Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Australian History Study Material: School Certificate Course - HSIE Civics and Citizenship
Hochgeladen von
Shubham ShahOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Australian History Study Material: School Certificate Course - HSIE Civics and Citizenship
Hochgeladen von
Shubham ShahCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
School Certificate Course HSIE Civics and Citizenship
Australian History Study Material
Hayden Smith 2009
Australia History \ General Information
Never abbreviate the first time around o First mention = United Nations o Rest = UN Whitlam Dismissal Kerr (Gov. General) kicks out Whitlam in 75 Whitlam appointed Kerr Gov. General in that very year Referendum Majority of voters and states must say yes (Usual outcome is no) What have been the major social and cultural features of the post-war period
Syllabus Dot Points
Vietnam (Topic 5) Sequence the key events in Australias response to the threat of communism in Asia after WWII Explain the purpose of the treaties Australia contracted during this period Outline the key developments in Australias response to communism within Australia Explain the reasons for Australias involvement in the Vietnam War Explain the reasons why different groups within Australia supported or opposed Australias involvement in the Vietnam War Select appropriate sources that reflect different perspectives about Australias involvement in the Vietnam War Assess the impact of the war on the chosen study
Robert Menzies1949 Harold Holt 1966 John McEwen 1967 John Gorton 1968 William McMahon Gough Whitlam 1972 Malcolm Fraser 1975 Bob Hawke 1983 Paul Keating 1991 John Howard 1996
Liberal Liberal Nationals Liberal 1971 Liberal Labor Liberal Labor Labor Liberal
Inquiry Questions
Vietnam (Topic 5) How did the Australian government respond to the threat of communism after WWII Why did Australia become involved in the Vietnam War? How did various groups respond to Australias involvement in the Vietnam War? What was the impact of the war on Australia and /or neighboring countries
Changing Right (Topic 6) Account for continuity and/or change over time in the relevant study Examine the experiences of the chosen group(s) using a range of sources Outline the important developments in a key event/issue relating to the sturdy Explain the significance of the event/issue for the changing rights and freedoms of the chosen study
People Power and Politics (Topic 7) Outline key developments in Australias role within the UN in the post-war period Assess an achievement of Australia in its role within the UN Explain the purpose of Australias regional agreements Examine the role of Bob Brown in Greens politics Assess the significance of Green Politics for Australia in the post-war period Outline and explain a major policy or issue of the term of office of a chose Prime Minister Assess the contribution of the chosen Prime Minister to Australias post-war development
Changing Right (Topic 6) How have the rights and freedoms of Aboriginal peoples and other groups in Australia changed during the post-war period
People Power and Politics (Topic 7) What role has Australia played in international affairs in the post-war period? What have been some important political developments in post-war Australian History? How have significant individuals and groups exercised their democratic rights in the post-war period?
Social and Cultural History (Topic 8) Outline impact of Tech Changes on everyday life Describe main social and cultural features of 1950s Outline main influences of Britain or the USA on Aus pop culture Assess the impact of the 1950s in shaping Australian Identity
Social and Cultural History (Topic 8)
Page 2 \ Year 10 History Revision Summary Notes \ Topics 5-8 Hayden Smith
Australia in the Vietnam War (Part 1)
General: Influences Within Australia: Communist: Soviet Union (Eastern Bloc) Capitalist: United States (Western Bloc) 1949: Cold War (fear of global war), extended through Europe China Fell Felt countries would fall sequentially Domino Theory, Yellow Peril Lasted roughly 62 72 (47,000 troops served) Chinese communism was driving force behind North Vietnam war effort France controlled Vietnam for nearly 100 years Communist leader Ho Chi Minh claimed Viet independence from France took 30 years to create independent and unified Vietnam Communism: Ideology by Karl Marx communist political system that would provide everyone with equal share in the countrys wealth. Believed to be formed after revolutions overthrew the capitalist world. Communist Dissolution Bill
1. Menzies beats Chiefly (Labor): Election promise to
outlaw Communist Party 2. 1945: Communist Party had over 24,000 members 3. 1950: Communist Party Dissolution Bill stopped communists employment in government / union Guilty until proven innocent High Court declared Unconstitutional 4. 1951: Referendum to ban Communist Party No won, barely Petrov Affair 1945 - Accused Russian Spy Vladimir Petrov acquired political asylum questioned Australias security Evatt claimed Menzies plan to discredit Labor Labor portrayed as communist sympathizers Two weeks after asylum, Petrov wife taken by soviet officials Aus Police stopped them in Darwin Failed to prove any Australian communists were Russian spies
1.
2.
Response to the Threat:
3. 4.
1.
2. 3. 4.
5.
Korean War (50 53) N. Korea overtakes S. Korea in 1950 Viewed as communist threat to democracy. Troops in Korea was a stand against domino theory in Asia reinforced monolithic communist system significant step in affirming alliance between Australia and United States 1951 Menzies warns of war coming (3 years) compulsory military training / universal conscription 1955 Aus troops sent to Malaya to assist Britain against communist guerilla forces 1960 Indonesian President, Sukarno, claimed Dutch segment of Papua New Guinea independent Indonesia Strong communist influence in Indonesia close to Aus created paranoia and threat Vietnam War seen as continuing conflict from Korean Troops in Vietnam to avoid domino effect ANZUS (51) Attack on one, was an attack on all at attack, others would discuss response no guarantee of US response. 1986 NZ removed from treaty not allowing US nuclear subs in SEATO (54) SE Asia Treaty Organization created to protect SE Asia and pacific from communism forward defence strategy. (Aus, Britain, France, NZ, Pakistan, Philippines, Thailand, US) Dissolved 1977
Reasons:
Fear of Communism 1. Thought communism threatened national security paranoia grew idea of sending troops overseas to fight against potential enemies is best way to prevent war on Aus soil Forward Defence During Vietnam US called upon allies/SEATO to defend S. Vietnams (standing up against communism SE Asia) 7 countries Aus, NZ, S. Korea, Philippines, Thailand, Spain and Taiwan 1964 US claimed Viet attack on Gulf of Tonkin US bombing raids began 1965 - Menzies sent 1st infantry battalion + HMAS Sydney to fight 1966 Australia military commitment tripled war came to Vietnam and more US troops came United States Influence 1966 Lyndon Baines Johnson First US Head of state to visit welcome reserved for royalty US received criticism for war looked for Aus support Harold Hold You have an admiring friend, a staunch friend that will be all the way with LBJ. Many still opposed war, with placards / banners 1966 Liberal back in power majority of Aus support war number of troops in Vietnam increased
2.
3. 4. 5.
1.
2.
3. 4.
Page 3 \ Year 10 History Revision Summary Notes \ Topics 5-8 Hayden Smith
Australia in the Vietnam War (Part 2)
Differing Views Conscription 1. Conscription (National Service) found in some form for 42 years since federation Controversial during WWI 2. 1950 Menzies re-introduced limited conscription compulsory 3 months full time training / home service Abandoned in 1958 Re introduced in 1964 Had to sign up at age 20. Drawn from raffle based on birth dates 1 in 10 chance of being picked 3. 1966 Halt sends conscripts to Vietnam in May first conscripted solider KIA. Early protestors were usually religious groups or those from the communist party organizations using men to not register for call up (draft) Conscientious Objectors 1. Claimed if a person could prove they are a pacifist (opposes violence) those that were refused was a 2 year jail sentence 2. 1964 Save our Sons and Youth against conscription formed 3. 1966 Protests became more extreme due to election 4. 1967 Monash Uni Labor club collecting money for North Viet war effort burning draft registration Government took a stand to stop refusal creating more protests Moratorium Movement
6. 1972 - Labor Government Election heavily based on the intensity of involvement in Vietnam Gough Whitlam abolished National Service, recalled army Involvement in Vietnam was over. 7. 1974 US reduces involvement and ceased all bombing throughout indo china 8. 1975 Communists took over S. Vietnam making it longest war in century 9. Made Australians critical about Cold War, Vietnam, arms race + social issues. 10. 1973 Establishment of diplomatic relations with communist china 11. 1979 War breaks out between China and Vietnam shows incorrectness of monolithic views
Impacts on Veterans
1. 1970 By this time television had brought daily footage of horror from Vietnam result in huge rallies, marches, church services etc Showed varied opinion Headmaster of Methodist College encouraged young meant to defy national service in Sydney Morning Herald. 2. 1970s Moratorium rally in the US 100s of thousands of people want immediate US withdraw 3. 1970s Aus Moratorium rally Jim Cairns (Labor MP) joined two demands: 4. Immediate, total and unconditional withdrawal of Australian and allied troops from Indochina 5. Immediate abolition of conscription
9.
1. 1987 Official Welcome Home parade for veterans (Sydney) Welfare ignored since 72 2. Experienced difficulties settling back for following reasons: a. Vietnam veterans came home to contempt and hostilely rather than gratitude b. Many left untreated for Post-traumatic Stress (battle fatigue) c. Drugs widely available in Vietnam many had drug related illnesses 3. Exposure to dangerous chemicals in defoliation campaign. 4. 1980 Viet. Veterans Association of Australia established lobby governments for money / support and political recognition getting no support from Department of Veteran affairs 5. Agent Orange most common chemical used used to deprive Vietcong of cover cause cancer, birth abnormalities, and toxic brain dysfunction 6. 1983 Hawke Labor Government royal commission to investigate effects of chemical agents reported insufficient data to show disabilities caused by chemical defoliation except psychological. 7. 1994 Labor acknowledged Agent Orange as direct cause of illnesses for veterans. 8. Work of Veterans is an example of how citizens use democracy to influence government they felt needs and wishes being ignored. Veterans association (interest group) established to influence
Page 4 \ Year 10 History Revision Summary Notes \ Topics 5-8 Hayden Smith
Changing Rights & Freedoms \ Women
General
1. Breadwinner: Person responsible for earning main 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
income Modern Homemaker Wanted marriage, family, no work Germaine Greer Inspiration to many women to question their position First Wave feminist movement in late 1800s and early 1900s Second Wave - 1960s and 70s when women fought for equal opportunity Third Wave womens struggle from mid 1980s on continued work of earlier movements. 1997 Report Sticky Floor and Glass Ceilings showed that womens jobs were characterized by being part time, having lower skill levels, providing fewer promotion opportunities
1958 Australia acts (NSW first) and phases in equal pay over 5 years 1969 Equal Pay Case Women to receive same wage as men in same work Only applied in areas where majority of workers are men only 18% of female workforce benefitted 1972 Equal Pay Case Different jobs with the same worth should be paid at the same rate Meant that equal valued work would receive same wage 1974 Minimum adult wage both sexes had same wage 1987 Wage increases based on productivity pushed women further behind 2000+ - On average women earn 85% that of a male wage
Womens liberation (from 1970)
Post-WWII 1. Women taken out of male jobs and placed back in the home 2. Society expected to stay home a womans place is in the home womens wedding vows to love, honour and obey 3. Rape only became a criminal offence in marriages in 1981 4. Nuclear family home in suburbs image of security man works and women looks after private sphere that is the home - Sex-role stereotyping re-enforced by advertising 5. Schools focus higher education on males many employers would expect women to resign if they marry 6. Some women stood out for example Dawn Fraser Equal Pay
1960s Gradual changes in attitudes and expectations of women 1966 Introduction of pain maternity leave for women Women who work in federal government no long have to resign if they marry 1969 Zelda DAprano chained to Commonwealth buildings in Melbourne protesting against equal pay issues formed womens action committee forerunner of womens liberation movement Fought for Choice of children, child care, discrimination from banks, divorce, domestic violence, family planning, parental leave Wanted illegal to discriminate on sex, promote equal opportunity for women / protection of rights 1972 Womens electoral lobby discovered many political bodies did not recognize women nor their rights eventually resulted in women becoming an important group electorally 1973 Elizabeth Reid appointed first Womens adviser for PM showed womens recognition 1975 Family Law Act No-fault divorce removed social stigma during divorce used to escape husband without being labeled guilty party. 1987 Mary Gaudron first woman to be appointed judge of High Court of Australia 1977 Anti-discrimination act illegal to discriminate based on the grounds of sex, and marital status 1984 Sex-Discrimination Act illegal to discriminate based on the grounds of sex, marital status and pregnancy
1961 Women made 21% of workforce (generally nursing, teaching etc) 1961 Contraceptive pill allowed controlled fertility sough to improve family economic security 1907 Harvester case allowed men to earn enough for family but women much less 1949-50 case to Basic Wage Inquiry established basic wage for women as 75% of male wage 1948 UN recommends equal pay unequal pay is discrimination
Page 5 \ Year 10 History Revision Summary Notes \ Topics 5-8 Hayden Smith
Changing Rights & Freedoms \ Aborigines
Aborigines: General 1967 Referendum
Certificate of Exemption step towards full citizenship give up aboriginal status aboriginal communities ridiculed
1937 Aborigines Progressive Association campaigning for citizenship and assimilation 1940 Assimilation became accepted policy <1948 Aborigines had to give up aboriginality and have certificate of exemption 1959 Recognised as citizens Commonwealth Budget gave eligibility for pensions and benefits (such as unemployment) like all other Australians 1961 - NSW, VIC, SA could vote Rest could not 1962 Voting Rights act Aborigines could vote in federal elections status of Australian citizen 1967 Referendum Count aboriginal people as part of the population (removing section 127) Allow commonwealth laws to help improve conditions for no matter where they live (alter section 51) 90% of voters said yes
Change over Time
Protectionism: Smooth pillow of a dying race Thought Aboriginals were dying out children could be taken if at risk Assimilation: 1951 Paul Hasluck Aboriginals blend into community had to be exempt from Aboriginal status later considered another attempt to destroy aboriginal culture Integration: To join two cultures together accepted varied culture diversity seen as enriching rather than threatening Self-Determination: Right to choose where to live and control own life Three distinct Aboriginal groups Tribal, live on sacred land those on reserves, protected and under government control living in fringe camps and major cities. Activism By 1930 armed resistance was replaced by political resistance Workers Rights Until 1965 there was discrimination in working rights boys expected to do rural work and girls expected domestic
Land Rights Importance Song Lines Ceremonies are held (direct contact with ancestors) Spirituality with land 1963 Barke Petition Yolungu people lands taken over by Bauxite Mine Asking for control of land 1965 Freedom Ride Aboriginal people led group of supporters through NSW, protesting discrimination against Aboriginal People 1966 Wave Hill Walk Off Led by Vincent Lingiari Walked off station to protest for their unjust wages 1971 Tent Embassy Calling for change in discrimination and injustice in land rights 1973 Woodward Commission Commission with a role to investigate ways to recognize aboriginal land rights 1975 Gurindji hand back by Whitlam 1976- Aboriginal Land Rights act Provided some recognition of indigenous land rights 1989-90 Royal commission into Aboriginal deaths in custody 1989 ATSIC established Indigenous people spending money on Indigenous 1991 Council for Aboriginal Reconciliation Sorry Day 1992 Mabo Decision of High Court Overturned legal concept of Terra Nullius Accepted that Native Title existed prior to 1788 Native title can be claimed on Crown Land (if not freehold / leasehold traditional lifestyle maintained / continuous occupation of land) 1996 Wik Decision Decided that native title and leasehold title could co-exist For ceremonies / hunting / living & grazing
Stolen Generations Most under 5 years aboriginal no judicial process placed in church / state institutions very little education Kinship/Family important to Aboriginal People Once taken often issued new names / birthdates 1921 NT Aboriginal Childrens home housed 52 children in iron sheds behind a local hotel bad condition Part Aboriginal = Half cast, quarter = quadroons Children told they were orphans parents not allowed to know visits were prohibited As adults suffered issues insecurity, self esteem, depression, suicide, violence etc 1997 Bringing them home - Removal of children was in gross violation of human rights and Australian law showed detailed information and helped fix problems caused to the stolen generation Being Sorry HREOC inquiry suggested a formal apology should be made to Aboriginal People
Page 6 \ Year 10 History Revision Summary Notes \ Topics 5-8 Hayden Smith
1997 Howards 10 point plan Make it difficult for Aboriginal people to claim Native Title
Page 7 \ Year 10 History Revision Summary Notes \ Topics 5-8 Hayden Smith
People Power and Politics \ United Nations
United Nations
Australias Role in the UN United Nations Introduced 1945 Australia founding member - Bring all nations together, work for peace, based on principles of justice Doc Evatt Aussie at the start President of general assembly 48-49 Role in the UN primarily general assembly, WHO and UNESCO Promotes nation concerns through UN discussions on disarmament, environment, refugees etc encouraging international action on issues effecting Australia Being a member signifies commitment to working to avoid military conflict Peacekeeping Role Began 1947, four observers to Indonesia conflict Gareth Evans promoted expansion of UNs peacekeeping role 1999, Australia establish and lead INTERFET, peace keeping in East Timor Modern Day Generally speaking labor support UN more than Liberal controversy on Mandatory Detention, indigenous rights and treatment of asylum seekers Helped with Korean War, Suez Crisis and Gulf War
Regional Agreements
SEATO See Vietnam Sheet ANZUS See Vietnam Sheet
Colombo Plan 1. Began 1950 Changed name to Colombo Plan in 77 because countries left to communism 2. 25 members (Asia/pacific and commonwealth/communist) Purpose: Provide support for developing countries within the region skills in public administration, private development, drug advice (Development of human resources) 3. Originally to care about Commonwealth but later expanded APEC 1. Began 1989 Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation promote economic development/trade/investment in A/P 2. 21 members, making up 1/3 of global population and of world trade works to reduce tariffs 3. Members act on consensus and are not linked by treaty commitments East Timor
UN Conventions
1948 Universal Declaration of Human Rights Over 50 years UN Incorporated into international law through conventions and treaties. Australia ratified two Covenant on civil and politic rights, Covenant on Economic, Social and cultural rights Number of conventions attached to: Human Rights and Equal Opportunity (1986), rights of children, mentally disabled and employment Racial Discrimination Act (1975), Sex Discrimination Act (1984)
1949 West Timor became part of Indonesia 1975 Portuguese relinquished all colonies East Timor left with high mortality rate, low literacy rate 1975 - ET attempted to gain independence Indonesia refused, sending in 3000 troops Dili (capital) fell 1976 Australia accepted the takeover increased public interest 1976 UN wants recall of all Indonesian troops immediately By 1979 almost 200,000 dead as result of conflict 1991 Brutal massacre of 300 broadcast on TV 1992 Capture of leader Xanana Gusmao 1997 Replacement of Indonesian president 1998 New leader Issued immediate referendum 1999 Choice between remaining part of Indo or being independent 2002 Claimed independence After independence an AUS-led UN peacekeeping group went into East Timor to contain the transition 2002 Xanana Gusmao First President / Own Nation
UNESCO
1945 - UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organistaion (UNESCO) Based in Paris works towards ending poverty and encourages sustainable development focus on co-operation through mutual respect Gough Whitlam served as Ambassador to UN in 83-6 Supported UN, even when US, Britain and Singapore dropped out claimed it was AntiWestern Memory of the World program ensures preservation of important documents that might otherwise be destroyed
Page 8 \ Year 10 History Revision Summary Notes \ Topics 5-8 Hayden Smith
People Power and Politics \ Important People
Bob Brown / Green Politics
Green Politics focus on environment for future generations exist in over 100 countries non-violent approach
Gough Whitlam \ Womens Rights
Gough Whitlam 1. Slogan: Its Time 2. 2% vote swing, not major 9 seat win in House of Reps 3. 23 years of liberal-country people wanted a change 4. Fought for Womens Pay
Bob Brown 1. Leader of Aus Greens and represents state of Tasmania in Senate 2. 1968 1980: Medicine at Uni and GP 3. 1979 1984: Director of the Tasmanian Wilderness Society Franklin Dam Issue 1. Tasmanian Government passed Gordan River Hydro Power Dev. Act 1982 to assist generation of Tasmanias electricity 2. Environmentalists all protested Bob Brown tried to increase public awareness to the issue used photos as examples 3. 1983: Wilderness society led blockage 2000 people arrested, 600 in jail + brown 4. 1983 New labor government prevent construction of dam 5. Commonwealth used legislation to prevent work occurring on dam Classified whole area as natural heritage and cultural heritage 6. Tasmanian government called unfair taken to High Court in favour of Com. Wealth Impacts of Green Politics 1. Made Aus aware of importance of Natural environment 2. Bob Brown fought for freedom of information, euthanasia, decreasing politicians salaries, nuclear free Tasmania 3. 1987 attempt to ban semi automatics failed 7 years later, port Arthur 4. Protested in involvement in Iraq Casting vote for Aus Republic 5. Provided an alternate to two main parties (L&L)
1. 2. 3. 4. 1. 2. 3.
Womens Pay (Economic) 1974 Adult Wage No Discrimination Equal Pay for women (72) Single mothers allowance to support children Removed sales tax on contraceptive pill Womens Position (Political) Elizabeth Reid first womens advisor to Prime Minister Office of womens affairs Home tutoring for migrant women (English) Family Law Act (Social) No Fault Divorce leave without social stigma Childrens are Best Interest Property Division non-financial values included Spousal Maintenance De Facto Couples Directly changed family structure
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Other Impacts (Health and Education) 1. No Uni Fees More women jobs 2. Legal aid office women get legal aid if are poor Contribution 1. Substantial change to society, especially women 2. More change in 3 years than in previous 23 3. Establishment of equal pay for women 4. Enabled more women to go to uni 5. Substantial change to sexual relations in Australia 6. Direct influence to changing nature of families more divorces in the modern era
Page 9 \ Year 10 History Revision Summary Notes \ Topics 5-8 Hayden Smith
Social and Cultural in Post War Period
Housing After WWII Telephones and communication became vital 1970: STD Calls were available Access to worldwide communication and globalization through fax, mobile phones, emails Australia not as geographically isolated to other nations
1949: New Government: Removed Price Controls Cost of housing doubled Economic Boom: Driven by need to support growing population (estimated 200,000 homes needed) Australian Dream: Brick home on a quarter acre block Government Response: o Cheap war service loans for servicemen o Ex-army camps, tents and temp dwellings made from fibro o Flats to provide high density at a low cost o Beaufort houses: Prefabricated and mass produced house design
Fashion
Music
Clothing: Comfortable, sporty and practical separates designed for mix and match Popular: Jeans, T Shirts, Leather Jackets Beatniks blurred male and female styles
Home Appliances
1946: 2% of Australian Homes had a washing machine Hire Purchase Allow people to but without having the cash in hand pay off over time Provided release from heavy domestic work (i.e. Vacuum) Shift of values - nothing bought without money in hand. Accepted - high and reliable employment levels
1954: Rock and Roll came into Australia radio devoted to music 1956: Elvis Presley Heartbreak Hotel Broadcast wait up critiscised encouraged bad behavior, sexually suggestive
Entertainment
Entertainment
1956 (16/09): TV arrived in Australia. (Weeks before Olympics) License fee paid by television owners Televisions were expensive 1960: Over 600,000 license holders and half a million homes in Sydney with TV Allowed the youth of Australia to be openly exposed to American culture and influence, through American TV Shows and film. Children spending more time watching TV than recreational activities.
1959: 15 year olds watching 9 12 hours a week of television more than recreational activities Rebel Without a case: Movie about generation of young people who rejected conduct and values of parents.
Sport
Prosperity: More time / Money for sporting new facilities constructed (e.g. swimming pools) 1956: Melbourne Olympic Games First time in Sth Hemisphere Millions watched worldwide Aus Team: 287 people Success: Beth Cuthbert (Won 100m and 200m)
US Influence Transport Music (Elvis) and Entertainment (Rebel with. Cause) rebellious teenage boys adults saw sign of juvenile delinquency Chuck Faulkner introduction of TV American accent showed how influenced Aus culture was by US 74% of films imported to Aus came from US expectation of hit film / song being US Fashion: Youth Mass Market Influenced by US cinema. Women looking for cheaper and more relaxed fashion options (US > Parisian)
1948: Australians Own Car 10 cars / day - Holden 1960: 1 million cars produced Financed by Commonwealth Bank / Bank of Adelaide Made in Aus Designed by US Governments plan for post-war reconstruction Build housing away from tram / railways Suburban supermarkets with car parks, drive-in bottle shops Families transport between shops, beach, sporting and surfing (created a generation of surfers)
Impact on Australian Identity
Communications Before WWII Communication through post / telegram
Olympic Success gave Australia international recognition, aided by TV Coverage (e.g. Dawn Fraser) Johnny OKeefe was Australian Rock idol showed Australia had its own R&R industry
Page 10 \ Year 10 History Revision Summary Notes \ Topics 5-8 Hayden Smith
Highly based US culture showed to the world our alliance and close relations with the US and break off of Britain
Page 11 \ Year 10 History Revision Summary Notes \ Topics 5-8 Hayden Smith
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Aluminium: Atomic Number Symbol NameDokument1 SeiteAluminium: Atomic Number Symbol Namefocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Variable Characteristic Observations: Ypes OF Data Concept AND JargonsDokument2 SeitenVariable Characteristic Observations: Ypes OF Data Concept AND Jargonsfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- 1.1 Define The Role of Marketing in OrganisationsDokument2 Seiten1.1 Define The Role of Marketing in Organisationsfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- MenuDokument7 SeitenMenufocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Average My Result Beep Test 4.6 4Dokument22 SeitenAverage My Result Beep Test 4.6 4focuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Determining Main Idea Chart PDFDokument1 SeiteDetermining Main Idea Chart PDFfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Quadratic Inequalities: Preliminary Mathematics Extension 1 (3unit)Dokument1 SeiteQuadratic Inequalities: Preliminary Mathematics Extension 1 (3unit)focuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Section 3 HSC Chemistry NotesDokument2 SeitenSection 3 HSC Chemistry Notesfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- My Name Is Shiela Ki JawaniDokument1 SeiteMy Name Is Shiela Ki Jawanifocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Scrib MssDokument1 SeiteScrib Mssfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Question: Calculate The Chances of A Couple Who Are Heterozygous For Albinism Having An AlbinoDokument1 SeiteQuestion: Calculate The Chances of A Couple Who Are Heterozygous For Albinism Having An Albinofocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Math FractionsDokument11 SeitenMath Fractionsfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
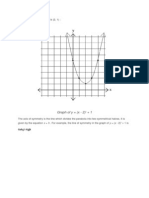
- Graph of y (X - 2) + 1: Gukg I RTGJHDokument1 SeiteGraph of y (X - 2) + 1: Gukg I RTGJHfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Non-Linear FunctionsDokument1 SeiteNon-Linear Functionsfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Ument For Free Download Access.: Select Files From Your Computer or Choose Other Ways To Upload BelowDokument1 SeiteUment For Free Download Access.: Select Files From Your Computer or Choose Other Ways To Upload Belowfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Maths in Focus - Margaret Grove - ch10Dokument52 SeitenMaths in Focus - Margaret Grove - ch10Sam Scheding100% (2)
- Grade 3 Math FractionsDokument11 SeitenGrade 3 Math Fractionsfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptation of An Echidna and SkunkDokument9 SeitenAdaptation of An Echidna and Skunkfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Structural Adaptations of Plants: Plant Adaptations - Honors BiologyDokument1 SeiteStructural Adaptations of Plants: Plant Adaptations - Honors Biologyfocuc98Noch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)