Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Learn
Hochgeladen von
Aya ElkerdanyOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Learn
Hochgeladen von
Aya ElkerdanyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
How to make E1ABS
models
Email . engmmkhotmail.com
Tel . 2/012/6227563
Note : for intermediate student in computer program not beginner
Please any note call me to discuss it .
Exampl
e :
Our example
residential
building
consist of 20
story need to
make
ANALYSIS &
DESIGN with
ETABS
program :
we choose default oI program
$tarting ETAB$.
At start convert unit to the unit you work with
From file list new model we get this massage
efine the Grid.
en c48e default t8
wnd4w appear8
choose grid only
in our example
number of stories 20
story height 3m
units kN N
#lan view / 3D view.
our screen should
show one window
with a grid plan view
oI your model and one
window with a grid
3D view oI your
model.
Make sure the KN-M
is selected as your
units in the lower right
hand side oI the
window.
Now is a good time to
save your model, so
click on the File/Save
and Iind a suitable
location Ior your Iile.
Now import your DXF file from *file / import / DXF floor plan
Choose your file and open it
Choose layers to
each element
(beams ,floors
,etc..)
Choose the story you insert
DXF in it
efine the Materials.
Next, we will deIine the
materials used in the model.
Concrete & 6 grade will
be used.
The two materials will be
deIined in successive steps.
Click Material Properties.
Irom the DeIine pull down
menu.
Click Add New Material.
For concrete 40 N/mm
Type C4 Ior the Material
Name.
Select Isotropic Ior the Type
oI Material.
Type 2.5 Ior the Mass per
unit Volume.
Type 25 Ior the Weight per
unit Volume.
Type 28E Ior the Modulus
oI Elasticity.
Type .2 Ior Poisson`s Ratio.
Type 9.9E- Ior the
CoeII oI Thermal Expansion.
Select Concrete Ior the Type
oI Design.
Type 4 Ior I`c.
Type 4 Ior Iy
Type 4 Ior Iys.
Click OK
For concrete 60 N/mm
The diIIerence here
Modulus oI elasticity equal
.2(grade ) + 2 32
efine the columns.
Next, we will deIine the
concrete columns used in the
model. 25x80 cm columns
will be used.
The two concrete materials
deIined in the previous step
will be used to deIine the
columns.
Click efine/Frame
Sections. Irom the pull
down menu.
Select Add Rectangular.
efine the 25x80 Cm column.
Type C25X8C6 as the
Section Name.
Select C6 as the
Material.
Type .8mIor the Depth.
Type .25m Ior Width.
Click OK.
Cracked 8ect4n
de8gn
efine the $hear walls.
Next, deIine the concrete shear
walls used in the model.
C shear walls will be used.
The concrete material deIined
earlier in the tutorial will be
used to deIine the shear walls.
Click Wall/Slab/eck
Sections.Irom the efine
pull down menu.
Select Add Aew Wall Irom the
Click to: menu.
efine the C60 shear wall.
Type 25C6 as the Section Name.
Select C6 as the Material.
Type .25 Ior the Membrane Thickness.
Type .25 Ior the Bending Thickness.
Select Sell as the Type.
Click OK.
Cracked 8ect4n
de8gn
efine the slab.
Next, deIine the concrete slabs
used in the model.
C4 slabs will be used.
Click Wall/Slab/eck
Sections.Irom the efine
pull down menu.
Select Add Aew slab Irom the
Click to: menu.
efine the slab 22 cm post tension C40.
Type S22CMPT as the Section Name.
Select C as the Material.
Type .22 Ior the Membrane Thickness.
Type .22 Ior the Bending Thickness.
Select Sell as the Type.
Click OK.
Imp4rtant n4te:-
Te 8lab 8 p48t ten84n 84
tere 8 n4 cracked 8ect4n
de8gn tat mean n4
m4dfer8
Assigning slab section
Select the slab
Click wall/8lab/deck 8ect4n Irom
8ell/area From a88gn menu.
Select S22CMPT.
Click OK.
rawing & assigning column and shear wall
First drawing column
Select the point u want to be a column
Click trude p4nt8 t4 lne8 Irom
dt menu.
Type -3 Ior dz.
Click OK.
Assigning column section
Select the column
Click rame 8ect4n Irom frame/lne
From dt menu.
Select C258.
Click OK.
$econd drawing shear wall
Select the lines u want to be a shear
wall
Click trude lne8 t4 Area8 Irom
dt menu.
Type -3 Ior dz.
click Delete S4urce Object8.
Click OK.
Assigning shear wall section
Select the shear wall
Click wall/8lab/deck 8ect4n Irom
8ell/area From a88gn menu..
Select 25C6.
Click OK.
Save y4ur m4del.
Assigning Biers for wall sections
Select the shear wall each part alone
II the shear wall consist oI HZ & VL
part (core) select HZ alone and VL
alone
Click per label Irom 8ell/area Irom
a88gn menu
Write name P1 then click add new
name then 4k
Do that Ior all walls HZ or VL
Te name appear8 4n te
wall
Each wall appears its name on it
Edit the story data and relationships.
Now, set up the story
relationship to aid us in the
development oI the model.
Relationships between stories
are used to eIIiciently draw
elements on similar stories.
Select dt St4ry Data Irom
the Edit pull down menu.
Continue to edit the story data and relationships.
Set STORY 1 as a
Master Story by
selection es Irom the
Master Story Column.
Set ALL STORIS as
similar to STOR.
Click OK
Activate the $imilar $tories Command.
Now activate the Similar Stories Command so that elements
drawn on the master stories will be automatically drawn on
similar stories .
Select Smlar St4re8 Irom the pull down menu located near
the bottom right hand corner oI the ETABS screen.
$et the Building Jiew Options. $et the Building Jiew Options.
Now is a good time to save your model, so click on the
le/Save.
Now adjust the model to view options.
Select the Set Buldng Vew Opt4n8.Irom the View
pull down menu.
Click the Object ll and tru84n check boxes.
Click OK.
Assigning slab loads
Click 8tatc l4ad ca8e From Defne menu..
Select slabs
Click &nf4rm From Sell/area l4ad8 From
A88gn menu..
Load Case Name Dead
Load 5
Direction Gravty
Load Case Name Lve
Load 3
Direction Gravty
Reselect slabs and click uniIorm surIace loads
- Select floor area
Click dapragm8 Irom 8ell/area Irom
a88gn menu
Add new dapragm then write D2 then
4k the shape oI diaphragm appears
Making diaphragm
Select all restraint
Click re8trant8 (8upp4rt8 Irom
j4nt/p4nt Irom a88gn menu
Choose free re8trant
Now good time to save your model
This step Ior replcatng
!cn zu gczrq
un n n nn
rplinz zu cl
Click icon all to choose all members
#eplicating the story
Click replcate Irom edt menu
Choose 8t4ry then select stories u want to
replicate in Ior example in our model
select Irom story 2 to 20 then click 4k
3 Model Jiew
The 3D view oI your model should have
extruded Iilledin elements.
Sometimes view changes are not updated
automatically. ou may have to save the
Iile and exit ETABS. Then restart
ETABS to get the updated view.
Now is a good time to save your model,
so click on the le/Save.
Analysis And Design
De8gn 4pt4n
Click c4ncrete frame de8gn
Change ACI 38-99 to BS81197
De8gn 4pt4n
Click 8ear wall de8gn
Change &BC 97 to BS81197
Change rebar unt Irom n^2 to mm^2
Change rebar/lengt unt Irom
n^2/ft to mm^2/m
Ca8e 4f l4adng f4r 8e8mc and wnd
Click 8tatc l4ad ca8e Irom defne menu.
Make a new case named QX type quake
selI weight auto lateral load &BC 97
1 1- - 8e8mc l4ad (8tatc 8e8mc l4ad (8tatc
Click m4dfy lateral l4ad.
Ct .2
Over strength factor R 5.5
Zone factor .15
Importance factor 1
* To know more about time period see UBC -
1630-2 static force procedure page 2-14
chapter 16
R numerical coefficient representative of the
inherent over strength and global ductility
capacity of lateral force resisting system
table (16-N) (16-P) pages (2-32) (2-34)
UBC chapter 16
Click 8tatc l4ad ca8e Irom defne menu.
Make a new case named QY type quake
selI weight auto lateral load &BC 97
Click m4dfy lateral l4ad.
Ct .2
Over strength factor R 5.5
Zone factor .15
Importance factor 1
NOTE : we do cases -QX & -
QY when the structure is not
symmetric
Click 8tatc l4ad ca8e Irom
defne menu.
Make a new case named
X type wnd selI weight
auto lateral load BS 6399-
95
Click m4dfy lateral l4ad.
22- - wnd l4ad wnd l4ad
Click 8tatc l4ad ca8e Irom
defne menu.
Make a new case named
X type wnd selI weight
auto lateral load BS 6399-
95
Click m4dfy lateral l4ad.
Change wnd angel drect4n
9
11- - 8e8mc l4ad (dynamc8 8e8mc l4ad (dynamc8
Click re8p4n8e 8pectrum funct4n Irom defne menu.
Click add &BC 97 8pectrum
Put Ca & Cv Irom UBC tables
At pages 234 , 235 chapter
Ca .18
Cv .25
Click re8p4n8e 8pectrum
ca8e8 Irom defne menu.
Add new 8pectrum
Scale factor 9.81/(R5.5)
" Eccentricity .5
Click Add new 8pectrum
Scale factor 9.81/(R5.5)
" Eccentricity .5
AO1E AO1E :
U2 for Y case & U1 for X case
Any FORCE equal
MASS ACCELERA1IOA
So we need to get mass
source
Click ma88 84urce Irom
defne menu .
Mass deIinition fr4m l4ad8
Load Dead multiplier 1 I
re8dental 8tructure lve le88
tan 5 kn/m^2
e ncrea8e ca8e 4f lve I
lve > 5 kn/m^2
Load lve multiplier .5
(c4mmercal buldng
#emove EL Z
Number of iteration from to 5 seIect 3
Now u can run the
model and see
your result
- Deformation according to
dead load case
Time period is very important
$upport reaction
Click support/spring
reaction from show
member force stress
diagram from dispIay
menu
-Choose the case u need
reaction in it
Click
rame/pier/spandreI
forces
from show member force
stress diagram from
dispIay menu
Frame/pier forces
If you need pier forces cIick pier
Click $heII
stresses/forces from show
member force stress
diagram from dispIay
menu
$hell stresses/forces
Before resuming design we must careful some point
1-The last mode must reach percentage more than 90%
How to check that?
Click show tabIes from
dispIay menu
$elect table modaI participation mass ratio
The last mode must reach or more than
f modes not enough increase it from dynamic analysis parameter
form set option from analysis menu
1-The base shear from dynamic analysis must equal base
shear from static analysis
How to do that?
Click show tabIes from
dispIay menu
$elect table story shear
$elect cases of seismic analysis
By diving Qx/$PECx factor is (6469/4200) 1.54
By diving Qy/$PECy factor is (6469/4043) 1.6
1.7818*1.54 2.743972
1.7818182*1.6 2.85090912
Now we can design with dynamic results
Concrete design
$hear wall design
Note : DCON15 to DCON26 removed
because its cases for static analysis in
concrete and shear wall design and
we use dynamic analysis in design
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Design of Structural Decking System For PDFDokument86 SeitenDesign of Structural Decking System For PDFVengatesh HariNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Femap-154 508Dokument388 SeitenFemap-154 508acupatee100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Loadings - NSCP 2015 - 2 Storey Residential Concrete Structure1Dokument52 SeitenLoadings - NSCP 2015 - 2 Storey Residential Concrete Structure1Renvil PedernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sustainable Bridge StructuresDokument331 SeitenSustainable Bridge StructureskesharinareshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Built Up Rates (Drainage)Dokument6 SeitenBuilt Up Rates (Drainage)Julian KitingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Cube TestDokument6 SeitenConcrete Cube TestMd. Mynul HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Arch BridgeDokument6 SeitenConcrete Arch BridgeSubhashree VenkateshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab BridgeDokument10 SeitenSlab BridgeGolam Mostofa50% (2)
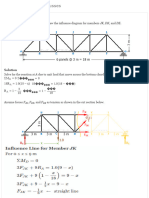
- Influence Lines For Trusses - Structural Analysis Review at MATHalinoDokument4 SeitenInfluence Lines For Trusses - Structural Analysis Review at MATHalinofasih_baqai4252Noch keine Bewertungen
- EJOT Application Poster Roofing Cladding ENDokument1 SeiteEJOT Application Poster Roofing Cladding ENJohn SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- T5 CalculationsDokument14 SeitenT5 CalculationsMatAlengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design: Structural ElementsDokument8 SeitenDesign: Structural ElementsIMJ JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progress Report: Large-Scale Tests of A Low-Rise Unreinforced Masonry Building SystemDokument330 SeitenProgress Report: Large-Scale Tests of A Low-Rise Unreinforced Masonry Building SystemJalal KeNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Drift Limits Associated With Different Damage Levels: June 2004Dokument13 SeitenOn Drift Limits Associated With Different Damage Levels: June 2004RaviKanthSrivastavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ugalde (Two Storey Estimate)Dokument17 SeitenUgalde (Two Storey Estimate)Philip Joshua MalitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of ProppingDokument16 SeitenCalculation of ProppingFurqan FarrukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gregor Wollmann HNTB Arch BridgeDokument75 SeitenGregor Wollmann HNTB Arch BridgeAdhil ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BeshywapDokument5 SeitenBeshywapAldinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reinforced Concrete Design - Palestine Ii - ACI 318M-08Dokument282 SeitenReinforced Concrete Design - Palestine Ii - ACI 318M-08EVER GUZMAN BALCASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hamdiya BedruDokument116 SeitenHamdiya BedruAbraham KefelegnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conplast WLDokument2 SeitenConplast WLady999Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Word For SCRDokument5 SeitenA Word For SCRJulius BatiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConcretingDokument26 SeitenConcretingDhruvin KagdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developing A Sustainable Concrete Using Sugarcane Bagasse Ash (SBA) With Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate and CementDokument12 SeitenDeveloping A Sustainable Concrete Using Sugarcane Bagasse Ash (SBA) With Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate and CementIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- P DeltaDokument4 SeitenP DeltaTahmidur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Example Set 5Dokument4 SeitenChapter 3 Example Set 5alaa altaeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compound Wall Design (1) - Layout1Dokument1 SeiteCompound Wall Design (1) - Layout1SandeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimum Design of Suspension BridgeDokument15 SeitenOptimum Design of Suspension BridgeshubhadipNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 626 - Final Examination May 2021Dokument3 SeitenCE 626 - Final Examination May 2021Gnanachandren ArrunNoch keine Bewertungen
- DK Kzy Iapk R Lfefr Uksgj Ftyk GuqekuxDokument5 SeitenDK Kzy Iapk R Lfefr Uksgj Ftyk GuqekuxJulfikar KhanNoch keine Bewertungen