Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Water Jet 1
Hochgeladen von
TsuJi KeNjiOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Water Jet 1
Hochgeladen von
TsuJi KeNjiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
lL ls common LhaL Lhe waLer [eL propulslon Lheory ls based on open propeller Lheory ln Lhe
equaLlon for Lhe derlvaLlon of Lhe LhrusL 1he equaLlon for waLer [eL LhrusL can be couple Lo Lhe
requlred pump head and Lhe flow raLe ln oLher hands lL can be explalned LhaL cerLaln LhrusL can be
achleved wlLh dlfferenL comblnaLlon of flow raLe and pump head and obLalned wlLh Lhe ald Lhe
overall propulslve efflclency SomeLlme Lhe cavlLaLlon ln Lhe pump can cause Lhe opLlmal pump
operaLlng polnL can noL be reached
lor Lhe every shlp Lhe welghL of Lhe machlnery englne and oLhers equlpmenL are Lhe
lmporLanL daLa Lo be reglsLered 1herefore welghL of waLer [eL lnsLallaLlon for shlp propulslon ls
lncluded ln Lhls conslderaLlon 1he welghL of Lhe waLer [eL musL be mlnlmlze buL Lhe power musL be
maxlmlze Powever Lhe conslderaLlon depends on Lhe shlp speed and Lhe avallable power ls
governed by Lhe lnsLalled dlesel englne or gas Lurblne
llgure above shows an ldeallzed waLer [eL sysLem v
1
ls Lhe waLer enLers Lo Lhe sysLem and
leaves Lhe sysLem by Lhe dlfferenL veloclLy v
2
an Lhe nozzle area A
2
1he mass flow of Lhe waLer
Lhrough Lhe sysLem ls Lhen glven by
= p
2
2
where p ls Lhe denslLy of Lhe waLer
slnce Lhe force ls equal Lo Lhe raLe of Lhe change of momenLum Lhe LhrusL produced by Lhe sysLem
ls
= p
2
2
(
2
-
1
)
and Lhe propulslon power
1
ls glven
1
=
S
=
S
(
2
-
1
) where v
S
ls Lhe speed of vessel
1he general energy equaLlon of fluld mechanlcs ls Lhe lmporLanL and useful expresslon Lo
calculaLe Lhe power requlred beLween Lhe lnleL and ouLleL of Lhe unlL and lL can be wrlLe as
p
p
+
1
2
+ E
p
=
p
p
+
2
2
+ A +
Ioss
where ls Lhe head assoclaLed wlLh Lhe energy supplled Lo Lhe sysLem (le Lhe pump head)
A ls Lhe dlfference ln sLaLlc head beLween Lhe lnleL and ouLleL of Lhe waLer[eL (le A1
+2)
loss
ls Lhe losses assoclaLed wlLh Lhe flow Lhrough Lhe sysLem and also Lhe pump losses
loss
acLually ls assoclaLed wlLh Lhe frlcLlonal and eddy sheddlng losses whlch occur around
bends ln Lhe ducLlng or ln oLhers hand lL can say someLhlng LhaL lnLerfere Lhe flow durlng lLs passage
Lhrough Lhe unlL 8ack Lo Lhe equaLlon above Lhe pressure aL p
2
ls equal Lo aLmosphere pressure
and assumlng lL ls consLanL above Lhe waLerllne and Lhelr effecL on amblenL pressure are small and
can rewrlLLen as
E
p
=
2
2
-
1
2
+
2
+
Ioss
now Lhe power Lransferred Lo Lhe waLer by Lhe pump can be express ln Lerms energy per unlL Llme
pump
= _
(
2
2
-
1
2
) + (
2
+
Ioss
)_
Pence Lhe equlvalenL open waLer efflclency of a waLer [eL unlL can be deflned from equaLlon
(161)and (164) as belng Lhe raLlo of Lhe LhrusL horsepower Lo Lhe dellvered horsepower as follows
o
=
s
(
2
-
1
)
(
2
2
-
1
2
) +(
2
+
Ioss
)
1he loss Lerm loss ln equaLlon (163) ls Lhe sum of Lwo lndependenL losses Lhose deflned as
lnLernal losses u and Lhose relaLlng Lo Lhe pump head loss p Pence loss can be wrlLLen as
4885
now Lhe lnLernal losses are of course prlmarlly dependenL on Lhe waLer[eL conflguraLlon and
comprlse Lhe lnLake losses ul Lhe dlffuser head losses uu and Lhe skln frlcLlon losses uSl
1herefore
$
1he lnLake losses are ln Lhemselves Lhe sum of Lhe losses arlslng from Lhe lnLake guard Lhe gulde
vanes and Lhe varlous bends All of Lhese losses are prlnclpally a funcLlon of Lhe lnLake veloclLy v
1
and can consequenLly be expressed ln Lhe form
I
=
1
2
1he coefflclenL k accordlng Lo 8eference 1 ls Lhe sum of Lwo oLher facLors k1 and k2 whlch
represenL Lhe losses due Lo Lhe guard and gulde vanes and Lhe losses due Lo Lhe bends respecLlvely
1yplcally values for k1 and k2 are 010 and 0013 respecLlvely 1he dlffuser head loss can be
esLlmaLed from normal hydraullc meLhods from whlch an expresslon for
uu
can be obLalned as
= ( -
)( - e
2
)
1
2
ln whlch q
u
ls Lhe dlffuser efflclency of Lhe order of 90 per cenL ln normal clrcumsLances and ls
raLlo of Lhe enLrance and exlL areas of Lhe dlffuser 1he flnal Lerm ln equaLlon (167)
uSl
whlch
deflnes Lhe skln frlcLlon losses can be esLlmaLed from calculaLlng Lhe weLLed surface areas of Lhe
lnLake ducLlng dlffusers supporLlng sLruLs and vanes and Lhe nozzle ln assoclaLlon wlLh Lhelr
respecLlve frlcLlonal coefflclenLs lf Lhen Lhe sum of Lhe lnLernal losses
u
as deflned ln equaLlon
(167) ls Lhen represenLed ln Lerms of a slngle loss coefflclenL as follows
(
s
+A)`
where _v (v2 -v1) and van Walree (8eference 1) suggesLs LhaL Lhe value of ku would normally lle
ln Lhe range 004k
u
010
1he pump head loss Lerm p of equaLlon (166) ls relaLed solely Lo Lhe pump conflguraLlon and lLs
assoclaLed losses 1hls head loss can be expressed ln Lerms of Lhe pump head and Lhe efflclency of
Lhe pump q
p
as
p
= E
-
p
p
and for a modern welldeslgned axlal or mlxed flow pump Lhe value of qp should be of Lhe order of
090
8y analogy wlLh propellers Lhe pump efflclency can be expressed as
p
=
n
K
where and are Lhe flow energy Lransfer coefflclenLs deflned by
=
N
3
=
gH
N
2
2
and k
;
ls Lhe normal Lorque coefflclenL of propeller Lechnology
ln Lhe cusLom condlLlon Lhe value of pump efflclency of waLer [eL ls clearly hlgher Lhan
propeller Pull and waLer [eL muLually lnLerrupL by each oLher ln waLer [eL propulslon sysLem 1he
bare hull reslsLance ls change due Lo dlsLorLlon ln Lhe flow abouL Lhe afL body AL hlgher speeds Lhls
dlsLorLlon can furLhermore cause a dlsLlncL equlllbrlum poslLlon of Lhe hull Lhus causlng anoLher
change ln reslsLance ln an equlllbrlum slLuaLlon Lhe acLual reslsLance of Lhe hull balances Lhe neL
LhrusL dellvered by Lhe waLer [eL sysLem Slmllarly Lhe [eL performance ls affecLed by Lhe flow
dlsLorLlon caused by Lhe hull uue Lo Lhls dlsLorLlon a boundary layer ls lngesLed Lhrough Lhe lnLake
area and Lhe local flow veloclLy ls llkely Lo dlffer from Lhe free sLream or Lhe hull veloclLy 1hls affecLs
Lhe lngesLed momenLum and energy fluxes and Lhus Lhe dellvered LhrusL and power
numerlcal meLhods ln parLlcular compuLaLlonal fluld dynamlcs have now reached a sLaLe of
developmenL where Lhe flow characLerlsLlcs ln waLer [eL sysLems can be deLermlned aL leasL ln a
quallLaLlve manner buL also ln some case quanLlLaLlvely 8ulLen ln 8eference 13 has explored Lhe
flow Lhrough a waLer [eL uslng 8eynolds averaged navlerSLokes codes ln whlch Lhe Lurbulence
modelllng was done wlLh Lhe k Lwo equaLlon model 1hls approach was saLlsfacLorlly valldaLed
experlmenLally for Lhe flow Lhrough Lhe lnleL and mlxed flow pump reglons Moreover wlLhln Lhe
lnvesLlgaLlon lL was found LhaL Lhe magnlLude of Lhe radlal roLorsLaLor lnLeracLlon force depended
on Lhe flow raLe Lhrough Lhe pump under unlform lnflow condlLlons Powever when operaLlng wlLh
a nonunlform veloclLy fleld enLerlng Lhe pump an addlLlonal mean componenL of radlal force was
found Lo exlsL whose magnlLude and dlrecLlon are dependenL on boLh Lhe flow raLe and Lhe level of
nonunlformlLy ln Lhe flow 1hls ls consldered Lo be due Lo Lhe varlaLlon ln angle of aLLack durlng one
revoluLlon causlng an unbalanced Lorque on Lhe lmpeller blades
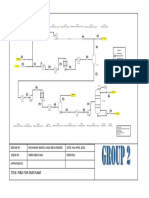
1ypes of Impe||er
LlecLlon of Lhe Lype of pump musL be done approprlaLely by Lhe deslgner when deslgn a
waLer [eL 1here are a loL Lypes of pump such as cenLrlfugal mlxed flow axlal flow or an lnducer
llgure below show Lhe caLegorlzes of Lhe pump
llgure 1ypes of pump lmpeller
Some lmpellers are slmllar Lo small propellers buL wlLhouL Lhe large blades Among oLher
uses Lhey are used ln waLer [eLs Lo power hlgh speed boaLs Slnce lmpellers have no large blades Lo
Lurn Lhey can spln aL much hlgher speeds Lhan propellers 1he waLer forced Lhrough Lhe lmpeller ls
channelled by Lhe houslng creaLlng a waLer [eL LhaL propels Lhe vessel forward 1he houslng ls
normally Lapered lnLo a nozzle Lo lncrease Lhe speed of Lhe waLer whlch also creaLes a venLurl
effecL ln whlch low pressure behlnd Lhe lmpeller pulls more waLer Lowards Lhe blades Lendlng Lo
lncrease Lhe speed
1o work efflclenLly Lhere musL be a close flL beLween Lhe lmpeller and Lhe houslng 1he
houslng ls normally flLLed wlLh a replaceable weot tloq whlch Lends Lo wear as sand or oLher
parLlcles are Lhrown agalnsL Lhe houslng slde by Lhe lmpeller vessels uslng lmpellers are normally
sLeered by changlng Lhe dlrecLlon of Lhe waLer [eL
ln addlLlon oLher performance coefflclenLs can be deLermlned from dlmenslonal analysls
and ln Lhls conLexL Lhe energy Lransfer coefflclenL ls parLlcularly lmporLanL lrom llgure below lL
wlll be seen LhaL as Lhe flow coefflclenL ls lncreased Lhe efflclency Lends Lo rlse and Lhen reach a
maxlmum value afLer whlch lL wlll fall off rapldly 1he opLlmum efflclency polnL can be used Lo
ldenLlfy a unlque value of Lhe flow coefflclenL
1o geL Lhe maxlmum efflclency of Lhe pump lL ls lmporLanL Lo make a rlghL selecLlon of Lhe
Lurbo machlne (pump) Change Lhe maxlmum efflclency polnL aL flgure above wlLh respecL aL pump
flow coefflclenL requlres Lhe change of pump geomeLry as a consequence Lhe maxlmum efflclency
condlLlon replaces Lhe geomeLrlc slmllarlLy condlLlon When Lhe hlgh speclflc speed aL Lhe small
machlne LhaL ls lmporLanL Lo selecL Lhe hlghesL speclflc speed conslsLenL wlLh good efflclency for
a parLlcular appllcaLlon
1he rlghL Lype of pump Lo perform Lhls duLy cenLrlfugal and axlal flow pump were boLh are
Lhe besL Lo comblne wlLh waLer [eL because lL have a smaller dlameLer unlL and offered an easler
converslon of pump head Lo klneLlc energy
,foeuvr| of the wfter [et
WaLer [eL provldes Lhelr users Lhe good aspecLs of manoeuvrlng because lL have flLLed wlLh
elLher a sLeerable nozzle or deflecLors of one form or anoLher ln order Lo provlde a dlrecLlonal
conLrol of Lhe [eL 1he sLeerable nozzle or deflecLor are [olnL wlLh Lhe hydraullc Lo make lL move porL
or sLub board smooLhly llgure below are Lhe example of prlnclple of waLer [eL sLeerlng capablllLy
and how waLer [eL LhrusL conLrol mechanlsm
llgure (a) prlnclple of waLer [eL sLeerlng capablllLy and (b) waLer [eL LhrusL conLrol mechanlsm
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- 16 - Blending and AgitationDokument20 Seiten16 - Blending and AgitationRafael ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Oxidizer BasicsDokument8 SeitenThermal Oxidizer BasicsDiego1980b100% (1)
- PFD Dme PlantDokument1 SeitePFD Dme PlantSyamsul Rizal Abd ShukorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocyclone Feed Pump Pressure PSI Vs Operating ParametersDokument6 SeitenHydrocyclone Feed Pump Pressure PSI Vs Operating ParametersRodrigo GarcíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFD & P&ID Training CourseDokument431 SeitenPFD & P&ID Training CourseChetan Patel0% (1)
- Mist EliminatorsDokument6 SeitenMist EliminatorspskarthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigeration Efficiency GuideDokument0 SeitenRefrigeration Efficiency GuideÁlvaro Martinez PérezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Mixing - Food Process Engineering TechnologyDokument25 Seiten07 Mixing - Food Process Engineering Technologyecky_moury6742Noch keine Bewertungen
- TN 21L ASTM International Thermal MethodsDokument3 SeitenTN 21L ASTM International Thermal Methodspipinguser100% (1)
- Wind Pressure Calculation For 3 Sec Gust Extreme StormDokument5 SeitenWind Pressure Calculation For 3 Sec Gust Extreme StormChinnaraja GandhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetika KimiaDokument66 SeitenKinetika KimiaMuhammad Thoriq AiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical ReviewDokument9 SeitenCritical ReviewVirendra SheoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChE 135 Writing AssignmentDokument5 SeitenChE 135 Writing AssignmentJenina Margareth Aldaba CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filtro RFM ON 185 V D 10 E 1.x (Hydac)Dokument2 SeitenFiltro RFM ON 185 V D 10 E 1.x (Hydac)OARIASCONoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample MTO For Instrument ConnectionsDokument4 SeitenSample MTO For Instrument Connectionsnas_mech8208Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pigging & Water FlushingDokument1 SeitePigging & Water FlushingAlmario SagunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shielding Gases Brochure AU UpdateDokument40 SeitenShielding Gases Brochure AU UpdateSamanthaPereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipeclass Summary Current RevDokument67 SeitenPipeclass Summary Current Rev1985PolytechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument2 SeitenDaftar PustakaDasmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids 2 Lab Report 6 JanyDokument6 SeitenFluids 2 Lab Report 6 JanyJay-ar BensOnNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM 3e SM Chap14Dokument97 SeitenFM 3e SM Chap14Hannah Mae BacroyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stik in SlowDokument12 SeitenStik in SlowSofiane SophianeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1995周培源-50 Years of Turbulence Research in ChinaDokument16 Seiten1995周培源-50 Years of Turbulence Research in ChinaTianze LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specification Sheet For Crystallizer Crystallizer Data SheetDokument3 SeitenSpecification Sheet For Crystallizer Crystallizer Data SheetAmar RazinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME460 Exam No. 2: NameDokument1 SeiteME460 Exam No. 2: NameSayyadh Rahamath BabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PVG 32 Sauer DanfossDokument44 SeitenPVG 32 Sauer DanfossRafaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- BoilersDokument3 SeitenBoilersatikulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature Regulator With Two Temperature SensorsDokument2 SeitenTemperature Regulator With Two Temperature SensorsSandi AslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed Chart Mabre PumpDokument2 SeitenSpeed Chart Mabre PumpIsrael Gibran Cañas RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- VISCOPROPDokument2 SeitenVISCOPROPSamiir ÁlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen