Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Untitled
Hochgeladen von
alpram_stelOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Untitled
Hochgeladen von
alpram_stelCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
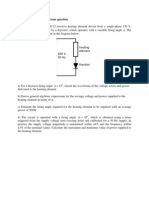
http://ece.pec.edu 47 EC P33 - ELECTRON DEVICES LABORATORY 1.
V-I characteristics of semiconductor diodes a) PN Junction diode b) Point contact diode c) Zener diode 2. Characteristics of BJT in CB configuration a) Determination of input and output characteristics b) Determination of voltage gain, current gain, input and output resistances fro m the characteristics 3. Characteristics of BJT in CE configuration a) Determination of input and output characteristics b) Determination of voltage gain, current gain, input and output resistances fro m the characteristics 4. Characteristics of JFET a) Determination of output and transfer characteristics b) Determination of pinch off voltage, rd, gm and from the characteristics 5. Characteristics of MOSFET a) Determination of output and transfer characteristics b) Determination of rd, gm and from the characteristics 6. Characteristics of SCR and TRIAC 7. Characteristics of UJT Determination of intrinsic stand off ratio 8. Characteristics of photonic devices a) Determination of V-I characteristics of LED b) Determination of V-I and intensity characteristics of phototransistor 9. Clipper circuits using diodes Positive, negative, biased and combinational clippers 10. Switching circuit a) AND and OR logic gates using diodes b) NOT gate using transistor
EC T34 - ELECTRON DEVICES UNIT- I Electron Ballistics and Semiconductor Theory: Force on charge in electric field two dimensional motion- force in a magnetic field - parallel and perpendicular elect ric and magnetic field electrostatic and magnetic deflection in CRT. Energy band structu re of insulators, conductors and semiconductors conductivity of an intrinsic semicondu ctor Fermi Dirac distribution and energy band diagram Fermi levels in extrinsic semiconductor Hall effect. UNIT- II Semiconductor Diodes: PN Junction Diode operation, forward, reverse bias characteristics- Diode equation, Temperature effects DC and AC resistance Diode equivalent circuit Transition and diffusion capacitance Diode switching times Di ode applications- Logic gates AND and OR, Series and parallel clippers. Zener diodec
haracteristics Breakdown concepts- Zener/Avalanche breakdown. UNIT- III Transistors: Transistor operation Current components CB, CE, CC configuration an d characteristics Early effect Eber-Moll model of transistor Transistor as an ampl ifierTransistor as a switch Transistor switching times. Construction and characterist ics of JFET Relation between pinch off voltage and drain current JFET as voltage variab le resistor MOSFET Depletion and enhancement types, CMOS Its construction and characteristics. UNIT- IV Special Diodes and Photonic Devices: Construction, Principle of operation, appli cation and characteristics of Schottky barrier diode, Varactor diode, Tunnel diode, PIN diode. LED, LCD, Seven segment display, Photoconductivity Photodiode, APD, Phototransistor, Solar cells- Concept of DLP. UNIT- V Power Devices: SCR, Two transistor model- operation and characteristics, Phase c ontrol using SCR, SCS and light activated SCR, Schottky diode, DIAC, TRIAC and their applications. Characteristics and equivalent circuit of UJT intrinsic standoff r atio UJT relaxation oscillator, triggering circuit for SCR programmable UJT. Text Books: 1. Jacob Millman and Christos C. Halkias, Electronic Devices and Circuits Tata McGraw Hill 2. R.L. Boylestad and L. Nashelsky, Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, PHI Learning Private Limited, Ninth Edition, 2008 Reference Books: 1. David A. Bell, Electronic Devices and Circuits, PHI Learning Private Limit ed,
EE T56 COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING UNIT I: MODULATION SYSTEMS Time and frequency domain representation of signals, amplitude modulation and demodulation, frequency modulation and demodulation, super heterodyne radio rece iver. Frequency division multiplexing. Pulse width modulation. UNIT II: TRANSMISSION MEDIUM Transmission lines Types, equivalent circuit, losses, standing waves, impedance matching, bandwidth; radio propagation Ground wave and space wave propagation, critical frequency, maximum usable frequency, path loss, white Gaussian noise. UNIT III: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Pulse code modulation, time division multiplexing, digital T-carrier system. Dig ital radio system. Digital modulation: Frequency and phase shift keying Modulator and demod ulator, bit error rate calculation. UNIT IV: DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORK PROTOCOL Data Communication codes, error control. Serial and parallel interface, telephon e network, data modem, ISDN, LAN, ISO-OSI seven layer architecture for WAN.
UNIT V: SATELLITE AND OPTICAL FIBRE COMMUNICATIONS Orbital satellites, geostationary satellites, look angles, satellite system link models, satellite system link equations; advantages of optical fibre communication - Light propaga tion through fibre, fibre loss, light sources and detectors. TEXT BOOKS 1.Wayne Tomasi, Electronic Communication Systems, Pearson Education, Third Edition , 2001. 2.Roy Blake, Electronic Communication Systems, Thomson Delmar, 2nd Edition, 2002. REFERENCE BOOKS 1.William Schweber, Electronic Communication Systems, Prentice Hall of India, 2002 . 2.G. Kennedy, Electronic Communication Systems, McGraw Hill, 4th edition, 2002. 3.Miller, Modern Electronic Communication, Prentice Hall of India, 2003
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Infineon IGBT POWER SUPPLYDokument22 SeitenInfineon IGBT POWER SUPPLYorkun burkayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Islamic University of Technology (Iut) : Course: Experiment No Name of The ExperimentDokument2 SeitenIslamic University of Technology (Iut) : Course: Experiment No Name of The ExperimentshiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Directional CouplerDokument8 Seiten4 Directional CouplerAkshay Karve100% (1)
- 6md663 664 enDokument448 Seiten6md663 664 enngocanhvyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Considerations For A Fast Stacked-MOSFET SwitchDokument7 SeitenDesign Considerations For A Fast Stacked-MOSFET SwitchBruna RibeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bourns Inductors: Product Selection Guide - Applications Guide - Cross-Reference GuideDokument28 SeitenBourns Inductors: Product Selection Guide - Applications Guide - Cross-Reference Guidekatie farrellNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDC Model PapersDokument12 SeitenEDC Model PapersanithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Panasonic HDTV TH 42px80uDokument116 SeitenPanasonic HDTV TH 42px80uSergio Alexander Pérez ChotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE207 Quiz2Dokument2 SeitenEE207 Quiz2Anonymous 1.0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Course: Yr. & Sec: Section: Time: Room: Instructor:: I. ObjectivesDokument8 SeitenName: Course: Yr. & Sec: Section: Time: Room: Instructor:: I. Objectiveskeempee meeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remocon LRT 1Dokument2 SeitenRemocon LRT 1siluma11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Hardware & NetworkingDokument34 SeitenComputer Hardware & NetworkingMahjub Mohammed100% (1)
- TP Link Router Basic SetupDokument2 SeitenTP Link Router Basic Setupjohn_karavasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication CircuitsDokument37 SeitenCommunication CircuitsDenzel Ivan PalatinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallien Krueger 700rbDokument16 SeitenGallien Krueger 700rbmichael hildebrandNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Sa 1020Dokument3 Seiten2 Sa 1020Luiz Clemente PimentaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE-ND-2020-EE 6702-Protection and Switchgear-466397335-X20498 (EE6702)Dokument3 SeitenEEE-ND-2020-EE 6702-Protection and Switchgear-466397335-X20498 (EE6702)ramalingasaravananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pignose G40V Mods - Remy ChanDokument8 SeitenPignose G40V Mods - Remy ChanMarcio Lima de CarvalhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRX3200 IngDokument16 SeitenDRX3200 IngAlbra KononaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyristor Control QuestionDokument3 SeitenThyristor Control QuestionAnonymous TJRX7CNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3com End of Sale 20dates PDFDokument110 Seiten3com End of Sale 20dates PDFRodrigo SenadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- T'DJ 609015deh 65FDokument1 SeiteT'DJ 609015deh 65Fzeb066Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5A Step-Down/Step-Up/Inverting DC-DC Converter Az34063UDokument14 Seiten1.5A Step-Down/Step-Up/Inverting DC-DC Converter Az34063UProducciones3NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isa Cba 1000 ManualDokument29 SeitenIsa Cba 1000 ManualYugie OktavianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Analysis of Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers: Technical PaperDokument15 SeitenComplete Analysis of Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers: Technical Paperhanhnguyen2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atmel 0036Dokument1 SeiteAtmel 0036namerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Basics DSP AV Z Filters NoiseDokument31 Seiten2 Basics DSP AV Z Filters NoisevignanarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eink Segmented DisplaysDokument12 SeitenEink Segmented DisplaysBen ArcherNoch keine Bewertungen
- DDR5-Anil Pandey PDFDokument3 SeitenDDR5-Anil Pandey PDFSmile Selva KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Microwave PDM ABP 30122011 PDFDokument4 SeitenMCQ Microwave PDM ABP 30122011 PDFAnonymous IXvuFde100% (1)