Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
01 1-LifeProcess
Hochgeladen von
Rama RaoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
01 1-LifeProcess
Hochgeladen von
Rama RaoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Life Process
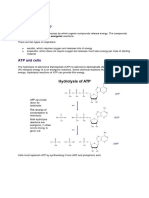
1. Photo = Light Synthesis = Process / system / Reaction 2. 3. 4. 5. i.e. Photosynthesis means Light Process. Wave Lengths of visible light is 400 700 nm Amount of CO2 present in atmosphere 0.03% Photolysis: Photo = light; Lysis = Breaking down Formation A.T.P. is called Phosphorylation AMP + Phosphate ADP + Phosphate How AMP is formed? Adenosine + Phosphate AMP ADP (Adenosine Di phosphate) ATP (Adenosine Tri Phosphate)
Equation of Photo Synthesis sun light 6CO2 + 12H 2O Chlorophyll
C6 H12O6 + 6CO2
+6H2O
Photolysis of water: The splitting of water molecule into H+ OH- ions by light activated chlorophyll is called photolysis of water Dark reaction: The Reduction of CO2 into Glucose is called dark Reaction. Pigment: Pigment is a complex molecule that absorbs light of specific wavelength in the visible Region. Chloroplast is green in colour because of a pigment called chlorophyll. The Pigment present in chloroplast converts light energy into chemical energy Ex: Formula of chlorophyll. A is C55H72O6N4 Mg.
RESPIRATION:
It is derived from Greek word called Respirare = to breaks Oxidation of food materials into CO2 + H2O for the production of Energy is called Respiration; as these processes occur in the cell hence it is cellular respiration. (Food material like carbohydrates and Fats) Respiration is of two types. They are Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration Oxidation of food materials into CO2 and H2O for the production of Energy (in the form of A.T.P.) in the presence of Oxygen (air) is called Aerobic Respiration C6H12O6 + 6O2 Anaerobic Respiration: Oxidation of food materials into Ethyle alcohol and CO2 in the absence of oxygen is called Anaerobic Respiration. 6CO2 + 6H2O + 686 K.cal
C6H12O6 Stages of Aerobic Respiration:
2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + 54 kcal
1. Glycolysis: Glyco = Sugar; Lysis = Breakingdown i.e. Breaking down of sugar (Glucose) molecule is called Glycolysis or The Oxidation of glucose into two molecules of pyruvic acid is called Glycolysis. Glycolysis takes place is Cytoplasm of the cell. 2. Krebs Cycle: Oxidation of pyruvic acid to CO2 and water in the presence of O2 is called Krebs cycle. It takes place in Matrix of mitochondria. Krebs Cycle requires O2 During Krebs cycle 2. A.T.P. are formed 2. Electron Transport: It is the 3rd stage of Aerobic Respiration. It takes place in membrane of mitochondria. During Glycolysis and Krebs cycle some electrons carries and reach to O2 and formed water. This process is called electron transport
NADH A AH2 A
A AH2
AH2
H2O
NAD
AH2
AH2
O2
Fermentation: In the absence of oxygen pyruvic acid is in completely oxidized into Ethyl Alcohol (Ethanol). This process is called Fermentation. It takes place in cytoplasm of the cell (Yeast) Molasses, Grape Juice, Germinating barley or wheat grains are used as raw materials for production of Alcohol and other beverages. Numbers of A.T.P. are formed in Aerobic. Respiration Glycolysis Krebs cycle Electron Transport Total = 40 A.T.P. = 4 A.T.P. = 2 A.T.P. = 34 A.T.P. = 40 A.T.P.
Net gain of A.T.P. are in Aerobic Respiration = 38 A.T.P. Number of A.T.P. are in Anaerobic Respiration = 10 A.T.P. i.e. Glycolysis 1 NADH = = 4. A.T.P. + 2 NADH 3. A.T.P.
2 NADH Total
= 6 A.T.P. = 10 A.T.P.
Net grain of A.T.P. in Anaerobic Respiration = 8 A.T.P. Respiratory substrates: Substances which are oxidized in the body during respiration to produce energy are called as Respiratory substrates Eg: Glucose, Amino Acids and Fatty Acids. ATP Provides Energy for various reactions and function in the organism. 1. A.T.P is required for the synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and Nucleic Acids. 2. A.T.P. is required for transport of ions, conduction of nerve impulses, Amoeboid movement, movement of cilia and flagella 3. A .T.P. is required for muscle contraction and Transport of nutrients. Factors of Respiration are 1. Oxygen 2. Temperature 3. Enzymes Optimum temperature: The temperature at which the rate of respiration is maximum is called optimum temperature.
Organs of Respiration in Animals:
Through surface of the body 1. Amoeba - Protozoa 2. Euglena Protozoa 3. Paramecium Protozoa Through skin 4. Earthworm - Annelida 5. Leech Annelida 6. Neries - Annelida
7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14.
Insects like Cockroach Scorpion Fish Prawn Frog Reptiles Aves Mammals
Trachea Book lungs Gills Gills Skin & Lungs Lungs Lungs Lungs
Respiration through skin is called Cutaneous Respiration Eg: Earth worm, Leech, frog etc. Respiration through gills is called Bronchial Respiration
Eg: Fish, Prawn & Lara of Frog (Tadpole) Respiration through Lungs is called Pulmonary Respiration Eg: Reptiles, Aves and mammals. Respiration through Trachea is called Tracheal Respiration. Eg: Cockroach, House fly, Butter fly etc.i.e. in All insects Check Yourself 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Wave lengths of visible light _____ Number A.T.P.s that are utilized during Glycolysis is _____ Net gain of A.T.P.s is Aerobic Respiration _____ Net gain of A.T.P.s is anaerobic Respiration _____ Respiratory organ in cockroach is _____ _____ is the respiratory organ in scorpion Optimal temperature is _____ Full form of A.M.P. is _____ Electron transport is takes place is _____ A.T.P. is required for synthesis of ____ & ___ ____ Which gas was evolved during respiration is ___ Fermentation Produces ____ Respiration takes place in presence of ____ Conversion of CO2 into Glucose is called ___ One NADH oxidizes to give ____ A.T.Ps
Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
7. 8. 9. 10. 11.
400 700 nm 2 38 8 Trachea Book Lungs
45C
Adenosine mono Phosphate Membrane of mitochondria Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic Oxygen
12. 13. 14. 15.
Ethyl Alcohol and CO2 Optimum temperature. Dark Reaction 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Bio Factsheet: Answering Exam Questions On RespirationDokument4 SeitenBio Factsheet: Answering Exam Questions On Respirationapi-213276898Noch keine Bewertungen
- RespirationDokument3 SeitenRespirationBio Sciences75% (4)
- 12 RespirationDokument3 Seiten12 RespirationSan Siddz100% (1)
- 2018 QuizDokument16 Seiten2018 QuizrobsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Novel Types of Kombucha Beverages With YarrowDokument8 SeitenChemical Composition and Biological Activity of Novel Types of Kombucha Beverages With YarrowAdauto AlvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Handout 1 For Grade 12Dokument10 SeitenRevision Handout 1 For Grade 12babaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiration Is of Two TypesDokument3 SeitenRespiration Is of Two TypesKyng GamariNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Respiration?Dokument10 SeitenWhat Is Respiration?Yana LouisseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular RespirationDokument52 SeitenCellular RespirationCici SintamayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid-Term Review Sheet John FarmerDokument2 SeitenMid-Term Review Sheet John FarmerJohn FarmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerobic Respiration in Animals.Dokument4 SeitenAerobic Respiration in Animals.studyklieNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants Important Questions 2022-23Dokument13 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants Important Questions 2022-23tytytfbfvhbvb dhbvNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4 RespirationDokument11 Seiten1.4 RespirationPema GaleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDokument13 SeitenJinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDEVIL GAMINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration NewDokument15 SeitenPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration NewMaria Valerie BaculiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To RespirationDokument14 SeitenIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in PlantsDokument6 SeitenNCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in PlantsHafiz HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2: The Reactants For Photosynthesis Are Light Energy, Water, CarbonDokument6 SeitenLesson 2: The Reactants For Photosynthesis Are Light Energy, Water, CarbonMarielle RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Dokument46 Seiten2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A in Agri 501-BiochemistryDokument14 SeitenA in Agri 501-BiochemistryIvan Jhon AnamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calvin CycleDokument36 SeitenCalvin CycleJane Marry IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pp19 Cellular RespirationDokument71 SeitenPp19 Cellular Respirationu22811495Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resp and Photo Study GuideDokument3 SeitenResp and Photo Study GuidenikvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Respiration Hans Krebs Aerobic OrganismsDokument1 SeiteCellular Respiration Hans Krebs Aerobic OrganismsMia SoteloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 3 ChapDokument22 SeitenClass 11 3 ChapMani TsheringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis Respiration Report FinalDokument53 SeitenPhotosynthesis Respiration Report FinalIvan Jhon AnamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiration in Plants-NotesDokument6 SeitenRespiration in Plants-NotesAnirudh KhannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Cellular RespirationDokument4 SeitenSummary of Cellular RespirationchiomasingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Dokument3 SeitenBiology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Sel 7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Dokument14 SeitenLecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Andre NesbethNoch keine Bewertungen
- RESPIRATIONDokument2 SeitenRESPIRATIONHaidar RifkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 11,12 Energy of Life RMDokument9 SeitenLec 11,12 Energy of Life RMEnmuskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14Dokument14 SeitenChapter 14Yash Singh 11th BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular RespirationDokument13 SeitenCellular Respirationmanojtbgri5793Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 Group 1Dokument7 SeitenLesson 2 Group 1Zyreine MenoriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS100 G1 Respiration in PlantsDokument80 SeitenCS100 G1 Respiration in PlantsJanrick CabuñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 2 Week 3 Lesson 2 Week 4 Lesson 1Dokument50 SeitenQuarter 2 Week 3 Lesson 2 Week 4 Lesson 1champimiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy and Respiration Part 1Dokument17 SeitenEnergy and Respiration Part 1Eva SugarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chloroplast Photosynthesis-FileDokument17 SeitenChloroplast Photosynthesis-Filesiguro hwahahahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerDokument17 SeitenMeasure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerTootsie100% (12)
- Coupled Reaction ProcessesDokument6 SeitenCoupled Reaction Processesmamariljasmine03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-14 Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes BiologyDokument5 SeitenCh-14 Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes BiologyMANDAL VIKRAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Notes - Topic 12 CIE Biology A-LevelDokument5 SeitenSummary Notes - Topic 12 CIE Biology A-LevelbeiyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOENERGETICSDokument3 SeitenBIOENERGETICSJaemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy MetabolismDokument4 SeitenEnergy MetabolismKaren ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN in EARTH ANF LIFE - 12Dokument1 SeiteCN in EARTH ANF LIFE - 12Andro RomanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Module 3 Genbio1Dokument7 SeitenStudent Module 3 Genbio1Lezel LaracasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Chapter Life Processes Class 10Dokument10 SeitenBiology Chapter Life Processes Class 10Âåřøhī MāhåjáňNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio1610 Discussion q2Dokument1 SeiteBio1610 Discussion q2api-241205310Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2Dokument5 SeitenReviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2alamagelyzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Option (B) Is The Answer.: NCERT Exemplar Solution of Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in PlantsDokument12 SeitenOption (B) Is The Answer.: NCERT Exemplar Solution of Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in PlantsMalhar DaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5 RespirationDokument11 SeitenTopic 5 RespirationPriya Kumar100% (1)
- Grade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialDokument19 SeitenGrade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialJake LacanlaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDokument4 SeitenPhotosynthesis and RespirationChristian BaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration 2 UpdatedDokument17 SeitenPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration 2 Updatedharold carbonelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 2 Module 1 General Biology 1 SCDokument31 SeitenQuarter 2 Module 1 General Biology 1 SCAldrin James DafunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 5Dokument15 SeitenPresentation 5Rahanie Gadungan PajijiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular RespirationDokument29 SeitenCellular RespirationromiifreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerDokument4 SeitenMYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerRishar bokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 14 Cellular RespirationDokument18 SeitenLesson 14 Cellular RespirationGinalyn QuimsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksVon EverandFun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular RespirationDokument6 SeitenCellular RespirationBrian Reyes GangcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVAC Design Guide For Pharmaceutical FacilitiesDokument59 SeitenHVAC Design Guide For Pharmaceutical FacilitiesKasturirangan NarayananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fermentation of Black Tea Broth (Kombucha) - I. Effects of Sucrose Concentration and Fermentation Time On The Yield of Microbial Cellulose PDFDokument9 SeitenFermentation of Black Tea Broth (Kombucha) - I. Effects of Sucrose Concentration and Fermentation Time On The Yield of Microbial Cellulose PDFRisa DedewwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agatha M. Thrash, M.D. Preventive Medicine DuringDokument2 SeitenAgatha M. Thrash, M.D. Preventive Medicine Duringapi-26198026Noch keine Bewertungen
- Compare Rate of FermentationDokument8 SeitenCompare Rate of FermentationMurugappan Sekar100% (1)
- BIOPROCESSDokument814 SeitenBIOPROCESSSumedha sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Physiology1Dokument20 SeitenExercise Physiology1BGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoichiometry of Cell Growth and Product FormationDokument2 SeitenStoichiometry of Cell Growth and Product Formationmneilg0% (1)
- TemperatureDokument3 SeitenTemperatureRuifa Huang100% (1)
- Fermentation Lab ReportDokument4 SeitenFermentation Lab ReportJulia StephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijresm V2 I12 111Dokument4 SeitenIjresm V2 I12 111Manish ShashikantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making Yoghurt (Irgo) : Unit 1: BiotechnologyDokument1 SeiteMaking Yoghurt (Irgo) : Unit 1: BiotechnologyZemetu Gimjaw AlemuNoch keine Bewertungen
- FermentationDokument7 SeitenFermentationSyed D Kings'Noch keine Bewertungen
- SCP, Its Production, Usefulness: FungiDokument4 SeitenSCP, Its Production, Usefulness: FungiRoshan jaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Onion Waste Based-Biorefinery For Sustainable Generation of Value-Added ProductsDokument8 SeitenOnion Waste Based-Biorefinery For Sustainable Generation of Value-Added ProductsMSc Yoisdel CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- It Cannot Be Used Without Prior Permission: Prof. Vaibhav V. GoudDokument176 SeitenIt Cannot Be Used Without Prior Permission: Prof. Vaibhav V. GoudshubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Aspects of Silage Making Lynn M. Johnson and Joe H. HarrisonDokument8 SeitenScientific Aspects of Silage Making Lynn M. Johnson and Joe H. Harrisoninjamul hasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Microbiology: David Laureys, Maarten Aerts, Peter Vandamme, Luc de VuystDokument11 SeitenFood Microbiology: David Laureys, Maarten Aerts, Peter Vandamme, Luc de VuystAngeles SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tle - Afa-Fp: Quarter 4 - Module 4Dokument15 SeitenTle - Afa-Fp: Quarter 4 - Module 4Erl CasiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deterioration of Cane Juice-Sources and IndicatorsDokument9 SeitenDeterioration of Cane Juice-Sources and IndicatorsMarcio SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehensive Exam Syll Rev 2010 IITDDokument5 SeitenComprehensive Exam Syll Rev 2010 IITDswjaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio IA Lab Design NaomiDokument10 SeitenBio IA Lab Design NaomiGabriella NaomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Respiration.Dokument12 SeitenLesson Plan Respiration.csamarina100% (2)
- Food Mic Lab 2Dokument6 SeitenFood Mic Lab 2Afiqah Sufi FiqaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Preservation Processing: NT30903. andDokument47 SeitenFood Preservation Processing: NT30903. andAhmad Syamil Muhamad ZinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fitri Aprilia Pratiwi, A.A.P. Agung Suryawan Wiranatha, Sri MulyaniDokument10 SeitenFitri Aprilia Pratiwi, A.A.P. Agung Suryawan Wiranatha, Sri MulyanijacquelinesindartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amylolytic Bacterial Lactic Acid Fermentation - A Review PDFDokument13 SeitenAmylolytic Bacterial Lactic Acid Fermentation - A Review PDFArturo ParedesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studies On Production of Griseofulvin: Bioprocess Engineering 21 (1999) 489 495 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999Dokument7 SeitenStudies On Production of Griseofulvin: Bioprocess Engineering 21 (1999) 489 495 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999DimasdwiNoch keine Bewertungen