Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Understanding States of Matter and Density
Hochgeladen von
Wong Kee BoonOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Understanding States of Matter and Density
Hochgeladen von
Wong Kee BoonCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
13
MODULE 3: MATTER SECTION A
Figure 1
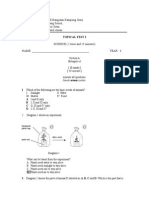
1.
Figure 1 shows two liquids at different temperatures. What is the difference between the particles at Q and R? A B C D Size of particles Mass of particles Volume of particles Distance between particles
Figure 2
2.
Figure 2 shows the arrangement of particles in 3 different states P, Q and R at room temperature. Which of the following represents oxygen, mercury and carbon? A B C D Oxygen P Q Q R Mercury Q P R Q Carbon R R P P
3.
In an experiment, 50 cm3 of alcohol and 50 cm3 of water are mixed. The final volume of the mixture is less than 100 cm3 because the alcohol molecules
Science Enrichment Module (PMR)
14
A B C D 4.
move faster than the water molecules. combine chemically with the water molecules. fill the spaces between the water molecules. molecules evaporate when mixed with the water molecules.
Figure 3 shows the set up of an experiment.
Figure 3 What is the possible explanation for the observation? A B C D The particles of copper sulphate move faster than the gel particles. The particles of copper sulphate are smaller than the gel particles. The particles of copper sulphate are attracted by the gel particles. The particles of copper sulphate diffused into the spaces between the gel particles.
5.
The experiment shown in Figure 4 is to prove the movement of particles in solid, liquid and gas.
Figure 4 The conclusion that can be made from the above experiment is
Science Enrichment Module (PMR)
15
A B C D 6.
the movement of particles is the fastest in solid. the movement of particles is the fastest in gas. the gas particles are arranged very closely together. the movement of particles is the same both in gas and solid.
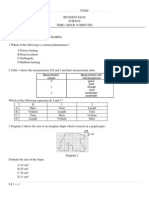
Table 1 shows the properties of three states of matters P, Q and R. State of matter P Q R The kinetic energy of particles Very low Very high Average Table 1 What are the states of matter P, Q and R? A B C D P solid solid gas liquid Q gas liquid solid gas R liquid gas liquid solid The attractive forces between the particles Very strong Very weak Weak
7.
Table 2 shows the density of five types of substances. Substance V W X Y Z State of substance Liquid Solid Solid Solid Solid Table 2 Which solid will float on top of liquid V? A B C D Solid Z only. Solids X and Y only. Solids W and X only. Solids X, Y and Z only. Density 1.2 0.8 0.6 2.5 1.4
Science Enrichment Module (PMR)
16
8.
An iron ball is dropped into four gas jars containing liquids O, P, Q and R as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 The density of liquids O, P, Q and R in a descending sequence is A P Q R O B O P R Q C Q R P O D R P O Q
9.
Figure 6 shows two objects P and Q in liquids S, T and U in a gas jar.
Figure 6 The explanation about the objects and liquids P and Q are I Object P is less dense than object Q and liquid U. II Liquid T is denser than liquid S and object P. III Object Q is denser than liquid T and object P. A B C D I and II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III
Science Enrichment Module (PMR)
17
10.
The mass of substances H, I, J and K is stated in Table 2 below. The volume for all the substances is 5 cm3. Substance H I J K Table 2 If the density of glass is 2.5 g cm-3, which of the following labeled as H, I, J and K is glass? A B C D SECTION B H I J K Mass (g) 8.8 10.0 12.5 15.6
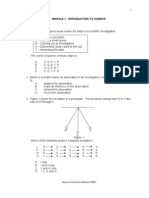
1. Diagram 1 shows three sets of apparatus P, Q and R used in an
experiments to study the movement of particles in a solid, liquid and gas. Table 1 shows the results of the experiments.
Diagram 1
Science Enrichment Module (PMR)
18
Observations Time taken The gel turns purple. 2 days The water turns purple. 2 hours Both gas jars are filled with 5 minutes smoke. Table 1 a) (i) In which experiment does the movement of particles is the slowest? ____________________________________________________________ [1 mark] (ii) Arrange the sets of P, Q and R in the order of the movement of particles, from the fastest to the slowest.
Experiment P Q R
[1 mark] b) In experiment R, the smoke rises to the top of the gas jar after a few minutes. Why do smoke particles move so quickly in air? ______________________________________________________________ [1 mark] c) A student realises that there is a gas leakage in the laboratory. (i) How would he identify that the gas is leaking? _________________________________________________________ [1 mark] (ii) State two actions that the student needs to take before he reports about the leakage to his science teacher? _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ [2 marks]
Science Enrichment Module (PMR)
19
2. Diagram 2 shows an experiment carried out to determine the density of a
stone, with a mass of 21 g.
t h m e a s u r i n c y li n d e r g r e a d
a t e r
l s t o n e
a)
Diagram 2 Define the density of an object. ____________________________________________________________ [1 mark]
b)
i)
Find the volume of the stone. _________________________________________________________ [1 mark]
ii) Calculate the density of the stone. [2 marks]
c)
Name the method used in determining the density of the stone above. ____________________________________________________________ [1 mark]
d)
Suggest a precaution that must be taken during the experiment. ____________________________________________________________ [1 mark]
Science Enrichment Module (PMR)
20
3. Diagram 3 shows an experiment to determine the density of sugar solution.
Empty beaker mass= 15g
Beaker with 30 cm3 of sugar solution mass= 100g Diagram 3
a) What is meant by density? _______________________________________________________________ [1 mark] Based on the information in Diagram 3, calculate the mass of sugar solution. _______________________________________________________________ [1 mark] c) (i) Calculate the density of sugar solution.
b)
[2 marks] (ii) Suggest one way to increase the density of sugar solution. __________________________________________________________ [1 mark] (iii) What happens to an eraser if it is dropped into the beaker of sugar solution above? (Density of eraser = 3.30 g/cm3 ) __________________________________________________________ [1 mark]
Science Enrichment Module (PMR)
21
4. Diagram 4 below shows three objects of various densities placed in the liquids of various densities. P A Q R B Diagram 4 a) Arrange the objects and liquids in descending order of density. _______________________________________________________________ [1 mark] b) Suggest an example of each liquid A and B. A: ____________________________________________________________ B: ____________________________________________________________ [2 marks] c) Give examples of objects P and R. P: ____________________________________________________________ R: ____________________________________________________________ [2 marks] d) State two examples of transportation that use the principle of density of matter. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ [2 marks]
Science Enrichment Module (PMR)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MatterDokument8 SeitenMatterHasmi MohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Sains Ting 1Dokument10 SeitenModul Sains Ting 1miznaqibahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MID-TERM EXAMINATION (Chapter 1 To Chapter 4)Dokument8 SeitenMID-TERM EXAMINATION (Chapter 1 To Chapter 4)Shakilla HamzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 1Dokument3 SeitenPaper 1Shida Md ZainNoch keine Bewertungen
- C and D. Choose The Best Answer For Each QuestionDokument14 SeitenC and D. Choose The Best Answer For Each QuestionIntelek Pusat TuisyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Papaer 1Dokument9 SeitenScience Papaer 1Noor Mazita IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ujian Selaras 1 Sains Tingkatan 3Dokument9 SeitenUjian Selaras 1 Sains Tingkatan 3Ridzuan Mohd AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMJK PHOR TAY PAPER 1 SCIENCE EXAMDokument12 SeitenSMJK PHOR TAY PAPER 1 SCIENCE EXAMshng84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sci F1 FY (E)Dokument9 SeitenSci F1 FY (E)Shakilla HamzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - MatterDokument14 SeitenChapter 3 - MatternwahidawomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Science PMR 1994-2010 GuideDokument44 SeitenIntroduction to Science PMR 1994-2010 GuideRiha DinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sains Tingkatan 1 (Bab 3)Dokument8 SeitenSains Tingkatan 1 (Bab 3)JeyShida100% (1)
- Soalan f1 Paper 1Dokument11 SeitenSoalan f1 Paper 1Zaidee RazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOLAF CHEMISTRY SPM 2014 Matter StructureDokument3 SeitenSOLAF CHEMISTRY SPM 2014 Matter StructureSiva GuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPT, Form 4 (Chemistry) - 2014Dokument19 SeitenPPT, Form 4 (Chemistry) - 2014Nur HafezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formative Test of Form 4 ChemistryDokument5 SeitenFormative Test of Form 4 ChemistryMarinda YieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midyearscf12010Dokument9 SeitenMidyearscf12010Nor Izhharuddin ZainyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate of Reaction FactorsDokument8 SeitenRate of Reaction FactorssmcmasaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Particular Nature of Matter, DiffusionDokument14 SeitenParticular Nature of Matter, DiffusionChaudhryAbdullah50% (4)
- Modul Soalan Jirim Dan Bahan (Bab 4) LatestDokument35 SeitenModul Soalan Jirim Dan Bahan (Bab 4) Latestitamuadz85% (13)
- Chemistry Exam Form 5Dokument35 SeitenChemistry Exam Form 5Tan Phei LingNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAME: FORM: . DATE: B1D3E1 - Menyenaraikan Benda-Benda Yang Mempunyai Jisim Dan Memenuhi RuangDokument11 SeitenNAME: FORM: . DATE: B1D3E1 - Menyenaraikan Benda-Benda Yang Mempunyai Jisim Dan Memenuhi RuangCtk RazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Matter 1. Diagram 1 Shows Pictures ofDokument17 SeitenChapter 3 - Matter 1. Diagram 1 Shows Pictures ofRozaini Othman100% (15)
- Esters food flavouring purity check boiling pointDokument17 SeitenEsters food flavouring purity check boiling pointAlley EioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFDokument70 SeitenKimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFJuan DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theme: Matter in NatureDokument11 SeitenTheme: Matter in NatureChee Jin TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Cemerlang Kimia JPNDokument86 SeitenModul Cemerlang Kimia JPNA9951983% (6)
- Sekolah Kebangsaan Kampong Jawa, Kota Sarang Semut, 06800 Alor Setar, Kedah Darul AmanDokument15 SeitenSekolah Kebangsaan Kampong Jawa, Kota Sarang Semut, 06800 Alor Setar, Kedah Darul AmanSurida Abdul HamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock Trial 2Dokument23 SeitenMock Trial 2Azreen IzetNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam L6 Semester 1 2019 (Chemistry)Dokument9 SeitenSMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam L6 Semester 1 2019 (Chemistry)AlyciaLeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 (Air Around Us)Dokument8 SeitenModule 5 (Air Around Us)nor shafiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Ting 1.Dokument7 SeitenSoalan Ting 1.Dia Aizan HamdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topical Test Chapter 5: The Air Around Us Name: FormDokument5 SeitenTopical Test Chapter 5: The Air Around Us Name: Formkmrol85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trial STPM Term1 2017Dokument12 SeitenTrial STPM Term1 2017Earliany Mohd ShahriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Dokument21 SeitenRevision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Shureen Baskaran100% (1)
- Matter Module Form 1Dokument8 SeitenMatter Module Form 1AnnaalPhilip100% (1)
- ChemistryDokument285 SeitenChemistryYeechin Ng100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Chapter 3 Objective QuestionsDokument6 SeitenChapter 1 - Chapter 3 Objective Questionsaida0205Noch keine Bewertungen
- SECTION A (30 Marks) Instructions: Each Question Is Followed by Four Options, A, B, C and D. ChooseDokument22 SeitenSECTION A (30 Marks) Instructions: Each Question Is Followed by Four Options, A, B, C and D. ChooseAnonymous GTCOMvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marl/Ysra Fiziif, Jam Lima: MinitDokument14 SeitenMarl/Ysra Fiziif, Jam Lima: MinitCheng WLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stage 9 Chemistry Pe1Dokument8 SeitenStage 9 Chemistry Pe1sneakyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2 SPM Trial2007Dokument10 SeitenPaper 2 SPM Trial2007Saya Menang100% (1)
- Revision Test No.1-C-IDokument6 SeitenRevision Test No.1-C-IaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penang Trial SPM 2013 ChemistryDokument51 SeitenPenang Trial SPM 2013 ChemistryTzer Harn Tan0% (1)
- SMK BANDAR BARU SG LONG SCIENCE TEST 1Dokument6 SeitenSMK BANDAR BARU SG LONG SCIENCE TEST 1Wati WatakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (E)Dokument10 SeitenIT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (E)Norzawati NoordinNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEKOLAH MENENGAH KEBANGSAAN PANGKOR SCIENCE EXAMDokument5 SeitenSEKOLAH MENENGAH KEBANGSAAN PANGKOR SCIENCE EXAMnazgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryDokument285 SeitenPahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryJeyShida100% (1)
- Ujian Pengesanan Pertengahan Tahun 2009 - Chemistry 1Dokument33 SeitenUjian Pengesanan Pertengahan Tahun 2009 - Chemistry 1Chew Gee LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peperiksaan Percubaan Sem 1 2020Dokument12 SeitenPeperiksaan Percubaan Sem 1 2020Wong WengSiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elegantia College (Sponsored by Education Convergence) Second Term Uniform Test (2018 - 19) Form 5 Combined Science - PhysicsDokument8 SeitenElegantia College (Sponsored by Education Convergence) Second Term Uniform Test (2018 - 19) Form 5 Combined Science - Physicsedmond 黃Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jitsin P1 Trial 2015Dokument21 SeitenJitsin P1 Trial 2015Lam WEn SiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- End-Of-Year Test: Name: - Class: - DateDokument15 SeitenEnd-Of-Year Test: Name: - Class: - Dateniezma2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Latih Tubi Sains PMR (SET 2) : Jabatan Pelajaran Kedah Darul AmanDokument19 SeitenLatih Tubi Sains PMR (SET 2) : Jabatan Pelajaran Kedah Darul AmanNorazian Binti TaatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Particles and States of Matter QuestionsDokument19 SeitenParticles and States of Matter QuestionsAnand Kumar ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesVon EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesVon EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.1 Changes in The States of MatterDokument2 Seiten4.1 Changes in The States of MatterWong Kee BoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 (Introduction To Science)Dokument6 SeitenModule 1 (Introduction To Science)lccjane8504Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 (Introduction To Science)Dokument6 SeitenModule 1 (Introduction To Science)lccjane8504Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sains Tingkatan 1Dokument49 SeitenSains Tingkatan 1Sekolah Portal83% (24)
- Probe PH Meter Ultraglass For Orion STARA2115Dokument33 SeitenProbe PH Meter Ultraglass For Orion STARA2115chaerul.anwar554Noch keine Bewertungen
- Meclizine HCLDokument10 SeitenMeclizine HCLChEng_Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tuning Equation of State ModelsDokument34 SeitenTuning Equation of State Modelswelltest vspNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Slides Fourier Series and Fourier TransformDokument79 SeitenLecture Slides Fourier Series and Fourier TransformRatish DhimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chocolate RheologyDokument7 SeitenChocolate RheologyAdil AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- E401Dokument4 SeitenE401Katrina BucudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation of Soil Compaction With Vibratory Rollers PDFDokument13 SeitenSimulation of Soil Compaction With Vibratory Rollers PDFSandeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pelton TurbineDokument18 SeitenPelton Turbinetiwarishbhm0% (1)
- Laser Dismantling of PHWR Spent Fuel Bundles and De-Cladding of Fuel Pins in The Highly Radioactive Hot CellsDokument6 SeitenLaser Dismantling of PHWR Spent Fuel Bundles and De-Cladding of Fuel Pins in The Highly Radioactive Hot CellsK. JayarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working of Steam Turbines and Its AuxillariesDokument48 SeitenWorking of Steam Turbines and Its AuxillariesbalajigandhirajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement Chapter 4Dokument11 SeitenCement Chapter 4shani5573100% (2)
- Luo Shu Ancient Chinese Magic Square On Linear AlgDokument12 SeitenLuo Shu Ancient Chinese Magic Square On Linear AlgAJAY KUMAR JAINNoch keine Bewertungen
- P Ractical Approaches To Fast Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Muy BuenoDokument28 SeitenP Ractical Approaches To Fast Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Muy BuenoJavier Joao Lloyd IglesiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latent Heat of Fusion VaporizationDokument18 SeitenLatent Heat of Fusion Vaporizationapi-449002661Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cracking Moment Analysis of Prestressed Concrete BeamDokument18 SeitenCracking Moment Analysis of Prestressed Concrete Beamharshil gandhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cylinders Shall Be Produced As Per IS 7285 and Approved by Chief Controller of ExplosiveDokument1 SeiteCylinders Shall Be Produced As Per IS 7285 and Approved by Chief Controller of ExplosiveAlanka Prasad100% (1)
- Fortran (For NACA)Dokument7 SeitenFortran (For NACA)hdslmnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synperonic EthoxylatesDokument2 SeitenSynperonic Ethoxylatesjacky ye100% (1)
- Turbocharger Test GuidelinesDokument13 SeitenTurbocharger Test Guidelinespardomu0% (1)
- The role of root canal fillings in endodontic successDokument9 SeitenThe role of root canal fillings in endodontic successYassir MudharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separation and Purification of Triacylglycerols From Nyamplung (Calophyllum Inophyllum) Oil by Batchwise Solvent ExtractionDokument24 SeitenSeparation and Purification of Triacylglycerols From Nyamplung (Calophyllum Inophyllum) Oil by Batchwise Solvent ExtractionAfifatul JannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite MaterialsDokument278 SeitenComposite Materialsjaddddd100% (8)
- Steam Drum Design CalsDokument78 SeitenSteam Drum Design Calsabdulrehmandescon100% (1)
- Module - 6 - Slides - Part 1 PDFDokument124 SeitenModule - 6 - Slides - Part 1 PDFvarniktpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Graphics and AnimationDokument2 SeitenComputer Graphics and AnimationManoj PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolation and Characterization of Degradation Products of Moxidectin PDFDokument20 SeitenIsolation and Characterization of Degradation Products of Moxidectin PDFAnonymous 7aE6O6Noch keine Bewertungen
- How retinal adaptation maintains visual perception despite illumination changesDokument1 SeiteHow retinal adaptation maintains visual perception despite illumination changesAkicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Theory PDFDokument280 SeitenGroup Theory PDFLuis Cancino Arancibia100% (1)
- Martin Hermann, Masoud Saravi - Nonlinear Ordinary Differential Equations - Analytical Approximation and Numerical Methods-Springer (2016) PDFDokument320 SeitenMartin Hermann, Masoud Saravi - Nonlinear Ordinary Differential Equations - Analytical Approximation and Numerical Methods-Springer (2016) PDFHugo Mayorga100% (1)
- IEEE Paper For Image ProcessingDokument32 SeitenIEEE Paper For Image Processingsaravanan_dijucsNoch keine Bewertungen