Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CP Biology Notes - Unit 1
Hochgeladen von
Rachel FrankenfieldOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CP Biology Notes - Unit 1
Hochgeladen von
Rachel FrankenfieldCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Rachel Frankenfield September 22, 2011 CP Bio; Tucker Unit 1 Notes Summary Vocabulary: Science- organized way of using
evidence to learn abut the natural world Observation- using 1 or more senses to gather info Data- the information gathered from an observation Qualitative; description, judgement (ex: color, texture, look) Quantitative; measurements, amounts (ex: mass, weight, length)
Inference- logical interpretation based on prior knowledge and experience Hypothesis- a possible explanation for a set of observations or an answer to a scientific question Spontaneous Generation- hypothesis that life could arrive from nonliving matter Controlled Experiment- an experiment where only 1 variable changes at a time Manipulated Variable- variable that is changed on purpose Responding Variable- variable that changes due to the manipulated variable Theory- well tested explanation, unifies many observations Biology- the science that sets out to understand the living world Cell- a collection of living matter enclosed by a barrier separating it from surroundings Sexual Reproduction- two cells from different parents unite to produce the first cell of an organism Asexual Reproduction- the new cell has only one parent, parent may have split to create offspring
Metabolism- the combo of chemical reactions through which an organism breaks down or builds up Evolve- change over time Questions: 1. Inference vs. Hypothesis? Inference: reasoning involved in drawing a conclusion or making a logical judgement (ex: the sun will probably rise tomorrow, because it rises daily) Hypothesis: a tentative theory; a concept that must be proven (ex: I hypothesize that fiberglass 2. What are two areas of science that threaten morals? Medicine _________________________
3. What are the five steps of setting up an experiment? Control group Experimental group Manipulated variable Responding variable Controlled variables (constants)
4. Manipulated variable vs. responding variable? The manipulated variable is the variable that the scientist changes in the experiment. The responding variable changes due to the manipulated variable. 5. Who were Pasteur and Redi? Pasteur did an experiment of boiling broth and leaving it untouched with a curved neck attached, which remained free of micro organisms for a year. When the neck was removed, it was teeming with organisms.
Redi ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ____________________________________________
6. What are the eight characteristics of living things? Made up of cells Reproduction Based on a genetic code Maintain a stable internal environment Need for materials and energy Response to environment Growth and development Evolution
7. Unicellular organisms vs. multicellular organisms? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 8. Define Sexual reproduction and Asexual reproduction, and give an example of a species that use s each form. Sexual reproduction- two cells from diff. parents untie to produce the first cell of an organism (ex: humans) Asexual reprocuction- new cell has one single parent (ex: _____________) 9. Give three examples of genetic traits that are passed from parent to offspring. Eye color Hair color ______________
10. Why do species and organisms evolve? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 11. Give an example of each level of organization. Population- a bison herd Community- hawk, snake, prarie dog, grass, bison Ecosystem- stream, rocks, air, hawk, snake, prarie dog, grass, bison Biosphere- the part of Earth that contains all ecosystems
12. What are the advantages to the metric system? The rest of the world uses it 10, 100, 1000
13. Name 4 lab setting precautions scientists should take. Wearing safety goggles Washing hands after touching hazardous substances Using Eye Wash Station Never putting anything from the lab into their body (eating it, etc.)
Other Important Information: An important goal of scientists is to use evidence to learn about the natural world. The smallest units considered to be alive are organisms atoms. Living things can be studied at different levels of organization, from molecular level to the largest level, the ecosystem biosphere.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- World Exploration Study GuideDokument4 SeitenWorld Exploration Study GuideRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Renaissance and Reformation Study GuideDokument5 SeitenRenaissance and Reformation Study GuideRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Abigail Stinson Final WH Study GuideDokument16 SeitenAbigail Stinson Final WH Study GuideRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Renaissance and Reformation Study GuideDokument6 SeitenRenaissance and Reformation Study GuideRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
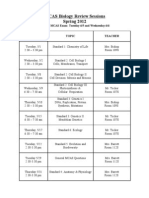
- MCAS Biology Review Nights 2012Dokument1 SeiteMCAS Biology Review Nights 2012Rachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- ROMEO AND JULIET: Act V Reading and Study Guide: I. QUESTIONS: Answer The Following QuestionsDokument2 SeitenROMEO AND JULIET: Act V Reading and Study Guide: I. QUESTIONS: Answer The Following QuestionsRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- ROMEO AND JULIET: Act III Reading and Study Guide: I. Questions: Answer The Following QuestionsDokument3 SeitenROMEO AND JULIET: Act III Reading and Study Guide: I. Questions: Answer The Following QuestionsRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Romeo and Juliet Act 4 Study GuideDokument2 SeitenRomeo and Juliet Act 4 Study GuideRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Romeo and Juliet, Act 1 Study GuideDokument2 SeitenRomeo and Juliet, Act 1 Study GuideRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Romeo and Juliet Act 2 Study GuideDokument2 SeitenRomeo and Juliet Act 2 Study GuideRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Chapter 7 Bio Test Study Guide BDokument4 SeitenChapter 7 Bio Test Study Guide BRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Grammar Review, Parts of Speech and Parts of SentencesDokument2 SeitenGrammar Review, Parts of Speech and Parts of SentencesRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Charlemagne and Feudalism QuizDokument2 SeitenCharlemagne and Feudalism QuizRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Biology MCAS Standards For Cell MaterialDokument9 SeitenBiology MCAS Standards For Cell MaterialRachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Chapter 7 Bio Test Study Guide ADokument3 SeitenChapter 7 Bio Test Study Guide ARachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Odyssey Notes, Books 1-7Dokument8 SeitenOdyssey Notes, Books 1-7Rachel FrankenfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alstom BFB PDFDokument18 SeitenAlstom BFB PDFNaveed RabbaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrate and DehydrationDokument46 SeitenHydrate and DehydrationOlvis Guillen100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- AGS Guide To Environmental SamplingDokument9 SeitenAGS Guide To Environmental SamplingmoulzedNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Ieag, 1979) Classification of Rocks and Soils For Engineering Geological MappingDokument8 Seiten(Ieag, 1979) Classification of Rocks and Soils For Engineering Geological MappingCarolina LemosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter4 BiogasDokument36 SeitenChapter4 BiogasNirob MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Lecture 18 - Phase Transformations - July 7 2022Dokument18 SeitenLecture 18 - Phase Transformations - July 7 2022Ryan MaxwellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Index - AMMDokument4 SeitenReference Index - AMMAman DeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study On Thermal Comfort in Istiqlal MosqueDokument9 SeitenStudy On Thermal Comfort in Istiqlal MosqueIndoplacesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radioactive Pollution: An Overview The Holistic Approach To EnvironmentDokument19 SeitenRadioactive Pollution: An Overview The Holistic Approach To EnvironmentTanishqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Thesis, Solar Dish Engine System 1 Uet TaxilaDokument114 SeitenFinal Thesis, Solar Dish Engine System 1 Uet TaxilaAitazaz Ahsan100% (6)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Room Air Conditioner Sizing and Choosing ChartDokument6 SeitenRoom Air Conditioner Sizing and Choosing ChartNero NoiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion Through A Stagnant Gas FilmDokument16 SeitenDiffusion Through A Stagnant Gas FilmSuleman Tariq100% (3)
- Chap4 STS Till 5jan12Dokument39 SeitenChap4 STS Till 5jan12Imran Sajid ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Classification of Seepage Control Mechanisms in Geotechnical EngineeringDokument15 SeitenA New Classification of Seepage Control Mechanisms in Geotechnical EngineeringHadia WarraichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstracts 2013 Fuel and Energy AbstractsDokument97 SeitenAbstracts 2013 Fuel and Energy AbstractsY lepayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dictionary of Energy Efficiency TechnologiesDokument367 SeitenDictionary of Energy Efficiency TechnologieskhalijimhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy End 3 1111Dokument7 SeitenPhy End 3 1111Yussuf HirowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geothermal Powerplants in The Philipiines ListDokument3 SeitenGeothermal Powerplants in The Philipiines ListJohn WhallyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disaster Preparedness, Vital Records Protection and Recovery of Archival Records - Introduction. FinalDokument22 SeitenDisaster Preparedness, Vital Records Protection and Recovery of Archival Records - Introduction. FinalJessan Badong100% (1)
- Malleability and Metallography of Nickel - MericaDokument28 SeitenMalleability and Metallography of Nickel - MericaJ. GirotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of ThermodynamicsDokument55 SeitenFundamentals of Thermodynamicsudoye kachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout 6Dokument46 SeitenHandout 6erwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAE Use of English ExercisesDokument2 SeitenCAE Use of English ExercisesIsabelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 08 02 GWRA - India - 2020Dokument401 Seiten2021 08 02 GWRA - India - 2020Channel ZeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Science Nat Parallel Test2Dokument11 SeitenScience Nat Parallel Test2Kristine BarredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 8 Geography Worksheet - All ChaptersDokument15 SeitenCBSE Class 8 Geography Worksheet - All Chapterssana0% (1)
- 12 PV3000 VPMDokument1 Seite12 PV3000 VPMyo8rmhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Filled Out SMRDokument18 SeitenSample Filled Out SMRBill CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flood Contingency Plan - TrcaDokument29 SeitenFlood Contingency Plan - TrcaMarieta AlejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Circulation of Radiocerium Isotopes From The May 14, 1965, Nuclear ExplosioDokument8 SeitenGlobal Circulation of Radiocerium Isotopes From The May 14, 1965, Nuclear ExplosioAnonymous d1CGjMTiNoch keine Bewertungen