Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cell Junction
Hochgeladen von
api-3812274Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cell Junction
Hochgeladen von
api-3812274Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CELL BIOLOGY
LESSON 18:
CELL JUNCTIONS
Learning Objectives • They prevent the passage of molecules and ions through the
In this lecture, you will learn space between cells. So materials must actually enter the cells
(by diffusion or active transport in order to pass through the
• Types of cell junctions
tissue. This pathway provides control over what substances
• Functions of cell junctions are allowed through.
Junctions Between Cells • They block the movement of integral membrane proteins
(red and green ovals) between the apical and basolateral
surfaces of the cell. Thus the special functions of each
surface, for example
• receptor-mediated endocytosis at the apical surface
• exocytosis at the basolateral surface can be preserved.
The Epithelia of the Human Lung: an example
The epithelial cells of the human lung express
• a growth stimulant, called heregulin, on their apical surface
• its receptors, called erbB, on the basolateral surface. (ErbB
receptors also respond to epidermal growth factor (EGF),
and mutant versions have been implicated in cancer.
As long as the sheet of cells is intact, there is no stimulation of
erbB by heregulin thanks to the seal provided by tight
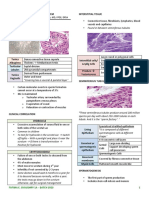
FIG(3-6) Junction between cells junctions.
In many animal tissues (e.g., connective tissue), each cell is However, if the sheet of cells becomes broken, heregulin can
separated from the next by an extracellular coating or matrix. reach its receptors. The result is an autocrine stimulation of
mitosis leading to healing of the wound.
However, in some tissues (e.g., epithelia), the plasma
membranes of adjacent cells are pressed together. Four kinds of Several Disorders of the Lung
junctions occur in vertebrates: See FIG(3-6) • the chronic bronchitis of cigarette smokers
• Tight junctions • asthma
• Adherens junctions • cystic fibrosis
• Gap junction increase the permeability of the airway epithelium. The resulting
• Desmosomes opportunity for autocrine stimulation may account for the
proliferation (piling up) of the epithelial cells characteristic of
In many plant tissues, it turns out that the plasma membrane
of each cell is continuous with that of the adjacent cells. The these disorders.
membranes contact each other through openings in the cell wall
called
• Plasmodesmata.
Tight Junctions
Epithelia are sheets of cells that provide the interface between
masses of cells and a cavity or space (a lumen).
• The portion of the cell exposed to the lumen is called its
apical surface.
• The rest of the cell (i.e., its sides and base) make up the
basolateral surface.
Tight junctions seal adjacent epithelial cells in a narrow band
just beneath their apical surface.
Tight junctions perform two vital functions: FIG(3-7)
© Copy Right: Rai University
68 2.102
Adherens Junctions desmosomes. The loosening of the adhesion between adjacent
CELL BIOLOGY
Adherens junctions provide strong mechanical attachments epithelial cells causes blistering.
between adjacent cells. Carcinomas are cancers of epithelia. However, the cells of
• They hold cardiac muscle cells tightly together as the heart carcinomas no longer have desmosomes. This may account for
expands and contracts. their ability to metastasize.
• They hold epithelial cells together. Hemidesmosomes
• They seem to be responsible for contact inhibition These are similar to desmosomes but attach epithelial cells to
• Some adherens junctions are present in narrow bands the basal lamina (“basement membrane” – View) instead of to
connecting adjacent cells. each other.
• Others are present in discrete patches holding the cells Pemphigoid is an autoimmune disease in which the patient
together. develops antibodies against proteins (integrins) in
hemidesmosomes. This, too, causes severe blistering of
Adherens junctions are built from:
epithelia.
• cadherins - transmembrane proteins (shown in red) whose
Plasmodesmata
• extracellular segments bind to each other and
• whose intracellular segments bind to
• catenins (yellow). Catenins are connected to actin
microfilaments
One of the oncogenes that is frequently found in colon cancer
appears to be the mutated version of a protein that normally
interacts with catenins. Loss of functioning adherens junctions
may also lead to tumor metastasis. FIG(3-7)
Gap Junctions
Gap junctions are intercellular channels some 1.5 - 2 nm in
diameter. These permit the free passage between the cells of
ions and small molecules (up to a molecular weight of about
1000 daltons).
They are constructed from 4 (sometimes 6) copies of one of a
FIG(3-8) Plasmodesmata
family of a transmembrane proteins called connexins.
Although each plant cell is encased in a boxlike cell wall, it turns
Because ions can flow through them, gap junctions permit
out that communication between cells is just as easy, if not
changes in membrane potential to pass from cell to cell.
easier, than between animal cells. Fine strands of cytoplasm,
Examples called plasmodesmata, extend through pores in the cell wall
• The action potential in heart (cardiac) muscle flows from cell connecting the cytoplasm of each cell with that of its neighbors.
to cell through the heart providing the rhythmic contraction Plasmodesmata provide an easy route for the movement of
of the heartbeat. ions, small molecules like sugars and amino acids, and even
• At some synapses in the brain, gap junctions permit the macromolecules like RNA between cells.
arrival of an action potential at the synaptic terminals to be A report in the 6 March 1998 issue of Science (Jorgensen et al.,
transmitted across to the postsynaptic cell without the delay p. 1486) describes how plasmodesmata enable plants to
needed for release of a neurotransmitter. transmit signals - such as the need to mount a defense against a
• As the time of birth approaches, gap junctions between the viral infection - from one part of the plant to another.
smooth muscle cells of the uterus enable coordinated, Plasmodesmata are sheathed by a plasma membrane that is
powerful contractions to begin. simply an extension of the plasma membrane of the adjoining
Several inherited disorders of humans such as cells. This raises the intriguing question of whether a plant
• certain congenital heart defects and tissue is really made up of separate cells or is, instead, a
syncytium: a single, multinucleated cell distributed throughout
• certain cases of congenital deafness have been found to be
hundreds of tiny compartments!
caused by mutant genes encoding connexins.
Desmosomes
Desmosomes are localized patches that hold two cells tightly
together. They are common in epithelia (e.g., the skin).
Desmosomes are attached to intermediate filaments of keratin
in the cytoplasm.
Pemphigus is an autoimmune disease in which the patient has
developed antibodies against proteins (cadherins) in
© Copy Right: Rai University
2.102 69
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cell Modification: Mr. Kevin Francis E. MagaoayDokument22 SeitenCell Modification: Mr. Kevin Francis E. MagaoayDesiree Ann MarasiganNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4lesson4cellmodifications 191023082822Dokument22 Seiten4lesson4cellmodifications 191023082822Kimberly Ramon PalmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epithelial Tissues 2024-01Dokument45 SeitenEpithelial Tissues 2024-01jcrosa137Noch keine Bewertungen
- epiTHITE TissueDokument10 SeitenepiTHITE TissueDandel G. GollosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 CellmodificationsDokument24 SeitenLesson 4 CellmodificationsAmado Sarangay Banawa Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- In Molecular Cell Biology: January 1995Dokument39 SeitenIn Molecular Cell Biology: January 1995avinmanzanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histo: Histology, Lecture: Homework Written ActivityDokument25 SeitenHisto: Histology, Lecture: Homework Written ActivityChristin SchlittNoch keine Bewertungen
- Celladhesion Epithel KissADokument51 SeitenCelladhesion Epithel KissAamdusuf33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Histology and Epithelium TissueDokument48 SeitenIntroduction To Histology and Epithelium TissuejabirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epithelium Tissues: CellularityDokument6 SeitenEpithelium Tissues: CellularityErika VerastigueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corneal Epithelial Wound Healing: PerspectiveDokument8 SeitenCorneal Epithelial Wound Healing: PerspectiveHanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2004 4 JW CellJunctions ELShhhhhhDokument7 Seiten2004 4 JW CellJunctions ELShhhhhhhfqjhrpjncNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histoloji NotlarıDokument4 SeitenHistoloji NotlarıisuhaserkeklerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology LecDokument258 SeitenHistology LecBan JMNoch keine Bewertungen
- W4 Tissue Level of OrgDokument13 SeitenW4 Tissue Level of OrgWisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem PrelimsDokument25 SeitenBiochem Prelimslcpanaligan4175antNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueDokument8 SeitenHistology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueHIEL MAALIHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Modification, Cell Cycle, MitosisDokument9 SeitenCell Modification, Cell Cycle, MitosisIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Histology: Unit Three By: Fikre BDokument133 SeitenGeneral Histology: Unit Three By: Fikre BHenok GirmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05lect Adhesion Summary2017Dokument5 Seiten05lect Adhesion Summary2017Dan ChoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Cell JunctionsDokument25 Seiten4 - Cell JunctionsKhdhir M. Salem100% (1)
- Cell Adhesion Molecules 300107Dokument32 SeitenCell Adhesion Molecules 300107V Lee 'Nozhat'100% (1)
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDokument54 SeitenCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99Noch keine Bewertungen
- JI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 7-8Dokument2 SeitenJI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 7-8Shubham PawadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDokument54 SeitenCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsDokument16 SeitenCH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsREENA GULERIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of EpitheliumDokument51 SeitenBasics of EpitheliumPatrick Ngo'nga ChifwemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4 Tissue Levels of OrganizatioDokument49 SeitenWeek 4 Tissue Levels of OrganizatioDayledaniel SorvetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytoskeleton:: Structure and MovementDokument23 SeitenCytoskeleton:: Structure and MovementAbhishek SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytoskeleton:: Structure and MovementDokument23 SeitenCytoskeleton:: Structure and MovementDaniloFRNoch keine Bewertungen
- محاضره 2 انسجهDokument44 Seitenمحاضره 2 انسجهYahya Daham Zafeer SakhrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oup2 LateralModification FINALDokument34 SeitenOup2 LateralModification FINALPatrick Rómulo CabilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- IV. Chapter 4 (Epithelium)Dokument9 SeitenIV. Chapter 4 (Epithelium)rosalesjirehrNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology Lesson 4Dokument5 SeitenGeneral Biology Lesson 4Danilo JR. BuaquiñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bmat Biology KnowledgeDokument22 SeitenBmat Biology KnowledgeAngel SyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEU2020 Adfinex HDokument23 SeitenEEU2020 Adfinex HZainab Jamal SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EpitheliumDokument4 SeitenEpitheliumaliceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology 2 EpitheliumDokument53 SeitenHistology 2 EpitheliumAbdul RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yellow Green Blue and Red Handwritten Zones of Regulation SEL Social and Emotional Learning Education PresentationDokument15 SeitenYellow Green Blue and Red Handwritten Zones of Regulation SEL Social and Emotional Learning Education PresentationAngel ChrisleneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell - The Unit of Life Mind MapDokument2 SeitenCell - The Unit of Life Mind MapAshwath Kuttuva100% (1)
- Cell Modification Lecture ReviewerDokument2 SeitenCell Modification Lecture ReviewerIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy ReviewerDokument32 SeitenAnaphy Reviewerpatientsafety100% (1)
- CelladhesionDokument51 SeitenCelladhesionNina Difla MuflikhahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.the Tissue Level of OrganizationDokument49 Seiten4.the Tissue Level of OrganizationKojo Yeboah EnchillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology Exam I OutlineDokument76 SeitenHistology Exam I OutlinePrinceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repaso Histologi ADokument132 SeitenRepaso Histologi AMichael Rivera MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Células y Tejidos VegetalesDokument5 SeitenCélulas y Tejidos VegetalesNathalyVargasFreireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell ModificationDokument1 SeiteCell ModificationAPZELIA ANGEL DURUINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Tissues ReviewerDokument9 SeitenAnaphy Tissues ReviewerleyluuuuuhNoch keine Bewertungen
- HISTOLOGY 4 - Glandular Epithelium, Epithelium, and Adipose TissueDokument22 SeitenHISTOLOGY 4 - Glandular Epithelium, Epithelium, and Adipose TissueShariffa KhadijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Quick Notes by Disha PublicationDokument27 SeitenBiology Quick Notes by Disha PublicationMunish Mechie100% (1)
- Histology (Epithelial Tissue)Dokument23 SeitenHistology (Epithelial Tissue)FazilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesDokument6 Seiten8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesBhavanya RavichandrenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell JunctionsDokument27 SeitenCell JunctionsEgg TorNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Cell Carry Out EnergyDokument43 SeitenHow Cell Carry Out EnergyKeanno HipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Human Histology - Epithelial TissuesDokument7 SeitenChapter 3 Human Histology - Epithelial TissuesDessirie EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Quick Notes in EnglishDokument28 SeitenBiology Quick Notes in EnglishJai JaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L 9 Epithelium and GlandsDokument38 SeitenL 9 Epithelium and GlandssNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICRO - 1S07 Epithelial CellsDokument4 SeitenMICRO - 1S07 Epithelial CellsKeith Arleigh JosonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Global Epidemiology of Carbapenemase Producing EnterobacteriaceaeDokument11 SeitenThe Global Epidemiology of Carbapenemase Producing EnterobacteriaceaeM Farid Alwan ZakyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge O Level: Biology 3172/12Dokument20 SeitenCambridge O Level: Biology 3172/12Sasaki MeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monounsaturated Fatty Acids and Immune FunctionDokument5 SeitenMonounsaturated Fatty Acids and Immune FunctionLucas PolizzeliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacteria-Genetic TransferDokument57 SeitenBacteria-Genetic TransferKA AngappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Discovery of DNA and RNA - 12-10-21Dokument6 Seiten01 Discovery of DNA and RNA - 12-10-21a192062Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 8 MedtechDokument17 SeitenCHAPTER 8 MedtechKisen DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 44: Nursing Care of The Client With An Hematologic DisordersDokument18 SeitenChapter 44: Nursing Care of The Client With An Hematologic DisordersfLOR_ZIANE_MAENoch keine Bewertungen
- PYQ Micro MPMSUDokument22 SeitenPYQ Micro MPMSUShahzaib Gouri100% (1)
- Obsfetrics Gynecology: & DepartmentDokument222 SeitenObsfetrics Gynecology: & DepartmentFatma AlbakoushNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 SqualeneDokument41 Seiten2018 SqualeneRidwan YusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Case 1Dokument37 SeitenDrug Study Case 1Maria Charis Anne IndananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Pseudomonas PutidaDokument29 SeitenImportance of Pseudomonas PutidaShashi Sharma100% (1)
- Monoclonal AntibodiesDokument16 SeitenMonoclonal AntibodiesAndrei TatomirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antifungi Activity On PlantsDokument23 SeitenAntifungi Activity On PlantsBAYODE MAYOWANoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology, Lecture 10, NeoplasiaDokument190 SeitenPathology, Lecture 10, NeoplasiaAli Al-Qudsi97% (35)
- Acfrogdny3we1zkabz7ooaocl2 Ryjfdmxsgfsf7vnow4ocsgtpvej h7bxmqxkr351cdggvxshhx1sl Msjslh-Ebntbyvzq6uu9yry0p N7jy-Iz5bs K03fa70qjwmowd-6zokqasm-NlwyliDokument35 SeitenAcfrogdny3we1zkabz7ooaocl2 Ryjfdmxsgfsf7vnow4ocsgtpvej h7bxmqxkr351cdggvxshhx1sl Msjslh-Ebntbyvzq6uu9yry0p N7jy-Iz5bs K03fa70qjwmowd-6zokqasm-NlwyliRosario RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abx Welcomes The Simel April 29Th, 2004Dokument61 SeitenAbx Welcomes The Simel April 29Th, 2004Arnold HarfiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Racgp Combined Pdfs Single FileDokument1.983 SeitenRacgp Combined Pdfs Single FileVikrant100% (1)
- Bacillus Coagulans Probiotic of Choice Nutracos March April 2012Dokument3 SeitenBacillus Coagulans Probiotic of Choice Nutracos March April 2012Gabriel ManriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phage BacteriaDokument65 SeitenPhage Bacteriamaniiiiiiii100% (1)
- Gertrude Belle ElionDokument29 SeitenGertrude Belle Elionapi-3714421Noch keine Bewertungen
- Foods: A Review of Health-Beneficial Properties of OatsDokument23 SeitenFoods: A Review of Health-Beneficial Properties of OatsAbraham Jesús Arzeta RíosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terishna - MICR215 SI Worksheet 7 - 3octDokument2 SeitenTerishna - MICR215 SI Worksheet 7 - 3octNondumiso MavundlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wheat Rust EnglishDokument10 SeitenWheat Rust EnglishAanand JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Novel Antibiotics From Marine Sources: G.M. Doshi, G.V. Aggarwal, E.A. Martis and P.P. ShanbhagDokument17 SeitenNovel Antibiotics From Marine Sources: G.M. Doshi, G.V. Aggarwal, E.A. Martis and P.P. ShanbhagFrangky SangandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- R. L. M. Pierik (Auth.) - in Vitro Culture of Higher Plants-Springer Netherlands (1987) PDFDokument345 SeitenR. L. M. Pierik (Auth.) - in Vitro Culture of Higher Plants-Springer Netherlands (1987) PDFPablo GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics: Uses ActionDokument11 SeitenAntibiotics: Uses Actionammar amerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qasim Internship Report On GSKDokument39 SeitenQasim Internship Report On GSKhfhfhfhfhfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro - Male Repro (Sec A) PDFDokument5 SeitenMicro - Male Repro (Sec A) PDFKaren ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi-Analyte ELISArrayDokument1 SeiteMulti-Analyte ELISArrayShi Jie PangNoch keine Bewertungen