Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Glaossary & Abbreviations: 0.1: 0.1.1 GLOSSARY
Hochgeladen von
Narendra GiriOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Glaossary & Abbreviations: 0.1: 0.1.1 GLOSSARY
Hochgeladen von
Narendra GiriCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SULPHUR COMPLEX UNIT- 431
RELIANCE INDUSTRIES LIMITED REFINERY DIVISION JAMNAGAR
AMINE TREATING UNIT
0.1 0.1.1
GLAOSSARY & ABBREVIATIONS:
GLOSSARY:
A term describing any combination of hydrocarbon or nonhydrocarbon gas compounds containing hydrogen sulfide and, or Acid gas
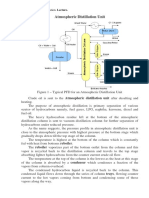
Atmospheric Distillation Back pressure Battery limit Bleeder
carbon dioxide.. A process where hydrocarbons are heated, reduced in pressure, and separated by boiling point ranges under near atmospheric pressure conditions. Pressure on the discharge side of a pump, valve, fan, vessels or other piece of equipment that resists a flow from that equipment. The outer boundaries of the area assigned to a unit. A valve located on the low point of a line, pump or vessel that can be used to drain equipment or piping. Bleeders are also located in areas of process equipment or piping. Bleeders are also located in areas of process equipments from where samples are taken. A solid metal plate inserted into a line to prevent to flow of process fluids into that line or other process equipment. A vessel or process that draws process fluids into a ``blow down`` vessel to keep undesirable material from accumulation. For example, a steam blowdown drum would be used to settle particulates and sediments out of a steam flow. Blowdown vessel is also used to reduce pressure on a process circuit or system. The temperature at which liquid changes to a vapor or that temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid to the pressure exerted on the liquid. A small cylindrical pressure vessel that is used to take high pressure samples of materials that must remain pressurized, Such as propane and butane. Flow through process equipment where most of the fluid flows
Blind Blowdown
Boiling point
Bomb
Channeling
through certain portions of the catalyst bed or equipment PAGE No. : 1 OF 5 REVIEWED BY: EJ REV. : 02 OPERATING MANUAL ISSUE : 01 APPROVED BY: SSS DATE : 01/03/2004 AUTHOR : SBS
SULPHUR COMPLEX UNIT- 431
RELIANCE INDUSTRIES LIMITED REFINERY DIVISION JAMNAGAR
AMINE TREATING UNIT
Condensate
bypassing other portions. Liquids, which are formed when the vapor phase of a compound turns to liquid at a temperature below the liquid dew point. The term condensate usually refers to condensate water products. The process of heating crude oil to a vaporization point and condensing of various components of the crude within specific boiling point ranges. A connection which allows liquid to flow from the side or bottom of a vessel. Liquid droplets or coke particles carried up a distillation tower by raising vapors. The flash point of a fuel is the minimum temperature at which it flashes and catches fire in presence of external spark. A minimum limits on flash point because of fire hazard consideration. The flash point has no significance on performance of engine. Auto ignition temperature is not influenced generally by variations in flash point not are other properties such as fuel injection and combustion performance. The zone in a distillation tower where pressure falls suddenly in relation to the pressure of the feed being introduced, causing the feed to flash into its vapor phase. Will not support combustion. In refinery inert gas is generally
Distillation
Draw off Entrainment Flash point
Flash zone
Inert gas Initial
nitrogen or carbon dioxide. boiling On a laboratory distillation, it is the temperature at which the first drop distillate drops from the distillation flask. Steam that comes directly from boiler or steam generator, as opposed to steam which has been exhausted from equipment. Vapor or liquid product that is removed from top of a distillation or fractionation or stripping column. The volume of oil which is vaporized in a distillation process over PAGE No. REV. ISSUE DATE AUTHOR : 2 OF 5 : 02 : 01 : 01/03/2004 : SBS
point Live steam Over head Over flash
REVIEWED BY: EJ OPERATING MANUAL APPROVED BY: SSS
SULPHUR COMPLEX UNIT- 431
RELIANCE INDUSTRIES LIMITED REFINERY DIVISION JAMNAGAR
AMINE TREATING UNIT
Pour point
and above the overhead and side products. The pour point is the lowest temperature at which fuel can be pumped. This temperature often occurs 8-10 deg F below the cloud point. The process of removing heat from a hydrocarbon liquid by pumping it from a process tower or vessel, cooling the liquid, and returning the liquid to vessel, usually at a different level from where the liquid was removed. The process of removing heat from a fractionation tower by partially condensing the overhead hydrocarbon vapor and returning the liquid to the top of the tower. The returning reflux flows downward through the tower. Controlling the tower temperature and absorbing a greater fraction of the heavier components for removal at the bottom. A valve pre-set to release excessive pressure on a vessel or
Pump around
Reflux
Safety valve Split control
system. range The use of two control element in parallel to provide finer control over a process than could be accomplished with a single controller. The smaller control element provides control over the 10-20% of the control range, while the larger controller provides control over the higher end of the control range. The process which uses steam to release lighter fractions of hydrocarbon from a hydrocarbon liquid by lowering the hydrocarbon vapor pressure. limit The highest concentration of toxic substance in air which an individual can be exposed to for an eight hour workday without apparent adverse health effects. The internal pressure a liquid exerts against itself by the vapor phase molecules of a liquid or solid.
Steam
Threshold
value or TLV Vapor pressure
REVIEWED BY: EJ OPERATING MANUAL APPROVED BY: SSS
PAGE No. REV. ISSUE DATE AUTHOR
: 3 OF 5 : 02 : 01 : 01/03/2004 : SBS
SULPHUR COMPLEX UNIT- 431 Viscosity
RELIANCE INDUSTRIES LIMITED REFINERY DIVISION JAMNAGAR
AMINE TREATING UNIT
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid resistance to flow. Fuel viscosity affects the shape of a fuel spray. High viscosity can cause poor atomization resulting large droplets and high spray penetration. This causes poor fuel/air mixing and combustion. In some cases, the fuel then wash the lubrication off cylinder wall, causing excessive wear. Low fuel viscosity result in a spray that is too soft and does not penetrate far enough onto combustion chamber, which causes poor combustion. Low fuel viscosities can lead to excessive injection pump plunger leakage and fuel metering inaccuracies.
0.1.2 Abbreviations 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 LNHT CDU HNUU ATU BFW MDEA BPSD FCCU VGO PIB H2S CO2 PPM LPG Light naphtha hydro treater Crude distillation unit Heavy naphtha union fining unit Amine treatment unit Boiler feed water Methyl di ethanol amine Barrels per stream day Fluidized catalytic cracking unit Vacuum gas oil Plant interface building Hydrogen sulfide Carbon dioxide Parts per million Liquefied petroleum gas PAGE No. REV. ISSUE DATE AUTHOR : 4 OF 5 : 02 : 01 : 01/03/2004 : SBS
REVIEWED BY: EJ OPERATING MANUAL APPROVED BY: SSS
SULPHUR COMPLEX UNIT- 431 15 NNF
RELIANCE INDUSTRIES LIMITED REFINERY DIVISION JAMNAGAR Normally no flow.
AMINE TREATING UNIT
REVIEWED BY: EJ OPERATING MANUAL APPROVED BY: SSS
PAGE No. REV. ISSUE DATE AUTHOR
: 5 OF 5 : 02 : 01 : 01/03/2004 : SBS
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PSH AaaaaaaaaaaaDokument7 SeitenPSH AaaaaaaaaaaaEdris SalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vacuum DistillationDokument6 SeitenVacuum DistillationKhaqan AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- $r117hue PDFDokument51 Seiten$r117hue PDFDeep SinojiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crude Unit Corrosion and Corrosion Control: Technical PaperDokument14 SeitenCrude Unit Corrosion and Corrosion Control: Technical PaperprasobhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crude Unit Corrosion and Corrosion ControlDokument14 SeitenCrude Unit Corrosion and Corrosion Controlparmindarrana86% (7)
- Fuel's and Energy Engineering-5th. LectureDokument30 SeitenFuel's and Energy Engineering-5th. Lectureahmed JaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmospheric Distillation UnitDokument3 SeitenAtmospheric Distillation UnitGilles DakouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmospheric Crude Distillation UnitDokument2 SeitenAtmospheric Crude Distillation UnitFahmi Ramadhan PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect FractionizationDokument57 SeitenLect Fractionizationraja.mtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Elements 1Dokument310 SeitenPipe Elements 1Ryan Llona FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adu & VduDokument25 SeitenAdu & VduPrashanth ChidambaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crude Oil Refining (Crude Oil DistillationDokument12 SeitenCrude Oil Refining (Crude Oil Distillationشيبوب shaibobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haldia Institute of Technology: Name: Bipasha Barai Class Roll No: 17/CHE/054 University Roll No: 10300617054Dokument9 SeitenHaldia Institute of Technology: Name: Bipasha Barai Class Roll No: 17/CHE/054 University Roll No: 10300617054Roshan Kumar LohaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Gas Fractionation PlantDokument16 SeitenUnit 4 Gas Fractionation PlantKha Mn100% (1)
- Fractional Distillation Is The Separation of A Mixture Into Its Component PartsDokument4 SeitenFractional Distillation Is The Separation of A Mixture Into Its Component PartsMariana MarchenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe TermsDokument38 SeitenPipe Termseuphris starfellNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEAERATORSDokument33 SeitenDEAERATORS1029384765qazwsx100% (4)
- PRP Unit - 3Dokument17 SeitenPRP Unit - 3Abdul GhafoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vacuum DistillationDokument8 SeitenVacuum DistillationPrashanth Chidambaram100% (1)
- Distillation PresentationDokument38 SeitenDistillation PresentationMohamed BalbaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vacuum DistillationDokument6 SeitenVacuum DistillationnuclearengineerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Manual-Piping: Piping Study Column PipingDokument52 SeitenTraining Manual-Piping: Piping Study Column Pipingusman_hafeez86100% (5)
- Term Report 2Dokument9 SeitenTerm Report 2Faizan FareedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Products of Primary Distillation Separation by Vacuum DistillationDokument36 SeitenChapter 6 Products of Primary Distillation Separation by Vacuum DistillationAbdurabu AL-MontaserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect 4 FractionationDokument49 SeitenLect 4 FractionationKashif hussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- EvaporatingDokument5 SeitenEvaporatingFadhil KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Basis For Feed & ProductsDokument42 SeitenDesign Basis For Feed & ProductsHumair AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument8 SeitenChapter 2Micaiah Cyril DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crude Distillation PosterDokument1 SeiteCrude Distillation Postervivek_rec100% (1)
- Crude DistillationDokument35 SeitenCrude DistillationraisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vacuum Creating SystemsDokument3 SeitenVacuum Creating SystemsAlla VijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fractional DistillationDokument17 SeitenFractional DistillationSubash KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DesuperheatersDokument6 SeitenDesuperheaterskparthypan100% (1)
- Vacuum Distillation Colume: Mass Transfer Lab AssignmentDokument4 SeitenVacuum Distillation Colume: Mass Transfer Lab AssignmentMalik HamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch3 Lect 3 - Crude DistillationDokument7 SeitenCh3 Lect 3 - Crude DistillationTarlan AllahverdiyevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air CompressorDokument36 SeitenAir CompressorThilanga Thusith100% (1)
- Stem Exchanger (Heater) : Hydrate PreventionDokument10 SeitenStem Exchanger (Heater) : Hydrate PreventionMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Process Description (Draft)Dokument4 SeitenChapter 4 Process Description (Draft)ezraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refinery PDFDokument22 SeitenRefinery PDFromulussikalitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmospheric and Vacuum UnitDokument14 SeitenAtmospheric and Vacuum Unitbhavesh jangidNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDU Training PowerpointDokument144 SeitenCDU Training Powerpointviettanct92% (13)
- C 5 Vacuum DistillationDokument20 SeitenC 5 Vacuum DistillationAhmed Mohamed KhalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coc Oral Exam PreparationDokument105 SeitenCoc Oral Exam PreparationAshok Kumar0% (1)
- Vacuum Distillation (Ok)Dokument112 SeitenVacuum Distillation (Ok)Ahmed Mohamed Khalil100% (1)
- Distillation Coulmn Internals, Principles and OperationDokument185 SeitenDistillation Coulmn Internals, Principles and OperationAhmad Deyab100% (3)
- Packed Column Distillation ProcessDokument8 SeitenPacked Column Distillation ProcessKhairin RenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petroleum Refinary 4Dokument10 SeitenPetroleum Refinary 48wmswyzy8tNoch keine Bewertungen
- P174136Dokument9 SeitenP174136Mohamed Atia100% (1)
- DEAERATORDokument14 SeitenDEAERATORHassan Faraz0% (1)
- Vacuum Distillation UnitDokument15 SeitenVacuum Distillation Unitshaz100% (2)
- Refinery Definitions - FAQDokument7 SeitenRefinery Definitions - FAQbalajiupesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vacuum Distillation in Petroleum RefiningDokument3 SeitenVacuum Distillation in Petroleum RefiningUsama Malik100% (1)
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingVon EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Process Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesVon EverandProcess Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Understanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersVon EverandUnderstanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Troubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesVon EverandTroubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (2)
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitVon EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SVon EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICNIRPemfgdl 1Dokument38 SeitenICNIRPemfgdl 1lukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co3 LPDokument8 SeitenCo3 LPChiara Yasmin HanduganNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Physics Kinematics Test 01Dokument1 Seite11 Physics Kinematics Test 01Nikhil SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- City College of San Jose Del MonteDokument13 SeitenCity College of San Jose Del MonteLopez Marc JaysonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Carbon and Nitrogen Determination in Soil: Application NoteDokument3 SeitenTotal Carbon and Nitrogen Determination in Soil: Application Notelaoying qdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Exercise # 6 - Cell Membrane TransportDokument4 SeitenLab Exercise # 6 - Cell Membrane TransportMei KurunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying Prelim ReviewerDokument4 SeitenSurveying Prelim ReviewerBanana QNoch keine Bewertungen
- Issn: IssnDokument9 SeitenIssn: IssnEnelico SasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zaretsky (1987) Parameter Estimation Using Microdielectrometry With Application To Transformer Monitoring - UnlockedDokument593 SeitenZaretsky (1987) Parameter Estimation Using Microdielectrometry With Application To Transformer Monitoring - Unlockedrom009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rouba Abdel Malak Rached: Page 1 of 7 - Curriculum VitaeDokument7 SeitenRouba Abdel Malak Rached: Page 1 of 7 - Curriculum Vitaerouba.rachedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: Free Web Support in EducationDokument30 SeitenChemistry: Free Web Support in EducationsakshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Validation of Bellows As Per EJMA-FEA (White Paper) PDFDokument5 SeitenDesign and Validation of Bellows As Per EJMA-FEA (White Paper) PDFJaveed A. KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ID NoneDokument8 SeitenID NoneHans SihalohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Thermodynamics - 2 PDFDokument126 SeitenHeat and Thermodynamics - 2 PDFPurvi Binani100% (1)
- Ic-0014 Kit Refrifluid B Uc-0020-1700 (En)Dokument2 SeitenIc-0014 Kit Refrifluid B Uc-0020-1700 (En)Lluis Cuevas EstradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter No One First Year Physics by Asif Rasheed ShortDokument4 SeitenChapter No One First Year Physics by Asif Rasheed ShortAsif Rasheed Rajput100% (1)
- Bradford Protein-Determination of Milk ProteinDokument3 SeitenBradford Protein-Determination of Milk Proteinanitram yo50% (2)
- Chapter 11.Dokument45 SeitenChapter 11.HalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enantiotropically Related Albendazole PolymorphsDokument12 SeitenEnantiotropically Related Albendazole PolymorphsPaulo DantasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleaching of WoolDokument5 SeitenBleaching of Woolahmer adnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook For Cogeneration and Combined Cycle Power Plants: Second EditionDokument18 SeitenHandbook For Cogeneration and Combined Cycle Power Plants: Second Editionsetyo nugrohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCBL Ic 15nov23Dokument40 SeitenPCBL Ic 15nov23VM ONoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Sciences P2 Grade 11 Nov 2018 Memo Eng & Afr FinalDokument16 SeitenPhysical Sciences P2 Grade 11 Nov 2018 Memo Eng & Afr FinalFaizal JumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atterberg Limits - Set 1Dokument8 SeitenAtterberg Limits - Set 1ahm531Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Fuel CELL?Dokument49 SeitenWhat Is A Fuel CELL?raveendrareddyeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 AL Physics Paper I AnswerDokument2 Seiten2011 AL Physics Paper I AnswerKWONG1940100% (1)
- Prepared By: Julkarnain Ahemad. L&T-QA/QC-DDIP-SambalpurDokument26 SeitenPrepared By: Julkarnain Ahemad. L&T-QA/QC-DDIP-SambalpurKarna Satish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TE - Mech - RAC - Chapter 3 - RefrigerantsDokument57 SeitenTE - Mech - RAC - Chapter 3 - RefrigerantsAniket MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Bell AnsDokument4 SeitenElectric Bell AnsManishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of The Accelerated Hydrogen Sulfide Breakthrough Capacity of Granular and Pelletized Activated CarbonDokument9 SeitenDetermination of The Accelerated Hydrogen Sulfide Breakthrough Capacity of Granular and Pelletized Activated Carbonmohammed karasnehNoch keine Bewertungen