Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Home Work 3
Hochgeladen von
Husiyandi HusniOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Home Work 3
Hochgeladen von
Husiyandi HusniCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
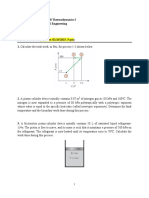
Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS Geoscience and Petroleum Engineering Department PCB1043 Petroleum Engineering Thermodynamics
Dr Reza Ettehadi Osgouei
ASSIGNMENTS-2 Date due: June 27.2011
Problem No 1 Two tanks are connected together as shown in Fig. 1, both containing water. Tank A is at 30 lbf/in.2, v = 8 ft3/lbm, V = 40 ft3 and tank B contains 8 lbm at 80 lbf/in. 2, 750 F. The valve is now opened and the two come to a uniform state. Find the final specific volume
Tank A H2o PA=30 lbf/in.2, vA = 8 ft3/lbm VA = 40 ft3
Tank B H2o mB=8 lbm PB=80 lbf/in.2, TB=750F
Figure 1 Problem No 2 A mass of 50 kg is placed on a 10 cm2 area weightless piston (cf. Figure 2). The ambient is a vacuum, i.e., the pressure is zero in it. The initial gas pressure is 100 bar, and the initial volume is 10 cm3. The cylinder height is 10 cm. A pin, constraining the piston in place is suddenly released. Consider the gases in the pistoncylinder assembly to constitute a system A. If the process in system A is internally reversible and isothermal, determine the work output of the gas. Let system B be such that it includes the piston, weight, and ambient, but excludes the gases. What is the velocity of the piston when its position is at the cylinder rim? Assume system B to be adiabatic.
Figure 2 Problem No: 3 A cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston contains 5 kg of superheated refrigerant R-134a vapor at 1000 kPa, 140C. The setup is cooled at constant pressure until the R-134a reaches a quality of 25%. Calculate the work done in the process. Problem No: 4 A cylinder and a frictionless-piston assembly is to be used for raising a weight by heat transfer from a constant temperature heat reservoir at 450 C, as shown in the figure below. The working fluid is steam. The pressure on the steam due to the total weight plus atmospheric pressure is 1.4MPa. Initially the temperature of the steam is 250 C and its volume is 0.01m3. Heat is transferred until the temperature of the steam is 450 C. Determine the work for this process.
Problem No: 5 A vertical cylinder fitted with a piston contains 0.003m3 of steam at 235 C and a quality of 95%. The piston has a mass of 200 kg, cross-sectional area of 98 cm2, and is held by a pin as shown in the figure below. The ambient pressure is 1bar.
The piston is now removed, allowing the piston to move. After a period of time, the system comes to equilibrium, with the final temperature being 235 C. a) Determine the final pressure and volume of the steam, b) Calculate the work done by the steam during this process. Problem No: 6 4.5 moles of air undergoes a cyclic process as shown by the path 1 2 3 1 in the P V diagram.
Calculate the unknown quantities in the table shown below:
Problem No: 7 Two moles of N2 (ideal gas) at 10 bar and 330K (state 1) undergoes the following reversible changes: a) Compressed isothermally to 14 bar (state 2), b) Heated at constant pressure to 660K (state 3), c) Cooled at constant volume until the pressure drops to 6bar (state 4), d) Compressed adiabatically to 10 bar (state 5), e) Heated at constant pressure to state 1. i) Sketch the paths followed in each process on a single P V diagram. ii) Calculate the work required, the heat transferred, and the changes in internal energy and enthalpy for each of the five processes and for the entire cycle. Problem No: 8 a) A block of copper weighing 0.2kg has an intial temperature of 400K; 4kg of water initially at 300K is contained in a perfectly insulated tank, also made of copper and weighing 0.5kg. The copper block is immersed in the water and allowed to come to equilibrium. What is the change in internal energy of the water? Ignore effects of expansion and contraction, and assume that the heat capacities are constant at 4200 J/ kg.K for water and 380 J/ kg.K for copper. b) Suppose that the copper block is dropped into the water from a height of 50m. Assuming no loss of water from the tank, what is the change in internal energy of the water? Problem No: 9 A piston/cylinder arrangement initially contains air at 150 kPa, 400C. The setup is allowed to cool to the ambient temperature of 20C. a. Is the piston resting on the stops in the final state? What is the final pressure in the cylinder? b. What is the specific work done by the air during this process? Problem No: 10 A piston/cylinder contains 50 kg of water at 200 kPa with a volume of 0.1 m3. Stops in the cylinder restricts the enclosed volume to 0.5 m3, similar to the setup in Problem 9. The water is now heated to 200C. Find the final pressure, volume and the work done by the water. Problem No: 11 A horizontal, perfectly insulated piston-cylinder device contains 1.6mol of helium at 800 kPa. Its volume is 0.005m3 and the ambient pressure is 100 kPa. a) Calculate the work done when the gas is expanded reversibly until the internal pressure is equal to the ambient pressure. Also sketch the process on a P v diagram. b) Calculate the work done when the gas is expanded very suddenly until the internal pressure is equal to the ambient pressure.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Solar Energy StorageDokument18 SeitenSolar Energy StorageAkash Bhanse100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Lab ReportDokument5 SeitenHeat Exchanger Lab ReportJohnConor92% (73)
- Batch Processing Safely: Jim Bickerton Jbsafety ConsultancyDokument4 SeitenBatch Processing Safely: Jim Bickerton Jbsafety Consultancykirandevi1981Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDokument32 SeitenChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuiderospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)Dokument22 SeitenThermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)cwidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upstream Process Engineering Course: 1. Physical PropertiesDokument20 SeitenUpstream Process Engineering Course: 1. Physical PropertiesMohamed SelimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler RatingsDokument15 SeitenBoiler Ratingssandeep kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiling Point of WaterDokument5 SeitenBoiling Point of Watermukund1027Noch keine Bewertungen
- ChE 204 HW-4 and HW-5 Together, Spring 2014, See Changes!Dokument5 SeitenChE 204 HW-4 and HW-5 Together, Spring 2014, See Changes!Irene Kaye AceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems On First Law For Closed SystemDokument3 SeitenPractice Problems On First Law For Closed SystemNetra PujarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 63 Prob Set 2Dokument2 SeitenME 63 Prob Set 2RamonVannCleffRaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR Closed System 2Dokument2 SeitenPR Closed System 2Mareta DanarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicios 1a Ley-04-03-2021Dokument6 SeitenEjercicios 1a Ley-04-03-2021Angelica PobladorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tut 3Dokument4 SeitenTut 3SamarthNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 5927173555606259377 PDFDokument5 Seiten4 5927173555606259377 PDFabel derejeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1 (ME206)Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 1 (ME206)deshrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermoDokument5 SeitenThermoTerry Clarice DecatoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Questions 1111Dokument6 SeitenTutorial Questions 1111Fahmy Muhd100% (1)
- ThermoDokument4 SeitenThermowong zhi chengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics Tutorial ProblemsDokument20 SeitenThermodynamics Tutorial ProblemsRishabh Sharma100% (1)
- Tutorial QuestionsDokument6 SeitenTutorial QuestionsLadnilrebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Thermo I PDF 1Dokument13 SeitenWorksheet Thermo I PDF 1roba angasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- KF 1Dokument19 SeitenKF 1Diana Fitriani SurtikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taller 2 2023-1Dokument8 SeitenTaller 2 2023-1anderson ortizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problemas TermoDokument3 SeitenProblemas TermocleonardoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ned University of Engineering & Technology Department of Food Engineering Thermodynamics - Assignment SPRING SEMESTER 2020-2021Dokument4 SeitenNed University of Engineering & Technology Department of Food Engineering Thermodynamics - Assignment SPRING SEMESTER 2020-2021Sahar Batool QaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 5 PDFDokument3 SeitenTutorial 5 PDFAnonymous hxyDxxcoJNoch keine Bewertungen
- T 2Dokument1 SeiteT 2jfl2096Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment # 4 (Chapter 5) Due 3:00 PM of February 07, 2008 1Dokument2 SeitenAssignment # 4 (Chapter 5) Due 3:00 PM of February 07, 2008 1Adam SchellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 10Dokument7 SeitenAssignment 10Mohamed RaafatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual ThermodynamicsDokument10 SeitenSolution Manual ThermodynamicsNur HanifahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChE204 20181HWIIDokument1 SeiteChE204 20181HWIIGG MMNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 220-FALL23-Homework VDokument2 SeitenCHE 220-FALL23-Homework Vsemikonino35Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work Sheet 1Dokument3 SeitenWork Sheet 1TMedhin MisganawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet #7Dokument4 SeitenSheet #7AHMED BAKRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 First Law 2016Dokument8 SeitenAssignment 1 First Law 2016PabitraBadhuk0% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Numerical With Old Question 2Dokument7 SeitenChapter 2 - Numerical With Old Question 2Sudeep magarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics QuestionsDokument4 SeitenThermodynamics Questionsprateek vyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Sheet 3Dokument2 SeitenTutorial Sheet 3Syed YousufuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 1Zakaria HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 4Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 4tehpohkee50% (2)
- ETD - Question BankDokument6 SeitenETD - Question BankGopinath VNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2Dokument3 SeitenChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2googley71Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment ProblemsDokument2 SeitenAssignment ProblemsRam SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Problems - Ch3Dokument3 SeitenTutorial Problems - Ch3X AbcNoch keine Bewertungen
- TT P1Dokument4 SeitenTT P1Juan Manuel Uceda PérezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Biomedical Engineering (Aait) : Work Sheet #3Dokument4 SeitenDepartment of Biomedical Engineering (Aait) : Work Sheet #3gfsfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet No. 2Dokument3 SeitenSheet No. 2Nazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Sheet No 4Dokument4 SeitenProblem Sheet No 4Ali RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics Assignment SheetDokument3 SeitenThermodynamics Assignment SheetSatwikMohantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Problems-Ch 3Dokument4 SeitenTutorial Problems-Ch 3Aryan NayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- KasdkfjDokument10 SeitenKasdkfjPravallika KolliparaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 4Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 4JayZx WayNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionsDokument3 SeitenQuestionsmonalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermodynamicsDokument13 SeitenThermodynamicsNaveed Khan0% (1)
- Exercise 2Dokument3 SeitenExercise 2mehmet candanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo 2Dokument14 SeitenThermo 2Yato QtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo Finals - Questionnaire Quizzes and Sample Probs With AnswersDokument21 SeitenThermo Finals - Questionnaire Quizzes and Sample Probs With Answersmarc rodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 - Applied Thermodynamics - Fall 2023Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 2 - Applied Thermodynamics - Fall 2023areebarajpoot0453879Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 Numerical ProblemsDokument3 SeitenAssignment 1 Numerical ProblemsNetra PujarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 MidsemDokument2 Seiten2011 MidsemPrashant PrabhakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 With AnsDokument4 SeitenTest 1 With AnsKavinesh GanesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 4 - MEEN 2300 - Spring 2015Dokument3 SeitenHomework 4 - MEEN 2300 - Spring 2015MichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermodynamicsDokument35 SeitenThermodynamicsmaheshluintelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 Tut 5Dokument2 Seiten2022 Tut 5Kethavath Sunil ch21b047Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Casting Powders Book Mills Dacker 2017Dokument550 SeitenThe Casting Powders Book Mills Dacker 2017chao songNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Extended Weighted-Sum-Of-Gray-GasesDokument7 SeitenAn Extended Weighted-Sum-Of-Gray-Gasesabdelhak khourchafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal PerformanceofparabolictroughsolarcollectorsDokument15 SeitenThermal PerformanceofparabolictroughsolarcollectorshussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edibon SCADADokument37 SeitenEdibon SCADAMusa MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 2018 10 17!09 00 37 PM PDFDokument7 Seiten5 2018 10 17!09 00 37 PM PDFMuhammad Irsan SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal EnergyDokument6 SeitenThermal EnergyRendrab G. LolebNoch keine Bewertungen
- T2voc ManualDokument168 SeitenT2voc ManualThanh PhongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Gradient of A Scalar Function: F X F y F ZDokument1 Seite6 Gradient of A Scalar Function: F X F y F ZakshathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition: in Heat Transfer, Conduction (Or Heat Conduction) Is The Transfer of Heat Energy byDokument2 SeitenDefinition: in Heat Transfer, Conduction (Or Heat Conduction) Is The Transfer of Heat Energy byMicaiah DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 Thermal Physics Measuring Specific Heat Capacities (3.3)Dokument1 SeiteTopic 3 Thermal Physics Measuring Specific Heat Capacities (3.3)Mary Ann OrsuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Enhancement in A Circular Tube Twisted With Swirl Generator: A ReviewDokument5 SeitenHeat Transfer Enhancement in A Circular Tube Twisted With Swirl Generator: A ReviewAvinash RoshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laplace EquationDokument23 SeitenLaplace Equationfahim faisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Cooling Tower Experimental ManualDokument12 SeitenWater Cooling Tower Experimental ManualShoaib PathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies: Analysis of Water-Cooled Intercooler Thermal CharacteristicsDokument11 SeitenEnergies: Analysis of Water-Cooled Intercooler Thermal CharacteristicswasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Paper 2 Uneb Question BankDokument116 SeitenPhysics Paper 2 Uneb Question BankOnen-can Hendry Nyeko100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Basic ConceptDokument58 SeitenChapter 2 Basic ConceptIdham SazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobatec Modeller Intorduction Course Tutorial V PDFDokument17 SeitenMobatec Modeller Intorduction Course Tutorial V PDFMohammad Yasser RamzanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Physics Assignment 2013Dokument10 SeitenThermal Physics Assignment 2013asdsadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.8 Using The General Method: 7. Propagation of Uncertainty 82aDokument3 Seiten7.8 Using The General Method: 7. Propagation of Uncertainty 82aPataki SandorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Practice No. 29 Steam Tracing Design and InstallationDokument6 SeitenBest Practice No. 29 Steam Tracing Design and InstallationDnyanehswar KinhalkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment - 5: AIM: Study and Calculate The Efficiency of Fin in Natural and Forced ConvectionDokument17 SeitenExperiment - 5: AIM: Study and Calculate The Efficiency of Fin in Natural and Forced ConvectionRushabh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe - 1Dokument4 SeitenPipe - 1Victor John PingkianNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMAT Physics Guide: Topics and AnswersDokument5 SeitenNMAT Physics Guide: Topics and AnswersCiullaeNoch keine Bewertungen