Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Endocrine System Note
Hochgeladen von
Andy LeeOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Endocrine System Note
Hochgeladen von
Andy LeeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
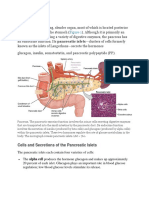
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Nervous (N) + Endocrine (E)= primary communicating & coordinating system in the body N communicates through
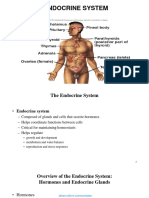
rough nerve impulses E communicates through chemical substances (hormones) reproduction, G&D, energy regulation E composed of glands produce, store, secrete hormones (though blood) target organs/tissues E glands: hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries, testes, & pineal.
Structures & Functions of E system: NOT all glands belong to E system Glands = organs of E system 2 types o Exocrine secrete substance into ducts empty into (body cavity) or onto (body surface skin) o Endocrine secrete substance directly into blood target tissues (organ/tissue hormones effect on) Hormones o Common characteristics: Secretions (variable & predictable rates) Circulation through blood Binding to receptors (membranes or within cell) o Classified by chemical structures: Lipid-soluble hormones steroid (adrenal cortex & sex glands) & thyroid hormones Water-soluble hormones all other hormones o Functions: Reproduction Response to stress & injury Electrolyte balance Energy metabolism Growth, maturation, & aging Some play a role in NS (act as neurotransmitters) Some influence behaviors (mood swing, depression) o Transport: Carried by blood to specific organ/tissue Water-soluble hormones circulate freely in the blood, not dependent on proteins Lipid-soluble hormones bound to blood plasma proteins (inactive stage) release their action at target tissue o Targets & Receptors: Hormones recognize target tissue through receptors on/within cells in lock & key mechanism Hormone acts only on cells that have specific receptors for that hormone Location of receptor sites affects mechanism of action for hormone Steroid & Thyroid hormone receptors: Are lipid soluble & locate inside cells 1. Pass through cell membrane bind to receptor sites at cytoplasm/nucleus 2. Intracellular hormone complexes bind to specific sites on DNA stimulate/ inhibit synthesis mRNA 3. mRNA is synthesized migrates to cytoplasm stimulates protein synthesis produce specific effects Protein Hormone Receptors: Located in target cell membrane, act in two steps process 1st messenger = receptor hormone itself stimulate 2nd messenger production such as, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) activating enzymes to regulate intracellular activity o Regulation of Hormonal Secretions: Hypothalamus Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pancreas
Gerontologic Considerations: Assessments Subjective Data Objective Data Diagnostic Studies Laboratory
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Endocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideVon EverandEndocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- AP 18 Endocrine OverviewDokument19 SeitenAP 18 Endocrine OverviewMARICRIS NEBIARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 - The Endocrine SystemDokument73 SeitenChapter 16 - The Endocrine SystemAbdullah AlghamdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine System Anaphy ReviewDokument4 SeitenThe Endocrine System Anaphy ReviewAdiel CalsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System-1Dokument90 SeitenEndocrine System-1markmuiruri581Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine System Part 1Dokument64 SeitenThe Endocrine System Part 1rizwanbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- EndocrinologyDokument4 SeitenEndocrinologyRekesh SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- EndocrineDokument2 SeitenEndocrineHoney Mie MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Endocrine, 1Dokument50 SeitenMolecular Endocrine, 1Dedi IrwansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forelæsning 3Dokument8 SeitenForelæsning 3natashathelinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Endocrine 1 (Introduction) - MedicineDokument36 Seiten1 - Endocrine 1 (Introduction) - MedicineBHUWAN BASKOTANoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOCHEM, Hormones (Reviewer)Dokument4 SeitenBIOCHEM, Hormones (Reviewer)michaelamontanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System PDFDokument38 SeitenEndocrine System PDFUlfat NiazyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System HandoutsDokument5 SeitenEndocrine System HandoutsBeatriz IcayNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiologyDokument2 SeitenBiologyumaimahomer42Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 132 Chapter 18 NotesDokument8 SeitenBio 132 Chapter 18 Noteslovelyc95100% (1)
- Endocrine PhysiologyDokument76 SeitenEndocrine Physiologykidusabeje7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System Endocrine System: "The Body Regulator"Dokument31 SeitenEndocrine System Endocrine System: "The Body Regulator"angelus008Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5endocrlect3 191011165740Dokument55 Seiten5endocrlect3 191011165740OROKE JOHN EJENoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 17 PhysiologyDokument49 SeitenChapter - 17 PhysiologyAhsanullah PathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine SystemDokument41 SeitenThe Endocrine SystemОксана КрасильниковаNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System 2Dokument28 SeitenEndocrine System 2KELVINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 225 Concordia NotesDokument5 SeitenBio 225 Concordia NotesretterateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Click To Edit Master Text Styles: - Second LevelDokument37 SeitenClick To Edit Master Text Styles: - Second Leveljamaliganteng88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 Endocrine SystemDokument53 SeitenLecture 2 Endocrine SystemLouella ArtatesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2402 CH 17 Endocrine System (Part 1) PDFDokument23 Seiten2402 CH 17 Endocrine System (Part 1) PDFHarry RussellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 The Endocrine SystemDokument7 SeitenChapter 9 The Endocrine SystemAshy LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Endocrine-SystemDokument8 SeitenAnaphy Endocrine-SystemKert trocioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry HormonesDokument13 SeitenBiochemistry HormonesKeziah GillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Hormone Lecture PDFDokument13 SeitenBiochemistry Hormone Lecture PDFKeziah GillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Physiology For Pharmacy Students-2023Dokument118 SeitenEndocrine Physiology For Pharmacy Students-2023Alemnew YohannesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument10 SeitenENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Anatomy and PhysiologyJay Crishnan Morales CajandingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument95 SeitenEndocrine SystemUmar Ilyasu JibrilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormones, ClassificationDokument10 SeitenHormones, ClassificationMenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System: EndocrinologyDokument10 SeitenEndocrine System: EndocrinologyAnya IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument27 SeitenEndocrine SystemJuan Miguel TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument34 SeitenEndocrine SystemNada DardeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Physiology - Part 1Dokument40 SeitenEndocrine Physiology - Part 1Terrence Beniasi CharumbiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument10 SeitenEndocrine SystemSuzette MalibagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrinology Course OutllokDokument59 SeitenEndocrinology Course OutllokJeff ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of The Endocrine SystemDokument225 SeitenStudy of The Endocrine SystemHuzaifa RashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Johanna Jane H. Macasero - Endocrine System TranscriptDokument13 SeitenJohanna Jane H. Macasero - Endocrine System TranscriptJohanna MacaseroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Glands & Their Functions: Anatomy & Physiology II Georgia Perimeter College K. Donaldson, InstructorDokument55 SeitenEndocrine Glands & Their Functions: Anatomy & Physiology II Georgia Perimeter College K. Donaldson, InstructorIsaacJ22Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine SystemDokument5 SeitenThe Endocrine SystemMary Christelle100% (1)
- Endocrine Pathophysiology Nursing NotesDokument4 SeitenEndocrine Pathophysiology Nursing Notesgrad_nurse_2015100% (2)
- Endocrine SystemDokument133 SeitenEndocrine SystemAudrey KenfacNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - LABORATORY With Side NotesDokument68 SeitenENDOCRINE SYSTEM - LABORATORY With Side Notesp2zspgtchjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document 1Dokument19 SeitenDocument 1Binte IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy2021 NotesDokument2 SeitenPhy2021 Notesseraaa1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 The Endocrine SystemDokument9 SeitenLecture 2 The Endocrine SystemJanvi MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HormonesDokument21 SeitenHormonesShohag HosenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 04Dokument14 SeitenModule 04acrehell8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Endrocrinology - PPTX Version 1Dokument40 SeitenEndrocrinology - PPTX Version 1Abishek BhadraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrinology IntroductionDokument43 SeitenEndocrinology IntroductionDICKSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction Endocrine Physiology 2Dokument52 SeitenIntroduction Endocrine Physiology 2IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Notes - All in One FileDokument182 SeitenEndocrine Notes - All in One FilekjNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Endocrine 1Dokument18 Seiten4 Endocrine 1ShenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 Endocrine SystemDokument140 SeitenTopic 1 Endocrine SystemmasdfgNoch keine Bewertungen
- A&p - All Files in One PDFDokument52 SeitenA&p - All Files in One PDFSreejith Jagal KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors That Influence Human Behaviour or Indicators of BehaviourDokument8 SeitenFactors That Influence Human Behaviour or Indicators of BehaviourSalma LyambilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 30 - Pituitary DrugsDokument3 SeitenCHAPTER 30 - Pituitary DrugsBre BistanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormones and BehaviourDokument16 SeitenHormones and BehaviourSushmit KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology: Topic - Endocrine System Class-VIII Board - ICSEDokument3 SeitenBiology: Topic - Endocrine System Class-VIII Board - ICSEItu DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questions: A. B. C. DDokument42 SeitenMultiple Choice Questions: A. B. C. DwanderagroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenLesson Planapi-247662207Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6-10 NCERT - BABA Science-Compilaton - CompressedDokument22 Seiten6-10 NCERT - BABA Science-Compilaton - Compressedsagartheshine666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pancreas: Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsDokument8 SeitenPancreas: Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsansahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ana 18.01.24Dokument24 SeitenAna 18.01.24alexandrunita763Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Action of Thyroid HormoneDokument4 SeitenMechanism of Action of Thyroid HormonejaleelkabdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes CHPTR 12Dokument14 SeitenBiology Notes CHPTR 12Wan HasliraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bartos Bubenik Kuzmova 2012 FBDokument17 SeitenBartos Bubenik Kuzmova 2012 FBYuki TanakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0764 Group 1 Magallanes, Maricris Manuel, Einna Milo, Juna Mogamog, Trisha Nacion, KaelaDokument5 Seiten0764 Group 1 Magallanes, Maricris Manuel, Einna Milo, Juna Mogamog, Trisha Nacion, KaelaCarrie Joy DecalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSC-CGL 2017 (PDFDrive - Com) PDFDokument152 SeitenSSC-CGL 2017 (PDFDrive - Com) PDFSumit PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hormone Reset Diet: Lose Up To 15 Pounds in 21 Days (Excerpt) - Maria ShriverDokument11 SeitenThe Hormone Reset Diet: Lose Up To 15 Pounds in 21 Days (Excerpt) - Maria ShrivermusatiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secondary MessengerDokument50 SeitenSecondary MessengerFlorlin Grace YradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whispering Between CellsDokument7 SeitenWhispering Between CellsOdessa FileNoch keine Bewertungen
- 359 - B.Sc-Zoology Semester V KUDokument12 Seiten359 - B.Sc-Zoology Semester V KURamya GoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Receent Syllabus of M.sc. Zoology - 19Dokument39 SeitenReceent Syllabus of M.sc. Zoology - 19abdul haseebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell CommunicationDokument25 SeitenCell Communicationprehealthhelp100% (12)
- Oral Physioloy Lecture 1 PDFDokument33 SeitenOral Physioloy Lecture 1 PDFHabeeb AL-AbsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation of Plasma Protein DisordersDokument10 SeitenInvestigation of Plasma Protein DisordersJosiah BimabamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Quarter ExamDokument7 Seiten3rd Quarter ExamHarold HusayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module QuestionsDokument11 SeitenModule QuestionszulkarnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Endocrine Glands, The Hormone They Secrete & Their FunctionDokument50 SeitenImportant Endocrine Glands, The Hormone They Secrete & Their FunctionSiva SubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 TH Science Practical Guide EM PDFDokument15 Seiten10 TH Science Practical Guide EM PDFSRI VISHNUNoch keine Bewertungen
- HL Paper3Dokument29 SeitenHL Paper3RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology II Final ExamDokument5 SeitenGeneral Biology II Final ExamMayar Hasan100% (1)
- Thyroid HormoneDokument396 SeitenThyroid HormoneuiliftengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Gland Review of SystemsDokument3 SeitenThyroid Gland Review of Systemssyderman999Noch keine Bewertungen