Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
3G Umts
Hochgeladen von
Navaneeth KrishnanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
3G Umts
Hochgeladen von
Navaneeth KrishnanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
WCDMA
Overview
WCDMA Features
High data rates in 5 MHz
384 kbps with wide-area coverage
2 Mbps with local coverage
High service flexibility
support for services with variable rate
support for simultaneous services
support of multiple parallel variable-rate
services on one connection
packet and circuit switched services
Fast and efficient packet access
Higher capacity
Orthogonal in frequency within cell
Narrow bandwidth per carrier
Continuous transmission and reception
No synchronization in time
f
t
Power
MS1 MS 2 MS 3
NMT
AMPS
TACS
Frequency Division Multiple
Access (FDMA)
Orthogonal in time within cell
Increased bandwidth per carrier
Discontinuous transmission and reception
Synchronization in time
Power
t
f
MS 1
MS 2
MS 3
200 kHz
GSM
PDC
D-AMPS
Time Division Multiple Access
(TDMA)
Separate users through different codes
Large bandwidth
Continuous transmission and reception
f
Code
t
MS 1
MS 2
MS 3
5 MHz
IS-95 (1.25 MHz)
CDMA2000 (3.75 MHz)
WCDMA (5 MHz)
Direct Sequence - Code Division
Multiple Access (DS-CDMA)
WCDMA technical
characteristics
f
t
10 ms frame
4.4-5.0 MHz
P
Optimized packet access on common or
dedicated channel
High spectrum efficiency
5 MHz carriers
Frequency Division Duplex,
FDD
3.84 Mcps chip rate
Variable spreading codes
Advantage of Spread Spectrum
Wideband transmission being less sensitive to frequency
selective interference and fading
Power density of spectrum is decreased several times
and the transfer of information is still possible even below
background noise.
Radio Network planning is easier compared to Networks
using FDMA or TDMA as all the available freqencies can
be used in all cells (frequency re-use = 1)
CDMA is very spectrum efficient due to the possibility of
using each carrier in each cell.
There is no fixed capacity limit (number of users at the
same time). The main limit is the increase in the level of
interference from other subscribers which reduces the
quality of service.
The possibility of having soft handover in WCDMA can
be an advantage.
Disadvantage of Spread
Spectrum
The power level of all UE transmission received at the
BTS must be equal if the bit rates are equal and
therefore fast power control is necessary.
A UE in soft handover mode require the resources of
more than one cell, the system capacity is reduced.
BITS 11001
SPREADING
CHIPS 1101001001
Chip rate = Spreading Factor * Symbol Rate = Constant = 3.84 Mchip/s
Spreading Factor (SF) is the ratio between chip rate and the symbol rate!
Relation between Chips and Bits
Direct Sequence Spread
Spectrum Signals
T
S
t
d(t)
Information signal
T
C
t
c(t)
Spreading signal
(Unique & Given)
t
d(t)c(t)
Transmission signal
User Bitrate and Spreading Factor
SF Chiprate
Mchips/s
User Bitrate
Uplink
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
256
128
64
32
16
8
4
15
30
60
120
240
480
960
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
512
256
128
64
32
16
8
4
15
30
60
120
240
480
960
1920
SF Chiprate
Mchips/s
User Bitrate
Downlink
SF Chiprate
Mchips/s
User Bitrate
Uplink
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
3,84
256
128
64
32
16
8
4
15
30
60
120
240
480
960
Overview
Of
3G Mobile Core
Layered Architecture
Connectivity Layer
Control Layer
Application Layer
UOO 4 E C UU M +] + }
The Application Layer is responsible for providing services to users via
applications regardless of the device and method in which the user accesses
the network. The Application Layer itself is not a real network as such important
operator parts of the application Layer may, however, be realized in what are
called Service Networks.
UE4ME C UU M }
The Control Layer contains nodes that control and direct traffic (both
Circuit and Packet Switched). The Control Layer is realized in a Core
Network. The WCDMA Core Network will contain, for example, MSCs,
HLR/HSS, GMSC/TSC, SGW and possibly IMS.
UE 4 + 4U C UU M }] + + }
* E 4 + 4U C U M E 4 E 4 =} ] }] + + } ] + = }
4M OEM4 E WUUU UU U U UU E -} - - ]
4 4E 4 + M E4 4EMUU }] =} + ]]} }
* U 4EMU E 4 E 4 4 4 =} ]]} } ] + =} } +
E E4ME M 4 CE 4EMUW - ] } + =} + } }
UUU U*UU U UUU EM U 4M OEM4 + }- ]]} - ]
E 4 + 4U 4EMU 4 4 M 4E }] + + } = } } = -
M 4 4UO E 4M W U U U M 4U 4 } -+} } } +] } ^+ ] +
U 4 U U 4 U 4 4 UU EM UU UUU + ]=}- - ] }+ ] =}- -
4 U 4EMU M 4 UU UU < =} ]]} } + } +#}- =}
E U 4EMUU -+ ]]} }
UU UU 4 M U 4 * M M 4 E + - -+#}- =} =+ - } } +
U M4 M O UMEU 4 WU UUUU } =+ }]
U E 4 U UU M M 4EMU CE U 4 }- =} }} } ]} } -} =
UU UU 4EMU E M 4E E 4 E } } ] } ] +-} }- ] +
E4M C UEM ECOE 4U ] }
M UO4 OC 4 WUU } + }
U 4EMU WUU ]]} }
UEM 4EMU WUU } }
4EMU U4 M 4E UU UU } }
UU UU U*UU<C U<U U*UU*<U
3GPP Network Reference
Model
GMSC
GMSC
GGSN
GGSN
HLR
HLR
EIR
EIR
AUC
AUC
SCF
SCF
SMS-
IWMSC
SMS-
IWMSC
RNC
BS
Uu
CN External
Networks
Iur
D
USIM
USIM
ME
ME
RNC
BS
Uu
USIM
USIM
ME
ME
Iub
Iub
Iu
Gd ,
Gp ,
Gn+
SGSN
SGSN
MSC
MSC
E,
G
Cu
Cu
SMS-
GMSC
SMS-
GMSC
SGSN
SGSN
MSC
MSC
Gb
SMS-SC
ISDN
PSTN
PSPDN
CSPDN
PDN:
-Intranet
-Extranet
-Internet
Iu
AN UE
BSC
BTS
Um
SIM
SIM
MT
MT
Abis A
BSS
RNS
RNS
UTRAN
Note:
Not all interfaces
are shown and named
F
Gf
Gr
Gn +
H
GMSC
GMSC
GGSN
GGSN
HLR
HLR
EIR
EIR
AUC
AUC
SCF
SCF
SMS-
IWMSC
SMS-
IWMSC
RNC
BS
Uu
CN External
Networks
Iur
D
USIM
USIM
ME
ME
RNC
BS
Uu
USIM
USIM
ME
ME
Iub
Iub
Iu
Gd ,
Gp ,
Gn+
SGSN
SGSN
MSC
MSC
E,
G
Cu
Cu
SMS-
GMSC
SMS-
GMSC
SGSN
SGSN
MSC
MSC-S
Gb
SMS-SC
ISDN
PSTN
PSPDN
CSPDN
PDN:
-Intranet
-Extranet
-Internet
Iu
AN UE
BSC
BTS
Um
SIM
SIM
MT
MT
Abis A
BSS
Iu
AN UE
BSC
BTS
Um
SIM
SIM
MT
MT
Abis A
BSS
RNS
RNS
UTRAN
Note:
Not all interfaces
are shown and named
F
Gf
Gr
Gn +
H
Mobile Soft switch Solution
Mobile soft switch enable a layered
architecture design for the mobile
circuit core , where the network
functions responsible for service
management & control and for
transport of service data are
physically & logically separated
Mobile Soft switch Solution
Advantages of Mobile Soft switch Solution
1. Packet backbone technology (IP or ATM) enables
more efficient transmission of voice traffic over
the backbone by retaining the same voice coding
in the backbone as is used in the air interface
2. Access independent (GSM/WCDMA) core network
3. Reduction of backbone traffic
4. Simplification of network planning through
common core for WCDMA & GSM
Core Network Overview
SGSN G
GMSC
Server
GGSN
RNC
BSC
C-MGw
SDH
Network
C-MGw
MSC
Server
IP or ATM
Backbone
IP
R
I
P
R
IP
R
PSTN
ISDN
PLMN
Internet,
Intranet
SGSN W
USER DATA
HLR/
FNR/AUC
CONTROL
Ericsson
Multi
Activation
Ericsson
Multi
Mediation
RANOS
GSMOSS
SGSN
GGSN
BSC
MGw
MGw
MSC
Server
GMSC
Server
Internet/
Intranets
Internet/
Intranets
PSTN/
ISDN/
PLMN
PSTN/
ISDN/
PLMN
IP or ATM
Backbone
IP
R
I
P
R
IP
R
IP v4/v6,
QoS
, VPN
RNC
GSM RAN
WCDMA RAN
RANOS
GSMOSS
SGSN
GGSN
BSC
MGw
MGw
MSC
Server
GMSC
Server
Internet/
Intranets
Internet/
Intranets
PSTN/
ISDN/
PLMN
PSTN/
ISDN/
PLMN
IP
R
I
P
R
IP
R
RNC
SGSN
GGSN
BSC
MGw
MGw
MSC
Server
GMSC
Server
Internet/
Intranets
Internet/
Intranets
PSTN/
ISDN/
PLMN
PSTN/
ISDN/
PLMN
IP
R
I
P
R
IP
R
RNC
HLR/AUC/FNR
GSM RAN
WCDMA RAN
WCDMA Core Network Overview
Network 1
Network 2 MGW
Handles payload,
processing traffic and
signaling interworking
between networks
Payload Format 1
Transport Type 1
Signaling 1
Payload Format 2
Transport Type 2
Signaling 2
What does a MGW do?
Media Gateway
Inter-working between different transport technologies (TDM, ATM
and IP bearer).
Media Stream handling (Speech Coder, Echo Canceller, Multi-Party
call, Tone Sender, DTMF sender/receiver, Interactive Messaging,
Code Answer and Tone Sender (CAT), Continuity Check)
Adapting the circuit-switched data services in WCDMA and GSM.
Signaling bearer conversion at the network edges in order to allow
unified signaling bearers to be used within the core network.
Supporting Radio Access Network interfaces.
Routing and switching.
Element Management.
Serving GPRS Support Node
(SGSN)
Session and mobility management (paging, attach, detach, Packet
Data Protocol (PDP) context handling, intra- and inter-SGSN routing
area update).
Payload Handling
Security includes features such as user and network authentication
and data confidentiality through ciphering.
CDR based charging includes functions for collecting charging
information from various sources within the SGSN
CAMEL based charging provides a real-time charging mechanism
Configuration management functions that support definition and
handling of logical relations with other network elements
SMS over GPRS
Support for SS7 signaling.
Gateway GPRS Support Node
(GGSN)
Tunnel management
IP-address management
Charging data collection/output
Security management
Packet filtering
Packet routing / forwarding
QOS management
Element management
MSC Server
Circuit based connection management i.e. traffic
control, roaming, call routing and handover.
Media Gateway Control
Mobility Management
Authentication
Charging data collection/output
Supporting a comprehensive set of Supplementary
Services that complement and modify the Tele-
services and Bearer Services.
IN and CAMEL Services
Security and Fraud
UUU U M+ M WUE 4 4 U } } + ]=
* UUU U M+ M UE4ME C U M 4 4U E =} } } = - } } ] +
M 4 4E M 4 4UCE ECC4 4 E M } }- ]+ ] + -} ] +] + }
+ 4 UE E 4 4 E44 E +]} + =+ + } + ]= + }
+ MEC 4U EM CO U CE 4U C C + } } } + + ^} }
4 E 4 E C C 4 M+ U * UUU - ] }] + ^} } } +]} =}
U M+ M EMU EU4 4 E 4 4 UUU U } } + ] ] + + = =}
UUU W UUU
* UUU W UUU UE4ME C U M 4 4U E =} = - } } ] +
M 4 4E M 4 4UCE ECC4 4 E } }- ]+ ] + -} ] +] + }
M+ 4 U 4 U +]} + =+ +] + =+ +]
UUU UM 4 44M 4EMU EM CO U ]=+ }] } }- } } }
CE 4U C C 4 E 4 E C + + ^} } - ] }] + ^}
C 4 M+ U } } +]}
4 U UUU U M+ M W UUU U M+ } } } }
MU }
* C 4 4 E E UUU M+ M EM ME44 =} + ] + } } + +
4E CE 4 M M U E 4 ^ ] + } ] +} + + ^
ME44 EMC 4 E MEC 4 4 M M C + ^ + + =} ] +}
<U
UE U 4 U WUUU UU + } }-+ }
* UUU U E 4 4 UE UEM 4EMU 4 =} ] }] =} + } } } + =
4 M 4EMU 4 UU UU UU < E U } } } ]= - -+ ]
4EMUU UU* 4EMU EM E4 M UE 4 ]} } } =} + } }
EMU 4 UUU EMU EU4 4 E 4 4 UU =} + ] ] + + = =}
U U M+ M WUE 4 4 UU } } + ]=
U M+ U<U U4OOEM4 E W } + ^ -}
U UU
* U U OME+ U E CE 4U C =} +-} } + - + + ^}
C 4 WO U 44 U 4 4 UME4E E } ^+ ^ ]= -} ]= ]
U E4 4 U 4M U 4 MUU U ME4 ] } = - + ^ + - + }
4 M 4O 4 UU * U U 4OOEM4 O UU 4 + ^ } - } =} ] }
M+ EM 4 UU < E U 4EMU 4 } +]} =} -+ ]]} } -
U U U 4OOEM4 O U 4 M+ EM 4 UU UU =} ] }} + ]} =}
< E U 4EMUU -+ ]]} }
4 U U<U U4OOEM4 E } -}
W UU
The GGSN provides an interface between mobile radio core networks (GSM
and WCDMA) and other packet data networks, such as the Internet,
corporate intranets, and private data networks.
EC CE 4 E < 4 M W } ] + }^+ }
C<U
EC CE 4 E < 4 M W C<U M+ 4 } ] + }^+ } } } =}
OM C MU 4 E 4 M M EMC 4 E + - } ] +} + +
4 4E OME+ E4ME 4 }- +-} ] - + } +^}
4 4 UUU U<U UU UU U 4EMUU ]} + =+ =} - }
* C< C CE 4 M OME =} ^} + } ] +} + }
4 M M E 4 E 4 + } ] +} ] + - ] + +
4UU E 4OO C 4 MU M+ - = - } } } } +]}
U
U44 4 4 E U 4M WU =} +] + } }
UU
* U44 4 4 E U 4M WUUU E4 =} =} +] + } } ] +
4 4 E EM 4M 4EM E + 4 ] + }] } ^} + -+ +-
4 M M 4 M U UU UU E ] +} +-} ++} - }
4 EM 4 C MU EM M + ] -} ^ + = }]} ^} }
4 44 4 4 E O M 4 + ^ =} +] + - ]+ =} + ^ -
E 4 4 M M U UU * 44 4 }- =} ] +} } =} =} +
4 E O M 4 U OME+ U 4 ] + - ]+ =} + ^ - +-}-
UU 4OE M O4 4U M 4 U M 4 =} } } } }- -+} }
4EMU C 4 4E OME4 4 4 4EMUU } } } } }] =} }
4 M EO M 4EM 4 4 44 EM } - } ^+ = +#}-
4 E 4 U4 CU } =} }
UO4 OC 4 U 4 4U < + } -} + }^+
4 M WUU<U }
* UU< 4 + 4 CE O4 OC =} - } +- } + } } +
4 M M 4 4UU * UUU M O4 4 } = - } +-} + =} ] } }
4 UU< 4E U UU 4E EM =} ]=}] + = }} }
44U W U 4 UU E4 4UO UU OOME+ + ] + }- }
W M U 4 UU EMC M 4 M W 4 }- ^ + }- }^+ } }- =+
4 UU EM 4UEU } + }-
4C M < 4 M } + } } }^+ }
W <U
* < E E MU =} -} }
Mobile Number Portability (MNP): This feature permits an end-user to keep
his MSISDN identity when changing service provider or moving subscription
between two service domains within the same country.
Flexible Allocation of MSISDN for the GSM and WCDMA networks. This
feature provides mobile operators with free allocation of subscription
identity without considering the relation between MSISDN and IMSI series
in the HLR.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- AAU5339w Technical Specifications (V100R015C10 - 01) (PDF) - ENDokument25 SeitenAAU5339w Technical Specifications (V100R015C10 - 01) (PDF) - ENlilith137933% (3)
- Amr (Ran19.1 03)Dokument669 SeitenAmr (Ran19.1 03)anthonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- About Helios TelecomDokument29 SeitenAbout Helios Telecomehab1976Noch keine Bewertungen
- UMTS ChannelsDokument5 SeitenUMTS ChannelsNeoRa Ndivo Rams100% (1)
- 3 - LTE - FDD - TDD - Link - Budget - TrainingDokument110 Seiten3 - LTE - FDD - TDD - Link - Budget - TrainingKhalid Waleed KhaleelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of Wireless CommunicationDokument71 SeitenEvolution of Wireless CommunicationvmspraneethNoch keine Bewertungen
- ဖုန်းပြုပြင်နည်းDokument214 Seitenဖုန်းပြုပြင်နည်းk56511953Noch keine Bewertungen
- EVOLUTION OF CELLULAR NETWORKS FROM 1G TO 5GDokument24 SeitenEVOLUTION OF CELLULAR NETWORKS FROM 1G TO 5GAneesh ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoll Vs Planet PDF FreeDokument4 SeitenAtoll Vs Planet PDF FreeAmjad MsoukerNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF-R586 User Manual EngDokument124 SeitenRF-R586 User Manual EngRadosław RatyńskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parameter Name Meaning Feature Name Actual Value Range UnitDokument23 SeitenParameter Name Meaning Feature Name Actual Value Range UnitVarun V MaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
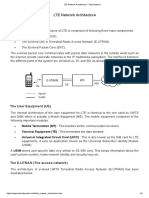
- LTE Network Architecture - TutorialspointDokument4 SeitenLTE Network Architecture - TutorialspointChristopher AiyapiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uc20 STK: AT Commands ManualDokument40 SeitenUc20 STK: AT Commands ManualsilvinorobertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alta Telecom Resume FormatDokument3 SeitenAlta Telecom Resume Formatmaddymad52Noch keine Bewertungen
- JDSU Drive Test SetupDokument22 SeitenJDSU Drive Test SetupashokrvnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part8Dokument45 SeitenCellular Network Planning and Optimization Part8Watchrara BoonyodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDokument129 SeitenDigital Modulation Techniquessit nurhamizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tlte FDD TTDDokument5 SeitenTlte FDD TTDpapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5G Seminar Report on "5G Wireless SystemDokument32 Seiten5G Seminar Report on "5G Wireless SystemNATIONAL XEROXNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZXSDR R8852E Product DescriptionDokument19 SeitenZXSDR R8852E Product DescriptionMuh IkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- HL15 Module-1 Radio Optimization Guideline, KPI OverviewDokument70 SeitenHL15 Module-1 Radio Optimization Guideline, KPI OverviewprakashbaranwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tems Tutorial 13Dokument8 SeitenTems Tutorial 13William HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual V.3: by Wilysis, IncDokument30 SeitenManual V.3: by Wilysis, IncChik LienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Umts Call FlowDokument4 SeitenComplete Umts Call FlowDavid ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 PKI Flyer Jamming Systems 2015Dokument20 Seiten2 PKI Flyer Jamming Systems 2015Falanta SandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nokia Flexi EDGE Base Station DatasheetDokument6 SeitenNokia Flexi EDGE Base Station Datasheetrogeriomb1972Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit V - Wireless and Mobile Technologies and Protocols and Their Performance EvaluationDokument75 SeitenUnit V - Wireless and Mobile Technologies and Protocols and Their Performance EvaluationShreya MankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Network Basics: Cell Phones Operate in This Frequency Range (Note The Logarithmic Scale)Dokument36 SeitenCellular Network Basics: Cell Phones Operate in This Frequency Range (Note The Logarithmic Scale)Ashley MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Handovers PDFDokument92 SeitenLTE Handovers PDFAlfredo LevaNoch keine Bewertungen