Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
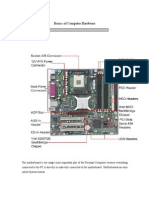
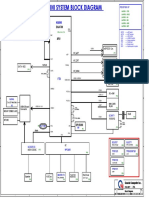
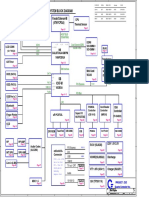
Hot Swapable Devices
Hochgeladen von
Joe O Shea RenovatorOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hot Swapable Devices
Hochgeladen von
Joe O Shea RenovatorCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hot Swapable Devices SERIAL ATA STANDARDS A consortium of manufacturers, called the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO;
see www.sata-io.org) and led by Intel, developed the serial ATA (SATA) standards. These standards also have the oversight of the T13 Committee. SATA uses a serial data path rather than the traditional parallel data path. (Essentially, the difference between the two is that data is placed on a serial cable one bit following the next, but with parallel cabling, all data in a byte is placed on the cable at one time.) The three major revisions to SATA are summarized in Table 8-2. Serial ATA interfaces are much faster than PATA interfaces and are used by all types of drives, including hard drives, CD, DVD, Blu-ray, and tape drives. A motherboard can have two, four, six, or more SATA connectors, which are much easier to configure and use than PATA connectors. SATA supports hot-swapping, also called hot-plugging. With hot-swapping, you can connect and disconnect a drive while the system is running. A SATA drive connects to one internal SATA connector on the motherboard by way of a SATA data cable. An internal SATA data cable can be up to 1 meter in length, has 7 pins, and is much narrower compared to the 40-pin parallel IDE cable (see Figure 8-12). The thin cables dont hinder airflow inside a case as much as the wide parallel ATA cables do. RAID For file servers using RAID 5 that must work continuously and hold important data, it might be practical to use hardware that allows for hard drive hot-swapping, which means you can remove one hard drive and insert another without powering down the computer. However, hard drives that can be hot-swapped cost significantly more than regular hard drives. RAID hard drive arrays are sometimes used as part of a storage area network (SAN). USB Device Even though USB devices are hot-swappable, its not always a good idea to plug or unplug a device while it is turned on. If you do so, especially when using a low-quality USB cable, you can fry the port or the device if wires in the USB connectors touch (creating a short) as you plug or unplug the connectors. Also, to protect the data on a USB storage device, double-click the Safely Remove Hardware icon in the notification area (see Figure 9-5) before removing the device. Select the device and click Stop (see Figure 9-6). It is then safe to remove the device. The latest PCMCIA standard is ExpressCard, which uses the PCI Express bus standard or the USB 2.0 standard. Two sizes of ExpressCards exist: ExpressCard/34 is 34mm wide and ExpressCard/54 is 54mm wide. Both of these types of cards are 75mm long and 5mm high. Figure 21-19 compares a CardBus card to each of the two ExpressCard cards. An ExpressCard/34 card can fit into an ExpressCard/54 slot, but not vice versa. ExpressCard slots are not backward compatible with PC Card or CardBus cards. An ExpressCard slot is fully hot-pluggable (add a card while the system is on), hot-swappable (exchange or add a card while the system is on), and supports autoconfiguration, just as does a USB port. Figure 21-20 shows an ExpressCard/54 card that provides two eSATA ports for external SATA drives.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Peripheral Wires Used in ComputersDokument7 SeitenPeripheral Wires Used in Computersayesha amjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Processing UnitDokument4 SeitenCentral Processing UnitChandan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ide ScsiDokument52 SeitenIde ScsiPavel BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDD Types 1. Parallel Advances Technology Attachment-: 3. Small Computer System InterfaceDokument2 SeitenHDD Types 1. Parallel Advances Technology Attachment-: 3. Small Computer System InterfaceSanjay DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sata & IdeDokument14 SeitenSata & IdeAnkur SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- CompTIA A+ Lesson 3 Understanding, PATA, SATA, SCSIDokument8 SeitenCompTIA A+ Lesson 3 Understanding, PATA, SATA, SCSIAli Ghalehban - علی قلعه بانNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tech Master Guide: PC Hardware Basics - Must Know by A Hardware EngineerDokument4 SeitenTech Master Guide: PC Hardware Basics - Must Know by A Hardware Engineerppc032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Hard Disk: ConnectorsDokument5 SeitenUnderstanding Hard Disk: Connectorshiro_nakamura0% (1)
- Hard DiskDokument4 SeitenHard Diskmrpatil186Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hard Drive AcquisitionDokument19 SeitenHard Drive AcquisitionJason KeysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Types of Hard Disk DriveDokument7 SeitenDifferent Types of Hard Disk DriveMukesh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IDE/ATA Interface: ObjectivesDokument7 SeitenIDE/ATA Interface: ObjectivesjefroroxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel ATA (PATA), Originally ATA, Is An Interface Standard For TheDokument6 SeitenParallel ATA (PATA), Originally ATA, Is An Interface Standard For ThepavanguptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hard Disk DriveDokument8 SeitenHard Disk DriveHelner TaghapNoch keine Bewertungen
- InterDokument88 SeitenInterAnonymous totWxwnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jhs !Dokument25 SeitenJhs !Charles MensahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Hardware Servicing Safety and PrecautionsDokument70 SeitenComputer Hardware Servicing Safety and PrecautionsMary MillareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Driver Interface Standards: ASCOM Platform Developer ComponentsDokument4 SeitenDriver Interface Standards: ASCOM Platform Developer ComponentsZendie Carsido CabusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel and Serial Ata1Dokument3 SeitenParallel and Serial Ata1AtthulaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SATA PinoutsDokument8 SeitenSATA PinoutsMadhu ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motherboard and Other PartsDokument32 SeitenMotherboard and Other PartsJom's Mijares100% (1)
- Notes A+Dokument32 SeitenNotes A+Alex SchmittNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ide/Drive Failure: by Group 4Dokument11 SeitenIde/Drive Failure: by Group 4CharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Storage: Ratnadeep BhattacharyaDokument61 SeitenStorage: Ratnadeep BhattacharyaRatnadeep BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- تقرير احترافيDokument9 Seitenتقرير احترافيhayderjabbar686Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To It Hardware1Dokument32 SeitenIntro To It Hardware1tprastyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying Expansion Module CardsDokument44 SeitenIdentifying Expansion Module CardsMaria Norberta MandacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Kinds of HDDDokument5 SeitenDifferent Kinds of HDDDar N. AgasangNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDD InstallDokument93 SeitenHDD InstallVulebg VukoicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel ATADokument6 SeitenParallel ATAhusainibaharinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper SolutionDokument21 SeitenPaper SolutionUsama BashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 Personal Computer Hardware Components (Internal Devices)Dokument22 SeitenLesson 4 Personal Computer Hardware Components (Internal Devices)MELCHOR CASTRONoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibm Disk TechDokument18 SeitenIbm Disk TechDhaval ThakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying Expansion Module CardsDokument44 SeitenIdentifying Expansion Module CardsROSE TASINoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of A Computer and Their FunctionsDokument33 SeitenParts of A Computer and Their FunctionsMia Dess Angawa Ananayo100% (1)
- Cada U3a2 ManualDokument10 SeitenCada U3a2 ManualJoseph Yølk ChiocchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Types of Hard Disk DriveDokument2 SeitenDifferent Types of Hard Disk DrivesureshexecutiveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cassy AssignmentDokument8 SeitenCassy AssignmentrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic of Blades ServicesDokument10 SeitenBasic of Blades ServicesMuhammad KamranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hard Disk Interfaces, PortsDokument36 SeitenHard Disk Interfaces, Portsanurag_garg_20Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Firewire HeaderDokument4 Seiten1 - Firewire HeaderVishnu TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Motherboard: Basics of Computer HardwareDokument34 SeitenThe Motherboard: Basics of Computer Hardwareprashanth2222Noch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of A MotherboardDokument4 SeitenParts of A MotherboardPamieDyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeForce6100PM - M2 (2 - 0A) 24 PDFDokument1 SeiteGeForce6100PM - M2 (2 - 0A) 24 PDFhamfrostNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Parts of Mother Board: Function and Uses EIDE ConnectorsDokument5 SeitenBasic Parts of Mother Board: Function and Uses EIDE ConnectorsAudrey Kristina MaypaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of A Computer With Their FunctionsDokument17 SeitenParts of A Computer With Their FunctionsREZA TAGLENoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) : RAM DDRDokument3 SeitenBIOS (Basic Input/Output System) : RAM DDRsnag07Noch keine Bewertungen
- CSS8Dokument3 SeitenCSS8Chelsea EriveNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Hard DriveDokument4 SeitenA Hard DrivekarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sat ADokument3 SeitenSat Ahus1232Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hard Drive Types: HDD's and SSD'sDokument10 SeitenHard Drive Types: HDD's and SSD'srohitsingh2909Noch keine Bewertungen
- ATA - IDE Interface Pinout Diagram at PinoutsDokument2 SeitenATA - IDE Interface Pinout Diagram at PinoutsNabendu GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serial ATA: SATA (Pronounced SAT-ah)Dokument20 SeitenSerial ATA: SATA (Pronounced SAT-ah)Ludwig McwillsNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEE 1394 PortDokument4 SeitenIEEE 1394 PortPRincess ScarLetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hard DrivesDokument69 SeitenHard Drivesprerana sheteNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Storage Work Ultrium 1760 SCSIDokument11 SeitenHP Storage Work Ultrium 1760 SCSIAwal WahjudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 5 - Ata - Ide Interface - 2Dokument28 SeitenGroup 5 - Ata - Ide Interface - 2Oluwatimilehin AdebajoNoch keine Bewertungen
- How IDE Controllers WorkDokument6 SeitenHow IDE Controllers Workapi-19737301Noch keine Bewertungen
- Administrator & Helpdesk Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVon EverandAdministrator & Helpdesk Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNoch keine Bewertungen
- DebugDokument320 SeitenDebugomanevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sony MBX 268Dokument43 SeitenSony MBX 268Manuel GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Compaq Presario CQ40 - CQ45 1 Compal - La-4101p - Rev0.3 PDFDokument46 SeitenHP Compaq Presario CQ40 - CQ45 1 Compal - La-4101p - Rev0.3 PDFElectrolaptops PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uniwill X20ii1 X40ii4 - 37GX20200-C0Dokument33 SeitenUniwill X20ii1 X40ii4 - 37GX20200-C0André HipnotistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samsung SM-A217F Service ManualDokument24 SeitenSamsung SM-A217F Service ManualldanielmartinezmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apple Macbook A1181 (K36C MLB)Dokument76 SeitenApple Macbook A1181 (K36C MLB)GabrielMarteelNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNB - NM-A841 (CG521) Rev 1.0 PDFDokument50 SeitenUNB - NM-A841 (CG521) Rev 1.0 PDFToni SetyawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Processor Broadwell U: Ddr3LDokument44 SeitenProcessor Broadwell U: Ddr3LYanto Sae50% (2)
- Redmis2 6Dokument3 SeitenRedmis2 6DayronToroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acer Aspire One 725 (Quanta ZHG)Dokument26 SeitenAcer Aspire One 725 (Quanta ZHG)NetkomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecs q67h2 Ad q65h2 Ad h67h2 AdDokument44 SeitenEcs q67h2 Ad q65h2 Ad h67h2 AdDinuth DulsanduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lucky Tech 5V-1A Motherboard ManualDokument7 SeitenLucky Tech 5V-1A Motherboard Manualryan cooperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dell Inspiron 630M Wistron 04242 91.4C401.001 SchematicsDokument44 SeitenDell Inspiron 630M Wistron 04242 91.4C401.001 SchematicsSarah AndiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- VgaDokument13 SeitenVgaBonifaceNyandangNoch keine Bewertungen
- VL-Bus Super I-O Card PTI-255WDokument4 SeitenVL-Bus Super I-O Card PTI-255WRobertChobanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intrasystem Communication and Input/output: Computer Organization AND ArchitectureDokument6 SeitenIntrasystem Communication and Input/output: Computer Organization AND ArchitecturePrakhar PuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sony-Pcg-5k2t SCHEMATICDokument35 SeitenSony-Pcg-5k2t SCHEMATICvideosonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usefull Aix Commands-1Dokument8 SeitenUsefull Aix Commands-1sts100Noch keine Bewertungen
- GIGABYTE - f9912 - GA-8I945EF-RH42722Dokument38 SeitenGIGABYTE - f9912 - GA-8I945EF-RH42722Leo MeleanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acer Aspire 3610 - Wistron Morar - Rev SBDokument40 SeitenAcer Aspire 3610 - Wistron Morar - Rev SBPer JensenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debug 1214Dokument3 SeitenDebug 1214Andi Rahmat HeriawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comet 1 PDFDokument101 SeitenComet 1 PDFRaju KhajjidoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quanta Zu2 R1a SchematicsDokument36 SeitenQuanta Zu2 R1a SchematicsBalaji Pharmacy - GMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lenovo X200 PDFDokument62 SeitenLenovo X200 PDFu3a96e na1susNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dell 153537 Laptop SchematicsDokument55 SeitenDell 153537 Laptop SchematicsMustafa BozkurtNoch keine Bewertungen
- WWW - Vinafix.Vn: Golf Amd Uma/Muxless System DiagramDokument37 SeitenWWW - Vinafix.Vn: Golf Amd Uma/Muxless System DiagramAdmin 01Noch keine Bewertungen
- NI Serial Hardware Specifications PDFDokument62 SeitenNI Serial Hardware Specifications PDFKmilo RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LLW-1/LGG-1 Schematics Sandy Bridge: Cover Page Cover Page Cover PageDokument94 SeitenLLW-1/LGG-1 Schematics Sandy Bridge: Cover Page Cover Page Cover PageAndy GersonNoch keine Bewertungen