Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Xid-2025857 1
Hochgeladen von
Thanh NguyenOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Xid-2025857 1
Hochgeladen von
Thanh NguyenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
E-Switching Case Study, v5.3.
1a
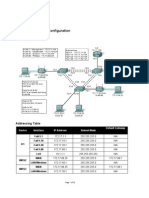
VLANs, Wireless, Router & Switch Configuration PHASE I IP Addressing and VLANS
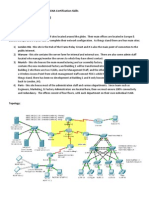
The Carl I. Samson Company (C.I.S. Co) of Bangor, Maine has recently been acquired by CorpHQ in Detroit Michigan. Prior to the merger C.I.S. Co had been running a RIP based network with an IP address of 169.254.40.0/21 equally sub-netted to support their users in Phoenix, Chicago and Bangor. CorpHQ requires that all subsidiaries use the company standard EIGRP as a routing protocol. Additionally CorpHQ has allocated the network address of 172.25.64.0./20 for the internal networks in the C.I.S. Co division. Internet access for the C.I.S. Co LAN is through the Border Router that is part of the Bangor LAN. The C.I.S. Co. IT Director wants to more efficiently allocate IP addresses and consequently has implemented Variable Length Subnet Masking. They have implemented trunked Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) to streamline cabling and switch-port allocation, which allows easier moves, adds and changes in the network while increasing security. Your job is to configure all of the routers, switches, Access points, and PCs to support the new design. Refer to Table 1 for a breakdown of the assigned networks and VLANS, and the network diagram for the new network topology.
Table 1 IP Addresses
Subnet Address Subnet Mask # of Hosts Needed Phoenix 50 150 75 5 50 12 Chicago 90 10 9 Bangor 1024 125 275 100 12 WAN Links 5 2 2 2 Network Assignment Summary Route PHX-LAN1 PHX-LAN2 PHX-LAN3 PHX-WIFI-LNK PHX-WIFI PHX-MGMT Summary Route CHG-LAN1 CHG-LAN2 CHG-MGMT Summary Route BAN-LAN1 BAN-LAN2 BAN-WIFI BAN-MGMT BAN-BRDR PHX-BAN PHX-CHG CHG-BAN VLAN Assignment n/a 110 LAN1 120 LAN2 130 LAN3 140 WIFI n/a 100 MGMT n/a 210 LAN1 220 LAN2 200 MGMT n/a 310 LAN1 320 LAN2 330 WIFI 300 MGMT 500 BAN-BRDR n/a n/a n/a
172.25.65.192
/26 255.255.255.192
172.25.72.128
/28 255.255.255.240
172.25.68.0
/22 255.255.252.0
172.25.70.128
/25 255.255.255.128
192.168.100.40 192.168.100.48 192.168.100.52 192.168.100.56
/29 /30 /30 /30
255.255.255.248 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252
Case Study VLANS, Wireless, Router & Switch Configuration
Page 2 of 5
Diagram 1 Network Topology
Last updated: 1/15/2011
Case Study VLANS, Wireless, Router & Switch Configuration
Page 3 of 5
PHASE II - Router Configuration
The following table outlines the configuration tasks you need to perform on the routers in the topology. Where specific configurations are required they are noted below; otherwise it is to your discretion which names and/or addresses you will use.
Configuration
Console password use cisco Enable Password use class Device name Banner use Any text Create a username of guest with a password of cisco Set the Domain name to cisco.com Set the DNS server as indicated in the Network Diagram Configure all interfaces and sub-interfaces as appropriate using the information provided in Table 1 and the network diagram with the following: -Descriptions -IP addresses (1st available address in range) -Subnet masks -Encapsulations and VLAN assignments -Clock rates (Were necessary) -Bandwidths Configure EIGRP routing using AS 100 Disable automatic summarization and enter network statements for each directly connected subnet Passive interfaces and sub-interfaces
Phoenix Router
X X PHX-RTR X X X X
Chicago Router
X X CHG-RTR X X X X
Bangor Router
X X BAN-RTR X X X X
Border Router
X X BRDR-RTR X X X X
Use VLAN 199 as the native VLAN
Use VLAN 299 as the native VLAN
Use VLAN 399 as the native VLAN
Do not use subinterfaces on this router
X X All workstation LANS & WiFi Link Send summaries on S0/0 & S0/1 No static routes X
X X All workstation LANS Send summaries on S0/0 & S0/1 No static routes X
X X All workstation LANS Send summaries on S0/0. S0/1 and F0/0.500 No static routes X
X X (Not S0/0) S0/0 is passive
Create EIGRP summary routes for PHX, CHG and BAN and send them out their Serial links. A summary route for all the CISco LAN should be sent from the BAN-RTR to the BRDR-RTR.
n/a
Assign Static routes Enable SSH
Default route out S0/0 and propagate using EIGRP X
Configure the Phoenix wireless router with internet and network IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS servers. Set the SSID to Phoenix with no encryption. The Bangor wireless access point has an SSID of Bangor and no encryption. The Bangor wireless laptop has already been configured with an IP address but needs an SSID.
Last updated: 1/15/2011
Case Study VLANS, Wireless, Router & Switch Configuration
Page 4 of 5
PHASE III - Switch & Access Point Configuration
The following table outlines the configuration tasks you need to perform on the switches in the topology. Where specific configurations are required they are noted below; otherwise it is to your discretion which names and/or addresses you will use.
Configuration
Console password use cisco Enable Password use class Device name Banner use Any text Disable IP domain lookup Configure trunks as indicated in the diagram VTP version 2 VTP domain & password Define VLANS as indicated in Table 1 Assign VLANs as indicated in the diagram. NOTE: assign ports on either side of a connected port to the same VLAN Enable port security with a maximum of 25 MAC address per port. Include descriptions. Management VLAN with IP address, mask, description, default gateway Enable telnet with a password of cisco Set as Spanning-Tree root for the indicated VLANs
Phoenix SW1
X
Phoenix SW2
X
Phoenix SW3
X
Chicago SW1
X
Bangor SW1
X
Bangor SW2
X
Bangor SW3
X
X PHX-SW1 X X Native VLAN 199 Server Domain: VTP-PHX Password: cisco X
X PHX-SW2 X X Native VLAN 199 Client Domain: VTP-PHX Password: cisco n/a
X PHX-SW3 X X Native VLAN 199 Client Domain: VTP-PHX Password: cisco n/a
X CHG-SW1 X X Native VLAN 299 Server Domain: VTP-CHG Password: cisco X
X BAN-SW1 X X Native VLAN 399 Server Domain: VTP-BAN Password: cisco X
X BAN-SW2 X X Native VLAN 399 Client Domain: VTP-BAN Password: cisco n/a
X BAN-SW3 X X Native VLAN 399 Client Domain: VTP-BAN Password: cisco n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
110, 140
100, 120
130
210, 220
300, 310
320
330
Last updated: 1/15/2011
Case Study VLANS, Wireless, Router & Switch Configuration
Page 5 of 5
PHASE IV Host Configuration
Configure all workstations and servers with appropriate IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS servers. Where appropriate also set the SSID. Note: The Phoenix wireless clients will use DHCP from the Phoenix wireless router.
PHASE V - Test
Confirm that all workstations, routers, and switches can ping each other, their local default gateways and the Internet addresses of www.cisco.com and www.msn.com. Confirm that workstations can SSH to the routers and telnet to the switches.
PHASE VI Documentation & Presentation
Document the network to include: Project Description IP Scheme Running configurations IP route output VLAN assignments
Last updated: 1/15/2011
Case Study VLANS, Wireless, Router & Switch Configuration
Page 6 of 5
Grading Rubric
VLSM IP Addressing, Trunking VLANs, Router & Switch Configuration
Objective Configurations for all routers: Interfaces, sub-interfaces, IP addresses, passwords, banners, descriptions, hostnames Routing protocol and static routes Default Routes to the Internet All other configurations as indicated Configurations of all switches: Hostnames, passwords, banners, descriptions Trunk links configured At least 3 ports assigned for each VLAN Management VLAN All other configurations as indicated Configurations of all hosts: IP addresses Subnet masks DNS servers Default Gateways Documentation of the Network. Presentation: A 5-minute PowerPoint presentation on one aspect of the solution. Your instructor will provide you with the topic. Possible topics might include: Inter-switch Trunking Router-on-a-stick WAN routing Configuring switch management Wireless router configuration Creating VLANs with VTP Spanning-tree Phase Points Completed
II
25
III
25
IV
25
VI
25
Final
25
TOTAL POINTS =>
125
Last updated: 1/15/2011
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CCNA Challenge QuestionDokument7 SeitenCCNA Challenge Questionfarmd684Noch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 3 Case Study Spring 2022Dokument7 SeitenCCNA 3 Case Study Spring 2022Mohammed El-SaadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA2 Case Study 2022Dokument6 SeitenCCNA2 Case Study 2022Mohammed El-SaadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- VXLAN Deployment - Use Cases and Best PracticesDokument76 SeitenVXLAN Deployment - Use Cases and Best PracticesMalesPulangNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESwitching Lab 7 5 2 Brent v2.1Dokument11 SeitenESwitching Lab 7 5 2 Brent v2.1Surapich ChairgulprasertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuración y Resolución de Problemas Del Servicio de Telefonía Cisco IOS (ITS)Dokument26 SeitenConfiguración y Resolución de Problemas Del Servicio de Telefonía Cisco IOS (ITS)Richard BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Sous Gns3-Configuring A Site-To-Site Ipsec VPN Using CCP and AsdmDokument31 SeitenLab Sous Gns3-Configuring A Site-To-Site Ipsec VPN Using CCP and Asdmaboubakeriam djibirldararNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pid (HBL) For Asa, CSC & CSMDokument100 SeitenPid (HBL) For Asa, CSC & CSMapi-3733153Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeDokument15 Seiten3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeANDRESSRCONoch keine Bewertungen
- PT Ccna TasksDokument6 SeitenPT Ccna TasksAnn LleideneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.3.3.2 Lab - Troubleshoot LAN Traffic Using SPANDokument6 Seiten5.3.3.2 Lab - Troubleshoot LAN Traffic Using SPANYaser Samer0% (6)
- 3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - ILMDokument6 Seiten3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - ILMElectronica EdwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sonicwall - Network Behind Router - Adding Static RoutesDokument4 SeitenSonicwall - Network Behind Router - Adding Static RoutesAnoj DixitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packet Tracer - CCNA Skills Integration Challenge: TopologyDokument7 SeitenPacket Tracer - CCNA Skills Integration Challenge: TopologymianarguNoch keine Bewertungen
- LabsDokument35 SeitenLabsznabugrmay20adiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 2 v5.0 Final Exam AnswersDokument17 SeitenCCNA 2 v5.0 Final Exam AnswersziriusnakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.8.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - InstructorDokument11 Seiten10.8.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - InstructorMichael oliverosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenge Wireless Configuration: Topology DiagramDokument23 SeitenChallenge Wireless Configuration: Topology Diagramsteen919Noch keine Bewertungen
- ESwitching Student Lab Skills Based AssessmentDokument4 SeitenESwitching Student Lab Skills Based AssessmentJessica Carol OwensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step 4: Step 5: Step 6:: Table 72 Private DMZ Firewall Network ObjectsDokument20 SeitenStep 4: Step 5: Step 6:: Table 72 Private DMZ Firewall Network ObjectsPriscila FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVD IWANDesignGuide FEB16 13Dokument20 SeitenCVD IWANDesignGuide FEB16 13Priscila FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB 4 - Create Server Farm Prototype To Test RSTP PDFDokument6 SeitenLAB 4 - Create Server Farm Prototype To Test RSTP PDFvigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDokument7 Seiten4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPLeo Leo17% (6)
- Huawei Training Day 1 NotesDokument28 SeitenHuawei Training Day 1 NotesMutumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.3.2.3 Lab - Implement Local SPANDokument7 Seiten5.3.2.3 Lab - Implement Local SPANcrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei AR 160 Series Configuration.Dokument15 SeitenHuawei AR 160 Series Configuration.Ojijo Kevin100% (3)
- Ccna 2.3Dokument40 SeitenCcna 2.3Prayudha LazuardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5300xl Ospf Singlearea PDFDokument9 Seiten5300xl Ospf Singlearea PDFNesta FaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA ReviewDokument375 SeitenCCNA ReviewEmanuel GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.3.2.3 Lab - Implement Local SPAN (Satinder Singh) PDFDokument6 Seiten5.3.2.3 Lab - Implement Local SPAN (Satinder Singh) PDFSatinder SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configure ACI Multi-Site Deployment: RequirementsDokument16 SeitenConfigure ACI Multi-Site Deployment: RequirementscoolboyasifNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESwitching Student Lab Skills Based Assessment Answer KeyDokument16 SeitenESwitching Student Lab Skills Based Assessment Answer Keytroit100% (10)
- CCNA3 ProjectDokument9 SeitenCCNA3 ProjectMalik HaroonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESwitching Lab 7 5 2Dokument23 SeitenESwitching Lab 7 5 2Ninja NuggetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Training Ppt1Dokument277 SeitenNetwork Training Ppt1aravindanjulie100% (1)
- HRRPDokument7 SeitenHRRPJavier CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 3Dokument22 SeitenFinal 3Tạ Thịnh PhátNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Packet Tracer StatementDokument7 SeitenCisco Packet Tracer StatementPrawesh AcharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UCF All QuestionsDokument132 SeitenUCF All Questionshimanshu joshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFDokument8 Seiten9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFEl Amrani MoutiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity - 8 6 1Dokument7 SeitenActivity - 8 6 1Licitaciones GerelcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccnasv1.1 Chp10 Lab D Asa Isr s2s VPN StudentDokument36 SeitenCcnasv1.1 Chp10 Lab D Asa Isr s2s VPN Studentmuscle260% (1)
- Example Templates CCNADokument5 SeitenExample Templates CCNAjuboysabulaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityVon EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityNoch keine Bewertungen
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksVon EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNoch keine Bewertungen
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkVon EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewVon EverandCisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- Ethernet Networks: Design, Implementation, Operation, ManagementVon EverandEthernet Networks: Design, Implementation, Operation, ManagementBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsVon EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationVon EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Von EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network Infrastructure and Architecture: Designing High-Availability NetworksVon EverandNetwork Infrastructure and Architecture: Designing High-Availability NetworksNoch keine Bewertungen
- VCD 90 Admin Guide PDFDokument235 SeitenVCD 90 Admin Guide PDFGheorghe GeorgelNoch keine Bewertungen
- OptiX OSN 550 Configuration Guide (V100R003)Dokument470 SeitenOptiX OSN 550 Configuration Guide (V100R003)Thunder-Link.com100% (3)
- OS6450 AOS 6.6.3 R01 Hardware GuideDokument140 SeitenOS6450 AOS 6.6.3 R01 Hardware GuideBesugoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cấu Hình Ring l2 Về 2 Upe Của Vnpt Nghệ AnDokument23 SeitenCấu Hình Ring l2 Về 2 Upe Của Vnpt Nghệ AnHoàng Tuấn NgọcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Examination - Spring 2021 Semester Sajid Ali - 40760: Faculty of Engineering, Sciences and TechnologyDokument4 SeitenFinal Examination - Spring 2021 Semester Sajid Ali - 40760: Faculty of Engineering, Sciences and TechnologyAtec TeamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mtorrent: A Multicast Enabled Bittorrent ProtocolDokument63 SeitenMtorrent: A Multicast Enabled Bittorrent ProtocolTuyet TamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ForeScout Company BrochureDokument6 SeitenForeScout Company BrochureSyed ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- College NetworkDokument19 SeitenCollege NetworkSankalp SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlvariSTAR 4motion Device Manager Ver.2.5.2 User Manual 090909Dokument360 SeitenAlvariSTAR 4motion Device Manager Ver.2.5.2 User Manual 090909Jones BettoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Routeros MikrotikDokument448 SeitenRouteros MikrotikcrismajoviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer: DDokument478 SeitenAnswer: DDragan KneževićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paloalto Lab Part 1 2019Dokument39 SeitenPaloalto Lab Part 1 2019Quang Anh100% (1)
- Red Hat Openstack Platform-16.2-High Availability Deployment and Usage-En-usDokument59 SeitenRed Hat Openstack Platform-16.2-High Availability Deployment and Usage-En-usabc abcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Superlab Cisco IDN Competition 2017Dokument22 SeitenSoal Superlab Cisco IDN Competition 2017wizgoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVM Lab 04Dokument4 SeitenCVM Lab 04AdedayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skypilot Network Administration GuideDokument288 SeitenSkypilot Network Administration GuideMatt HonanNoch keine Bewertungen
- U2000 FTTH Predeployment Technical GuideDokument26 SeitenU2000 FTTH Predeployment Technical GuideGeorgios S. TsolisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae of Nasim Ahmed: ObjectiveDokument2 SeitenCurriculum Vitae of Nasim Ahmed: Objectiveশেষের কবিতাNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security PDFDokument251 SeitenSecurity PDFEdison Caiza0% (1)
- The Switch Book: The Complete Guide To LAN Switching Technology (Book Review)Dokument2 SeitenThe Switch Book: The Complete Guide To LAN Switching Technology (Book Review)ravindra reddy AvuduriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deploying NetScalerVPX On OCI - KVM On BM - v0.3Dokument49 SeitenDeploying NetScalerVPX On OCI - KVM On BM - v0.3Adrian Alexandru BirzuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco 7000 NX-OS 4.2Dokument36 SeitenCisco 7000 NX-OS 4.2Salis AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Eth-Trunk Istack and CSSDokument29 Seiten07 Eth-Trunk Istack and CSSJasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundry FastIron User GuideDokument814 SeitenFoundry FastIron User GuideKam Bing OeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 640-802 CCNA® Exam Topics (Blueprint)Dokument6 Seiten640-802 CCNA® Exam Topics (Blueprint)AXRISTEASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switch Al Cat ElDokument8 SeitenSwitch Al Cat ElAgus YulfizarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN RoutingDokument5 Seiten5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN RoutingNery Cifuentes0% (1)
- Ip-Vlan Planning For Routed Access DesignDokument5 SeitenIp-Vlan Planning For Routed Access DesignrngwenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Link Trunking in Dell EMC OS10 Enterprise Edition: Reference ArchitectureDokument49 SeitenVirtual Link Trunking in Dell EMC OS10 Enterprise Edition: Reference Architecturelyax1365Noch keine Bewertungen