Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bios
Hochgeladen von
Santosh ArjunanOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bios
Hochgeladen von
Santosh ArjunanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BIOS:
The OS communicates with the hardware through the BIOS programs stored in the ROM . The hardware in a PC requires some sort of interface to work with the OS and application software The BIOS provides the necessary interface between the OS software and hardware and hence often referred to be as firmware without BIOS ROM , no OS can be of use for a personal computer The BIOS is a set of programs or routines stored in a ROM chip on the M\B and therefore it is called as a ROMBIOS In earlier PC M\Bs , this special chip was usually a PROM or EPROM . Current M\B s store the BIOS in a FLASH ROM chip, and thats why it is also refered to as the FLASH BIOS BIOS consists of a startup programs and driver routines which are essential to operate the system hardware and get the system in the running condition It keeps the hardware configuration of the system in a CMOS non volatile RAM(NVRAM) ,which is required for the system boot operation . The BIOS also performs a power-on self test ( POST) the moment we switch on or reboot a system BIOS occupies only a fraction of an application program typically 128 KB It is the basic control for the system hardware . the set of Routines in a BIOS interpret very strokes, display characters On the screen ,reads from or writes to the serial and parallel port ,floppy drive , hardisks etc.. If the existing BIOS of a system does not support a new pwece of Hardware ,a device between will have to be installed for that hardware EXAMPLE: CD ROM device support feature is absent in most 486 and classic Pentium personal computer ,which cannot boot from a bootable CD. in these systems after the system boots up and excecutes The CONFIGSYS file, a low level CD-ROM driver software Is loaded in the memory to make the device optional WORKING PRINCIPLE : FEATURES OF BIOS 1) IBM BIOS compatibility: The BIOS used in original IBM PC is taken as the
Standard BIOS . The clone PCs use BIOS programs that are compatible to The IMB BIOS, but not exactly the same because the Original IMB BIOS is protected by the copy right law And therefore the compatible BIOS makes provide the same routines by writing their own code. The clone BIOS developers try to design their routines accordingly, keeping more possible similarly with IBM BIOS. 2) OS compatibility : BIOS acts as a bridge between the non standard system Hardware and the standard operating system. Whatever be the BIOS code ,it should be compatible with The standard operating system like windows 9x/NT Windows 2000,linuxmunix,netware etc. 3) CPU support : BIOS should support a wide range of CPUs either form the same manufacturer or from different vendors. BIOS socket 370 /slot m/bs support ilet Celeron,P2,P3 CPUs. BIOS on socket 7 m/bssupport intel P/MMX,AMD K6/K6-2 ,CYRIX M-2,IBM 6X86 etc But a BIOS designed for a P-3 CPU in all portability wil not support AMD athlon CPUs 4) JUMPERLESS operation : Most BIOS versions support jumpless .that is they allow setting of the CPU speed ,M?Bs FSB speed, multiplier factor etc from CMOS setup itself . This has made M/Bs design simpler and system assembly an easier task. 5)CHIPEST support: BIOS should support the latest chipset family used on the M/B. chipset support is very important because it allows M/B designers to implement advanced features like USB,AGP 2X/4X , IRDA improved power managements etc 5) MEMORY support : BIOS should be able to auto size and support different types of SDRAM modules currently available in the market that is PC 100 and PC 133 SDRAM BIOS for i850 chipset based p4 M/B must support RDRAM BIOS for some Athlon Durin Systems
6)
support DDR-SDRAM apart from the PC100/PC133 SDRAM BIOS should support ECC and parity checking operations ACPI /APM support : BIOS should be fully complaint with the latest version of advanced configuration and power interface( ACPI) and Advanced power management specification .power management is important to reduce energy wastage .
WORKING PRINCIPLE :
Any desktop or portable PC exhibits a 4 layer architecture The standard application programs which interact with the user from the topmost layer Below it is the OS which is also standard that is the same program is loaded in the different PCs with the different pieces of hardware . The third layer is the BIOS and the system hardware forms the lowest or 4th layer FUNCTIONS OF BIOS : The function of BIOS is to form a bridge between the non standard
System hardware and the standard OS BIOS of a PC is also non- standard that is its specific to the PC hardware PC BIOS consists of 4 main modules 1) POST ( power on self test ) 2) Bootstrap loader 3) CMOS setup 4) System service routines COMMON TRACKS: 1) testing system hardware : Post is a system diagnostic program consisting of test routines Stored inside the BIOS ROM chip . As soon as a PC is switched on the CPU reads the X86 codes of the post to check for the different hardware components in the system order to ensure everything is working properly Through the POST ,BIOS does the following 1) check the processor and the ROM chip 2) initializes the system hardware and chipset registers 3) initializes the power management 4) tests the RAM 5) tests the serial and parallel ports 6) initializes the floppy drives and hardware contollers 7) displays system summary information
2)
running POST with CMOS setup information 3) booting by bootstrap loader 4) providing BIOS interrupts ans system service routine 5) searching and activating other BIOS present in the system BIOS SEVELOPERS : First PC BIOS was developed by IBM for its 8086/8088 Clone manufactures such as company AT & T have developed their own - BIOS program independently -American megatrends inc (AMI) : thy does not sell BIOS source codes To the m/b manufacture , but AWARD sells it -award software ( AWARD) -Phoenix technologies ( PHOENIX) -Micwid research ( MR BIOS) -Acerlabs and wimbond PHONEIX bought the AWARD BIOS IDENTIFICATION : BIOS displays identification strings is the group of ASCII characters to display various identification parameters AMI & AWARD BIOS have unique ID structure which identify the manufacturer & chipset of the board
PHONIEX dont provide such as ID structure diagnostic programs HSD OR DEBUG BIOS INTERRUPTS The various BIOS interrupts are 1) CPU 2) Hardware 3) Software
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 3-2 Syllabus (1) - MergedDokument14 Seiten3-2 Syllabus (1) - Mergededucational9hubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated Project ListDokument3 SeitenUpdated Project ListDevaraj ThanaraajNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM GUL Interoperability Performance Assessment and Optimization V1.0Dokument34 SeitenGSM GUL Interoperability Performance Assessment and Optimization V1.0mohyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifugal Blowers PDFDokument1 SeiteCentrifugal Blowers PDFKrishna PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- UBC ELEC 301 MP Report 4Dokument7 SeitenUBC ELEC 301 MP Report 4ednangiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datacom Report: Global ResultsDokument1 SeiteDatacom Report: Global ResultsmeddouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chartpilot 1100-Technical ManualDokument234 SeitenChartpilot 1100-Technical Manualartur.damascenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cts Selected ListDokument5 SeitenCts Selected ListaravinthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release NotesDokument6 SeitenRelease NotesVictor CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Industry ESDokument18 Seiten3 Industry ESDavid AriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- TL Sf1005d&Tl Sf1008d DatasheetDokument4 SeitenTL Sf1005d&Tl Sf1008d DatasheetMarko PoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Characteristics of A Circuit-Breaker - ScheiderDokument7 SeitenFundamental Characteristics of A Circuit-Breaker - Scheiderdavid_diaz_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sai Srujana Resume 2019Dokument2 SeitenSai Srujana Resume 2019Sai srujanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Acoustics 1000 Series Mini BeaconsDokument4 SeitenApplied Acoustics 1000 Series Mini BeaconsVishnoo PrathapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp LG 076641 - 0Dokument1 SeiteExp LG 076641 - 0Alejandro Moreno RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icom IC-703 Instruction ManualDokument112 SeitenIcom IC-703 Instruction ManualYayok S. AnggoroNoch keine Bewertungen
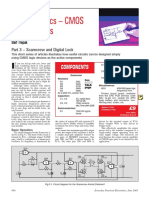
- Scarecrow and Digital LockDokument5 SeitenScarecrow and Digital Lockmiguelcali100% (1)
- Ecd LR - 8Dokument10 SeitenEcd LR - 8Faaran Ahmed Zaheer AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write A Code For 7 - Segment Display ProgramDokument2 SeitenWrite A Code For 7 - Segment Display Programeshwar_worldNoch keine Bewertungen
- PD FinalDokument25 SeitenPD FinalAnusha ChidagniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing Iot in Underwater Communication Using Li-Fi: S.Shakthivel MuruganDokument7 SeitenImplementing Iot in Underwater Communication Using Li-Fi: S.Shakthivel MuruganSsm 001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lenovo Legion T530 28ICB SpecDokument6 SeitenLenovo Legion T530 28ICB SpecDumitriuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS301 Series Piezoresistive Pressure Transmitters For Gas and LiquidDokument4 SeitenSS301 Series Piezoresistive Pressure Transmitters For Gas and LiquidGabriel MazzeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy301SolvedPaperSpring2010www Vuattach NingDokument14 SeitenPhy301SolvedPaperSpring2010www Vuattach NingAbdul Aziz ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Distributed Data InterfaceDokument4 SeitenFiber Distributed Data Interfacesukhbeer777Noch keine Bewertungen
- DP43BF TechProdSpecDokument88 SeitenDP43BF TechProdSpecenkgihNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE EC 2016 S1 Solved Paper PDFDokument52 SeitenGATE EC 2016 S1 Solved Paper PDFJKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Axell Wireless OMU I Product Spec V3-2Dokument2 SeitenAxell Wireless OMU I Product Spec V3-2zqandahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beamforming in LRPDDokument4 SeitenBeamforming in LRPDdylan LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Egx HandoutDokument2 SeitenEgx HandoutNixel SpielNoch keine Bewertungen