Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Transformer Selection Guide
Hochgeladen von
bmshivakumarOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Transformer Selection Guide
Hochgeladen von
bmshivakumarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Transformer Selection Guide
Follow these general guidelines when selecting a transformer: The National Electrical Code section 450-3 addresses the primary and secondary windings of transformers (600 volts or less). Primary fusing should not exceed 250% of full load amps; secondary fusing should not exceed 125% of full load amps
To achieve maximum transformer efficiency, maintain average transformer loading between 60 and 80 percent Temperature Rise represents the number of degrees using the Celsius scale at which a transformer is designed to operate above 40 ambient temperature
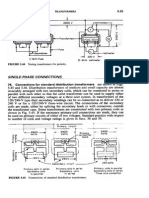
The three phases (legs) of a Delta transformer should be kept balanced within 5% of each other for maximum efficiency. Unbalanced loads can severely de-rate or even overload a transformer
Single-Phase Transformer Selection
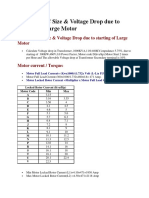
1. 2. 3a. 3b. 3c. How to Select a Single-Phase Transformer For Resistive Loads Determine the secondary voltage: 120 or 240. Determine the running amperage of your load. Multiply voltage x amperage to determine VA. Divide result of "A" by 1000 to determine = KVA (Kilo Volt Amp). Divide result of "B" by transformer KVA to determine load percentage. How to Select a Single-Phase Transformer For Motor Loads Determine the secondary voltage 120 or 240. Determine the running amperage of your load. Multiply voltage x amperage to determine VA. Divide the result of "A" by the PF (power factor) of motor. Take the result of "B" and multiply by the motor SF (service factor). Divide result of "C" by 1000 to determine KVA (Kilo Volt Amp). Divide result of "D" by transformer KVA to determine load percentage. Example 240V 10A 3 KVA Example 240V 10A 0.85 PF 1.25 SF 5 KVA Formula 240 x 10 2400 / 1000 2.4 / 3 Formula 240 x 10 2400 / 0.85 2824 x 1.25 3530 / 1000 3.53 / 5 Result 2400 2.4 KVA 0.8 or 80% Result 2400 2824 3530 3.53 KVA 0.7 or 70%
1. 2. 3a. 3b. 3c. 3d. 3e.
Three-Phase Transformer Selection
1. 2. 3a. 3b. 3c. How To Select A Three-Phase Transformer For Resistive Loads Determine the secondary voltage 208 or 240. Determine the running amperage of your load. Multiply voltage x amperage x 1.73 (square root of 3) to determine VA. Divide result of "A" by 1000 this = KVA (Kilo Volt Amp). Divide result of "B" by transformer KVA to determine load percentage. How To Select A Three-Phase Transformer For Motor Loads Determine the Secondary voltage 208 or 240. Determine the running amperage of your load . Multiply voltage x amperage x 1.73 (square root of 3) to determine VA. Divide the result of "A" by the PF (power factor) of motor. Take the result of "B" and multiply by the motor SF (service factor). Divide result of "A" by 1000 to determine KVA (Kilo Volt Amp). Divide result of "B" by transformer KVA to determine load percentage. Example 240V 80A 45 KVA Example 240V 80A 0.85 PF 1.25 SF 75 KVA Formula 240 x 80 x 1.73 33,216 / 1000 33.2 / 45 Formula 240 x 80 x 1.73 33,216 / 0.85 39,078 x 1.25 48,847 / 1000 48.8 / 75 Result 33,216 33.2 KVA 0.73 or 73% Result 33,216 39,078 48,847 48.8 KVA 0.65 or 65%
1. 2. 3a. 3b. 3c. 3d. 3e.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Power-system protection A Complete GuideVon EverandPower-system protection A Complete GuideBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Transformer SeminarDokument31 SeitenTransformer Seminarsahirprojects100% (1)
- Transformer Brochure Minera - SchneiderDokument4 SeitenTransformer Brochure Minera - SchneiderTino HardikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EcoDial 3.36Dokument92 SeitenEcoDial 3.36tatianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dry Type Transformer: Single-Phase, Three-Single, Three-Two and Three-Phase Transformers 1.1 KV To 7.2 KV ClassesDokument8 SeitenDry Type Transformer: Single-Phase, Three-Single, Three-Two and Three-Phase Transformers 1.1 KV To 7.2 KV ClassesJeison Osmar Altamirano SoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLIM®TransformerDokument6 SeitenSLIM®TransformerJayadevDamodaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- AL Spec. IGEN POWERTECHDokument13 SeitenAL Spec. IGEN POWERTECHJatupol PongsirisartNoch keine Bewertungen
- HPS Catalog Dry-Type Medium VoltageDokument15 SeitenHPS Catalog Dry-Type Medium VoltageEmilio SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Webex Transformerless UPS EATON 072313Dokument35 SeitenWebex Transformerless UPS EATON 072313ranita senNoch keine Bewertungen
- L&T GIC Catalogue 25 Sep 09Dokument24 SeitenL&T GIC Catalogue 25 Sep 09Naresh KapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data TrafoDokument6 SeitenData Trafo'bouUo' Jrs Season IINoch keine Bewertungen
- 1LCA000003-LTE SinglePh Overhead 10kVA 167kVA Rev01Dokument4 Seiten1LCA000003-LTE SinglePh Overhead 10kVA 167kVA Rev01thapa786mNoch keine Bewertungen
- OTM C 10,11D Manual EN PDFDokument20 SeitenOTM C 10,11D Manual EN PDFAlejandro Walter Lévano GuillénNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.035 Transformer-15KVA CooperDokument24 Seiten1.035 Transformer-15KVA CooperAra AkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trafo Loss CalDokument3 SeitenTrafo Loss Calashish sahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Presentation MSETCL KalwaDokument38 SeitenReport Presentation MSETCL KalwaManish Kumar Bhardwaj100% (1)
- WP Schneider Electric Renewable Energies CatalogDokument72 SeitenWP Schneider Electric Renewable Energies CatalognaveedfndNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Manufacturer EnquiryDokument26 SeitenTransformer Manufacturer EnquiryblaagicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modelling of Dry Lightning Impulse Test On 145 KV Oil Impregnated Paper Bushing For High Voltage TransformerDokument6 SeitenModelling of Dry Lightning Impulse Test On 145 KV Oil Impregnated Paper Bushing For High Voltage TransformerFaridah HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rex Distribution Transformer Catalog 2019 (6 19 2019) RegularDokument36 SeitenRex Distribution Transformer Catalog 2019 (6 19 2019) RegularHany NassimNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB TxpertDokument2 SeitenABB TxpertJohn-Doe OrdinaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymer InsulatorsDokument34 SeitenPolymer InsulatorsAbraiz Khan KhattakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature Indicator of TransformerDokument4 SeitenTemperature Indicator of Transformermayur3dhande100% (1)
- Section - 1 (Power Transformer) A. Purpose: The Purpose of This Document Is To Design (Sizing Calculation) MainDokument2 SeitenSection - 1 (Power Transformer) A. Purpose: The Purpose of This Document Is To Design (Sizing Calculation) Mainsrikanta100% (1)
- 62 Low Voltage TransformersDokument36 Seiten62 Low Voltage TransformersBob Mitzel NavarreteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grounding System MethodsDokument5 SeitenGrounding System MethodsgaxyvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surge Arresters For Cable Sheath Preventing Power Losses in M.V. NetworksDokument7 SeitenSurge Arresters For Cable Sheath Preventing Power Losses in M.V. NetworksKenobyUTPNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB UniPack Datasheet TERRA 1600kVA WEBDokument2 SeitenABB UniPack Datasheet TERRA 1600kVA WEBprashanth chandrashekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synergy Elektrik (PVT.) LTD PDFDokument3 SeitenSynergy Elektrik (PVT.) LTD PDFMuhammad KashifNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIL-Products-PUF-PIR Pipesection For Insulation Res17 PDFDokument2 SeitenLIL-Products-PUF-PIR Pipesection For Insulation Res17 PDFJoshua FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 110kV Power Electric TransformerDokument4 Seiten110kV Power Electric TransformerCristian Camilo Silva GuevaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sopan Pems Nayara (P) : CommentsDokument7 SeitenSopan Pems Nayara (P) : CommentssidharthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers ConnectionsDokument6 SeitenTransformers Connectionsgeorgel1980Noch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Test Methods For Crosslinked Insulations and Jackets For Wire and CableDokument25 SeitenStandard Test Methods For Crosslinked Insulations and Jackets For Wire and CableLina Rocio Gutierrez BarraganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caledoniana HT CableDokument100 SeitenCaledoniana HT Cable1382aceNoch keine Bewertungen
- LVDC Distribution SystemDokument52 SeitenLVDC Distribution SystemAhmad TouqirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 47 TS For Armoured 75 Ohm Coaxial Cable For PLCCDokument8 Seiten47 TS For Armoured 75 Ohm Coaxial Cable For PLCChiralalnhpcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Carrying Capacities & Other Technical TablesDokument7 SeitenCurrent Carrying Capacities & Other Technical TablesImran_firdousiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminum Cables For Power Distribution AECH - Chapter - 10Dokument22 SeitenAluminum Cables For Power Distribution AECH - Chapter - 10Anonymous XgX8kTNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2240 162 Pve U 004 SHT 3 3 01Dokument13 Seiten2240 162 Pve U 004 SHT 3 3 01Anagha DebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outdoor DisconnectorsDokument12 SeitenOutdoor DisconnectorsengmswilamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03HYUNDAI Intelligent Preventative Diagnostic System (HiPDS)Dokument12 Seiten03HYUNDAI Intelligent Preventative Diagnostic System (HiPDS)juliancansenNoch keine Bewertungen
- LVDC Distribution NetworkDokument47 SeitenLVDC Distribution Networkminsoo11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technical - Tables Siemens CablesDokument9 SeitenTechnical - Tables Siemens CablesIon Logofătu AlbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- REF Fuse Sizing GuideDokument11 SeitenREF Fuse Sizing GuideRa ArNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cable SizingDokument9 SeitenCable Sizingmuhammad nazirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Protective EquipmentDokument17 SeitenElectrical Protective EquipmentKhageswar SamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Available Fault Current Calculation: 0 I kVA X 1000 Trans. FLADokument8 SeitenAvailable Fault Current Calculation: 0 I kVA X 1000 Trans. FLAconsultnadeem70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Low Loss Conductor CatalogueDokument4 SeitenLow Loss Conductor Cataloguevishnu ojhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Over Head Conductors Technical DetailsDokument30 SeitenOver Head Conductors Technical DetailsKishore KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculate Transformer Size and MotorDokument2 SeitenCalculate Transformer Size and MotorThirumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cable Schedule P 90916 E D2 8532 124 01 PCS PARLI Revision 2Dokument18 SeitenCable Schedule P 90916 E D2 8532 124 01 PCS PARLI Revision 2AnilNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB in The Solar Inverter Space: Enabling The Digital Grid With A Renewing Solution PortfolioDokument53 SeitenABB in The Solar Inverter Space: Enabling The Digital Grid With A Renewing Solution Portfolioikan11Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Cable: Price ListDokument48 SeitenGeneral Cable: Price Listalfonso.parker100% (1)
- Transmission Line LossesDokument1 SeiteTransmission Line LossesLG TVNoch keine Bewertungen
- KSH International Enamelled Copper Conductors/Strips BrochureDokument2 SeitenKSH International Enamelled Copper Conductors/Strips Brochurekshintl100% (1)
- High Voltage Spike (DV - DT) and Motor Protection MethodsDokument5 SeitenHigh Voltage Spike (DV - DT) and Motor Protection MethodsAnonymous V6y1QL6hnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery Sizing: From Open ElectricalDokument11 SeitenBattery Sizing: From Open ElectricalBADRI VENKATESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 TransformerDokument58 SeitenChapter 2 Transformerquocdung NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- EWF PrintDokument8 SeitenEWF PrintbmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2706 22384 1 PBDokument7 Seiten2706 22384 1 PBbmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control and Data Flow Testing On Function Block DiagramsDokument14 SeitenControl and Data Flow Testing On Function Block DiagramsbmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motors and Motor StartersDokument32 SeitenMotors and Motor StartersbmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Ec Control StrategyDokument15 SeitenI Ec Control StrategybmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biotechnology: BiologyDokument18 SeitenBiotechnology: BiologyBrij Mohan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 27 PLC LanguagesDokument16 SeitenLecture 27 PLC LanguagesbmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Encoder Vs ResolverDokument4 SeitenEncoder Vs ResolverMarco AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carpenter Day 1Dokument47 SeitenCarpenter Day 1bmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principled SimplicityDokument148 SeitenPrincipled SimplicitybmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEC61131 3 BasicsDokument29 SeitenIEC61131 3 BasicsbmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1504 11 RelationshipsDokument37 Seiten1504 11 RelationshipsbmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buddhist Basic GuideDokument23 SeitenBuddhist Basic Guidebmshivakumar100% (1)
- AristotleDokument56 SeitenAristotlebmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ai 230 PLC-1Dokument105 SeitenAi 230 PLC-1Sonal Power UnlimitdNoch keine Bewertungen
- CamDokument12 SeitenCambmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATV32HU75N4Dokument11 SeitenATV32HU75N4bmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical SafetyDokument54 SeitenElectrical Safetybmshivakumar100% (1)
- Cable Routing 1Dokument1 SeiteCable Routing 1bmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MahabharataDokument8 SeitenMahabharatabmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens LOGO EthernetDokument5 SeitenSiemens LOGO EthernetbmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Excel/VBA To Speed-Up Daily Data ProcessingDokument39 SeitenUsing Excel/VBA To Speed-Up Daily Data ProcessingShrishaila ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- G-Code BasicsDokument10 SeitenG-Code BasicsNaman ModiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID KalkulatsioonDokument11 SeitenPID KalkulatsioonbmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 S and 2 S ComplementDokument1 Seite1 S and 2 S ComplementbmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Final Word On The 8051Dokument255 SeitenThe Final Word On The 8051Raja SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5th Sem AUTO 2010 SylDokument15 Seiten5th Sem AUTO 2010 Sylعبدالله عمرNoch keine Bewertungen
- HCR1200 BrochDokument4 SeitenHCR1200 Brochmed_tataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Analysis: Prepared For: Prepared byDokument10 SeitenSolar Analysis: Prepared For: Prepared byCesarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machine Lab ManualDokument61 SeitenElectrical Machine Lab ManualPrem SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Solar R and D and MarketingDokument35 SeitenPresentation On Solar R and D and MarketingSteeson MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Sem - Assignment - MD II (2962108)Dokument5 Seiten8th Sem - Assignment - MD II (2962108)rishabhk28995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Whitepaper Ground Potential Rise ExplainedDokument17 SeitenWhitepaper Ground Potential Rise ExplainedHaresh RenkutlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EKHB Daikin Altherma Operation ManualDokument60 SeitenEKHB Daikin Altherma Operation Manualangel_dos100% (1)
- Bomba de EngranagesDokument0 SeitenBomba de EngranagesPablo OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer ProtectionDokument23 SeitenTransformer Protectionsubbu2051100% (2)
- Metrode - P92 WPS PDFDokument3 SeitenMetrode - P92 WPS PDFXing ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnergyDokument19 SeitenEnergyPhuoc NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of CarburetorDokument12 SeitenFundamentals of Carburetorecasayang0% (1)
- Pedalpower ppg2 3 1Dokument7 SeitenPedalpower ppg2 3 1ramsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive ServicingDokument5 SeitenAutomotive ServicingLiezl SabadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everexceed - Lithium - Ep - 48100 - 15b - LCD - DatasheetDokument2 SeitenEverexceed - Lithium - Ep - 48100 - 15b - LCD - DatasheetmaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installation Instructions For Axial Fans For Bathroom, Toilets, Utility Rooms and KitchensDokument2 SeitenInstallation Instructions For Axial Fans For Bathroom, Toilets, Utility Rooms and KitchenstylerdurdaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agk SorularDokument4 SeitenAgk SorularSezgin BayrakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Test ReportDokument46 SeitenTransformer Test ReportAkshay GatkalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation From DR David Jacobs IetDokument47 SeitenPresentation From DR David Jacobs IetcookiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : Why Teach?Dokument2 SeitenFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : Why Teach?Austin Capal Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pi 5 3 en 1Dokument2 SeitenPi 5 3 en 1LidijaSpaseskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alteradores MarathonDokument8 SeitenAlteradores MarathonSalineñoApasionadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument5 SeitenChemistryapi-248750786Noch keine Bewertungen
- MAN 2848 LE Operation Manual PDFDokument46 SeitenMAN 2848 LE Operation Manual PDFFrancisco Mosquera Lopez100% (1)
- Climate Change Warning British English Upper Intermediate Advanced GroupDokument4 SeitenClimate Change Warning British English Upper Intermediate Advanced Groupsharondun1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- AHAC BookletDokument36 SeitenAHAC BookletsantiagovbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Report On Alternate FuelDokument10 SeitenSeminar Report On Alternate FuelDeepak Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 Assignment: Creating Your Prototype WorksheetDokument3 SeitenModule 5 Assignment: Creating Your Prototype WorksheetTARUN SHUKLANoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 GL For Selection of Turbine and Governing PDFDokument96 Seiten3.1 GL For Selection of Turbine and Governing PDFPablo German TouriñanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation Steca Solarix PliDokument27 SeitenPresentation Steca Solarix PliMahalmadane ToureNoch keine Bewertungen