Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Thermodynamics - Internal Combustion Engine
Hochgeladen von
Isuru KasthurirathneOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Thermodynamics - Internal Combustion Engine
Hochgeladen von
Isuru KasthurirathneCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
INTRODUCTION
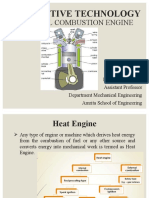
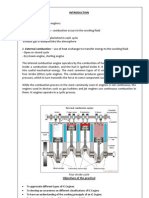
There are two types of engines: 1. Internal combustion - combustion occurs in the working fluid - Open cycle The working fluid is replenished in each cycle Exhaust gas is dumped into the atmosphere 2. External combustion use of heat exchanger to transfer energy to the working fluid - Open or closed cycle - Ex) steam engine, sterling engine The internal combustion engine operates by the combustion of fuel. The process takes place inside a combustion chamber, and the fuel is ignited inside it. It converts chemical energy into useful mechanical energy. The most common types of IC engines are two stroke and four stroke (Otto) cycle engines. The combustion produces gases at high temperature and pressure, which in turn transmits the force to some component such as the piston. While the combustion process in the most commonly seen IC engines is not continuous, the engines used in devices such as gas turbines and jet engines use continuous combustion in them. IC engines operate in a cyclic process.
Four stroke cycle Objectives of the practical
To appreciate different types of IC Engines. To develop an awareness on different classifications of IC Engine. To have an understanding of the working principals of an IC Engine. To have an understanding of the applications of IC Engine.
Apparatus required: The display boards of two stroke and four stroke IC Engines. The cut section of two stroke IC Engine. The side valve four stroke IC Engine. The display working model of the four stroke compression ignition IC Engine. Other display models in Automobile Laboratory.
DISCUSSION Working principle of IC engines: The working principle behind IC engines is that when a gas is ignited and burned in a small confined space, the resulting expanding exhaust gases release a large amount of energy, which can be converted to useful mechanical work by the means of a moving mechanical device such as a piston.
Classification of internal combustion engines: The following criteria are used to classify IC engines. Method of Ignition Spark ignition engine or Petrol Engine. Compression ignition engine or Diesel Engine. Hot spot ignition engine. Fuel Used Petrol Engines. Diesel Engines. Gas Engines. Number of Strokes per cycle Two stroke engines. Four stroke engines. Cycle for Operation Hot cycle engine. Diesel cycle engines. Dual combustion cycle engine. Number of Cylinders Single cylinder engines. Multi-cylinder or Double Cylinder engines. Cylinder Arrangement Horizontal Cylinder Engines. Vertical cylinder engines. Inline cylinder engines. Radial engines.
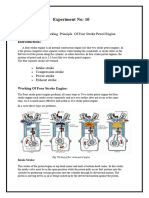
Engines Speed Low speed engines. Medium speed engines. High speed engines. Applications of IC engines: Internal combustion engines are in vehicles and many other moving machinery. We encounter IC engines in cars, boats, trucks, and even aircraft and jet engines. Operation of four stroke engines: In the four-stroke engine the cycle of operations of the engine are completed in four strokes of the piston inside the cylinder. The four strokes of the 4-stroke engine are: suction or intake of fuel, compression of fuel, expansion or power stroke, and exhaust stroke. In 4stroke engines the power is produced when piston performs expansion stroke. During four strokes of the engine two revolutions of the engine's crankshaft are produced. The piston moves twice from the top dead centre to the bottom dead centre in one cycle. In the suction stroke, only the inlet valve is open. The exhaust valve is closed and the gas/fuel is taken in. In the compression stroke, both valves are closed, and the piston moves in to compress the gas mixture, which increases in density and temperature. In the power stroke, the piston reaches the inner dead centre and the spark ignited the gas fuel mixture, which then starts to expand. Both valves are closed at this point. In the exhaust stroke, the exhaust valve opens and the exhaust gases are let out.
Operation of two stroke engines: In the 2-stroke, the suction and compression strokes occur at the same time, and the expansion and exhaust strokes occur at the same time. Power is produced during the expansion stroke. When two strokes of the piston are completed, one revolution of the engine's crankshaft is produced, thus completing the two stroke engine cycle. In 4-stroke engines the engine burns fuel once for two rotations of the wheel, while in 2stroke engine the fuel is burnt once for one rotation of the wheel. Hence the efficiency of 4stroke engines is greater than the 2-stroke engines. However, the power produced by the 2stroke engines is more than the 4-stroke engines.
Differences between two stroke and four stroke engines: The two stroke engine only requires two strokes of the piston to complete the cycle, in comparison to the four strokes in the four stroke engine. In the four stroke system, the spark plug fires only during the power stroke, which means that the firing takes place during once every other revolution of the piston. But in the two stroke system, the engine powers during every revolution, and this gives two stroke engines a power advantage. There is no need for valves in the two stroke engine. An inlet and an exhaust port is there in the combustion chamber wall itself. But the efficiency of the two stroke engines is lower than that of the four stroke engines. Two stroke engines have a higher power to weight ratio than the four stroke engines. But their engine wear is faster. Two stroke engines heavily contribute to pollution, and four stroke engines cause less pollution.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiVon EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combustion Ass 1Dokument6 SeitenCombustion Ass 1Shane Michael BacalsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics Lab ReportDokument49 SeitenThermodynamics Lab Reportjawad60% (5)
- Experiment 3 ThermoDokument11 SeitenExperiment 3 ThermoMuneeb NaveedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion Engines: Approved by AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Gujarat & GTU AffiliatedDokument21 SeitenInternal Combustion Engines: Approved by AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Gujarat & GTU AffiliatedAtif AttiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Types and ClassificationsDokument16 SeitenEngine Types and ClassificationsVõ Thanh Liêm100% (1)
- Review Six Stroke EngineDokument7 SeitenReview Six Stroke EngineSuhas G FADNISNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-1: Types of EngineDokument14 SeitenAssignment-1: Types of EngineRaj SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo Fluids Ime-241L Lab Report: Prof. DR Salman Habib Hassan Ali Butt 2017-IM-39Dokument19 SeitenThermo Fluids Ime-241L Lab Report: Prof. DR Salman Habib Hassan Ali Butt 2017-IM-39Mahrukh ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGINEDokument7 SeitenENGINEayesha amjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MD ProjectDokument35 SeitenMD ProjectDar AkhtNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Presentation On Six-Stroke EnginesDokument17 SeitenA Presentation On Six-Stroke EnginesHarshit AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Four Stroke EngineDokument5 SeitenFour Stroke Enginemnoorulain80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment - No.2: To Study The Parts and Working of Four Stroke Petrol EngineDokument6 SeitenExperiment - No.2: To Study The Parts and Working of Four Stroke Petrol EngineHafeez AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is EngineDokument25 SeitenWhat Is EngineSajib Chandra RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction IC Engine and Reciprocating Machine CH - 1Dokument57 SeitenIntroduction IC Engine and Reciprocating Machine CH - 1heonetubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab No: 02: ObjectiveDokument5 SeitenLab No: 02: ObjectiveMuhammad Nadeem KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Of Operation of Internal Combustion EnginesDokument31 SeitenOf Operation of Internal Combustion EnginesNaveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson One: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion EnginesDokument45 SeitenLesson One: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion Engineswaleed yehiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic EngineDokument23 SeitenIc EngineGanesh kumar100% (1)
- I.C EnginesDokument23 SeitenI.C EngineskolappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal 1unit3Dokument178 SeitenThermal 1unit3NAGU2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Four-Stroke Petrol Engine: Submited By: Aymen Gulzar Registeration No: 18-EE-88Dokument13 SeitenFour-Stroke Petrol Engine: Submited By: Aymen Gulzar Registeration No: 18-EE-88aymen gulzarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PJM Auto NotesDokument18 SeitenPJM Auto NotesAswin PrasannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Does An Internal Combustion Engine Work?Dokument5 SeitenHow Does An Internal Combustion Engine Work?AsraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Report 2ND PartDokument19 SeitenSeminar Report 2ND PartAshutosh RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation of Communication SkillsDokument32 SeitenPresentation of Communication SkillsFadhliana UzalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine and Motor (4 Stroke Engine and 2 Stroke Engine)Dokument27 SeitenEngine and Motor (4 Stroke Engine and 2 Stroke Engine)Bias PanduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic Engines& Gas TurbineDokument10 SeitenIc Engines& Gas TurbineBhairab BhowmikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical #11: To Study Cutaway Models of Petrol and Diesel Engine Heat EngineDokument9 SeitenPractical #11: To Study Cutaway Models of Petrol and Diesel Engine Heat EngineMuhammad Arslan AfzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is An EngineDokument15 SeitenWhat Is An Engineravidra markapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion EngineDokument136 SeitenInternal Combustion Enginepreethu02Noch keine Bewertungen
- IC EnginesDokument44 SeitenIC EnginesIbrahim KhaleelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument41 SeitenChapter 2Ibrahim KhaleelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic Engines Lab ManualDokument33 SeitenIc Engines Lab ManualupenderdhullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Heat Engines: What Is The Heat Engine?Dokument46 SeitenTypes of Heat Engines: What Is The Heat Engine?Mozammel HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 2 AutomotiveDokument55 SeitenGroup 2 AutomotivePELINA, Carlos Jade L.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - Internal CombussionDokument80 SeitenLecture 2 - Internal Combussionchoongwenkang100% (1)
- Heat Engine: Name: Joezel A. Entienza Date:May 1, 2018 Lab 4Dokument11 SeitenHeat Engine: Name: Joezel A. Entienza Date:May 1, 2018 Lab 4joshua jan allawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion EnginesDokument37 SeitenInternal Combustion EnginesFake IdentityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications: and TheirDokument88 SeitenApplications: and TheiralexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument29 SeitenChapter 3Hasif EnazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion EngineDokument4 SeitenInternal Combustion Enginesari hafizhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No 09Dokument3 SeitenExperiment No 0920MCE 01 Mehwish KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between 2 Stroke and 4 Stroke EngineDokument9 SeitenDifference Between 2 Stroke and 4 Stroke EnginesaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Stroke Petrol Engine1699240011Dokument7 Seiten4 Stroke Petrol Engine1699240011Masoud doski100% (1)
- Greater Noida Institute of Technology: 2-Stroke Petrol EngineDokument13 SeitenGreater Noida Institute of Technology: 2-Stroke Petrol EngineEr Raghvendra SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM ICEngines GTLabDokument37 SeitenLM ICEngines GTLabAdwi HantoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quasi Turbine: By-Shivam Agarwal Roll No - 12 Section-D 130909058 Dept. of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringDokument37 SeitenQuasi Turbine: By-Shivam Agarwal Roll No - 12 Section-D 130909058 Dept. of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringShivam AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine:: Single Cylinder Four Stroke Petrol EngineDokument8 SeitenEngine:: Single Cylinder Four Stroke Petrol EngineSâì ÇhârâñNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Intro Internal Combustion EngineDokument4 SeitenProject Intro Internal Combustion EngineAmit Kumar PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ae LabDokument53 SeitenAe LabAnkit DahiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument8 SeitenUnit 1Shivajee YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Stroke and 4 Stroke EngineDokument19 Seiten2 Stroke and 4 Stroke EngineArun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What You Should Know About Car EnginesDokument26 SeitenWhat You Should Know About Car EnginesJoahnna Pineda100% (1)
- Vehicle Design and Characteristics (Sathybama)Dokument95 SeitenVehicle Design and Characteristics (Sathybama)shaziya mehrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vroom! How Does A Car Engine Work for KidsVon EverandVroom! How Does A Car Engine Work for KidsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Small Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsVon EverandSmall Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Assignment SMDokument21 SeitenGroup Assignment SMIsuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM TM TM TMDokument2 SeitenTM TM TM TMIsuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application For Foreign Training (CEB)Dokument2 SeitenApplication For Foreign Training (CEB)Isuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Take-Home Assignment - MBA 1133 Statistics For BusinessDokument4 SeitenTake-Home Assignment - MBA 1133 Statistics For BusinessIsuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acceptance Test of All Concrete Poles PDFDokument24 SeitenAcceptance Test of All Concrete Poles PDFIsuru Kasthurirathne100% (1)
- Job Analysis For A Given Job Classification: Human Resource Management and Industry Relations (MN 4122)Dokument12 SeitenJob Analysis For A Given Job Classification: Human Resource Management and Industry Relations (MN 4122)Isuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acceptance Test of Concrete PolesDokument15 SeitenAcceptance Test of Concrete PolesLahiru De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Management System - Lecture 2Dokument157 SeitenBuilding Management System - Lecture 2Isuru Kasthurirathne100% (2)
- Human Resources Management: Amali Wijekoon Dept. of MOTDokument48 SeitenHuman Resources Management: Amali Wijekoon Dept. of MOTIsuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Decision Making - MBA-2017Dokument46 SeitenManagerial Decision Making - MBA-2017Isuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Lanka Building CodeDokument58 SeitenSri Lanka Building CodeIsuru Kasthurirathne33% (3)
- Tirappane Bio Mass PlantDokument2 SeitenTirappane Bio Mass PlantIsuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Acoustics Lecture 7Dokument34 SeitenEngineering Acoustics Lecture 7Isuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Acoustics Lecture 10Dokument30 SeitenEngineering Acoustics Lecture 10Isuru Kasthurirathne100% (2)
- Engineering Acoustics Lecture 11Dokument27 SeitenEngineering Acoustics Lecture 11Isuru Kasthurirathne100% (1)
- Engineering Acoustics Lecture 9Dokument30 SeitenEngineering Acoustics Lecture 9Isuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Acoustics Lecture 6Dokument25 SeitenEngineering Acoustics Lecture 6Isuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Acoustics Lecture 8Dokument33 SeitenEngineering Acoustics Lecture 8Isuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Acoustics Lecture 5Dokument30 SeitenEngineering Acoustics Lecture 5Isuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Acoustics Lecture 1Dokument23 SeitenEngineering Acoustics Lecture 1Isuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of Earth Resistance and ResistivityDokument9 SeitenMeasurement of Earth Resistance and ResistivityIsuru Kasthurirathne100% (4)
- Introduction To ThermoDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To ThermoIsuru KasthurirathneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Kotmale Field VisitDokument6 SeitenUpper Kotmale Field VisitIsuru Kasthurirathne50% (2)