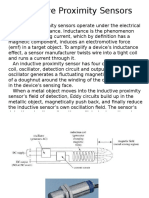
Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Metal Detector
Hochgeladen von
Ivan Maurits SondakhOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Metal Detector
Hochgeladen von
Ivan Maurits SondakhCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Metal Detector
Filemon XIIA1-14
Mention the words metal detector and you'll get completely different reactions from different people. For instance, some people think of combing a beach in search of coins or buried treasure. Other people think of airport security, or the handheld scanners at a concert or sporting event.
The fact is that all of these scenarios are valid. Metal-detector technology is a huge part of our lives, with a range of uses that spans from leisure to work to safety. The metal detectors in airports, office buildings, schools, government agencies and prisons help ensure that no one is bringing a weapon onto the premises. Consumer-oriented metal detectors provide millions of people around the world with an opportunity to discover hidden treasures (along with lots of junk). Anatomy of a Metal Detector A typical metal detector is light-weight and consists of just a few parts: 1. Stabilizer (optional) - used to keep the unit steady as you sweep it back and forth 2. Control box - contains the circuitry, controls, speaker, batteries and the microprocessor 3. Shaft - connects the control box and the coil; often adjustable so you can set it at a comfortable level for your height 4. Search coil - the part that actually senses the metal; also known as the "search head," "loop" or "antenna" Most systems also have a jack for connecting headphones, and some have the control box below the shaft and a small display unit above. Operating a metal detector is simple. Once you turn the unit on, you move slowly over the area you wish to search. In most cases, you sweep the coil (search head) back and forth over the ground in front of you. When you pass it over a target object, an audible signal occurs. More advanced metal detectors provide displays that pinpoint the type of metal it has detected and how deep in the ground the target object is located. Metal detectors use one of three technologies:
Very low frequency (VLF)
Pulse induction (PI) Beat-frequency oscillation (BFO)
VLF Technology
Very low frequency (VLF), also known as induction balance, is probably the most popular detector technology in use today. The current moving through the transmitter coil creates an electromagnetic field, which is like what happens in an electric motor. The polarity of the magnetic field is perpendicular to the coil of wire. Each time the current changes direction, the polarity of the magnetic field changes. This means that if the coil of wire is parallel to the ground, the magnetic field is constantly pushing down into the ground and then pulling back out of it. As the magnetic field pulses back and forth into the ground, it interacts with any conductive objects it encounters, causing them to generate weak magnetic fields of their own. The polarity of the object's magnetic field is directly opposite the transmitter coil's magnetic field. If the transmitter coil's field is pulsing downward, the object's field is pulsing upward.
The receiver coil is completely shielded from the magnetic field generated by the transmitter coil. However, it is not shielded from magnetic fields coming from objects in the ground. Therefore, when the receiver coil passes over an object giving off a magnetic field, a small electric current travels through the coil. This current oscillates at the same frequency as the object's magnetic field. The coil amplifies the frequency and sends it to the control box of the metal detector, where sensors analyze the signal.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Very Low Frequency (VLF) Metal DetectorDokument2 SeitenVery Low Frequency (VLF) Metal Detectorchiquicik0% (1)
- Airport Security SystemDokument13 SeitenAirport Security SystemSithu AungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter TwoDokument10 SeitenChapter TwoSithu AungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal DetectorDokument23 SeitenMetal Detectorelectrical engineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- SoisoiDokument2 SeitenSoisoiChalo NdikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Metal DetectorDokument17 SeitenSimple Metal DetectorBambang Gastomo75% (4)
- Metal DetectorDokument69 SeitenMetal DetectorMaximilian Sylvester33% (3)
- Как работят металдетекторите От Марк Роуън и Уилям ЛарDokument10 SeitenКак работят металдетекторите От Марк Роуън и Уилям ЛарFamily's FashionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal DetectorDokument13 SeitenMetal DetectorBrahmanand Singh100% (7)
- How Metal Detectors WorkDokument11 SeitenHow Metal Detectors WorkHoan Le100% (1)
- Metal DetectorsDokument1 SeiteMetal DetectorssudhirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edc AbsDokument5 SeitenEdc AbsHemanjani HoneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Detector-Project ReportDokument26 SeitenMetal Detector-Project ReportTimK77% (52)
- Metal Detectors ProjectDokument9 SeitenMetal Detectors ProjectYashrajSaxena100% (4)
- Chapter OneDokument3 SeitenChapter OneSithu AungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics ProjectDokument6 SeitenPhysics ProjectShad MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Detectors ProjectDokument9 SeitenMetal Detectors ProjectBeny StephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Detector Project ReportDokument9 SeitenMetal Detector Project ReportraunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal DetectorDokument8 SeitenMetal DetectorHusaini Baharin100% (3)
- Metal DetectorsDokument54 SeitenMetal DetectorsAchmad Fadhillah Kurniawan100% (2)
- Discussion EMTDokument3 SeitenDiscussion EMTm.irfanzaidi34Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Detector Project ReportDokument27 SeitenMetal Detector Project Reportskandesh suresh100% (1)
- Metal Detector Basics and TheoryDokument24 SeitenMetal Detector Basics and TheorySupachoke Eurthanaboon100% (2)
- Project ReportDokument8 SeitenProject ReportRukhama Azad0% (2)
- Metal DetectorDokument24 SeitenMetal Detectorramlala2591100% (1)
- Metal Detecting SensorDokument4 SeitenMetal Detecting SensorManjula HallkattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Detectors LagfgfgnDokument1 SeiteMetal Detectors LagfgfgnLan HoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- All About Metal DetectorsDokument4 SeitenAll About Metal DetectorsKi RilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Detector: Electronics LABDokument15 SeitenMetal Detector: Electronics LABMariam AshfaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Detecting Concise Guide - A Guide For Beginners To Metal Detecting Concepts With Best Tips & Tricks To Get You On The Right Way of Treasure HuntingDokument62 SeitenMetal Detecting Concise Guide - A Guide For Beginners To Metal Detecting Concepts With Best Tips & Tricks To Get You On The Right Way of Treasure HuntingWolfgangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rahul Metal Detector Full ReportDokument23 SeitenRahul Metal Detector Full ReportVishal Singh56% (9)
- Lorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet: AOY Team ProjectDokument3 SeitenLorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet: AOY Team ProjectOmer GadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Project Metal Detector Class 12 BoardsDokument11 SeitenPhysics Project Metal Detector Class 12 Boardsaditya agarwal100% (2)
- Basic Circuitry of Metal DetectionDokument30 SeitenBasic Circuitry of Metal Detectionramesh_jain_kirtikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Detector: Mital ChalodiyaDokument38 SeitenMetal Detector: Mital ChalodiyaUttam MavaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal DetectorDokument14 SeitenMetal Detectornithin0304100% (1)
- Basic Circuitry of Metal DetectionDokument45 SeitenBasic Circuitry of Metal Detectionverd leonardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Point1..metal Detector..final1Dokument27 SeitenPower Point1..metal Detector..final1Ziad100% (1)
- Simple Metal Detector Cir.8302953.PowerpointDokument8 SeitenSimple Metal Detector Cir.8302953.PowerpointMuhammad HozaifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Induction DetectorDokument3 SeitenPulse Induction DetectorZeeshanIrshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrons and Holes Put to Work in the Semiconductor ChipVon EverandElectrons and Holes Put to Work in the Semiconductor ChipBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- PH YSI CS PR OJ EC T: BY: Ribhav SarafDokument7 SeitenPH YSI CS PR OJ EC T: BY: Ribhav SarafcripyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Build An Induction Balance Metal Locator: Main FeaturesDokument8 SeitenBuild An Induction Balance Metal Locator: Main FeaturesBalbalaManiukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Level AlarmDokument22 SeitenWater Level AlarmDinesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction of A Beat Frequency Oscillator Metal DetectorDokument3 SeitenConstruction of A Beat Frequency Oscillator Metal Detectorlakshmanakumarchand100% (3)
- Technology Sensors: Acoustic WaveDokument12 SeitenTechnology Sensors: Acoustic WaveChloeMassyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ron Milione InterviewDokument6 SeitenRon Milione InterviewMárcia HungriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piezoelectricity Text2Dokument1 SeitePiezoelectricity Text2garamia alexandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- كاتلوج المنصور ١٦Dokument15 Seitenكاتلوج المنصور ١٦Salman YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasonic Waves: 1. Production of UltrasonicsDokument7 SeitenUltrasonic Waves: 1. Production of UltrasonicsAmit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Detector PradeedDokument7 SeitenMetal Detector PradeedPradeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inductive Proximity SensorsDokument9 SeitenInductive Proximity SensorsGnanasekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Detectors Are Effective and SafeDokument3 SeitenMetal Detectors Are Effective and SafeDanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spintronics BasicDokument10 SeitenSpintronics BasicDeeksha SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Detection AnalysisDokument5 SeitenMagnetic Detection AnalysisMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal DetectorsDokument9 SeitenMetal Detectorssri harsha100% (2)
- Inductive Proximity Sensor 1Dokument13 SeitenInductive Proximity Sensor 1Paul Joshua AmataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal DetectorDokument8 SeitenMetal DetectorPinky RajbharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strahlenfolter Stalking - TI - Mind Control - 51 - Voice To Skull (V2K)Dokument5 SeitenStrahlenfolter Stalking - TI - Mind Control - 51 - Voice To Skull (V2K)Hans-Georg-Jakobson0% (1)
- Mark 3E1 Service PDFDokument53 SeitenMark 3E1 Service PDFmapsengineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- FilmeDokument8 SeitenFilmeapi-3711358Noch keine Bewertungen
- CV - Ahmed Alnashaba Nov 2018Dokument1 SeiteCV - Ahmed Alnashaba Nov 2018AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Am CircuitsDokument14 SeitenAm CircuitsIngkz JeraeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8140 TM PDFDokument56 Seiten8140 TM PDFnascalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Inventor Mobile PhoneDokument2 SeitenTugas Bahasa Inggris Inventor Mobile PhoneErinda Dewi MayangsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDRDokument2 SeitenCDRMandeep BhullarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alpu-Cmm3: Motorola Canopy Surge ProtectionDokument2 SeitenAlpu-Cmm3: Motorola Canopy Surge ProtectionperuingenierosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacity CalculationDokument3 SeitenCapacity CalculationhnoamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project ReportDokument9 SeitenProject ReportJameelAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps For MOSFET Small Signal AnalysisDokument7 SeitenSteps For MOSFET Small Signal Analysisfrank wangNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMOS Static RAM 16K (2K X 8-Bit) IDT6116SA IDT6116LA: Features DescriptionDokument11 SeitenCMOS Static RAM 16K (2K X 8-Bit) IDT6116SA IDT6116LA: Features DescriptionFrancis Quintana JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- ODU-MAC Blue-Line Open Modular Connector System PDFDokument77 SeitenODU-MAC Blue-Line Open Modular Connector System PDFConstantin-Iulian TraiciuNoch keine Bewertungen
- B1300 SM Ver1Dokument73 SeitenB1300 SM Ver1Abd Elh AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starmaker Recording GuideDokument4 SeitenStarmaker Recording GuideVidyasagar Academy60% (5)
- Caliper Sylvac IP67Dokument2 SeitenCaliper Sylvac IP67Eric AndriantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear IC TrainerDokument2 SeitenLinear IC TrainerAdvanceElectronicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - Analog and Digital Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDokument31 SeitenUnit 2 - Analog and Digital Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inBatukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handover Parameters (Part 1 of 3) - Lauro - Expert Opinion - LTE UniversityDokument3 SeitenHandover Parameters (Part 1 of 3) - Lauro - Expert Opinion - LTE UniversityDipesh ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- LYNX Audio Amplifier 275W 4 OhmiDokument11 SeitenLYNX Audio Amplifier 275W 4 OhmiDanut777750% (2)
- Slyb 174 BDokument152 SeitenSlyb 174 BAdi PopaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1028 FBDokument28 Seiten1028 FBNguyễn Trung ThaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Call 1-800-252-5722: Having TROUBLE With Operation? Please Reset Your UnitDokument127 SeitenCall 1-800-252-5722: Having TROUBLE With Operation? Please Reset Your UnitRolando AndresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 GT E2530 Pspec 2Dokument15 Seiten02 GT E2530 Pspec 2FabiomarferreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet: HCPL-4506/J456/0466, HCNW4506Dokument21 SeitenData Sheet: HCPL-4506/J456/0466, HCNW4506Roozbeh BahmanyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selected MS AgentsDokument4 SeitenSelected MS AgentsprabhakarsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle Modulation NOTESDokument2 SeitenAngle Modulation NOTESJay Amiel Ajoc50% (2)
- L42 ECEN5817 NotesDokument17 SeitenL42 ECEN5817 NotesMuhammad Uzair BilalNoch keine Bewertungen