Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ss7 Architechure
Hochgeladen von
Preeti SinghOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ss7 Architechure
Hochgeladen von
Preeti SinghCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
/wEPDwUKLTExM
Links Contact Us Calculators Charts Home
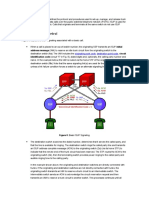
SS7 ISUP Network and Node Architecture
SS7 Network Architecture :
All nodes in a network may have different functions but they all must have necessary "within node" features to communicate using SS7. A node with SS7 within node features is known as SP (Signaling Point). All SPs in the SS7 network must be connected dedicated signaling channels or links.
Possible SPs in a SS7 Network :
- Switching Offices - OAM (Operational, Administrational and Maintenance) centers. Used in the management of SS7 network. Collecting statistics etc.
- SCP ( Service Control Point) is used to provide service to the network such as ANI, billing, 1-
800 number translations etc. It has a associated SSP (Switching Service Point) which is a dedicated STP and it's role is to send queries to SCP and recive replies from SCP. - STP (Signal Transfer Point) is used to concentrate signaling information from the switching office, switch messages in SS7 network, provide access to SCP. The nodes in the SS7 networks are connected via SLs (Signaling Links). Sometimes they are connected with more than one link and this time it's called LS (Link Set). the types of links between the nodes of the SS7 network are below : - A Link (Access Link) connect signaling end points such as offices, SCPs or STPs. - B Link (Bridge Link) connects different mated STPs. - C Link (Cross Link) connects members of a mated pair. - D Link connects local STP pair to regional STP pair. - E Link connects high traffic STP to an additional pair of STP. - F Link enables load sharing between SS7 offices, give extra redundancy and reliability.
SS7 Node Architecture :
SS7 is developed in a layered architecture like OSI model. It provides flexibility because changes can be made to one level without affecting the others. SS7 is a 4 Level Arthitecture : 3 of the 4 levels form MTP (Message Transfer Part) and the 4th level is the User Part. MTP : To provide reliable transport and delivery for messages. Messages from the User and Application part of an SS7 node are passed to the MTP. MTP then packages and delivers them accross the network. When a message is received MTP passes it to the destination, when a failure occurs, it detects and responds them. MTP corrosponds to the 3 OSI Layers . Physical, Data Link and Network layers On the other hand, SCCP (Signaling Connection Control Part) is introduced to enhance the message carriying facilities of MTP. The combination of MTP and SCCP forms the SS7 Network Services Part. SCCP provides some network layer protocol functions. The main users of SCCP are :
TCAP (Transcation Capabilities Application Part) to allow new applications to use SS7, communicating directly with SCCP services using nin-circuit related signalling. ISUP (ISDN User Part) and TUP (Telephone User Part) . ISUP is the most widely used one.
MTP Layer 1 protocol is called signaling data link. MTP Layer 2 is called signaling link and layer 2 packets are called signal units. The type of signal units are determined by it's LI (Length Indicator). There 3 tpes of signal units: MSU (Message Signal Unit), LSSU (Link Status Signal Unit), FISU (Fill in Signal Unit). MTP also detects and corrects the errors in transmission. It uses 2 types of errr correction procedures. Basic Error Correction where the signal units without bit errors are acknowledged. The signal units with bit errors are rejected and bad SU and all subsequent SUs are retansmitted. Preventive Cyclic Retansmission, there are acknowledgement but no rejection. After the timer expires if there is no acknowledgement then signal unit is retansmitted. Layer 2 also counts the errors and when count number reachs 64 then an indication is sent to upper layers for excessive error rates. MTP Layer 3 defines the signaling network functions. It transports the messages between the signaling points of the network. It handles messages and does network management. Also handles maintenance of signaling services, restoration of signaling conditions.
Internal Links
ISUP Messages What is SS7 and ISUP? What is Software Quality Assurance and Testing? What is Reliability? Terms and Concepts What is ISDN?
Conversions
Acceleration Area Base Numbers Calorie
Carbon Emission Circular/Angle Clothing/Shoe Size Computer Storage Cooking Currency Data Transfer Date/Time Density Electrical Energy/Work FlowRate Force Frequency Fuel Economy Heat Length/Distance Light Magnetic Power Pressure Radiation Sound Speed Temperature Torque Viscosity Volume Weight/Mass
2011 - Asknumbers.com. All rights reserved. Contact Us Privacy and Terms
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- SkyLock Product Description: Locate. Track. Manipulate. (January 2013)Dokument25 SeitenSkyLock Product Description: Locate. Track. Manipulate. (January 2013)LeakSourceInfo100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- 02 Sn2cvxzv010eu13sn 0002 System Overview EwsdDokument126 Seiten02 Sn2cvxzv010eu13sn 0002 System Overview Ewsdiboorose7Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- SS7MD PMDokument191 SeitenSS7MD PMAkhil GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Release 4 System OverviewDokument37 SeitenRelease 4 System OverviewGiorgi PapavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- 2600 19-3Dokument30 Seiten2600 19-3Derek P. MooreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Intro To SS7 Tutorial PDFDokument10 SeitenIntro To SS7 Tutorial PDFShravan SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Signalling in TelecommunicationDokument37 SeitenSignalling in Telecommunicationvpl_jhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Cdma zxc10 BtsDokument10 SeitenCdma zxc10 BtsghodkesmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Ewsd v16Dokument11 SeitenEwsd v16Eugen BleulerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- Lista de AcrónimosDokument7 SeitenLista de AcrónimosMitzy KathleenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oaa000009 Sigtran Protocol Issue2.0-20051111-ADokument37 SeitenOaa000009 Sigtran Protocol Issue2.0-20051111-AFranceNoch keine Bewertungen
- HIP2018 Sergey Puzankov Mobile Operators Vs HackersDokument60 SeitenHIP2018 Sergey Puzankov Mobile Operators Vs HackersOussama KammounNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- 01-SS7 Signaling SystemDokument128 Seiten01-SS7 Signaling SystemadeepcdmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Keygoe SS7Dokument61 SeitenKeygoe SS7Pritam Kumar SatapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- 1590 1122 01 VoIP BookletDokument13 Seiten1590 1122 01 VoIP Bookletapi-38076000% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- IS-41 SS7 SignalingDokument14 SeitenIS-41 SS7 SignalingqqqtttNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Layer Q and X ProtocolDokument46 SeitenLower Layer Q and X ProtocolSead KurtovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- IV ECE ESS Question BankDokument3 SeitenIV ECE ESS Question BankVeerayya JavvajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cti Buyers Guide 1996Dokument137 SeitenCti Buyers Guide 1996Pon KamaleshNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM questions on channels, quality, calls and dropsDokument11 SeitenGSM questions on channels, quality, calls and dropsalonindNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- S01 SCCP Signalling SDDokument24 SeitenS01 SCCP Signalling SDVimal Odedra100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Report On Digital Switching SystemDokument20 SeitenReport On Digital Switching SystemKurban UbulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtaul Media Gateway & MSC Pool ConceptDokument52 SeitenVirtaul Media Gateway & MSC Pool ConceptRajesh PorwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sigtran Ss7: Asri WulandariDokument44 SeitenSigtran Ss7: Asri WulandarifaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Sigtran Protocols-M3ua M2paDokument9 SeitenSigtran Protocols-M3ua M2paJawahar SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Series Completion Service: Mode of OperationDokument4 SeitenGlobal Series Completion Service: Mode of OperationEugen BleulerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skylock Product Description 2013 PDFDokument25 SeitenSkylock Product Description 2013 PDFCekidot GanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isup Call FlowDokument24 SeitenIsup Call Flownitish8102363eceNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- 03 Sn2073eu01sn 0002 Admin DN Subs PBXDokument66 Seiten03 Sn2073eu01sn 0002 Admin DN Subs PBXletiendungbktNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIGTRAN Analysis and SimulationDokument45 SeitenSIGTRAN Analysis and SimulationJesus Choque EchevarriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)