Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ab+Ab: Base X Base X Base X
Hochgeladen von
Vani Bindal AgarwalOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ab+Ab: Base X Base X Base X
Hochgeladen von
Vani Bindal AgarwalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
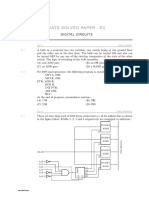
Q.1.
The output of the circuit shown below is equal to
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) A B+A B
(D) (A B) (A B)
Q.2. Given (135) base x (144) base x (323) base x . What is the value of base x? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6
Q.3. The logic operations of two combinational circuits given in figure I and figure II are
(A) Entirely different (C) Complementary Q.4. The logic function f (x.y) (x.y) is the same as (A) f (x y) (x y) (C) f (x.y) . (x.y)
(B) (D)
Identical Dual
(B) f (x y) (x y) (D) None of these.
Q.5. 11100, 1100 and 111100 corresponds to the 1's complement representation of which one of the following sets of number? (A) 28, 12 and 56 respectively (C) 7, 7 and 7 respectively (B) 3, 3 and 3 respectively (D) None of these.
Q.6. If (327)9 (x)5 , then the value of x is given by : (A) 327 (B) 268 (C) 2033
(D) 3302
Q.7. A digital multiplexer is basically a combinational logic circuit to perform following operation : (A) AND- AND Q.8. A PLA can be used (A) as a microprocessor. (C) to realize a sequential logic. (B) as a dynamic memory. (D) to realize a combinational logic. (B) OR-OR (C) AND-OR (D) OR-AND
Q.9. Consider the combinational circuit shown below
The output expression F of the above circuit is : (A) X + Y + Z (B) XYZ (C) XY + YZ + ZX (D) X YZ
Q.10. The Boolean function F implemented in the figure given below by using two input multiplexer is:
21
(A) A B C A B C Q.11
(B) ABC A B C
(C) A B C A B C
(D) A B C A B C
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer by using the codes given below the lists : List-I A. B. C. D. Multiplexer De-multiplexer Shift register Encoder A 3 4 3 1 B 4 3 4 2 1. 2. 3. 4. C 1 1 2 3 List-II Sequential memory Converts decimal number to binary Data selector Routes out many data output with single Input D 2 2 1 4
Codes : (A) (B) (C) (D)
Q.12. The logic circuit given below is:
(A) Half adder
(B) XOR
(C) Equality detector
(D) Full adder
Q.13. Race around condition always arises in a (A) Combinational circuit (C) Synchronous Circuit (B) Asynchronous circuit (D) Digital Circuit
Q.14. In the circuit shown in the figure, Q = 0 initially, when the clock pulses are applied, the subsequent states of 'Q' will be :
(A) 1, 0, 1, 0
(B) 0, 0, 0, 0
(C) 1, 1, 1, 1
(D) 0, 1, 0, 1
Q.15. The digital circuit shown in the figure works as a
(A) JK flip-flop (C) T flip-flop
(B) Clocked RS flip-flop (D) Ring counter
Q.16. How many flip-flops are required to make a MOD-32 binary counter? A. 3 C. 5 B. 45 D. 6
Q.17. Which digital system translates coded characters into a more useful form? A. encoder C. counter B. Display D. Decoder
Q.18. How many inputs will a decimal-to-BCD encoder have? A.4 C. 10 B. 8 D.16
Q.19. For a 4-bit parallel adder, if the carry-in is connected to a logical HIGH, the result is: A.the same as if the carry-in is tied LOW since the least significant carry-in is ignored. B. that carry-out will always be HIGH. C. a one will be added to the final result. D.the carry-out is ignored. Q.20. One example of the use of an S-R flip-flop is as a(n): A.racer B. Astable oscillator C. binary storage register D.transition pulse generator
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Digital Electronics Exercises With AnswersDokument157 SeitenDigital Electronics Exercises With Answersdineshdkj83% (6)
- IES - Electronics Engineering - Digital Electronic CircuitsDokument66 SeitenIES - Electronics Engineering - Digital Electronic Circuitsedwinaustine100% (4)
- CSEC Physics Review - Introduction To Logic GatesDokument16 SeitenCSEC Physics Review - Introduction To Logic GatesKevin Small100% (4)
- GATE - CS - Digital LogicDokument22 SeitenGATE - CS - Digital LogicAnonymous 8pCXXsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testpaper - 1 NTDokument13 SeitenTestpaper - 1 NTGattu SadashivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics and CircuitsDokument12 SeitenDigital Electronics and CircuitsGuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument7 SeitenAssignment 1Ishmum Monjur NilockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Logic Test Questions For InterviewDokument53 SeitenDigital Logic Test Questions For InterviewDwaraka OrugantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- D 09P3Dokument8 SeitenD 09P3Pavan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Logic DesignDokument4 SeitenDigital Logic DesignShareef KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9Dokument10 Seiten9Sachin RathodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 - Number Systems and Boolean AlgebraDokument8 SeitenModule 4 - Number Systems and Boolean AlgebraSuyog ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DigitalDokument18 SeitenDigitalSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Paper1Dokument5 SeitenDigital Paper1Iyyakutti GanapathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRB Junior Electronics Engineer Study Material 3Dokument66 SeitenRRB Junior Electronics Engineer Study Material 3thirumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ugc Papers With AnsDokument171 SeitenUgc Papers With Ansredhackerunknown07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Science Gcet Question Papers-2005Dokument10 SeitenComputer Science Gcet Question Papers-2005Lokesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics: Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument22 SeitenDigital Electronics: Multiple Choice QuestionsSenthilkumar KrishnamoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics - MCQsDokument38 SeitenDigital Electronics - MCQsAbhay ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IES - Electrical Engineering - Analog and Digital CircuitsDokument81 SeitenIES - Electrical Engineering - Analog and Digital CircuitsVishal KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DigitalDokument68 SeitenDigitalDibyarekha MaharanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Logic by NODIADokument49 SeitenDigital Logic by NODIAJyoti GoswamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MsqsDokument5 SeitenMsqsYusra MehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital ElectronicsDokument5 SeitenDigital Electronicstheguru2929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Organization Number SystemDokument5 SeitenComputer Organization Number SystemnagarakeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A04306 Digital Logic DesignDokument4 Seiten9A04306 Digital Logic DesignsivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 94 Gre CSDokument23 Seiten94 Gre CSSudhanshu IyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEST Question Bank - Digital ElectronicsDokument157 SeitenBEST Question Bank - Digital Electronicsabhinav_pundir0% (1)
- DE09 SolDokument157 SeitenDE09 SolRakesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer ScienceDokument16 SeitenComputer ScienceR2k OfficialNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIGITAL ELECTRONICS Questions and Answers PDFDokument5 SeitenDIGITAL ELECTRONICS Questions and Answers PDFBryanOviedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC Digital CircuitsDokument68 SeitenEC Digital Circuitsshreypachauri3Noch keine Bewertungen
- CS Gate 20101Dokument29 SeitenCS Gate 20101roshni_lingalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DigitalDokument182 SeitenDigitalYeshoda MallikarjunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Logic Solutions: 1. Consider The Following CircuitDokument8 SeitenDigital Logic Solutions: 1. Consider The Following CircuitergrehgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE370 Assignment-IDokument3 SeitenEE370 Assignment-ISandeep TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - 1EC Model Test Paper 2Dokument21 Seiten1 - 1EC Model Test Paper 2sacky3586Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs For Practice2Dokument9 SeitenMCQs For Practice2gsvsainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - 6255737462828565350 (10 Files Merged)Dokument307 Seiten5 - 6255737462828565350 (10 Files Merged)Aman PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- QBank DPSD cs2202Dokument6 SeitenQBank DPSD cs2202kunarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT WISE QUEST DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN - GIET 2019 II - I (3rd Sem)Dokument18 SeitenUNIT WISE QUEST DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN - GIET 2019 II - I (3rd Sem)Deepak NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate-Cs 2006Dokument31 SeitenGate-Cs 2006tomundaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsVon EverandDigital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Linear Programming and Resource Allocation ModelingVon EverandLinear Programming and Resource Allocation ModelingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attainable Region Theory: An Introduction to Choosing an Optimal ReactorVon EverandAttainable Region Theory: An Introduction to Choosing an Optimal ReactorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Matrix Analysis and Synthesis: With Applications to Electronic EngineeringVon EverandBasic Matrix Analysis and Synthesis: With Applications to Electronic EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsVon EverandFundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Vision in Vehicle Technology: Land, Sea, and AirVon EverandComputer Vision in Vehicle Technology: Land, Sea, and AirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topographical Tools for Filtering and Segmentation 2: Flooding and Marker-based Segmentation on Node- or Edge-weighted GraphsVon EverandTopographical Tools for Filtering and Segmentation 2: Flooding and Marker-based Segmentation on Node- or Edge-weighted GraphsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxVon EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Digital Signal Processing Using the ARM Cortex M4Von EverandDigital Signal Processing Using the ARM Cortex M4Bewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Combinatorial Algorithms: For Computers and CalculatorsVon EverandCombinatorial Algorithms: For Computers and CalculatorsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Oiling 2Dokument140 SeitenOiling 2Vani Bindal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4Dokument64 SeitenModule 4Vani Bindal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4Dokument64 SeitenModule 4Vani Bindal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oiling 2Dokument140 SeitenOiling 2Vani Bindal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Objective QuestionDokument32 SeitenModule 3 Objective QuestionVani Bindal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module #3 UNIT WISE EcontentuploadDokument211 SeitenModule #3 UNIT WISE EcontentuploadVani Bindal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module #3 UNIT WISE EcontentuploadDokument217 SeitenModule #3 UNIT WISE EcontentuploadVani Bindal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gla University Lab:-Simulation Lab (ECE-287) / Quiz-3Dokument2 SeitenGla University Lab:-Simulation Lab (ECE-287) / Quiz-3Vani Bindal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15eel57 MC Lab Manual PDFDokument74 Seiten15eel57 MC Lab Manual PDFMallik ArjunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UARTDokument26 SeitenUARTflyingdreams100% (2)
- Stick DiagramDokument21 SeitenStick DiagramVani Bindal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus Cycles (Chap. 7) : 4 System Bus Clock Periods For 8086/8088/80286Dokument8 SeitenBus Cycles (Chap. 7) : 4 System Bus Clock Periods For 8086/8088/80286नील दासNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome To IBPSDokument1 SeiteWelcome To IBPSVani Bindal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate Questions Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDokument32 SeitenGate Questions Microprocessor and Microcontrollersjo05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project ReportDokument64 SeitenProject ReportVani Bindal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shift Register and Its TypesDokument22 SeitenShift Register and Its TypeschoprahridyeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ripple Carry AdderDokument2 SeitenRipple Carry AdderAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- TTL 7400 Series List PDFDokument13 SeitenTTL 7400 Series List PDFLuis Fernando Garcia S100% (1)
- Verilog BasicsDokument35 SeitenVerilog BasicssouhithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect18 DatapathDokument31 SeitenLect18 DatapathAditya LocharlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vloglab v201901 PDFDokument32 SeitenVloglab v201901 PDF蔡仲耘Noch keine Bewertungen
- VERIFICATION OF GATES USING ICsDokument14 SeitenVERIFICATION OF GATES USING ICsAqib IrshadNoch keine Bewertungen
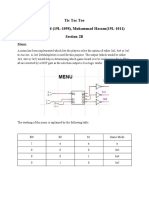
- Tic Tac Toe Nabeegh Ahmed (19L-1098), Muhammad Hassan (19L-1011) Section 2BDokument10 SeitenTic Tac Toe Nabeegh Ahmed (19L-1098), Muhammad Hassan (19L-1011) Section 2BMuhammad Ali Haider100% (1)
- Combinational Logic Circuit: University of Perpetual Help System DaltaDokument17 SeitenCombinational Logic Circuit: University of Perpetual Help System DaltaJohn Kenneth BulabosNoch keine Bewertungen
- FALLSEM2022-23 BECE102L TH VL2022230102875 Reference Material I 17-09-2022 Shift Registers CountersDokument28 SeitenFALLSEM2022-23 BECE102L TH VL2022230102875 Reference Material I 17-09-2022 Shift Registers CountersAakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bist For Xilinx 4000 and Spartan Series Fpgas: A Case Study: Charles E. Stroud Keshia N. Leach, and Thomas A. SlaughterDokument10 SeitenBist For Xilinx 4000 and Spartan Series Fpgas: A Case Study: Charles E. Stroud Keshia N. Leach, and Thomas A. Slaughtersumit.raj.iiit5613Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 301 - Digital Electronics: CountersDokument25 SeitenECE 301 - Digital Electronics: CountersddbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 54LS42 - DM54LS42 - DM74LS42 BCD - Decimal DecodersDokument1 Seite54LS42 - DM54LS42 - DM74LS42 BCD - Decimal DecodersIoan DarabanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The JK FlipDokument4 SeitenThe JK Flipraj2510Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basics and Overview of Flip FlopsDokument5 SeitenBasics and Overview of Flip FlopsMariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution For All Problems in Chapter 9Dokument3 SeitenSolution For All Problems in Chapter 9Rahmat Hidayat100% (1)
- DJM30073 Labwork1Dokument9 SeitenDJM30073 Labwork1Muhammad R IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digitals Electronics Important MCQ With SolutionDokument20 SeitenDigitals Electronics Important MCQ With SolutionPradeep Singh ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verlogic3 Chapter5Dokument90 SeitenVerlogic3 Chapter5rahul parmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Gates ProgramDokument34 SeitenBasic Gates ProgramJoychandra LoukrakpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Logic Gates & Boolean AlgebraDokument32 SeitenChapter 2 Logic Gates & Boolean AlgebraAmita PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CountersDokument23 SeitenCountersMuktinath rajbanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ripple Carry Adder CircuitDokument10 SeitenRipple Carry Adder CircuitniteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 2.13 Problem: Determine The Output Waveform For The Truth Table As Shown BelowDokument36 SeitenExample 2.13 Problem: Determine The Output Waveform For The Truth Table As Shown BelowShuvoshreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- WST-15 Logic TrainerDokument1 SeiteWST-15 Logic TrainerBABAKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programmable ASIC Logic CellsDokument36 SeitenProgrammable ASIC Logic CellsnandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 PDFDokument30 SeitenModule 4 PDFNoor HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Topics in Logic Design: Praveen MeduriDokument41 SeitenAdvanced Topics in Logic Design: Praveen MeduriPraveen MeduriNoch keine Bewertungen
- MultiplexersDokument20 SeitenMultiplexersسید یاور امام کاظمیNoch keine Bewertungen