Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Embryology Notes-Lecture 1-Intro To Embryo
Hochgeladen von
graycorypOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Embryology Notes-Lecture 1-Intro To Embryo
Hochgeladen von
graycorypCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Embryology: Lecture 1 Intro to Embryology Development of the embryo occurs in three main stages: 1.
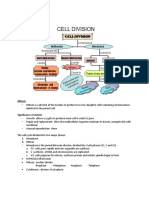
. early development: fertilization to week 3 2. embryonic period: week 3-8 3. fetal period: week 8 parturition Early development: Fertilization -> implantation -> proliferation of cells -> gastrulation -> formation of the placenta -> body axes Embryonic Period: Organogenesis and body part formation most organs and body parts VERY susceptible during this time. Beginning = flat disc, End = looks like a person Fetal Period: Rapid growth, both in length (uniform growth) and weight (non-uniform). Tissues and organs LESS susceptible to injury from teratogens, chemicals, etc. BEEPT G still very susceptible (brain, eyes, ears, palate, teeth, and ext. genitalia) Congenital Anomalies vs. Anatomical Variation - CA = abnormalities of development that are present at birth, detected inadvertently during life, or not detected until death and autopsy. - AV = fairly common anatomical discrepancies between members of the same species Clinically significant CA: - Malformations = occur during organogenesis in embryonic period; result = abnormal structure - Disruptions = result from ext. influences that cause alteration of already formed structures. - Deformations = abnormal form result from mech. Forces - Dysplasia = abnormal organization of cells into tissue Cell Cycle series of events by which all living things propogate VERY IMPORTANT that things happen when they should, usually happens rapidly. Under TIGHT CONTROL (highly regulated) monitors environment to be sure it is adequate for progeny Parts of cell cycle: G1 = gap phase of the cell cycle, gets bigger, grows up, series of checkpoints S = period of DNA synthesis G2 = b/n DNA synth and mitosis, safety gap to ensure correct replication and cell size. Organelles replicatied. G0 = non-grow, arrested in development muscle cells and neurons are usually stuck in G0. Mitosis. Result = two identical cells, same chromosome and content as parent Each parent has 22 autosomal pairs of chromosomes and one pair sex chromosomes. (XX, XY, 46) normal somatic cell = 2n, germ cell = 1n 4 main phases: - Prophase = chromosomes condense and each has two strands (chromatids), nucleolus disappears, replication of the centrioles and disintegration of nuclear envelope - Metaphase microtubules organize into the mitotic spindle, chromosomes line up. - Anaphase = chromosomes pulled apart - Telophase = nucleus reforms around the chromosomes, chromosomes uncoil, cytoplasm divides forming two cells Meiosis Sequence of two cell divisions that results in the formation of 4 cells that have the DNA of the parent cell and different genetic Limited to gamete forming cells. IMPORTANT PARTS of meiosis - Pachytene crossing over event, exchange of genetic material unique genetic combos. - Metaphase I alignment of maternal and paternal chromosomes RANDOMLY. - Meiosis II similar to mitosis, however end result is cells that are 1n
Meiosis differs in males and females: Males = 4 speratid Female = 1 viable ovum and 3 polar bodies (cell divisions are unequal-all E into one great cell with others being g.scrap) *PROPHASE I of Meiosis results in daughter cells that are genetically different that the parent cell.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 5 Bio f4Dokument20 SeitenChapter 5 Bio f4Madyha AzmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.introduction To EmbryologyDokument63 Seiten8.introduction To EmbryologyAhmed OrabyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO125ZusammenfassungLF 3Dokument43 SeitenBIO125ZusammenfassungLF 399rnbccdr8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embryology 1 GametogenesisDokument64 SeitenEmbryology 1 Gametogenesiselphas walelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis MeiosisDokument8 SeitenMitosis MeiosisJascha Isaac PangandianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell DivisionDokument19 SeitenCell DivisionAl FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Chapter 4 Notes (Grade 11)Dokument7 SeitenBio Chapter 4 Notes (Grade 11)Tammy Lam100% (2)
- EMBRYOLOGY 1 Intro-1-1Dokument64 SeitenEMBRYOLOGY 1 Intro-1-1Joseph MuimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Reviewer 2Dokument9 SeitenBiology Reviewer 2John Arnel BunquinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokument13 SeitenCell Cycle and Cell DivisionHeerak SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zoology: The Scientific Study of Animal LifeDokument9 SeitenZoology: The Scientific Study of Animal LifeShobithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1.6 Biology Ocr ADokument7 Seiten2.1.6 Biology Ocr AFatima AfifiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Module 5Dokument88 SeitenGrade 8 Module 5Lebiram Mabz86% (14)
- Introduction & Overview: Developmental BiologyDokument52 SeitenIntroduction & Overview: Developmental BiologyArtika Muliany TindaonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBC UNIT 4 - Cell Division and ReproductionDokument15 SeitenSBC UNIT 4 - Cell Division and ReproductionAdjoa AsiamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Ten:: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokument12 SeitenChapter Ten:: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionShivani Shree SundaramoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes 1st Quarter 1Dokument27 SeitenBiology Notes 1st Quarter 1Janelle Grace OrdanizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 Cell Repoduction NotesDokument56 SeitenUnit 6 Cell Repoduction NotesJocelyn CrosbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division - 2.structure of Chromosomes - 3.principles of GeneticsDokument148 SeitenCell Division - 2.structure of Chromosomes - 3.principles of Geneticsankurbiology0% (1)
- Lecture 4 Cell Division Mitosis and CancerDokument74 SeitenLecture 4 Cell Division Mitosis and CancerGerald AdolfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionDokument24 SeitenB.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionLAZY I LEoPARDNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationDokument12 Seiten1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationMo_Bash1Noch keine Bewertungen
- For Our WebsiteDokument7 SeitenFor Our Websiteapi-612362028Noch keine Bewertungen
- Meiosis and MitosisDokument6 SeitenMeiosis and MitosisSummer LoveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle To OsmosisDokument7 SeitenCell Cycle To OsmosisadlerollsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 5 Mitosis and MiosisDokument11 SeitenWeek 5 Mitosis and MiosisEarl RénzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELL CYCLE-WPS OfficeDokument4 SeitenCELL CYCLE-WPS OfficeEhiwario IkechukwuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Osmeña Q4 - Week 2Dokument48 SeitenGrade 8 Osmeña Q4 - Week 2SHAIRA LYN CUMILANGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle LectureDokument3 SeitenCell Cycle LectureR Jay LagdaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2b. Types of Egg and CleavageDokument55 Seiten2b. Types of Egg and CleavageManisha BishtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Done - Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument39 SeitenDone - Anatomy and PhysiologyMeryl RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDokument40 SeitenMitosis Vs Meiosiscmillica1176Noch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGY Final Worksheet ImportantDokument12 SeitenBIOLOGY Final Worksheet ImportantGhadi غديNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division - Key PointsDokument10 SeitenCell Division - Key PointssivarajeshwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 1 - Essential QuestionsDokument6 SeitenExam 1 - Essential QuestionsMartin De Haro GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell Cycle Activity 1Dokument5 SeitenThe Cell Cycle Activity 1sugarxglossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle Mitosis DividionDokument24 SeitenCell Cycle Mitosis DividionAshley Nicole VillegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 NotesDokument22 SeitenPart 1 Notesapi-299641879Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokument14 SeitenChapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionPhoenix RockiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELL DIVISION From BookDokument2 SeitenCELL DIVISION From BookJunell TadinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and OrganellesDokument6 SeitenCells and OrganellesNeelam NooraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 16 Cell NotesDokument9 SeitenChap 16 Cell NotesJane XuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology of CellDokument7 SeitenPathology of CellamanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meiosis: Dr. Shayma'a J. Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineerin& BiotechnologyDokument31 SeitenMeiosis: Dr. Shayma'a J. Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineerin& BiotechnologyMariam QaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Growth and DivisionDokument23 SeitenCell Growth and DivisionWolfwood ManilagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pateros Catholic School: Senior High School Department SY 2020-2021Dokument7 SeitenPateros Catholic School: Senior High School Department SY 2020-2021Mariz CarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell DivisionDokument24 SeitenCell DivisionSam MumoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle &division: Preexisting Cells Cell Division Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Some Tissues Must Be Repaired OftenDokument13 SeitenCell Cycle &division: Preexisting Cells Cell Division Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Some Tissues Must Be Repaired OftenHafidzul A'limNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and Cell DivisionDokument70 SeitenCell Structure and Cell DivisionAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Cell DivisionDokument7 SeitenBiology Form 4 Chapter 5 Cell Divisiongelgaban67% (3)
- Science 8 Q4 L2Dokument5 SeitenScience 8 Q4 L2Sheila mae CadiaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell DivisionDokument20 SeitenCell DivisionABHINABA GUPTANoch keine Bewertungen
- W9 Mitosis Chapter11Dokument26 SeitenW9 Mitosis Chapter11Ibrahim AlibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis Write UpDokument4 SeitenMitosis Write UpPrincessTNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Cell DivisionDokument43 Seiten4 Cell DivisionPrem ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksVon EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharma R&D Annual Review 2019: PharmaprojectsDokument32 SeitenPharma R&D Annual Review 2019: PharmaprojectsraviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transposons (Jumping Genes)Dokument4 SeitenTransposons (Jumping Genes)Aditya Kanwal100% (1)
- Steiner, 2002Dokument14 SeitenSteiner, 2002xicoalexandreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipidomics A Mass Spectrometry Based Systems Level Analysis of Cellular LipidsDokument6 SeitenLipidomics A Mass Spectrometry Based Systems Level Analysis of Cellular LipidsQingyang LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biosafety Resource Books PDFDokument573 SeitenBiosafety Resource Books PDFSerenityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology & Post Genomic EraDokument3 SeitenBiology & Post Genomic EraNani NaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- International User 2022Dokument13 SeitenInternational User 2022yahyaalmoalmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of MicroorganismsDokument29 SeitenClassification of MicroorganismsAbiassounNoorElhoudaBsdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monsanto and Its Indian Collaborators For BiopiracyDokument4 SeitenMonsanto and Its Indian Collaborators For Biopiracyasir39Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae of MD Murad MuftyDokument4 SeitenCurriculum Vitae of MD Murad MuftyMurad MuftyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abi 7300 RQ GuideDokument120 SeitenAbi 7300 RQ Guideashaw033Noch keine Bewertungen
- SickKids Research ProgramsDokument44 SeitenSickKids Research ProgramsKlutz4LifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Editorial Monoclonal AntibodiesDokument1 SeiteEditorial Monoclonal AntibodiesVishwas JeurkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Information Session 2010 11 of MD University, RohtakDokument98 SeitenHandbook of Information Session 2010 11 of MD University, Rohtakprabhakar ojhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 2011 Book For Web Low-ResDokument294 SeitenIs 2011 Book For Web Low-ResajaygradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms in Gram-Negative BacteriaDokument377 SeitenAntibiotic Resistance Mechanisms in Gram-Negative BacteriaahmicphdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.64 BE - Biotechnology Engg PDFDokument42 Seiten4.64 BE - Biotechnology Engg PDFVijay IyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCBI HandbookDokument391 SeitenNCBI HandbookRohnWoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Functional Organ PrintingDokument8 Seiten3D Functional Organ PrintingRobert JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 9 Protein Detection AnalysisDokument43 SeitenCH 9 Protein Detection AnalysisYan XiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buku 1Dokument4 SeitenBuku 1Amalia AnggreiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristic of Selected Soil Streptomycetes With Antimicrobial Potential Against Phytopathogenic MicroorganismsDokument21 SeitenCharacteristic of Selected Soil Streptomycetes With Antimicrobial Potential Against Phytopathogenic Microorganismsvijayrasigan786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hanafy Et Al, 2016Dokument7 SeitenHanafy Et Al, 2016Claudia HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Silico Tools For Gene Discovery PDFDokument377 SeitenIn Silico Tools For Gene Discovery PDFjunior5787Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genetically Modified OrganismsDokument2 SeitenGenetically Modified Organismsdamn creethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lean Maintenance Pfizer Case StudyDokument6 SeitenLean Maintenance Pfizer Case StudydenerspNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Biotech Companies in IndiaDokument3 SeitenList of Biotech Companies in IndiaDr-Shubhaneel Neogi100% (1)
- MitomapDokument1.079 SeitenMitomaproymalindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Graduate Degree Standard Paper - I Code:017Dokument2 SeitenPost Graduate Degree Standard Paper - I Code:017Mk.jeyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dragon Genetics WorksheetDokument4 SeitenDragon Genetics WorksheetlicservernoidaNoch keine Bewertungen