Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Human Resource Planning:: Determining The Organizational Objectives
Hochgeladen von
Adeel AhmedOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Human Resource Planning:: Determining The Organizational Objectives
Hochgeladen von
Adeel AhmedCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Human Resource Planning:
With the lapse of time changes do occur in organizations. But adapting to these changes requires all organizational members to understand where the organization is going and to support what the enterprise is about to do. We understand that before we can depart on a journey we have to know your destination. Suppose we have some holidays and we want to go for outing. First we have to decide where to go? Whether we have to go to Lahore or Islamabad, Murree or NathiaGali. This is we are deciding our destination. Secondly we have to decide how we have to go there mean by train, Daewoo, by air or by own car and we also apply some budget for it. This is what we can say all about planning. In simple words we can say that HRP is the systematic approach through which we assess the future human resource needs and determine the actions required to meet those needs. First challenge of HRP is to translate the organizational plans and objectives into a time schedule of employees requirements, after determining the employ requirements we have to device plans to for securing necessary employees. The long term success of any organization depends on having right people in the right jobs at right time. The organizational objectives and the strategies for achieving that objective are meaningful only when people with appropriate talents, skills, and desires are available to carry out those strategies. Effective HRP can also help to reduce turnover by keeping employees apprised of their carrier opportunities.
Steps in HRP Process
Determining the organizational objectives.
Objectives are actually written statements of expected results that are designed to give the organization and its members direction and purpose. For designing objectives we can also follow cascade approach. An objective setting process designed to involve all the levels of management in the organizational planning process. The objective setting process begins at the top of the organization with statement of mission, which defines the organizations current and future business. Long term objectives and strategies are formulated based on the organization mission statement. These can then be used to establish short term performance objectives. Short term performance objectives generally are time bounded and
expressed quantitatively. Divisional and departmental objectives are then derived from the organizations short term performance objectives. This approach leads to an upward and downward flow of information during planning. This also ensures that objectives are communicated and coordinated through all levels of organization.
Determining the skills and expertise required(demand)
After establishing organizational, divisional and departmental objectives, operating manager should determine the skills and expertise required to meet their respective objectives and to translate the needed skills and abilities into types and number of employees. Suppose an objective of production department is to increase total production by ten percent. Once this objective has been established, the production manager must determine precisely how this translates into human resource needs. A good starting point is to review and analyze current job descriptions. By doing this managers are in a better position to determine the skills and expertise to meet their objectives. Methods of forecasting human resource needs: Two methods are used for forecasting human resource needs, judgmental or mathematical. Judgmental methods: In this approach management make the decision for forecasting the demand on the basis of their accumulated judgment. This approach includes three methods Managerial estimates: In managerial estimates, managers estimate future human needs based on past experience. These estimates can be made by top level management and pass down. Delphi Technique: It is also judgmental approach. In this approach we forecast through panel of experts who make initially independent estimates of future demand. Then an intermediary presents each experts forecast to the other members of panel. Each
expert is then allowed to revise his forecast if required. This process leads to some mutual consensus. Scenario analysis:
Mathematical methods: Statistical methods use historical data to project the future demand. These Statistical methods are relatively more sophisticated and give more scientific results but these takes relatively more time than judgmental techniques. Some statistical methods are as follows Time series analysis. Personnel ratios. Productivity ratios. Regression analysis
Benchmarking: Despite of judgmental and mathematical approaches, there is another technique that is benchmarking. In this technique we thoroughly examine internal practices and procedures and measure them against the ways other successful organizations operate. A major advantage of benchmarking is that we aware some different new ways of doing things.
Determining Net human resource requirements:
Once the manager has determined the future demand, he analyzes these estimates in light of current and future human resource needs of the organization. Skills inventory: It is a profile of skilled human inventory which contain biographical data on all employees even at a simple lower level. Skills inventory is used as input into promotion and transfer decisions because it consists information about the versatile skills of employees, not just those relevant to the employees current job.
Management inventory: Management inventory is an extended form of skills inventory which contains information about managerial employees. In addition to biographical data management inventory also contains brief assessment of manager past performance and potential for advancement. Developing Action plans Once the net human resource requirements have been determined, managers must develop action plans for achieving the desired results. If the requirements are positive, the organization implements recruitment, selection, training and development. If the requirements are negative, human resource cost must be reduced through downsizing or through approaches that do not result in employees leaving the organization. Downsizing can be reduced through attrition, layoffs, termination, early retirements or voluntary resignation. Approaches that do not result in employees leaving the organization include reclassification, transfer or sharing.
Tools and techniques of HRP:
Many tools are available to assist the HRP process. One of which we have already discuss in determining the net human resource inventory, others will be discussed now. Succession planning: The technique that identifies specific people to fill future vacancies in key positions throughout the organizations. In this technique we before time plan for future by using replacement chart. A replacement chart is predetermined database chart that shows both incumbents and potential replacements for given positions within the organizations. Commitment manpower planning A systematic approach to HRP which is designed to get managers and their subordinates participating and involving in HRP. CMP generates three types of reports providing the following information.
The supply of the employees and their promotability and placement status. The organizations demand arising from new positions and turnover and projected vacancies. The balance or status of supply verses demand. Ratio Analysis: A tool in human resource planning to measure the organization human resource vitality by measuring the promotable personnel and their performance backup.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Module 5Dokument10 SeitenModule 5meet daftaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of HR Practices at Bank Alfalah and PepsiDokument37 SeitenComparison of HR Practices at Bank Alfalah and PepsiFaiSal MughalNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Chapter 2Dokument29 SeitenHRM Chapter 2mardyjanedahuyagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resource Planning Can Be Defined As A Process by Which An Organization Ensures That It Has The Right Number and Kinds of PeopleDokument35 SeitenHuman Resource Planning Can Be Defined As A Process by Which An Organization Ensures That It Has The Right Number and Kinds of PeoplekiranaishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Manpower Planning GuideDokument29 SeitenHRM Manpower Planning Guiderushikesh kambleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic HRP LessonDokument7 SeitenStrategic HRP LessonUsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Human Resource Planning ObjectivesDokument16 SeitenStrategic Human Resource Planning ObjectivesKristen CalderonNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR planning and competency mappingDokument7 SeitenHR planning and competency mappingRajni KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Module 2Dokument6 SeitenHRM Module 2soyoung kimNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Planning.1Dokument24 SeitenHR Planning.1Avro KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Lec 3Dokument38 SeitenHRM Lec 3ritish atttriNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSY 292 Human Resource Planning (1)Dokument25 SeitenPSY 292 Human Resource Planning (1)Sasha LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resource PlanningDokument38 SeitenHuman Resource PlanningTejas PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Strategic Human Resource Planning-1Dokument8 SeitenChapter 2 Strategic Human Resource Planning-1Nathaniel DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales ManagementDokument18 SeitenSales ManagementkunjapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resource Management - Unit 2 (B.com) - 2024Dokument19 SeitenHuman Resource Management - Unit 2 (B.com) - 2024Shrey BankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 Human Resource Planning (HRP) Human Resoucre Planning (HRP)Dokument9 SeitenCHAPTER 2 Human Resource Planning (HRP) Human Resoucre Planning (HRP)Belle Mendoza100% (1)
- HRP Lecture - Factors, Process & BarriersDokument38 SeitenHRP Lecture - Factors, Process & BarrierssuhaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 HRMDokument68 SeitenUnit 2 HRMakanshasrivastava557Noch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resources Planning ProcessDokument5 SeitenHuman Resources Planning ProcessAreeba ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Manpower PlanningDokument30 SeitenUnit 3 Manpower PlanningSmit ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of HRMDokument13 SeitenEssentials of HRMHimanshi YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resource Management - Unit 2 (B.com) - 2024Dokument26 SeitenHuman Resource Management - Unit 2 (B.com) - 2024Shrey BankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MB0043 - Human Resource Management: Assignment Set-1Dokument16 SeitenMB0043 - Human Resource Management: Assignment Set-1pandey_hariom12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resource PlanningDokument7 SeitenHuman Resource PlanningJasper DelacruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 3 (Human Resource Planning)Dokument16 SeitenCHAPTER 3 (Human Resource Planning)Akanksha Bisariya100% (2)
- 2.2 Human Resource Planning (HRP)Dokument12 Seiten2.2 Human Resource Planning (HRP)Priya BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Areas of Workforce PlanningDokument6 SeitenKey Areas of Workforce PlanningTejinder Singh BajajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 1 HR PlanningDokument11 SeitenUnit 2 1 HR PlanningAsfawosen DingamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument23 SeitenLecture 2ALIS VERİSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hrm-Human Resource PlanningDokument28 SeitenHrm-Human Resource PlanningMakrandDeouskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resource Strategy and PlanningDokument9 SeitenHuman Resource Strategy and PlanningTwiggey MaribaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 3 - HR Inventory PDFDokument15 SeitenUNIT 3 - HR Inventory PDFPurnima Singh67% (6)
- Outline - Demand Planning (Slide 14 Resource)Dokument6 SeitenOutline - Demand Planning (Slide 14 Resource)wootenr2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dmba106 - Human Resource ManagementDokument12 SeitenDmba106 - Human Resource ManagementSai Sneha KottapalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resource Planning: A Guide to the Key Concepts and ProcessesDokument27 SeitenHuman Resource Planning: A Guide to the Key Concepts and ProcessesgabisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER TWODokument10 SeitenCHAPTER TWOAbdu YaYa AbeshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manpower PlanningDokument12 SeitenManpower Plannings dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human ResourceDokument15 SeitenHuman ResourceMd.Ahsiqur Reza EfatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic HR PlanningDokument14 SeitenStrategic HR PlanningkarthikdhoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA Sem 3 AssignmentsDokument6 SeitenMBA Sem 3 AssignmentsRajini GrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid TermDokument16 SeitenMid TermPARAMESVARAN A/L SHAMUGOM (M23711277)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of HRMDokument10 SeitenEssentials of HRMmaazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To Human Resource Managementyasir habibNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Planning Forecasting Module 1 and Half of Module 2Dokument12 SeitenHR Planning Forecasting Module 1 and Half of Module 2Mich Albania100% (1)
- Mba Assignment HRDokument11 SeitenMba Assignment HRSandeep AcharekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process of Human Resource Planning - AssignmentDokument7 SeitenProcess of Human Resource Planning - Assignmentprincethomas147Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-3 PecmDokument8 SeitenUnit-3 PecmSusmitha AradhyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument31 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word Documentnvdp_singlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM General Model-CaramalesDokument3 SeitenHRM General Model-CaramalesCora CaramalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session # 3 HR PlanningDokument14 SeitenSession # 3 HR PlanningUsama UsamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Planning & Job Analysis ProcessDokument7 SeitenHR Planning & Job Analysis ProcessHassan ShakeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR's crucial role in strategic planningDokument5 SeitenHR's crucial role in strategic planningAnshu BhartiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning Happens Only When All The General Capabilities of The Employees Are Aligned With The Organization's Goals and ValuesDokument27 SeitenPlanning Happens Only When All The General Capabilities of The Employees Are Aligned With The Organization's Goals and ValuesUrbana Raquib RodoseeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 HRMDokument24 SeitenChapter 2 HRMMarc Franz R. BurceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of HRM NitinDokument9 SeitenEssentials of HRM NitinNageshwar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRKTG 24Dokument21 SeitenMRKTG 24archeilibaldemorNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Notes - 1 - 1Dokument294 SeitenHRM Notes - 1 - 1ZAKAYO NJONY100% (1)
- DocumentDokument92 SeitenDocumentGopi PrasnthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Name Student Number Assessment Title Module Title Module Code Module Coordinator Tutor (If Applicable)Dokument32 SeitenStudent Name Student Number Assessment Title Module Title Module Code Module Coordinator Tutor (If Applicable)Exelligent Academic SolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bamboo in AsiaDokument72 SeitenBamboo in Asiafitria lavitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diploma Engineer Question Paper-1Dokument1 SeiteDiploma Engineer Question Paper-1Nahid RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mediaplayer11 Text ResourcesDokument7 SeitenMediaplayer11 Text ResourcesRobert SchumannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affidavit in Support of ComplaintDokument3 SeitenAffidavit in Support of ComplaintTrevor DrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solaris 10 Service - (Management Facility (SMF: Oz Melamed E&M Computing Nov 2007Dokument18 SeitenSolaris 10 Service - (Management Facility (SMF: Oz Melamed E&M Computing Nov 2007Anonymous 4eoWsk3100% (3)
- Office of The Integrity Commissioner - Investigation Report Regarding The Conduct of Councillor Mark Grimes (July 05, 2016)Dokument44 SeitenOffice of The Integrity Commissioner - Investigation Report Regarding The Conduct of Councillor Mark Grimes (July 05, 2016)T.O. Nature & DevelopmentNoch keine Bewertungen
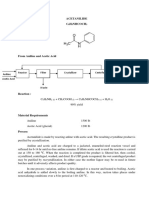
- Acetanilide C H Nhcoch: Aniline Acetic Acid Reactor Filter Crystallizer Centrifuge DryerDokument4 SeitenAcetanilide C H Nhcoch: Aniline Acetic Acid Reactor Filter Crystallizer Centrifuge DryerAnonymous 4hx84J3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trial Balance Entries ListingDokument3 SeitenTrial Balance Entries ListingIza ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 Ringgold County Fair EditionDokument16 Seiten2011 Ringgold County Fair EditionMountAyrRecordNewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 325W Bifacial Mono PERC Double Glass ModuleDokument2 Seiten325W Bifacial Mono PERC Double Glass ModuleJosue Enriquez EguigurenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABE College Manila. 2578 Legarda Avenue Sampaloc, ManilaDokument11 SeitenABE College Manila. 2578 Legarda Avenue Sampaloc, ManilaRonalie SustuedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Notes FOR Quantity SurveyorsDokument7 SeitenPractice Notes FOR Quantity SurveyorsYasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17th Edition OverviewDokument108 Seiten17th Edition OverviewJeremie Rameau100% (2)
- ArraysDokument36 SeitenArraysKAMBAULAYA NKANDANoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Payments in IndiaDokument6 SeitenDigital Payments in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Filmadora Panasonic Dvc20pDokument42 SeitenManual Filmadora Panasonic Dvc20pWilhan Jose GomesNoch keine Bewertungen
- HHF-1600 Direct-Drive Pump Utilization Parts ListDokument27 SeitenHHF-1600 Direct-Drive Pump Utilization Parts ListJohn Simanca100% (1)
- Hofa Iq Limiter Manual enDokument8 SeitenHofa Iq Limiter Manual enDrixNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCB, MCCB, ElcbDokument3 SeitenMCB, MCCB, ElcbMonirul Islam0% (1)
- Product Bulletin VHP7104GSI S5Dokument2 SeitenProduct Bulletin VHP7104GSI S5Wiliam SeguraNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New High Drive Class-AB FVF Based Second Generation Voltage ConveyorDokument5 SeitenA New High Drive Class-AB FVF Based Second Generation Voltage ConveyorShwetaGautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cave Management Plan OutlineDokument22 SeitenCave Management Plan OutlineJunneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying Social Engineering Attacks - Read World ScenarioDokument4 SeitenIdentifying Social Engineering Attacks - Read World Scenarioceleste jonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- En 12485Dokument184 SeitenEn 12485vishalmisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDokument1 SeiteNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternMarc Johnuel HumangitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm STP 855-Eb.1044238-1Dokument352 SeitenAstm STP 855-Eb.1044238-1Jayanta Mondal100% (1)
- Crusher RC Classic RC-II OM FN 23830 (En)Dokument128 SeitenCrusher RC Classic RC-II OM FN 23830 (En)julio cesarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopGearDokument188 SeitenTopGearbarborina10% (1)
- PfizerDokument4 SeitenPfizerliqu1dcourageNoch keine Bewertungen