Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Periodic Table Notes
Hochgeladen von
Malissa AliOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Periodic Table Notes
Hochgeladen von
Malissa AliCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Periodic Table notes Group 1: Alkali Metals Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr Soft, easily cut, slivery grey,
ey, can float Physical properties: Good conduc. Heat n elec When group: Atomic radius (distance v.e and nucleus ) Density Electropositivity Melting point Chemical properties: Same Reaction : cold water H2 n alkali O2 metal oxide Halogen metal halides Reactivity: 1. Reactivity , group 2. Atomic radius , group 3. Forces of attraction 4. Distance of nucleus n v.e far 5. Lose v.e to attain stable arrangement Precaution steps: Group 17: Halogens [F (colorless), Cl (yellowishgreen)] solid [Br (brown)] liquid [I, At (black)] solid Reactive metals Halide salts Diatomic molecules Physical properties: Non-metals Insulator of heat n elec. Low melting and boiling point When group: Atomic radius Electronegativity Malissa Ali No flammable organic solvents near Kept in paraffin oil (avoid from O2)
Periodic Table notes Colour darker Density , Molecular mass Melting/boiling points ( Van der Waals stronger, heat required to overcome the forces) Chemical properties: Same Water acid Metal metal halides NaO salts and H2O He ( airships) Ne (advertising light bulb) Ar ( elec. light bulb) Kr (flash lamps camera,lasers) Xe, Rn Physical properties: Insoluble in water Dont conduct elec. or heat Low melting/boiling point ( because very weak van der waals) Low density When group: Atomic radius Density Van der waals force Melting/boiling point Chemical properties: Mono atom Inert, Unreactive because it is already has stable electron arrangement. So, they dont need to share, gain, or release electron.
Reactivity: 1. Reactivity , group 2. Atomic radius , group 3. Forces of attraction , 4. Lower tendency to gain electron
Precaution step: Handle in fume cupboard
Group 18: Noble gases
Malissa Ali
Periodic Table notes
Transition Elements Has variable oxidation no. Form coloured compounds aqueous solution Catalytic properties Can form coloured ion Physical properties: Hard Silvery surface Ductile n malleable Electric conductor density tensile strength melting/boiling point Period 3 3 filled shells, proton no. increase by 1 unit Going across: Electrostatic force , pulled the valence electron closer to nucleus, thus atomic radius Based reasons above, the electronegativity. Elements on the left side, such as Na are electropositive while right sides are electronegative. Basic to amphoteric then acidic Amphoteric can reacts with both acids and bases form salts and water.
Malissa Ali
Periodic Table notes e.g: AlO Metals to metalloid to non-metals Na, Mg, Al at the left are metals, can form metals oxide and it is usually basic oxides. Basic oxides + water salts + water Silicon some metallic some non-metallic properties are metalloid Intermediate between metals and non-metals Silicon is nonmetals, is very poor conductor of elec. the conductivity increase with temp. it becomes of elec. at high temp. This is called semi-metals. Can be used to make semiconductors . With Group 13 p-type semiconductor produced. With Group 15 n-type semiconductor P, S, Cl, Ar at the right are non-metals. Non-metals oxides are acidic oxides. Acidic oxides + alkali salts + water Melting point increase from left to middle and decrease again to right. Na, Mg, Al have strong metallic bond ( melting point ) Silicon strong covalent bond ( melting point ) Phosphorus, Sulphur, Chlorine, Argon weak Van der Waals force.
Malissa Ali
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- NO Abatement With H2O2 (Ecom) (USPeroxide ) (2s) PDFDokument2 SeitenNO Abatement With H2O2 (Ecom) (USPeroxide ) (2s) PDFScribdManíacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Numericals of Chemical CalculationDokument4 SeitenNumericals of Chemical CalculationSaswata Sundar LagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Guentner Material Selection 2011 EnglishDokument8 SeitenGuentner Material Selection 2011 EnglishHoang100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- S BlockDokument84 SeitenS BlockPrakhar ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
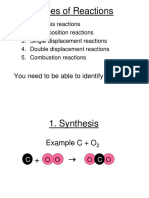
- Types of Reactions: You Need To Be Able To Identify Each TypeDokument19 SeitenTypes of Reactions: You Need To Be Able To Identify Each TypenickiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Chemistry Presentation: Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument118 SeitenChemistry Presentation: Multiple Choice QuestionsKhiZra ShahZadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 1016@j CSCM 2020 E00331Dokument20 Seiten10 1016@j CSCM 2020 E00331ValdésNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDokument17 SeitenChemical Reactions and EquationsRajesh Kumar RoushanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Geology Module 3 ReviewerDokument5 SeitenGeology Module 3 ReviewerElyssa Michelle Caringas MicuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Default (1) - PrintDokument18 SeitenDefault (1) - Printrohit SatputeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- MetallurgyDokument40 SeitenMetallurgyMothi KarunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Chemistry - IgcseDokument42 SeitenChemistry - IgcsekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Igcse Chemistry Practical Workbook仅40页Dokument40 SeitenCambridge Igcse Chemistry Practical Workbook仅40页jj75% (4)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Chem 11 PracticeDokument36 SeitenChem 11 PracticeMapleSkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Suitability and Sustainability of Sugarcane Bagasse Ash BricksDokument8 SeitenSuitability and Sustainability of Sugarcane Bagasse Ash BricksNaseeruddin Haris Naseeruddin HarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure: Question Paper 1Dokument8 SeitenAtomic Structure: Question Paper 1Willy TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Stars Without Number Alien GeneratorDokument40 SeitenStars Without Number Alien GeneratorKacper Andrzejak100% (1)
- 216 Body Lupo 3LDokument36 Seiten216 Body Lupo 3LvolkovwNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Ujian 1 Kimia Ting 4 2021Dokument11 SeitenUjian 1 Kimia Ting 4 2021ASMAHANIM BINTI MUSTAPA MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Cover Booklet KS4 Chemistry 1Dokument61 SeitenCover Booklet KS4 Chemistry 1Peter HoskinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Bangalore North District SSLC Exam 2022, Model Question Paper Set - 01 Subject: Science Max Marks: 80 Time: 3.15 Hrs. Code: 83E No. of Questions: 38Dokument26 SeitenBangalore North District SSLC Exam 2022, Model Question Paper Set - 01 Subject: Science Max Marks: 80 Time: 3.15 Hrs. Code: 83E No. of Questions: 38Rajasekaran MNoch keine Bewertungen
- My TestDokument6 SeitenMy TestLeslie MasiyandimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GentecDokument36 SeitenGentecFelipe Gagliardi de PaulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Naming Ionic Covalent CompoundsDokument2 SeitenPractice Naming Ionic Covalent CompoundsAjay NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fractional DistillationDokument9 SeitenFractional DistillationChristopher gotemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0620 s03 QP 1Dokument20 Seiten0620 s03 QP 1Sana DiwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionDokument5 SeitenPDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial Versionvictor555555100Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Science PaperDokument10 SeitenScience PaperParv GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- TP1 - 2301975423 - Hanif Wahyu SaputroDokument4 SeitenTP1 - 2301975423 - Hanif Wahyu Saputrohanif wNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1976-Morito - Transition From External To Internal Oxidation in Fe-Si Alloy As A Function of Oxygen Potential of The Ambient AtmosphereDokument4 Seiten1976-Morito - Transition From External To Internal Oxidation in Fe-Si Alloy As A Function of Oxygen Potential of The Ambient AtmosphereDavid Hernández EscobarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)