Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Itil Kpi
Hochgeladen von
katz3011Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Itil Kpi
Hochgeladen von
katz3011Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
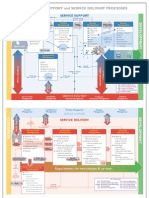
KPI's for ITIL V3 & V2 Processes
Service Portfolio Management No No No No No of of of of of planned new services unplanned new services Strategic Initiatives new customers lost customers
Financial Management Percentage of projects using the standard IT budgeting process Percentage of project files containing cost benefit estimates Percentage of projects where cost and benefits are verified after implementation Percent of IT expenses exceeding the approved budget Percent of expenses exceeding the planned budget for a project Number of proposals by Financial Management for the optimized use of financial resources Service Level Management Number Number Number Number Number Number plan of of of of of of services covered by SLAs Services where SLAs are backed up by corresponding OLAs/ UCs monitored Services/ SLAs, where weak-spots and counter-measures are reported Services/ SLAs which are regularly reviewed Services/ SLAs where the agreed service levels are fulfilled issues in the service provision, which are identified and addressed in an improvement
Capacity Management Number of incidents occurring because of insufficient service or component capacity Deviation of the predicted capacity development from actual course Number of adjustments to service and component capacities due to changing demand Number of unplanned increases to service or component capacity as result of capacity bottlenecks Resolution time for identified capacity bottlenecks Percentage of capacity reserves at times of normal and maximum demand Percentage of services and infrastructure components under capacity monitoring Availability Management Availability of IT Services relative to the availability agreed in SLAs and OLAs Number of service interruptions Average duration of service interruptions Percentage of services and infrastructure components under availability monitoring Number of implemented measures with the objective of increasing availability IT Service Continuity Management Percentage of business processes which are covered by explicit service continuity targets Number of identified gaps in the preparation for disaster events (major threats without any defined counter measures) Duration from the identification of of a disaster-related risk to the implementation of a suitable continuity mechanism Number of disaster practices actually carried out Number of identified shortcomings in the preparation for disaster events which are identified during practices
IT Supplier Management Number of Agreed UCs Percentage of contracts underpinned by UCs Number of Contract Reviews Number of conducted contract and supplier reviews Number of Identified Contract Breaches Number of contractual obligations which were not fulfilled by suppliers (identified during contract reviews) IT Security Management Number of preventive security measures which were implemented in response to identified security threats Duration from the identification of a security threat to the implementation of a suitable counter measure Number of identified security incidents, classified by severity category Number of security incidents causing service interruption or reduced availability Number of security tests and trainings carried out Number of identified shortcomings in security mechanisms which were identified during tests Change Management Number of major changes assessed by the CAB (Change Advisory Board) Number of CAB (Change Advisory Board) meetings Average time from registering an RFC with Change Management until Change clearance Number of accepted vs. rejected RFCs Number of urgent changes assessed by the ECAB (Emergency Change Advisory Board) Transition Planning and Support (Project Management) Number of major release rollouts under the control of Project Management Percentage of projects which are started with a signed Project Charter in place Number of changes to the Project Charter after project start Actual vs. planned consumption of financial and personnel resources Actual vs. planned project completion dates Release and Deployment Management Number of releases rolled out into the productive environment, grouped into Major and Minor Releases Average duration of major deployments from clearance until completion Number of releases which had to be reversed Proportion of new releases distributed automatically Service Validation & Testing Percentage of release components which fail to pass acceptance tests Number of identified errors during release testing per release Time until re-submission of fixed release components Number of Incidents attributable to new releases Percentage of Service Acceptance Tests which fail to obtain the customers sign-off Incident Management Number of Number of location) Number of Number of repeated Incidents, with known resolution methods incidents resolved remotely by the Service Desk (I.e. without carrying out work at user's escalations for incidents not resolved in the agreed resolution time incidents registered by the Service Desk per category
Average time for resolving an incident per category Percentage of incidents resolved at the Service Desk during the first call per category Rate of incidents resolved during solution times agreed in SLA per category Average work effort for resolving incidents per category
Problem Management Number of Problems registered by Problem Management per category Average time for resolving a problem per category Average number of incidents linked to the same problem before problem identification Average number of incidents linked to the same problem after problem identification Average time between first occurrence of an incident and identification of the underlying root cause Average work effort for resolving problems per category
As per ITIL V2 Process
Service Support Processes: Configuration Management Frequency and number of CMDB errors Duration that the CMDB has been consistently up-to-date Frequency of unregistered CIs Number and severity of breaches in SLAs caused by inaccurate CMDB information Frequency and impact of incidents affecting the configuration management system Number of occasions where distributed and remote software is at the wrong level Frequency and duration of bottlenecks caused by configuration management activity being too slow Timeliness of management reports Ability to cope with growth
Incident Management & Service Desk Number of calls received Number of calls missed Number of rings before the phone is answered Average duration of calls Number of calls logged Percentage number of incidents compared to incoming calls Percentage of repeat calls for the same incident Percentage of incidents resolved by help desk - first level Percentage of operations support requests closed Mean time to achieve incident resolution Number of calls escalated Initial trend analysis Results of customer satisfaction surveys Number of complaints and/or letters of praise Actual spend against budget Results of audits Number of staff suggestions, requests for transfer, disputes etc.
Problem Management Percentage of incidents defined as problems Number of problems logged
Percentage of problems escalated Number of problems fixed Resolution times with respect to service level requirements Number of problems outstanding Hardware, software and help desk support, response and performance
Change Management Total number of RFCs raised Percentage for each category Percentage of urgent changes Number of successful changes Number of changes backed out Number of failed changes Backlog of changes by CI/priority
Release Management Number of RFCs raised Percentage of urgent releases Number of changes made by Release Team Ratio of delta and package releases Number of successful software installations Percentage of installations performed to time Number of builds/distributions aborted during process Number of failed or backed out implementations plus builds rolled back after implementation Number of software builds from sources other than the DSL Number of unlicensed and/or unauthorized versions that have been detected within the organization Resource costs per release Service time lost due to Release activity Number of times the DSL is out of step with the CMDB Number of detected viruses within the organization
Service Delivery Processes: Availability Management Agreed service hours, per service Total down time per service Detection elapsed time per incident Response times per incident Time taken to repair per incident Actual availability compared with SLA requirements Reliability - compared to expectations Maintainability - compared to expectations Serviceability - supplier performance compared with contractual conditions. Capacity Management Processor usage by workload and application Relative resource consumption Min/max transactions per second On-line response times and trends Utilization statistics Business usage trends Processor and I/O usage trends Network usage trends Workload trends and forecasts
Growth forecasts IT Service Continuity Management Historical data on incidents, problems, emergencies and disasters Number and details of changes that require updates to the contingency plan Percentage of changes that have caused major issues CI details including dependencies, relationships and criticality Security data and requirements Analysis of services Test output SLA review information Contract review details
Financial Management Percentage of CIs with incorrect financial data Percentage of cost predictions that are incorrect Percentage of change management decisions where cost impact is omitted Staff time spent on costing activities Software/hardware overheads in collecting data for cost management Actual costs against budgeted costs Software license fees vs. available licenses Performance of suppliers Percentage of total IT costs not accounted for
Service Level Management Number of occasions when agreed service levels are not provided Service reviews with customers are regular and constructive The elapsed time to follow up and resolve issues Shortfalls in service level management are reducing over time Possible improvements in SLM are implemented more quickly, over time Active and accurate interfaces with other SM functions are growing Service reports are produced and distributed on time, and to right people
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Physical Security by Asis InternationalDokument508 SeitenPhysical Security by Asis InternationalЕвгенийБутырёв100% (8)
- ITSM Gap Analysis - TemplateDokument57 SeitenITSM Gap Analysis - TemplateAnuradha Lipare86% (7)
- Itil 2011 Process ModelDokument1 SeiteItil 2011 Process ModelAlexandru Dan GheorghiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL Process Maturity FrameworkDokument2 SeitenITIL Process Maturity FrameworkpdsramaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Catalog Template GuideDokument15 SeitenService Catalog Template GuideHello Word :-)100% (1)
- Determination of Nearshore Wave Climate Using A Transformation Matrix From Offshore Wave DataDokument8 SeitenDetermination of Nearshore Wave Climate Using A Transformation Matrix From Offshore Wave DataBenjamin HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL - Service Validation and TestingDokument17 SeitenITIL - Service Validation and TestingFederico MarzulloNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Help Desk SOP Template 9254Dokument6 SeitenIC Help Desk SOP Template 9254GuruPrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL Change ManagementDokument7 SeitenITIL Change ManagementAdarsha100% (2)
- ITIL Process Map WallchartDokument2 SeitenITIL Process Map Wallchartphilmeyer100% (3)
- ITIL Process Maturity Assessment and Roadmap v5Dokument38 SeitenITIL Process Maturity Assessment and Roadmap v5danrodd100% (1)
- Problem Management Overview: PM Process, KPIs, BenefitsDokument26 SeitenProblem Management Overview: PM Process, KPIs, Benefits1buckeyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Metrics For ITIL ProcessesDokument3 SeitenSample Metrics For ITIL ProcessessantuchetuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incident Management: What Makes A Standard Change Standard?Dokument5 SeitenIncident Management: What Makes A Standard Change Standard?beignaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itil and The CMDBDokument5 SeitenItil and The CMDBPaul James BirchallNoch keine Bewertungen
- REL Mindmap v4Dokument1 SeiteREL Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configure Service Desk PDFDokument48 SeitenConfigure Service Desk PDFreparraNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIN Mindmap v4Dokument1 SeiteFIN Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Improvement Calculations ToolsDokument65 SeitenProcess Improvement Calculations ToolsNevets Nonnac100% (1)
- Provance ITSM-ITAM WhitepaperDokument15 SeitenProvance ITSM-ITAM WhitepaperSimon Wright0% (1)
- HL - ITSM Assessment v0.2Dokument23 SeitenHL - ITSM Assessment v0.2Vamsi aravetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Help Desk Evaluation ChecklistDokument18 SeitenFree Help Desk Evaluation ChecklistNguyen Huu TrungNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAP Mindmap v4Dokument1 SeiteCAP Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service CatalogDokument10 SeitenService Catalogmarcelorgs100% (2)
- Service Desk TBDokument16 SeitenService Desk TBKent 'Keno' Daniels100% (1)
- ITSM ITIL Service Desk and Incident Management Product FlyerDokument2 SeitenITSM ITIL Service Desk and Incident Management Product FlyerAxiosSystems100% (3)
- Introduction To It Service Management: Slide 1Dokument10 SeitenIntroduction To It Service Management: Slide 1Chandra RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITSM Best PracticesDokument1 SeiteITSM Best PracticesАлексей Лукацкий0% (1)
- ABC's IT Services CatalogDokument14 SeitenABC's IT Services CatalogManav Patel100% (1)
- Process Vs PraticesDokument1 SeiteProcess Vs PraticesAndrea GiulianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Change Management Policies FinalDokument24 SeitenChange Management Policies FinalBPG ServiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITSCM Mindmap v4Dokument1 SeiteITSCM Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL 2011 Edition Quick Reference GuideDokument2 SeitenITIL 2011 Edition Quick Reference GuideMadhur Sawant100% (2)
- SLM Mindmap v4Dokument1 SeiteSLM Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVM Mindmap v4Dokument1 SeiteAVM Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL BasicsDokument22 SeitenITIL Basicshescribd100% (2)
- IT Service Catalogue GuidelinesDokument10 SeitenIT Service Catalogue GuidelinesmusabqNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Governance PlanningDokument6 SeitenIT Governance PlanningahmedrakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Level Management Leveraging Your Network InvestmentsDokument16 SeitenService Level Management Leveraging Your Network InvestmentsΟλυμπίδης ΙωάννηςNoch keine Bewertungen
- Director IT Service Delivery in Metro Atlanta GA Resume Burke MeanusDokument2 SeitenDirector IT Service Delivery in Metro Atlanta GA Resume Burke MeanusBurke MeanusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release and Deployment Management: A CA Service Management Process MapDokument15 SeitenRelease and Deployment Management: A CA Service Management Process MappjoseptNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL V3 Planning, Protection and OptimizationDokument167 SeitenITIL V3 Planning, Protection and OptimizationCarol Nzui100% (5)
- IT Governance Best Practice Guide Final June 2007Dokument71 SeitenIT Governance Best Practice Guide Final June 2007amojm1Noch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL v3 Service Request ManagementDokument3 SeitenITIL v3 Service Request ManagementAbhirup SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL Cobit MappingDokument16 SeitenITIL Cobit Mappingapi-383689667% (3)
- How To Create An IT Strategy Getting StartedDokument8 SeitenHow To Create An IT Strategy Getting StartedBoni AcebedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Achieving Business Availability Objectives through IT Service Continuity ManagementDokument1 SeiteAchieving Business Availability Objectives through IT Service Continuity ManagementgringoricanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL Change Management XXXDokument10 SeitenITIL Change Management XXXdev007Noch keine Bewertungen
- It Optimize The Service Desk With A Shift Left Strategy Phases 1 3 V1Dokument132 SeitenIt Optimize The Service Desk With A Shift Left Strategy Phases 1 3 V1Andres Guillermo CastiblancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL-Service StrategyDokument11 SeitenITIL-Service StrategyTùng Phạm100% (1)
- Ohio OAKS comparison of organization functions with ITIL servicesDokument3 SeitenOhio OAKS comparison of organization functions with ITIL servicesroddickersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mountainview ITILV3-2011 HiDef Process Function PosterDokument1 SeiteMountainview ITILV3-2011 HiDef Process Function PosterKaue Oliveira Marques0% (1)
- ITIL ITSM SlidesDokument110 SeitenITIL ITSM SlidesSP CFSINoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapping Cobit 5 To Itil 2011 v1.1Dokument1 SeiteMapping Cobit 5 To Itil 2011 v1.1aassafi100% (1)
- IT Governance CharterDokument34 SeitenIT Governance CharterIzoorViinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Service Management Improvement PlanDokument31 SeitenIT Service Management Improvement Planrajesh.j162763Noch keine Bewertungen
- IT Asset Management A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionVon EverandIT Asset Management A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service catalogue management Complete Self-Assessment GuideVon EverandService catalogue management Complete Self-Assessment GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist CMDBDokument3 SeitenChecklist CMDBkatz3011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ops Review Minutes TeleconferenceDokument1 SeiteOps Review Minutes Teleconferencekatz3011Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Seven Rs of Change ManagementDokument1 SeiteThe Seven Rs of Change Managementkatz3011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fishbone ModelDokument2 SeitenFishbone Modelkatz3011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Do's and Don'ts of RCADokument1 SeiteDo's and Don'ts of RCAkatz3011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle QueriesDokument14 SeitenOracle Queriesapi-3724182100% (1)
- Unix Commands PDFDokument9 SeitenUnix Commands PDFachalkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project IdentificationDokument7 SeitenProject Identificationsimmi33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating Variance and Standard Deviation of Discrete Random VariablesDokument3 SeitenCalculating Variance and Standard Deviation of Discrete Random VariablesGeosippi San Antonio LaymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Music Therapy On DementiaDokument6 SeitenImpact of Music Therapy On DementiaSaul MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA 427 - Assurance and Attestation Services: Tests of ControlsDokument27 SeitenBA 427 - Assurance and Attestation Services: Tests of ControlsLay TekchhayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group A - Consolidated Article Critique - Managing Family Business TensionsDokument4 SeitenGroup A - Consolidated Article Critique - Managing Family Business TensionsRonelyCalairoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comm 170 SyllabusDokument7 SeitenComm 170 SyllabushayleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mess Media Flow and Differential Growth in Knowedge PDFDokument13 SeitenMess Media Flow and Differential Growth in Knowedge PDFMeiQi LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dzurilla (1990) Development and Preliminary Evaluation of TheDokument8 SeitenDzurilla (1990) Development and Preliminary Evaluation of TheMourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ballb 4 Sem SyllabusDokument13 SeitenBallb 4 Sem Syllabusdivyarana123Noch keine Bewertungen
- For Progress ReportDokument6 SeitenFor Progress ReportReine Chiara B. ConchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Marketing and Sales AqualiteDokument41 SeitenAnalysis of Marketing and Sales AqualiteAnuj Dahiya100% (1)
- Comparative Study of Infrastructure, Teaching and Results in Girls and Boys Secondary SchoolsDokument48 SeitenComparative Study of Infrastructure, Teaching and Results in Girls and Boys Secondary SchoolsimranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Association Rule Mining: Applications in Various Areas: Akash Rajak and Mahendra Kumar GuptaDokument5 SeitenAssociation Rule Mining: Applications in Various Areas: Akash Rajak and Mahendra Kumar GuptaNylyam Dela Cruz SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Readings in The Philippine HistoryDokument4 SeitenReadings in The Philippine HistoryRecil Marie BoragayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Intelligence For Caries Detection: Value of Data and InformationDokument8 SeitenArtificial Intelligence For Caries Detection: Value of Data and InformationMihaela TuculinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Study of Romanian Folklore PDFDokument30 SeitenThe Study of Romanian Folklore PDFGabriela DristaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smu PM MB0050Dokument149 SeitenSmu PM MB0050Sunilkumar DesarajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 64 Ec 8 Eac 283 F 3Dokument13 Seiten64 Ec 8 Eac 283 F 3Sains Data MRendyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Women in ManagementDokument8 SeitenWomen in ManagementYus NordinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Linear Programming Optimization Approach To Costs Minimization in Port Terminal Operations in Nigerian PortsDokument6 SeitenA Linear Programming Optimization Approach To Costs Minimization in Port Terminal Operations in Nigerian PortsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEED 109 The Teaching of Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan EPP-1Dokument13 SeitenBEED 109 The Teaching of Edukasyong Pantahanan at Pangkabuhayan EPP-1CionbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Advanced Statistics First Sem 2019-20Dokument1 SeiteFinal Exam Advanced Statistics First Sem 2019-20Francis Joseph Malabayabas LopenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical analysis of public sanitation survey dataDokument1 SeiteStatistical analysis of public sanitation survey dataLara GatbontonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study of Consumer Satisfaction With Special Reference To Samsung Smart Phone GlaxysDokument7 SeitenA Study of Consumer Satisfaction With Special Reference To Samsung Smart Phone GlaxysArunKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term Paper Proposal - 20CH003Dokument6 SeitenTerm Paper Proposal - 20CH003Abdulla Mamun100% (1)
- Data Integrity and Compliance With Drug CGMP: Questions and Answers Guidance For IndustryDokument17 SeitenData Integrity and Compliance With Drug CGMP: Questions and Answers Guidance For IndustryRafatalghubariNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Causes of CorruptionDokument49 SeitenWhat Are The Causes of CorruptionquanglsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scholary Review: FadermanDokument5 SeitenScholary Review: FadermanCece SpencerNoch keine Bewertungen