Checklistfor 45 Yr OldsDokument1 SeiteChecklistfor 45 Yr OldsyohaneskoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disease of The Biliary TractDokument7 SeitenDisease of The Biliary TractMae DoctoleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heme Testing Aid/APLS: Some PGY-1Dokument4 SeitenHeme Testing Aid/APLS: Some PGY-1Swisskelly1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Enteral Versus Parenteral Nutrition in Critically Ill Patients - An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled TrialsDokument14 SeitenEnteral Versus Parenteral Nutrition in Critically Ill Patients - An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled TrialsLea Bali Ulina SinurayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Biliary DisorderDokument50 SeitenAssessment and Management of Patients With Biliary DisorderZanida ZainonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne History Taking PDFDokument6 SeitenGyne History Taking PDFGokul AdarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Divine Intervention Episode 5 Cardio A Physiology1Dokument18 SeitenDivine Intervention Episode 5 Cardio A Physiology1Swisskelly1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatrics Modern Day AnalysisDokument144 SeitenPediatrics Modern Day AnalysisDaniyal AzmatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal OsteodystrophyDokument4 SeitenRenal OsteodystrophyLuigiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaplan Books + Videos Essential USMLE ReviewDokument3 SeitenKaplan Books + Videos Essential USMLE ReviewAditya Pavankumar Ganti100% (1)
- The RX Study Planner - 2021 EditionDokument33 SeitenThe RX Study Planner - 2021 EditionYASSERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptive Leadership The Case of Jacinda New ZealandDokument4 SeitenAdaptive Leadership The Case of Jacinda New ZealandJahnvi AndhariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biliary Tree LectureDokument58 SeitenBiliary Tree Lecturesgod34Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Gastrointestinal TractDokument45 SeitenLower Gastrointestinal Tractsofia_245Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Stenosis Aorta + RegurgitationDokument58 SeitenCase Stenosis Aorta + RegurgitationRuth Faustine Jontah RayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orgo Cheat Sheets Leah4sci Collection 2018 5192018 PDFDokument32 SeitenOrgo Cheat Sheets Leah4sci Collection 2018 5192018 PDFGian BañaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiology: Dr. Abdulaziz Alsaad Neuroradiology Fellow King Fahad Medical CityDokument22 SeitenRadiology: Dr. Abdulaziz Alsaad Neuroradiology Fellow King Fahad Medical CityAjmal EnsanahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goljan Respiratory NotesDokument21 SeitenGoljan Respiratory Notesmedic2424100% (1)
- Obs & GynDokument121 SeitenObs & GynSaya K. AkremNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuroblastoma: A Cancer of the Sympathetic Nervous SystemDokument153 SeitenNeuroblastoma: A Cancer of the Sympathetic Nervous SystemWael ElsawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toxicology USMLE NotesDokument15 SeitenToxicology USMLE NotesDuncan JacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyVon EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fanconi Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandFanconi Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 - Toronto Notes 2011 - GynecologyDokument52 Seiten14 - Toronto Notes 2011 - GynecologyZiyad100% (4)
- Fluid Management in PediatricsDokument3 SeitenFluid Management in PediatricsZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDokument1 SeiteCyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prenatal Assessment of FetusDokument1 SeitePrenatal Assessment of FetusZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Most Common's" in Pediatric CardiologyDokument1 Seite"Most Common's" in Pediatric CardiologyZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDokument2 SeitenAcyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseZiyad100% (1)
- Typical CSF Findings in Pediatric MeningitisDokument1 SeiteTypical CSF Findings in Pediatric MeningitisZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruments & IndicationsDokument11 SeitenInstruments & IndicationsZiyad100% (2)
- Thyroid DiseaseDokument1 SeiteThyroid DiseaseZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetric BleedingDokument1 SeiteObstetric BleedingZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume Obs 21-27 Februari 21Dokument6 SeitenResume Obs 21-27 Februari 21imamsantos1191Noch keine Bewertungen
- SecretDokument1 SeiteSecretAyisha LoureliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre EclampsiaDokument1 SeitePre EclampsiaRajith AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- IUGR Case PresentationDokument21 SeitenIUGR Case PresentationAlice ChirilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Study of Intrauterine Fetal Death Cases and Associated Maternal ConditionsDokument5 SeitenAnalytical Study of Intrauterine Fetal Death Cases and Associated Maternal ConditionsNurvita WidyastutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intraoperative Surgical Complication During Cesarean SectionDokument14 SeitenIntraoperative Surgical Complication During Cesarean Sectioncarbolico100% (1)
- Lat XiDokument3 SeitenLat XiEsa NadhirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Germiston +27833736090 Dr. Jabulile/cheap Abortion Pills 4 Sale in Germiston/johannesburg ClinicDokument1 SeiteGermiston +27833736090 Dr. Jabulile/cheap Abortion Pills 4 Sale in Germiston/johannesburg Clinicsseruwagi miyodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hellp Syndrome ArticleDokument8 SeitenHellp Syndrome ArticleDIANNE FAYE LARAGANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postterm Pregnancy Risks & Management OptionsDokument5 SeitenPostterm Pregnancy Risks & Management OptionsOmar MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Bahasa Indonesia Kasus Kehamilan MelahirkanDokument164 Seiten10 Bahasa Indonesia Kasus Kehamilan Melahirkancuuphy meryliantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal and Fetal Outcomes in Term Premature Rupture of MembraneDokument6 SeitenMaternal and Fetal Outcomes in Term Premature Rupture of MembraneMuhammad Fikri RidhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Ilmu Kedokteran Dan Kesehatan, Volume 7, Nomor 1, Januari 2020 393Dokument8 SeitenJurnal Ilmu Kedokteran Dan Kesehatan, Volume 7, Nomor 1, Januari 2020 393Nurhalimah HarahapNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Persiapan Penanganan Bayi Baru LahirDokument54 Seiten1 Persiapan Penanganan Bayi Baru LahirRosa NinmusuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-11 Breech PresentationDokument27 SeitenLecture-11 Breech PresentationMadhu Sudhan PandeyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abnormalitiesofcordplacenta 140706120521 Phpapp01 PDFDokument65 SeitenAbnormalitiesofcordplacenta 140706120521 Phpapp01 PDFNise Mon KuriakoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHORIOAMNIONITISDokument32 SeitenCHORIOAMNIONITISnurul azareeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Eclampsia: Preeclampsia Is A Pregnancy Complication Characterized by High Blood Pressure and Signs of Damage ToDokument3 SeitenPre Eclampsia: Preeclampsia Is A Pregnancy Complication Characterized by High Blood Pressure and Signs of Damage ToSahaaneiy IlmeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Measure Cervical Length: Karl Oliver Kagan and Jiri SonekDokument14 SeitenHow To Measure Cervical Length: Karl Oliver Kagan and Jiri SoneknidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Antepartum Haemorrhage (APHDokument18 SeitenUnderstanding Antepartum Haemorrhage (APHSanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic - Version Subject - ObgDokument23 SeitenTopic - Version Subject - ObgMandeep KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbortionsDokument99 SeitenAbortionsAGERI PUSHPALATHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Icd 10 Revisi 2010Dokument45 SeitenIcd 10 Revisi 2010Lena ArdhiyantiNoch keine Bewertungen