Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Speech Oragns
Hochgeladen von
Krizzel ValeraOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Speech Oragns
Hochgeladen von
Krizzel ValeraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Phonetics 202
Not for Sale its Free for every body
Chapter 2
Speech Organs
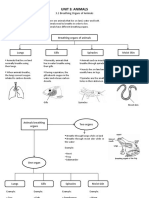
Speech organs are not created solely (only) for speech; they have other function as well. The nose and the mouth, for example are breath passages, the teeth and the tongue for chewing (( Most of Speech organs are in the Chest, throat and head.
Speech organs are those organs that take part in the speech act or speech process whether directly or indirectly. Some organs are articulator such as (Lower Lip and five part of tongue): 1- Lower Lip Moves upward to touch the upper lip as in /b , p/ or touch the upper teeth as in /f, v/ takes part in rounding process with the upper lip as in /w/. 1- Apex 2- The Tongue a. It located directly above the pharynx b. It is a major speech organ. c. One of the meaning of "tongue" is Language d. The Tongue have five part :
2- Front 3- Center 4- Dorsum Lower Lip 5-Root
1- The Apex It's also called "Tongue tip. It touches the alveolus as in / t / Come between the upper and lower teeth as in / / think Curves back as in the American / r /
2- The front It is the part of the tongue between the apex and the middle of the tongue. It touches or approaches the parallel part of the palate when producing some sound like /y /. 3- The Center Between the front of the tongue and the dorsum 4- The dorsum Back of the tongue. It usually touches or approaches the back part of the palate, i.e. the velum as with / k , g /. 5- The root /tongue back The farthest part of the tongue. It has a role in producing pharyngeal sound like / 9/ in Arabic but it has no role in English.
Prepared by Salah A. Mohalawi
Page 1 of 4
Mohalawisa@yanpet.sabic.com 0503343289
Phonetics 202
Not for Sale its Free for every body
Some organs are Point of Articulator such as (the Upper lip, upper teeth, lower teeth, alveolus, alveopalate, hard palate, velum and velum): 3- Upper Lip 4- Upper Teeth The upper teeth are used more than the lower teeth as a point of articulation (POA) 5- Lower Teeth The lower teeth co-operate with the upper teeth to make a point of articulation for sound called interdentals such as / , / when the apex comes between the two sets of teeth. 6- The Alveolus (gum ridge) It is the area easily touched by the apex to produce several sound called alveolar such as / n, I, s, z / It also called the gum ridge or the alveolar ridge. 7- The Alveopalate The front of the tongue may touch or approach this alveopalatal area to produce sound like /c, j, s, z / which called alveopalatals. 8- The Palate It consist of three parts 1- Hard Palate (called the Roof of the mouth), it touched or approached by the front of the tongue to produce sound called palatals such as / y / as in yes. 2- Soft Palate or Velum: it touched or approached by the dorsum to produce sound calls velars /k, g, / 3- Uvula if touched the dorsum to produce sound called uvular such as Arabic / q / Some organs are breath-stream (passages) such as (trachea, larynx, pharynx mouth and nose): 9 - The Trachea It is an air passage between the lungs and the larynx. It also called "Windpipe" 10- The larynx At the top end of the trachea. It also called the Voice Box. It consists of four parts: b. The Base c. Adam's Apples d. Vocal Cords (Most essential organ in the Larynx) e. The Glottis Vocal Cords a) Man's cords are longer and thicker than the woman's. b) Responsible for voice and voicelessness of speech sound. c) If the vocal cords vibrate, the sound is Voiced d) If the vocal cords not vibrate, the sound is Voiceless
Prepared by Salah A. Mohalawi
Page 2 of 4
Mohalawisa@yanpet.sabic.com 0503343289
Phonetics 202
Not for Sale its Free for every body
The Glottis a) The glottis may have one of these positions: 1- Opening with voiceless sound e.g., /p/. 2- Narrowing ,/with whispered sound. 3- Repeated opening and closing with voiced sound e.g. /b/. 4- Closing, with glottal sound, e.g., the Arabic hamza .
11- The Pharynx or (Throat) Is a cavity between the larynx and the mouth. It is one of the resonance cavities. 13- The Cavities There are four cavities or chambers related to the speech process: 1. The lung Cavity. 2. Pharyngeal Cavity. 3. Oral Cavity. 4. Nasal Cavity Some organs is energy source 14- The Lungs The Lungs are the source of energy, without which no speech can occur. Some organs are merely auxiliary organs (the abdomen, diaphragm and chest muscles) 15- Abdominal Muscles Speech is essentially dependent on the inhalation and exhalation It is located below the Diaphragm. 16- The Diaphragm The (most) speech usually happens during exhalation Above the abdomen, and between it and the chest. 17- Chest Muscles There is no speech without exhalation, the longer exhalation is, the longer speech continues. Classification of Speech Organs
1. Articulator It is a movable speech organ; it moves to touch or approach another static organ The Articulator are the tongue and the lower lip. 2. Point Of Articulation (POA) It is an immovable organ whose function is to receive the articulator such as (the upper lip, upper teeth, lower teeth, alveolus, alveopalate, hard palate, velum and uvula). 3. Stream source is the lung also lungs can be called energy source. 4- Vibrator The only vibrator in the speech system is the vocal cords. 5- Auxiliary Organ do not directly take part in speech Such as (abdominal muscles, diaphragm and chest muscles) Nose, mouth and pharynx have double or multiple functions a passage and resonator.
Prepared by Salah A. Mohalawi
Page 3 of 4
Mohalawisa@yanpet.sabic.com 0503343289
Phonetics 202
Not for Sale its Free for every body
Prepared by Salah A. Mohalawi
Page 4 of 4
Mohalawisa@yanpet.sabic.com 0503343289
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- UrologyDokument12 SeitenUrologyThakoon Tts100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Ultimate Sleep Optimization Guide - Oliva HealthDokument33 SeitenThe Ultimate Sleep Optimization Guide - Oliva HealthJoe Heyob0% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Circulatory System NotesDokument31 SeitenCirculatory System NotesJMHenry0% (1)
- Lymphatic System HistologyDokument88 SeitenLymphatic System Histologydajana212100% (1)
- Unit 3.1 Breathing Organs of AnimalsDokument4 SeitenUnit 3.1 Breathing Organs of AnimalsruszitasetapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE STUDY of AGE With Moderate DehydrationDokument24 SeitenCASE STUDY of AGE With Moderate DehydrationAnne Monique Moran Ongjoco100% (4)
- Airway Centric TMJ Airway Centric TMJDokument13 SeitenAirway Centric TMJ Airway Centric TMJBeatrix RednikNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBA #7 - Inhaled & Exhaled AirDokument3 SeitenSBA #7 - Inhaled & Exhaled AirlucyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Cycle of Breathing To Respiratory Rate in Patients With Lung TuberculosisDokument10 SeitenActive Cycle of Breathing To Respiratory Rate in Patients With Lung TuberculosissiskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gross Anatomy: RugaeDokument5 SeitenGross Anatomy: RugaeKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CasePresWeilsDisease Schematic DiagramDokument56 SeitenCasePresWeilsDisease Schematic DiagramLea Mari JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood ReadingDokument2 SeitenBlood Readingapi-383564780Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vocabulary Unit 4 PrintableDokument2 SeitenVocabulary Unit 4 PrintableLuis EnriqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fania Moza Siti Fajriah DAFTAR PUSTAKADokument3 SeitenFania Moza Siti Fajriah DAFTAR PUSTAKAmustakim takimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine System and Glands of The Human BodyDokument2 SeitenThe Endocrine System and Glands of The Human BodyFungo JasmineNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Power of SleepDokument35 SeitenThe Power of SleepEren PalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Pablito V. Mendoza Sr. High SchoolDokument2 SeitenDr. Pablito V. Mendoza Sr. High Schoolproject_genomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pengendalian Parasit Dengan: Genetic HostresistanceDokument13 SeitenPengendalian Parasit Dengan: Genetic HostresistanceHusnul khotimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form Blood RequisitionDokument2 SeitenForm Blood Requisitionshubham kumar ram100% (1)
- Chapter 05Dokument65 SeitenChapter 05Tony DiPierryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of Sleep ScriptDokument3 SeitenDisorders of Sleep ScriptIyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System - ReviewerDokument9 SeitenCirculatory System - ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ndlec SleepHygieneandRecoveryStrategiesinEliteSoccerPlayers SportsMed2015Dokument16 SeitenNdlec SleepHygieneandRecoveryStrategiesinEliteSoccerPlayers SportsMed2015JULIÁN PRIETONoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary SystemDokument8 SeitenUrinary Systemdeisy magaly uriarte tamayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Transfusion Therapy DefinitionDokument27 SeitenBlood Transfusion Therapy DefinitionEvangelin MelvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheet Body SystemDokument8 SeitenActivity Sheet Body Systemapi-340406981Noch keine Bewertungen
- Facts About FFPDokument5 SeitenFacts About FFPVicky HadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sleep Rest PatternDokument4 SeitenSleep Rest PatternCindy DelfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical - Teacher Book PDFDokument41 SeitenMedical - Teacher Book PDFSarah Auckland50% (10)
- Topic 1 - Pulmonary Anatomy, Physiology and Assessment (Hemo)Dokument39 SeitenTopic 1 - Pulmonary Anatomy, Physiology and Assessment (Hemo)Ben JilhanoNoch keine Bewertungen