Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Math PT #3.1,3.2
Hochgeladen von
Bill Joseph SuguitanOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Math PT #3.1,3.2
Hochgeladen von
Bill Joseph SuguitanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Name: Suguitan, Bill Joseph O.
Section: II-St. Sebastian
Operation
General Process
(Same) 1.Add the numerators. 2.retain the denominator 3.simplify. (different) 1.find the lcd 2.write the equivalent expression. 3.add the numerators; keep the lcd 4.simplify NOTE: IF THE DENOMINATORS ARE
(same) 1.4 +x
X+4 (add)
2.Those two are the same..they just oppose,following Commutative property the final answer is 1. (different) 1.Find LCD (10x) 2.Divide 3.2x2+20x
4+X X+4 = x+4/x+4 =1(final) 2.x+4x
5/10x 2x/10x
To find the least common denominator, simply list the multiples of each denominator (multiply by 2, 3, 4, etc.) then look for the smallest number that appears in each list.
(LCD:10x) 2x+20x 10X (final)
10x (final)
OPPOSITE, MULTIPLY IT BY -1/-1
Operation
General Process
(Same) 1.Subtract the numerators. 2.retain the denominator 3.simplify. (different) 1.find the lcd 2.write the equivalent expression. 3.SuBt. the numerators; keep the lcd 4.simplify NOTE: IF THE
(same) 1.4 -x
X+4 (add)
2.Those two are the different, thats the final answer. (different) 1.Find LCD (10x) 2.Divide 3.2x2-20x
4-X X+4 = x-4/x+4 x-4 =x+4 (final) 2.x-4x
5/10x 2x/10x
1.
(LCD:10x) 2x2-20x 10X (final)
10x (final)
DENOMINATORS ARE OPPOSITE, MULTIPLY IT BY -1/-1
Operation
General
1.WRITE EACH Process NUMERATOR and denominator IN FACTORED FORM 2.DIVIDE OUT ANY SAME FACTORS IN THE NUMERATOR TO DENOMINATOR
1.FACTOR THE NUMERATOR AND DENOMINATOR
2x
5(x-4)
1. 2x 5(x-4) 3(x-4) 5.2.2.x.x 2. 2x 5(x-4) 3(x-4) 5.2.2.x.x 1 3 Ans: 1 6x 1 2 x
3(x-4) 5.2.2.x.x 2.CROSS OUT COMMON FACTORS 2,x, (x-4),5 3.MULTIPLY 1 1 3 2 X = 1 6X
3.MULTIPLY 4.SIMPLIFY
Operation
General Process
1.Reciprocal The divisor
2.WRITE EACH NUMERATOR and denominator IN FACTORED FORM 3.DIVIDE OUT ANY SAME FACTORS IN THE NUMERATOR TO DENOMINATOR
1.RECIPROCAL,
2.FACTOR
THE NUMERATOR AND DENOMINATOR 5(a+b) 5a 5a (a-b)(a+b)
5(a+b) 5a 5a (a-b)(a+b)
3.CROSS OUT = COMMON FACTORS 5(a+b) 5a 5(a+b) 5a 5a (a-b)(a+b) 5a (a-b)(a+b) 4.MULTIPLY 5 (a-b)
4.MULTIPLY 5.SIMPLIFY
5 (a-b)(final)
Name: Suguitan, Bill Joseph O.
Section: II-St. Sebastian
What is IT? A Quadratic Equation in one variable is an equation in the form ax2+bx+c=0, where a is not equal to 0.
Important Features/Info
1. A Quadratic Equation cant be one if it doesnt have (ax2), it would be linear. 2. Its standard form is ax2+bx+c=0 (complete quadratic) 3. But it can be in ,ax2+bx=0,ax2=0.ax2+c=0(incomplete quad)
4. You can solve Quadratic Equations in 4 ways: Factor by Grouping, Factoring, Completing the square and by the Quadratic Formula
Examples(5)
X2+2x+4=0 4x2+6=0 5(x-3)=6x2+10(x-10) (4x+3)(6x-1)=9-10x 3m2-6m-5=5m-4m2
Non-Examples(5)
X=10 X+2+2x=3(2x+9) a(b+2)=19(x+2) x+10= -9 15-1=10(a[x+b])
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Lesson 2.4 Adding and Subtracting Rational ExpressionsDokument32 SeitenLesson 2.4 Adding and Subtracting Rational ExpressionsLyka FaustoNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8 Math Q1 - Week 3 - Simplifying Rational ExpressionDokument20 SeitenG8 Math Q1 - Week 3 - Simplifying Rational ExpressionWenilyn MananganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 2Dokument8 SeitenWorksheet 2GELYNNE LOPEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rational ExpressionsDokument9 SeitenRational ExpressionsShineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Division PF PolyDokument11 SeitenDivision PF PolyElle BalboaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compiled by Shivani Dogra Roll No 36 Class 10Dokument25 SeitenCompiled by Shivani Dogra Roll No 36 Class 10itsankurzNoch keine Bewertungen
- General-Mathematics Q1 Module-3aDokument13 SeitenGeneral-Mathematics Q1 Module-3aMalen GallegosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra 1 Chapter 3Dokument62 SeitenAlgebra 1 Chapter 3Bryce MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1.1 Basic Differentiation RulesDokument3 Seiten2.1.1 Basic Differentiation RulesEugenio Aranda MartínezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter TestDokument26 SeitenChapter TestJohn FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsVon EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 4th Quarter-PBADokument12 Seiten4th Quarter-PBAerinclareburkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 0362 Unit 2 Chapter 7 - Rationals: Updated: Summer 2015Dokument9 SeitenMath 0362 Unit 2 Chapter 7 - Rationals: Updated: Summer 2015Afsana MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2-2017 Unit 3 Worksheets CH 6 CP A2Dokument46 SeitenA2-2017 Unit 3 Worksheets CH 6 CP A2Guai PlayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluating FunctionsDokument9 SeitenEvaluating FunctionsEden SumilayNoch keine Bewertungen
- When You Multiply by A Negative Number The Inequality Sign Changes DirectionDokument16 SeitenWhen You Multiply by A Negative Number The Inequality Sign Changes Directionaly jacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 3 NotesDokument14 Seiten12 3 Notesapi-199670769Noch keine Bewertungen
- MalloDokument34 SeitenMalloBea DatayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 1.7Dokument28 SeitenDay 1.7Teacher JAY-AR LAGMANNoch keine Bewertungen
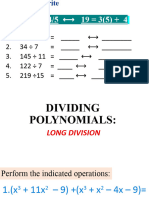
- Show Solutions Neatly and Orderly.: X 1 x+3 x+1 x+4Dokument1 SeiteShow Solutions Neatly and Orderly.: X 1 x+3 x+1 x+4Brandon Alforque EsmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes (Jan-Feb - 2024)Dokument73 SeitenLecture Notes (Jan-Feb - 2024)kishankumar patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section P6 Rational ExpressionsDokument33 SeitenSection P6 Rational ExpressionsdavogezuNoch keine Bewertungen
- JHJJNJNJN, NJNJDokument2 SeitenJHJJNJNJN, NJNJWilburNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors of PolynomialsDokument49 SeitenFactors of PolynomialsHeatblastNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEM HUMSS Q3AS 11 Basic CalculusDokument6 SeitenSTEM HUMSS Q3AS 11 Basic Calculusblockwriters20Noch keine Bewertungen
- PolynomialsDokument54 SeitenPolynomialsGimar Alingig ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 1 - Chapter 2 - Algebraic ExpressionsDokument7 SeitenMath 1 - Chapter 2 - Algebraic ExpressionsJose Arnaldo Bebita DrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combine PDFDokument53 SeitenCombine PDFAxel FangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Rational Equations: Lesson 5Dokument7 SeitenSolving Rational Equations: Lesson 5Jenray DacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.5 Complex Fractions PDFDokument7 Seiten7.5 Complex Fractions PDFLaiza Niña Gimenez LariegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honors Pre-Calc: REVIEW For Semester Exam January 2012Dokument10 SeitenHonors Pre-Calc: REVIEW For Semester Exam January 2012Mike PateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1. Factor - CommonDokument5 SeitenActivity 1. Factor - CommonJohair BalindongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factoring PolynomialsDokument50 SeitenFactoring PolynomialsAnne DivinagraciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLP 13.1 Addition and Subtraction of Rational Expressions With Different DenominatorDokument6 SeitenTLP 13.1 Addition and Subtraction of Rational Expressions With Different DenominatorMilan WanderlandNoch keine Bewertungen
- For All Alge-Tile Work It Is Essential To Remember That Means Minus and Any Other Colour Means PlusDokument32 SeitenFor All Alge-Tile Work It Is Essential To Remember That Means Minus and Any Other Colour Means PlusLouNVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 Operation On FunctionsDokument20 SeitenLesson 3 Operation On FunctionsShe Real LeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factorising ExpressionsDokument13 SeitenFactorising ExpressionsM.R.TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X: II. Find The Product and Simplify The AnswerDokument2 SeitenX X X X X X X X X X X X X X X: II. Find The Product and Simplify The AnswerFrancis GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2Q Week 6Dokument31 Seiten2Q Week 6Jackie Claire GuiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 1 Week 6 Mathematics 10: CompetencyDokument10 SeitenQuarter 1 Week 6 Mathematics 10: CompetencyBalod.Ace Richmond MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To PolynomialsDokument7 SeitenIntroduction To PolynomialsPierre FilerioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen MAth QuizDokument9 SeitenGen MAth QuizAna Rose S. LlameraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 7Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 7ntokozocecilia81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Activity SheetsDokument14 SeitenActivity SheetsPearl RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module1.1 PolynomialsDokument34 SeitenModule1.1 PolynomialsBrent Reyes PalayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan For DemonstrationDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan For DemonstrationBon PatiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen. Math Summary of Topics2Dokument7 SeitenGen. Math Summary of Topics2Rann MNoch keine Bewertungen
- @2 - Graphical Simplex and Big MDokument45 Seiten@2 - Graphical Simplex and Big MAyush MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calc MidtermsDokument1 SeiteCalc MidtermsEldee BalolongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.4 Add and Subtract PDFDokument6 Seiten7.4 Add and Subtract PDFyoonjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mat112 Week 7 Home Work SolutionDokument10 SeitenMat112 Week 7 Home Work SolutionolasunmboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addition and Subtraction of Rational ExpressionsDokument22 SeitenAddition and Subtraction of Rational ExpressionsDenielNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH112 Long Quiz 2 Reviewer 2nd Trimester AY 2013-2014Dokument2 SeitenMATH112 Long Quiz 2 Reviewer 2nd Trimester AY 2013-2014Ralph Gene Trabasas FloraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math10 - Q2 - Wk1 Illustrating Poly FunctionDokument3 SeitenMath10 - Q2 - Wk1 Illustrating Poly FunctionxunxhineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factoring Part 1 GCMF Grouping Year2Dokument16 SeitenFactoring Part 1 GCMF Grouping Year2BarbieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factoring and Finding Roots of PolynomialsDokument42 SeitenFactoring and Finding Roots of PolynomialsChristina Aguila NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Help Sheet For Week 1Dokument15 SeitenHelp Sheet For Week 1Kira L. MorrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- M100 Exercises - Review of FunctionsDokument1 SeiteM100 Exercises - Review of FunctionsDiyanikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SR - Maths Iib - Imp Questions-2024Dokument6 SeitenSR - Maths Iib - Imp Questions-2024ow123aisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of ComputationDokument5 SeitenTheory of ComputationHarsh ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in Translating Verbal To Mathematical SentenceDokument5 SeitenLesson Plan in Translating Verbal To Mathematical SentenceJenilyn Samaco96% (24)
- Riemann Hypothesis PDFDokument6 SeitenRiemann Hypothesis PDFRafik Zeraoulia100% (1)
- A Dynamical Systems Perspective On InteractionDokument43 SeitenA Dynamical Systems Perspective On InteractionAnonymous CjcDVK54Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment #1 2023 SolutionDokument7 SeitenAssignment #1 2023 Solutiongavindennis97Noch keine Bewertungen
- Master Thesis in Mathematics PDFDokument4 SeitenMaster Thesis in Mathematics PDFBuyEssaysOnlineForCollegeSiouxFalls100% (2)
- The Inclusion-Exclusion Principle: Problem 1Dokument14 SeitenThe Inclusion-Exclusion Principle: Problem 1parasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Intelligence PDFDokument75 SeitenArtificial Intelligence PDFJoel A. Murillo100% (3)
- 2014 MG Maths General 2Dokument23 Seiten2014 MG Maths General 2Kevin QuachNoch keine Bewertungen
- HJKKJKDokument79 SeitenHJKKJKDeepak ChandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deflection NptelDokument11 SeitenDeflection NptelhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- L 313 18.+270Dokument7 SeitenL 313 18.+270jpyusiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- G9 MATHS P2 (28 Copies)Dokument9 SeitenG9 MATHS P2 (28 Copies)Straight As StudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Study Lesson PlanDokument8 SeitenLesson Study Lesson Planapi-345200895Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Ramachandra School, Jangareddigudem Formative Assessment-I MathematicsDokument3 SeitenSri Ramachandra School, Jangareddigudem Formative Assessment-I MathematicsRamesh Babu KommuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Structuralist Theory of Economics PDFDokument235 SeitenA Structuralist Theory of Economics PDFAnahi CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fungsi Eksponen - 2Dokument14 SeitenFungsi Eksponen - 2Marsah IpgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture NotesDokument108 SeitenLecture NotesjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model For The Layout Problem (Part 1)Dokument43 SeitenModel For The Layout Problem (Part 1)Noormalita IrvianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Slides of Bessels Differential Equations 2Dokument41 SeitenLecture Slides of Bessels Differential Equations 2Priyanshu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Analysis II: by Dr. Saqib HussainDokument24 SeitenReal Analysis II: by Dr. Saqib Hussaininfiniti786100% (1)
- General Math DLL For SHS - (More DLL at Depedtambayanph - Blogspot.com) Q1, Week 01Dokument2 SeitenGeneral Math DLL For SHS - (More DLL at Depedtambayanph - Blogspot.com) Q1, Week 01Jester Guballa de Leon100% (1)
- Systematic Circuit Analysis: Nodal Analysis Chapter 4 Section 1Dokument55 SeitenSystematic Circuit Analysis: Nodal Analysis Chapter 4 Section 1Marvin - Soriente VILLALUNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter III Detailed LP MATH 6Dokument7 SeitenQuarter III Detailed LP MATH 6Genevieve MorilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selection Sort and Insertion SortDokument5 SeitenSelection Sort and Insertion SortcertifiedCrazyOZ HemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Measures of Central Tendency, Position, Variability PDFDokument24 Seiten4 Measures of Central Tendency, Position, Variability PDFJenny Estoconing Sardañas Jr.100% (1)
- السمات الفنية للزخارف الهندسية وزخارف الأطباق النجميةDokument20 Seitenالسمات الفنية للزخارف الهندسية وزخارف الأطباق النجميةabdelrahman elgawish (Dr)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sakurai Solutions 5-1 5-2Dokument8 SeitenSakurai Solutions 5-1 5-2Raza Ali RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 105 SAC Project 1Dokument2 SeitenMATH 105 SAC Project 1api-3808536Noch keine Bewertungen