Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Drug Study
Hochgeladen von
Alea SilveraOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Drug Study
Hochgeladen von
Alea SilveraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
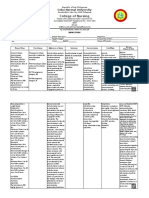
Drug
Classification
Action
Indications
Contraindications
Adverse Effects
Nursing Interventions
Tetanus Toxoid INJECTION (TET-un-us TOX-oid)
Tetanus vaccine
This medication is given to provide protection (immunity) against tetanus (lockjaw) in adults and children 7 years or older. Vaccination is the best way to protect against this life-threatening disease. Vaccines work by causing the body to produce its own protection (antibodies). Tetanus vaccine is usually first given to infants with 2 other vaccines for diphtheria and whooping cough (pertussis) in a series of 3 injections. This medication is usually used as a "booster" vaccine after this first series. Closely follow the vaccination schedule provided by the doctor.
For booster injection only for persons 7 years of age or older against tetanus. This vaccine is NOT indicated for primary immunization.
-Hypersensitivity to any component of the vaccine, including THIMEROSAL, and a MERCURY DERIVATIVE -Not for primary immunization. -A history of systemic allergic or neurologic reactions following a previous dose of Tetanus Toxoid
BODY AS A WHOLE: Redness warmth, edema Indurationwith or without tenderness as well as: urticaria rash Malaise transient fever,pain hypotension nausea arthralgia NERVOUS SYSTEM cochlear lesion brachial plexus neuropathies paralysis of the radial nerve paralysis of the recurrent nerve accommodation paresis Guillain-Barr syndrome EEG disturbances with encephalopathy
Before: >Postpone vaccination in patient with acute illness except in emergencies. >Determine Date of last tetanus immunization. During: >Be sure to know the age, duration and interval in giving TT After: >Instruct Patient to Report persistent or severe adverse reaction >Tell patient that nodule at injection site may be present for a few weeks >Advise patient for proper fever reducing drug dose for fever reaction
Drug
Classification
Action
Therapeutic Effects
Indications
Contraindications
Adverse Effects
Nursing Interventions
cefazolin Ancef, Kefzol
Cephalosporin antibiotic
Bind to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death. Active against many gram-positive cocci including: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci; Penicillinasproducing staphylococci.
-Treatment of systemic infections caused by susceptible strains of microorganisms
-Patients with known allergy to the Cephalosporin group of antibiotics -Solutions containing dextrose may be contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to corn products.
CNS:Fever, seizure Dermatologic: Rash, pruritus, StevensJohnson syndrome Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, anorexia, pseudomembranous colitis, oral candidiasis Genitourinary: Vaginitis Hepatic: Transaminases increased, hepatitis Hematologic: Eosinophilia, neutropenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis Local: Pain at injection site, phlebitis Renal: BUN
Assess patient for infection (vital signs; appearance of surgical site, urine; WBC) at beginning and during therapy. Before initiating therapy, obtain a history to determine previous use of and reactions to penicillins or cephalosphorins. Persons with a negative history of penicillin sensitivity may still have an allergic response. Obtain specimens for culture and sensitivity before initiating therapy. Observe patient for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis (rash, pruritis, laryngeal edema, wheezing). Discontinue drug and notify physician or other health care professional immediately if these problems occur. Keep epinephrine, an antihistamine, and resuscitation equipment close by in case of anaphylactic reaction. Monitor site for thrombophlebitis (pain, redness, swelling). Change sites every 48-72 hr to prevent phlebitis. Instruct patient to report
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Drug Study - Tetanus ToxoidDokument1 SeiteDrug Study - Tetanus ToxoidIrveen Joy Ramirez75% (4)
- DRUG STUDY RabiesDokument1 SeiteDRUG STUDY RabiesFranz RolfNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUGSTUDY Tetanus ToxoidDokument1 SeiteDRUGSTUDY Tetanus ToxoidMicaela Andrea CieloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hep B VaccineDokument2 SeitenHep B VaccineLegendX100% (2)
- Drug Study Tetanus ToxoidDokument1 SeiteDrug Study Tetanus ToxoidBunnie Alpha100% (3)
- Final Drug Study - PediaDokument2 SeitenFinal Drug Study - PediaMae Estillore100% (1)
- BNP (C)Dokument2 SeitenBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vit K Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenVit K Drug StudyPrisHee YhaRz SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ampicillin PDFDokument3 SeitenAmpicillin PDFandriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toxoid VaccinesDokument2 SeitenToxoid VaccinesKasandra Dawn Moquia Beriso100% (1)
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument4 SeitenName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesMinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyKrysNoch keine Bewertungen
- TAT and TIG Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenTAT and TIG Drug StudyMaria NorilynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study CloxacillinDokument2 SeitenDrug Study CloxacillinKen Ancheta Lagayada33% (3)
- OxacillinDokument2 SeitenOxacillinSatinderSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetanus Toxoid For Booster Use Only: (Not Recommended For Primary Immunization)Dokument5 SeitenTetanus Toxoid For Booster Use Only: (Not Recommended For Primary Immunization)Ade PurnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NalbuphineDokument5 SeitenNalbuphineGab PagalilauanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TergecefDokument2 SeitenTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug Studypiggypatty100% (1)
- Acetylcysteine Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenAcetylcysteine Drug StudyChelsea WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenDrug StudyJoshua VillarbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study in GentamicinDokument2 SeitenDrug Study in Gentamicinanthony_alviar100% (1)
- Drug Study EntecavirDokument4 SeitenDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDokument1 SeiteDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- CEFOXITINDokument30 SeitenCEFOXITINJaessa FelicianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Dokument2 SeitenBeclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- STREPTOMYCINDokument3 SeitenSTREPTOMYCINChad InongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics: TheDokument2 SeitenDrug Study: Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics: Theliza sianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Name: Amikacin SulfateDokument2 SeitenGeneric Name: Amikacin Sulfateichiro017100% (7)
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyJonica CamposNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursery Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenNursery Drug StudyNiña Dianne Rubin RustiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Sleep PatternDokument3 SeitenNCP Sleep PatternRA Balaoing100% (1)
- Sine CodDokument2 SeitenSine CodshayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Romeo Victor M. Valderrama BSN-2A: CNS: Confusion, Depression, BeforeDokument8 SeitenRomeo Victor M. Valderrama BSN-2A: CNS: Confusion, Depression, BeforeitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study CefuroximeDokument2 SeitenDrug Study CefuroximeTipey Segismundo100% (1)
- Drug Study - Hepatitis B VaccineDokument2 SeitenDrug Study - Hepatitis B VaccineJustin AncogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study NurseryDokument6 SeitenDrug Study NurseryPau-pau BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPI Nursing ConsiderationsDokument2 SeitenEPI Nursing ConsiderationsBel Allen83% (6)
- LOPERAMIDEDokument3 SeitenLOPERAMIDEfaye kimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methergine Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenMethergine Drug StudyjoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CefiximeDokument1 SeiteCefiximetaekado100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDrug StudySuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- BACILLUS CALMETTE - GUERIN (BCG) Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenBACILLUS CALMETTE - GUERIN (BCG) Drug StudyCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (2)
- AcetaminophenDokument1 SeiteAcetaminophenKristine YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paracetamol (Aeknil), Metoclopramide (Plasil), Cotrimoxazole Susp. (Macromed), PedialyteDokument4 SeitenParacetamol (Aeknil), Metoclopramide (Plasil), Cotrimoxazole Susp. (Macromed), PedialyteYum C100% (2)
- Acetaminophen Paracetamol Drug SummDokument1 SeiteAcetaminophen Paracetamol Drug SummWarren100% (1)
- Meropenem Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenMeropenem Drug StudyKullin RainNoch keine Bewertungen
- AcetylcysteineDokument1 SeiteAcetylcysteineLouie Pericon0% (1)
- PhytomenadioneDokument3 SeitenPhytomenadioneanareads100% (1)
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChlorideDokument4 SeitenCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChloridehahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study 2Dokument13 SeitenDrug Study 2Marialyn MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyDokument3 SeitenClonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyGrape JuiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem List Cues Problems Priority JustificationDokument3 SeitenProblem List Cues Problems Priority JustificationgrazheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study EditedDokument5 SeitenDrug Study EditedfabtaciousVeelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic NameDokument8 SeitenGeneric Namemel aquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study OrthoDokument17 SeitenDrug Study OrthoMc Crister SilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti-Infective Drugs: Jan Bazner-Chandler MSN, CNS, RN, CPNPDokument85 SeitenAnti-Infective Drugs: Jan Bazner-Chandler MSN, CNS, RN, CPNPralucaioana89100% (2)
- DrugsDokument2 SeitenDrugsgailannreyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument2 SeitenDrugsgailannreyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of DrugDokument17 SeitenName of DrugAllan DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cthulhu Hack From Unformed Realms v2Dokument20 SeitenThe Cthulhu Hack From Unformed Realms v2MrToad100% (2)
- Removing Contaminated Gown and Gloves ChecklistDokument3 SeitenRemoving Contaminated Gown and Gloves ChecklistFar Ri NaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasmids: Dr. P. Balaji Vysya College, HosurDokument23 SeitenPlasmids: Dr. P. Balaji Vysya College, HosurBalaji PaulrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- EpidemiologyDokument52 SeitenEpidemiologyasdfsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incentive SpirometryDokument5 SeitenIncentive Spirometryrachelmores12Noch keine Bewertungen
- 345-Article Text-1032-1-10-20180629Dokument4 Seiten345-Article Text-1032-1-10-20180629Regina AyediaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdrenalineDokument13 SeitenAdrenalineMobahil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saprolegnia Diclina IIIA and S. Parasitica Employ Different Infection Strategies When Colonizing Eggs of Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar LDokument10 SeitenSaprolegnia Diclina IIIA and S. Parasitica Employ Different Infection Strategies When Colonizing Eggs of Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar LcamilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Musicing Music Therapy or Music and Health Lars Olde Bonde 2011Dokument19 SeitenHealth Musicing Music Therapy or Music and Health Lars Olde Bonde 2011Martha Santos LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Strand, Grade & Section: - Maecy S. Paglinawan - STEM 12-15Dokument15 SeitenName: Strand, Grade & Section: - Maecy S. Paglinawan - STEM 12-15Maecy S. PaglinawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antifungal and Antibacterial Activity of ExtractsDokument30 SeitenAntifungal and Antibacterial Activity of ExtractsFrengkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Biology Revision SpreadsheetDokument124 SeitenIB Biology Revision SpreadsheetTanika SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Yoga & Stress ArticlesDokument11 SeitenCorporate Yoga & Stress Articless.gnanasekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Client Needs CategoriesDokument1 SeiteClient Needs CategoriesGwyn Mark Cadigal YapNoch keine Bewertungen
- FieldworkDokument22 SeitenFieldworkLusungu S. LupenzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report: Taufik Rizal, S.Ked PembimbingDokument12 SeitenCase Report: Taufik Rizal, S.Ked PembimbingRatna Ning Ayu KustiantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd PU Practical Viva QuestionsDokument10 Seiten2nd PU Practical Viva QuestionsSadhvi CNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEFI Surveillance and management-RVVDokument19 SeitenAEFI Surveillance and management-RVVadi100% (1)
- Wilson Soap Jordan SimDokument8 SeitenWilson Soap Jordan Simapi-704711481Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hornsby Girls High School: Trial HSC Examination 2019 HSC BiologyDokument29 SeitenHornsby Girls High School: Trial HSC Examination 2019 HSC BiologyDrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomic NeuropathyDokument20 SeitenAutonomic NeuropathyRegina CaeciliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Proposal DsaDokument2 SeitenProject Proposal DsaChristine Joy Pellos MacabeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Mucosal Ulceration - A Clinician's Guide To Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument9 SeitenOral Mucosal Ulceration - A Clinician's Guide To Diagnosis and TreatmentAnonymous pvuOXZNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs VTEDokument7 SeitenMCQs VTEMUHAMMADNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final CoachingDokument554 SeitenFinal CoachingGel Mi AmorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020-21 Big Game Status BookDokument200 Seiten2020-21 Big Game Status BookAaron Meier0% (1)
- 20 Soal Latihan Report Text Dalam Bahasa InggrisDokument3 Seiten20 Soal Latihan Report Text Dalam Bahasa InggrisDewi Lisna100% (1)
- Garcia, Nehemiah B. BSN 2Y2-2A: Ncma 219 Rle Course Task # 2Dokument3 SeitenGarcia, Nehemiah B. BSN 2Y2-2A: Ncma 219 Rle Course Task # 2Mushy_ayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peripheral Blood SmearDokument46 SeitenPeripheral Blood SmearAris ResurreccionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Om Algora SLE Exam-2 PDFDokument496 SeitenOm Algora SLE Exam-2 PDFGomathy DhanasekarNoch keine Bewertungen