Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Session 5 Rectifiers
Hochgeladen von
Devika PramodCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Session 5 Rectifiers
Hochgeladen von
Devika PramodCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Day -5
Rectifiers
Session Speaker
Stanley J.
2
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Session Objectives
To understand the operation and characteristic
of diodes
To understand the performance parameters of
diode rectifier
To study the effect of load inductance on the
load current
3
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Session Topics
Single phase half wave rectifiers
Single phase half wave rectifiers with RL load
Single phase full wave rectifiers
Single phase Full wave rectifier with RL Load
Bridge rectifier
Bridge rectifier with RL load
Three phase bridge rectifier
4
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Rectifier
A rectifier is a circuit that converts an ac signal
into a unidirectional signal.
The half-wave rectifier is the simplest power
electronics circuit that is used for low-cost
power supplies for electronics like radios
5
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Single-Phase Half-wave Rectifier
During the positive half-cycle of the input voltage,
diode D1 conducts and the input voltage appears
across the load.
During the negative half-cycle of the input voltage,
the diode is a blocking condition and the output
voltage is zero
6
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Single-Phase Half-wave Rectifier
7
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Waveforms for input voltage and current
8
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Single-Phase Half-wave Rectifier
2 2
2
2
1 1
dc dc dc ac rms rms
dc
ac rms dc
ac
rms ac
dc dc
rms
dc
P V I P V I
P
V V V
P
V V
FF RF
V V
V
RF FF
V
q
= =
= = +
= =
| |
= =
|
\ .
Output DC and AC power
Efficiency of rectifier
Form Factor
Ripple Factor
9
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Single-Phase Half-wave Rectifier
2
2 2
1
2
1 1
1 1
( )
cos
1
cos cos
dc
s s
s s s
s s
s S S
s S S
S peak
S
P
TUF DF
VI
I I I
HF
I I
VI I
PF
VI I
I
CF
I
|
| |
= =
| |
= =
|
\ .
= =
=
Transformer utilization
Factor
Harmonic Factor
Power Factor
Crest Factor
10
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Half-wave Rectifier with RL Load
Due to inductive load, the conductive period of
diode D1 will extend beyond 180o until the
current becomes zero
The average Vl of the inductor is zero
11
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Half-wave Rectifier with RL Load
The average output voltage and output current is
( )
( )
( )
0
( )
1
sin
2
1 cos
2
1 cos
2
o dc m
m
m
o dc
V V d
V
V
I
R
t o
u u
t
t o
t
t o
t
+
=
= + (
= + (
}
12
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Half-wave Rectifier with RL Load
13
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Half-wave Rectifier with RL Load
14
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Full-Wave Rectifier (center-tapped)
There is no dc current flowing through the
transformer, there is no dc saturation problem of the
transformer core
15
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Full-Wave Rectifier (center-tapped)
The average output voltage is
( )
0
2 2
sin
2
m
o dc m
V
V V d
t
u u
t t
= =
}
The rms value of the output voltage and
current is
2 2
( )
0
( )
2
sin
2
2
2
m
o rms m
m
o rms
V
V V d
V
I
R
t
u u
t
= =
=
}
16
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Full-Wave Rectifier (center-tapped)
17
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier
During the positive half cycle of the input voltage, the
power is supplied to the load through diodes D1 and
D2.
During the negative half cycle, diode D3 and D4
Conduct.
18
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Bridge Rectifier (motor load)
19
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Bridge Rectifier (RL load)
20
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Bridge Rectifier (RL load)
( )
( )
( / )
1
2
2 1
2 sin 0
2
sin
tan ( / )
o
o s o
R L t
o
di
L Ri E V t for i
dt
V E
i t Ae
Z R
Z R L L R
e
e u
e u e
+ + = >
= +
= + =
Case 1: Continuous conduction, I
o
>0
Case 2: Discontinuous conduction, Io =0
21
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Bridge Rectifier (RL load)
( )
( )
( / )
( / )( / )
0
2 2
sin
1
0 0
R L t
o
R L
V E
i t e
Z e R
for t and i
t e
e u
e u t
(
= +
(
s s >
Case 1: Continuous conduction, I
o
>0
Case 2: Discontinuous conduction, I
o
=0
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( / )( / )
0
1
tan
2 2
sin sin
0
sin , ( ) 0
sin sin 0
cos cos
R L t
o
o
m
V E V E
i t e
Z R Z R
for i
E
At t i t
V
x x
e
o e
o |
u
e u o u
o e | e |
| u o u
u u
(
= +
(
s
= = = =
| |
+ =
|
\ .
22
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Boundary of continuous and
discontinuous (single-phase)
23
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Multiphase Rectifiers
24
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Three-Phase Bridge Rectifier
25
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Waveforms and Conduction Times
26
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
3-Phase Bridge Rectifier (RL Load)
Figure 3.15
2
2 sin
3 3
2 sin 0
ab ab
o
o ab o
v V t for t
di
L Ri E V t for i
dt
t t
e e
e
= s s
+ + = >
27
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Three-Phase Bridge Rectifier (RL load)
( )
( )
( / )
1
2
2 1
2 sin 0
2
sin
tan ( / )
o
o ab o
R L t
ab
o
di
L Ri E V t for i
dt
V E
i t Ae
Z R
Z R L L R
e
e u
e u e
+ + = >
= +
= + =
28
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Three-Phase Bridge (RL load)
( )
( ) ( )
( / )( / 3 )
( / )( / 3 )
0
sin 2 / 3 sin / 3
2
sin
1
/ 3 2 / 3 0
R L t
ab
o
R L
V E
i t e
Z e R
for t and i
o e
t e
t u t u
e u
t e t
(
= +
(
s s >
Case 1: Continuous conduction, I
o
>0
Case 2: Discontinuous conduction, I
o
=0
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( / )( / 3 )
( / )( / 3 )
( )
2tan
( )
2tan
0 ( .3.47)
sin 2 / 3 sin / 3
2
0
1
sin 2 / 3 sin / 3
( ) cos
2
1
o
R L
ab
R L
ab
Setting I in Eq
e
V E
Z e R
e
E
x
V
e
t e
t e
t
u
t
u
t u t u
t u t u
u u
=
(
=
(
(
(
~ =
(
(
29
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Boundary of continuous and
discontinuous (three-phase)
30
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
DC Filters
Filters can be used to smooth out the dc output
voltage of the rectifier and these are known as
dc filters.
The DC filters are usually of L, C and LC type
31
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
AC Filters
Due to rectification action, the input current of the
rectifier contains harmonics and ac filter is used to
filter out some of the harmonics from the supply
system.
AC filter is normally of LC type.
32
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Single-Phase Rectifier with C-Filter
33
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Single-Phase Rectifier with C-Filter
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
4
2 2 4 2
1
2(4 1)
m
o dc m
e
r pp
m
rms ripple
e
rms ripple
o dc
e
V
V V
fRC
V
V
V
fRC
V
RF
V
fRC
=
= =
= =
34
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Output Voltage with C-Filter
35
M. S. Ramaiah School of Advanced St udies, Bangalore
PEMP ESE505
Summary
Diode rectifiers convert an ac voltage to a dc
voltage.
The output voltage contain ripples which can
be removed by filters.
Depending on time constant of the load, the
load current may be discontinuous.
Line inductances cause overlap and reduce the
effective dc output voltage.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- EE1303 Lab Manual: Power Electronics ExperimentsDokument45 SeitenEE1303 Lab Manual: Power Electronics ExperimentsChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe Lab ManualDokument41 SeitenPe Lab ManualGopalakrishna Murthy C RNoch keine Bewertungen
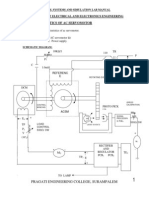
- Characteristics of Ac Servomotor: Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDokument47 SeitenCharacteristics of Ac Servomotor: Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringpragatinareshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead, lag and lag-lead compensation characteristicsDokument9 SeitenLead, lag and lag-lead compensation characteristicsvidya_sagar826Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 - Small Signal Analysis (2 SPP PDFDokument47 SeitenLecture 3 - Small Signal Analysis (2 SPP PDFAids Sumalde100% (2)
- 7034 Pclab RecordDokument80 Seiten7034 Pclab Recordmohana sundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- See 1302Dokument201 SeitenSee 1302Xiao Wang QingNoch keine Bewertungen
- KONGUNADU COLLEGE EC REVISION TEST PARTS A AND BDokument3 SeitenKONGUNADU COLLEGE EC REVISION TEST PARTS A AND Bjayj_5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee123 Final Examination 13WDokument6 SeitenEe123 Final Examination 13WJohn evergreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ayush ProjectDokument16 SeitenAyush ProjectAYUSH SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics and Drives Laboratory ManualDokument71 SeitenPower Electronics and Drives Laboratory ManualSureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 05Dokument80 SeitenPresentation 05Kesani Venkat Narsimha ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe Lab ManualDokument55 SeitenPe Lab ManualNorbert John IberaNoch keine Bewertungen
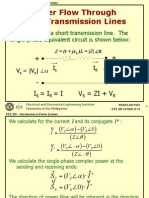
- EEE 103 - Load Flow AnalysisDokument107 SeitenEEE 103 - Load Flow AnalysisVanessa Tan100% (1)
- Power System Laboratory Experiment - 2023-24Dokument51 SeitenPower System Laboratory Experiment - 2023-24Manas Ranjan MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 電子10Dokument59 Seiten電子10YaKuan ChuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3330905-Electronic Components and CircuitsDokument8 Seiten3330905-Electronic Components and CircuitsELENoch keine Bewertungen
- SEEA1501Dokument215 SeitenSEEA1501Samsung TabletNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perform Transformer Over Current Protection Scheme: Prepared By: B.R.PrajapatiDokument3 SeitenPerform Transformer Over Current Protection Scheme: Prepared By: B.R.PrajapatiBhavik PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- State Feedback Controller Design for POESL DC-DC Luo ConverterDokument18 SeitenState Feedback Controller Design for POESL DC-DC Luo ConverterGabriel AlvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1Dokument32 SeitenLab 1Adhithyan KzhlmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Switched Reluctance Motor Behavior Under Electrical Fault ConditionsDokument8 SeitenAnalysis of Switched Reluctance Motor Behavior Under Electrical Fault ConditionsAndSolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machine Lab ManualDokument61 SeitenElectrical Machine Lab ManualPrem SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.circle Diagram of Three Phase Induction Motor From No Load & Blocked Rotor TestsDokument4 Seiten4.circle Diagram of Three Phase Induction Motor From No Load & Blocked Rotor Testsmandadi_sailesh50% (2)
- Lab 03Dokument11 SeitenLab 03Muhammad Owais RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Einstein: College of EngineeringDokument80 SeitenEinstein: College of EngineeringPoonkothaiMyilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Machines Laboratory Report-Eee371: To Determine The Polarity of A TransformerDokument3 SeitenElectric Machines Laboratory Report-Eee371: To Determine The Polarity of A TransformerKashif ZamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines - Ii Lab Manual Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDokument45 SeitenElectrical Machines - Ii Lab Manual Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringpragatinareshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Floyd CH 5Dokument40 SeitenFloyd CH 5aishahsuciutomo100% (1)
- Nonideal Effects in SC CircuitsDokument58 SeitenNonideal Effects in SC CircuitsvmspraneethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delta-Delta Transformer Connection OverviewDokument3 SeitenDelta-Delta Transformer Connection OverviewAnkadi Sikari ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PS-ii Lab Manual.Dokument70 SeitenPS-ii Lab Manual.ch manasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual 5-9Dokument20 SeitenLab Manual 5-9muhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification of Harmonics of Three-Phase Six-PulseDokument6 SeitenIdentification of Harmonics of Three-Phase Six-PulsePaulo FélixNoch keine Bewertungen
- ET1006 1112S2Exam Formulae SheetsDokument4 SeitenET1006 1112S2Exam Formulae SheetstestniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power ElectronicsDokument10 SeitenPower ElectronicsZeeshan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No.8Dokument4 SeitenExperiment No.8Sue SukmaNoch keine Bewertungen
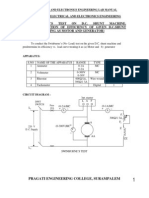
- Swinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)Dokument24 SeitenSwinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)pragatinareshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Average Current Mode Control For LLC SeriesDokument8 SeitenAverage Current Mode Control For LLC SeriesKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDC LAB ManualDokument142 SeitenEDC LAB Manualsangeethasiva67% (3)
- 3-Phase Diode Bridge RectifierDokument54 Seiten3-Phase Diode Bridge RectifierHimanshu Gupta50% (2)
- Electric Machines Lab Report 1 AnalysisDokument11 SeitenElectric Machines Lab Report 1 Analysistemp tempNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baek 2011Dokument6 SeitenBaek 2011Will TedjoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete LICA Lab ManualDokument54 SeitenComplete LICA Lab Manualnuthan9150% (2)
- MOSFET Biasing TechniquesDokument33 SeitenMOSFET Biasing TechniquesKesani Venkat Narsimha ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No: 03 Aim:: Rcoe Sem Viii B.E (Extc)Dokument7 SeitenExperiment No: 03 Aim:: Rcoe Sem Viii B.E (Extc)rahilshaikh78Noch keine Bewertungen
- El-323Electricalmachines: Experiment # 09Dokument23 SeitenEl-323Electricalmachines: Experiment # 09Lala's gamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE42 100 Cch-Lecure3 062813-F2Dokument34 SeitenEE42 100 Cch-Lecure3 062813-F2ozanistzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Machines Laboratory Report-Eee371: To Determine The Turn Ratio of A TransformerDokument5 SeitenElectric Machines Laboratory Report-Eee371: To Determine The Turn Ratio of A TransformerKashif ZamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note 4 Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amp) : Lecture Notes of ME 475: Introduction To MechatronicsDokument8 SeitenNote 4 Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amp) : Lecture Notes of ME 475: Introduction To MechatronicszailekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Methods in Power Systems Analysis with MATLABVon EverandComputer Methods in Power Systems Analysis with MATLABNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Von EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- 13.56 MHZ, Class D Push-Pull, 2KW RF GeneratorDokument17 Seiten13.56 MHZ, Class D Push-Pull, 2KW RF GeneratorettorepellegriniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode Rectifier Circuits and AnalysisDokument40 SeitenDiode Rectifier Circuits and AnalysisDina GaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- PTE 100 C Application ExamplesDokument8 SeitenPTE 100 C Application ExamplesbxteoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc Welding Power Source EvolutionDokument34 SeitenArc Welding Power Source EvolutionNatasa ZdravkovskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.2kw 28V & 48V DC Generator, 650-1200 RPM: SpecificationDokument12 Seiten7.2kw 28V & 48V DC Generator, 650-1200 RPM: SpecificationMd Jafri AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Si Eolian Comun Sistem PropusDokument8 SeitenSolar Si Eolian Comun Sistem PropusAndrei CocorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Grid Trainer - EdibonDokument4 SeitenSmart Grid Trainer - EdibonwrdlifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrancientDokument3 SeitenTrancientReneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHGDokument22 SeitenCHGDadang Lukmanul Hakim100% (1)
- Ham Mag EngDokument32 SeitenHam Mag EngKenbur100% (1)
- Cabin Fan Controller ManualDokument18 SeitenCabin Fan Controller ManualJohn DosherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factorio TND Mod Conceptual Design PDFDokument9 SeitenFactorio TND Mod Conceptual Design PDFwnnmawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 8 ElectromagnetismDokument35 SeitenModule 8 ElectromagnetismMelvin Cabonegro80% (10)
- 555 Timer TutorialDokument43 Seiten555 Timer TutorialcprofesionalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro 1Dokument48 SeitenHydro 1Rens Bakker100% (2)
- TSSPDCL 2015 PDFDokument14 SeitenTSSPDCL 2015 PDFRamakrishna Ragam0% (1)
- Dinamo TheoryDokument10 SeitenDinamo TheorytipescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uft Hobart Jet-Ex 4d São LuísDokument146 SeitenUft Hobart Jet-Ex 4d São LuísRonaldoePatricia Araujo100% (1)
- 0900766b812cdbee ABB Insulation Monitor RelayDokument15 Seiten0900766b812cdbee ABB Insulation Monitor RelaySousaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roof-top packaged air conditioners and heat pumps from 40 kW to 200 kWDokument12 SeitenRoof-top packaged air conditioners and heat pumps from 40 kW to 200 kWEduardgabrielescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Solar Energy Studies in the PhilippinesDokument4 SeitenReview of Solar Energy Studies in the PhilippinesRon Joseph Gonzales Gelogo75% (4)
- UPS & Battery SizingDokument0 SeitenUPS & Battery SizingShrikant Kajale100% (1)
- Spare Parts U012 - U014Dokument28 SeitenSpare Parts U012 - U014joaobaptistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tie Substance For Material BalanceDokument7 SeitenTie Substance For Material BalanceMukesh Tiwari100% (3)
- Marine Electrotechnology GuideDokument49 SeitenMarine Electrotechnology GuideFait HeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Lift For High-Volume ProductionDokument15 SeitenArtificial Lift For High-Volume ProductionRosa K Chang HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power PlnatDokument7 SeitenPower PlnatidigitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EatonDokument89 SeitenEatonhernangycNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Modified Sine Wave Inverter CircuitDokument6 SeitenDigital Modified Sine Wave Inverter CircuitMaster RajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iquest Solution Iquest SolutionDokument9 SeitenIquest Solution Iquest SolutionAakankshaNoch keine Bewertungen