Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Analysis of Physical Properties of Urine
Hochgeladen von
ameerabestOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Analysis of Physical Properties of Urine
Hochgeladen von
ameerabestCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
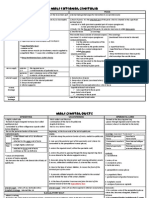
ANALYSIS OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF URINE Properties Normal state Volume - 1 -1.
5 liters/day - depends on : Water intake External temperature Diet Mental state Physical state Condition Physiological Pathological (polyuria) Physiological Pathological (oligouria) Anuria Level - winter, after excessive fluid intake - nervousness, excitement - diabetes mellitus (up to 5L/day) > 3L/day - diabetes insipidus (10-15L/day) - hyperparathyroidism - summer (dt sweating) - fasting / restricted fluis in diet - acute nephritis, HF, shock, burns, after <200ml/day hemorrhage -during & after vomiting & diarrhoea - late stages of renal & heart failure No urine > 2 L/day
acute RF can fall to zero moderate RF may (dt overfunction of normal nephrons) chronic RF - diminished
Colour
- amber yellow - dt the presence of urobilin / uribilinogen /other peptides
Odour
- uriniferous odour (normal aromatic odour) - acidic (pH 6) - depends on ratio of acid phosphate & alkaline phosphate - kidney mainly excretes acid to preserve the alkali clear (transparent)
Reaction
diabetes insipidus colourless/ pale yellow fever deep orange obstructive jaundice greenish (dt presence of cholebolirubin) hemorrhage in UT reddish brown alkaptonuria black (dt presence of oxidized homogenistic acid) ingestion of food containing dyes or coloured drug 1. different types of food : cabbage, onion, garlic 2. severe uncontrolled DM fruity odour (dt presence of acetone / acetoacetic acid) 3. putrefaction (dt bacterial growth in case of UTI) acidic dt excretion of excess phosphate & high protein diet (Lion urine) sulphate vegetable & alkaline dt Na & K content with excretion of fruit (horse urine) Na & K bicarbonate in urine an hour after meal on standing alkaline (alkaline tide) dt precipitation of muco- & nucleoproteins & epithelial cells turbid, opaque dt presence of albumin good medium for bacterial growth as its pH becomes alkaline precipitation of phosphate urates, oxalates, triple phosphate albuminoid substance released from epithelial/white cells in case of glomerulo-nephritits cloudy
Aspect
exposed urine Deposits devoid of deposits! *centrifugation
Specific gravity
- 1.015 1.025 - depends on water balance of the body & electrolyte balance -varies inversely with urine volume
crystals casts cells parasitic ova pus cells / RBCs diabetes insipidus (low) fever (high) diabetes mellitus haemodilution dehydration diseased kidney
1.004 > 1.030 (dt small volume of urine) 1.40 (dt presence of glucose) 1.002-1.003 1.025 / more lose power to concentrate/dilute urine
Test for specific gravity WATER DIURESIS TEST (Dilution test) 1. subject evacuates his bladder 2. drinks 1.5 liter of water 3. urine is collected every 1 hour for 5 hours 4. volume and specific gravity of each sample is determined - normally, urine volume after 5 hours must be >800 ml & specific gravity is <1010 - if the function of distal tubules is impared diuresis does not occur & specific gravity does not drop below 1010. WATER CONCENTRATION TEST 1. subject evacuates his bladder 2. prevented from taking fluids for 10-12 hours to produce dehydration 3. at the end of 12 hours, urine sample is taken & specific gravity is measured -normally, specific gravity should rise to 1025 - if with dehydration, the specific gravity remains below 1020 it indicates impairment in the function of loop of Henle & distal tubule
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Katz Index ADLDokument5 SeitenKatz Index ADLsaliansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Info-UT Unhelpful ThinkingDokument1 SeiteInfo-UT Unhelpful ThinkingMirjam LipstokNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM Lec Chemical Examination of UrineDokument50 SeitenCM Lec Chemical Examination of UrineThea MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLINICAL CHEMISTRY: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandCLINICAL CHEMISTRY: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hem311 Week 13 Lab - Reticulocyte CountDokument32 SeitenHem311 Week 13 Lab - Reticulocyte CountSheine EspinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacte TestDokument10 SeitenBacte TestRiondalionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification of Normal and Abnormal Forms of RedDokument32 SeitenIdentification of Normal and Abnormal Forms of RedNada hasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urine Specimen Collection: Ms. Sneha SehrawatDokument36 SeitenUrine Specimen Collection: Ms. Sneha SehrawatRajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinalysis and Body Fluid CollectionsDokument48 SeitenUrinalysis and Body Fluid CollectionsladydianamacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology II Notes - MagtalasDokument12 SeitenHematology II Notes - MagtalasAbhugz VosotrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUBF Questionnaires PDFDokument101 SeitenAUBF Questionnaires PDFDF DasallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coagulation NotesDokument14 SeitenCoagulation NotesthrowawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- RBCDokument66 SeitenRBCFarah mansourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Microscopy (Analysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids)Dokument14 SeitenClinical Microscopy (Analysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids)Jeanly DoctorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology 2 TEST QUESTIONSDokument4 SeitenHematology 2 TEST QUESTIONSa a r o n b a u t i s t aNoch keine Bewertungen
- UrinalysisDokument36 SeitenUrinalysisMarl EstradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC1 - Topic 1Dokument11 SeitenCC1 - Topic 1Marie MontemarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stool Exam - Routine, Conc. Method - Students'Dokument27 SeitenStool Exam - Routine, Conc. Method - Students'AnastasiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology BMLS 103Dokument88 SeitenHematology BMLS 103harpreetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semen AnalysisDokument3 SeitenSemen Analysisameerabest80% (5)
- Example Semen Analysis Report July 2019Dokument3 SeitenExample Semen Analysis Report July 2019Shahid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix ReimprintingDokument2 SeitenMatrix ReimprintingFedericoz ZarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of Coagulation and Thrombosis NotesDokument16 SeitenDisorders of Coagulation and Thrombosis NotesleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Smear Examination 1معدل Dokument74 SeitenBlood Smear Examination 1معدل Kenesa100% (1)
- Clinical MicrosDokument26 SeitenClinical MicrosDarla YsavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEMOSTASIS Coagulation PathwayDokument3 SeitenHEMOSTASIS Coagulation PathwayGianna SablanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urine AnalysisDokument69 SeitenUrine AnalysisAffan ElahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Banking Course BookDokument2 SeitenBlood Banking Course BookShukr Wesman BlbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDokument5 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanCamille Serrano100% (1)
- 68th AACC Annual Scientific Meeting Abstract eBookVon Everand68th AACC Annual Scientific Meeting Abstract eBookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gel TechnologyDokument2 SeitenGel TechnologyJai Carungay100% (1)
- Basic Clinical Chemistry TestsDokument49 SeitenBasic Clinical Chemistry TestsMegbaru100% (1)
- Microscopic Examination of UrineDokument4 SeitenMicroscopic Examination of UrineGlaiza Erika Baes GudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Chemical Examination of UrineDokument82 Seiten3 Chemical Examination of UrineJake Real Dela RocaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Diagnostic MycologyDokument78 Seiten02 Diagnostic MycologyNilda Quitquitan PatriarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Blood: RBC Platelet HemostasisDokument89 SeitenChapter Blood: RBC Platelet Hemostasisapi-19916399100% (1)
- Agglutination, Complement, Neutralization, and Inhibition: Methods in Immunology and Immunochemistry, Vol. 4Von EverandAgglutination, Complement, Neutralization, and Inhibition: Methods in Immunology and Immunochemistry, Vol. 4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Top 10 AnemiasDokument24 SeitenTop 10 AnemiasSim M ChangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Analytical Considerations in PhlebotomyDokument56 SeitenPre-Analytical Considerations in PhlebotomyAngel joyce ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination of UrineDokument7 SeitenExamination of UrineDaniel LamasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypnosis and Deep Relaxation in Static ApneaDokument16 SeitenHypnosis and Deep Relaxation in Static ApneaMichael LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSMLS Exam Guide Notes (Referrence Range)Dokument4 SeitenCSMLS Exam Guide Notes (Referrence Range)software4us.2023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Urinalysis and Body Fluids2020Dokument47 SeitenUrinalysis and Body Fluids2020MONFOLA100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Urinalysis: Urine CompositionDokument74 SeitenChapter 1: Introduction To Urinalysis: Urine CompositionMegumi TadokoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Examination of Urine SummaryDokument3 SeitenPhysical Examination of Urine SummaryBiancake Sta. AnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coagulation CascadeDokument4 SeitenCoagulation CascadezainabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Stack - ASCP Coag Hematology Table ReviewDokument2 SeitenStudy Stack - ASCP Coag Hematology Table Review장주연Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clearance and GFR: Major DR Arabinda Mohan Bhattarai Lecturer (Biochemistry), NAIHSDokument25 SeitenClearance and GFR: Major DR Arabinda Mohan Bhattarai Lecturer (Biochemistry), NAIHSChandan SahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aubf Lab Types of Urine SpecimenDokument18 SeitenAubf Lab Types of Urine SpecimenNerizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Introduction To Urinalysis PDFDokument4 SeitenChapter 2 Introduction To Urinalysis PDFJulie Anne Soro ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacteriology Laboratory OrganizationDokument65 SeitenBacteriology Laboratory Organizationtummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- HemaDokument59 SeitenHemaSteph VeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coombs TestDokument11 SeitenCoombs TestunilabreynosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Red Cell and White Cell Counting, BloodDokument89 SeitenRed Cell and White Cell Counting, BloodJovel GangcuangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology 2 Topic 2 Prelim2222Dokument73 SeitenHematology 2 Topic 2 Prelim2222Mary Lyka ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Renal FunctionDokument5 Seiten1 Renal FunctionChristopher BucuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decalcification ReviewerDokument4 SeitenDecalcification ReviewerKD Nudo0% (1)
- Clinical Laboratories: Standard Operating ProceduresDokument71 SeitenClinical Laboratories: Standard Operating ProceduresKirt AnonuevoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14 - Routine and Point of Care Testing in HematologyDokument10 SeitenChapter 14 - Routine and Point of Care Testing in HematologyNathaniel Sim100% (1)
- A. B. C. A. B. C. D.: Clinical Chemistry II - Prelims (Bandala)Dokument19 SeitenA. B. C. A. B. C. D.: Clinical Chemistry II - Prelims (Bandala)IceNoch keine Bewertungen
- M6 Histopath ImpregantionAndEmbeddingDokument4 SeitenM6 Histopath ImpregantionAndEmbeddingninaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Four: Chemical Analysis of UrineDokument174 SeitenChapter Four: Chemical Analysis of UrineRebuma BeleteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of Errors in Clinical ChemistryDokument9 SeitenSources of Errors in Clinical Chemistrykalantan23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wintrobe Test PDFDokument9 SeitenWintrobe Test PDFMaria Chacón CarbajalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBCDokument12 SeitenCBCDaNa Al-jomah100% (1)
- E.coli, Klebsiella, Proteus EtcDokument3 SeitenE.coli, Klebsiella, Proteus EtcameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cme Bronchial AsthmaDokument28 SeitenCme Bronchial AsthmaameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeDokument3 Seiten@acute Nephritic Syndromeameerabest100% (1)
- @acute Nephrotic SyndromeDokument1 Seite@acute Nephrotic SyndromeameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @ductal CarcinomaDokument1 Seite@ductal CarcinomaameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burn LectureDokument53 SeitenBurn LectureHusna NadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- @sex SteroidsDokument2 Seiten@sex SteroidsameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @hypothalamic HormonesDokument1 Seite@hypothalamic HormonesameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @contraceptives DrugsDokument1 Seite@contraceptives DrugsameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @drugs Acting On Uterus and Erectile DysfunctionDokument2 Seiten@drugs Acting On Uterus and Erectile DysfunctionameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @histology of Male Genital SystemDokument6 Seiten@histology of Male Genital SystemameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genital EmbryologyDokument6 SeitenGenital EmbryologyameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDokument2 Seiten@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @tumors of The Breast 1Dokument2 Seiten@tumors of The Breast 1ameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of Male GenitaliaDokument4 SeitenAnatomy of Male GenitaliaameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @ovarian Tumors ComparisonDokument6 Seiten@ovarian Tumors ComparisonameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDokument2 Seiten@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @male PathoDokument8 Seiten@male Pathoameerabest100% (2)
- Genitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFDokument7 SeitenGenitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFameerabest100% (1)
- Patho Male BreastDokument1 SeitePatho Male BreastameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology Female PDFDokument5 SeitenHistology Female PDFameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFDokument7 SeitenGenitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFameerabest100% (1)
- @non Neoplastic Non Inflammatory Lesions of The BreastDokument2 Seiten@non Neoplastic Non Inflammatory Lesions of The BreastameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nota Patho PDFDokument8 SeitenNota Patho PDFameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSCE DermaDokument8 SeitenOSCE DermaameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac ExamDokument7 SeitenCardiac ExamameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- #Chest TraumasDokument4 Seiten#Chest Traumasameerabest100% (3)
- Virology of Hepatitis ADokument33 SeitenVirology of Hepatitis AameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- PleuraDokument6 SeitenPleuraameerabest100% (1)
- Lot - 1 Weekly Progress Report (11th)Dokument27 SeitenLot - 1 Weekly Progress Report (11th)Mesfin DerbewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otorhinolaryngology: Therapeutic Approach To Pediatric Acute Mastoiditis - An UpdateDokument9 SeitenOtorhinolaryngology: Therapeutic Approach To Pediatric Acute Mastoiditis - An UpdateImelda LieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vergo 16: Betahistine Dihydrochloride Tablet 16 MGDokument4 SeitenVergo 16: Betahistine Dihydrochloride Tablet 16 MGmegha_okztNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP8 Lecture 2Dokument33 SeitenAP8 Lecture 2Christian MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and Controlling of Milk Fermentation Process Thesis - 2Dokument50 SeitenModeling and Controlling of Milk Fermentation Process Thesis - 2ajithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying and Correcting Blocked Learning Gates1Dokument4 SeitenIdentifying and Correcting Blocked Learning Gates1ramaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure PDFDokument16 SeitenBrochure PDFFebinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quizlet EndoDokument17 SeitenQuizlet EndoemmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure - Muscle Flexibility and StretchingDokument5 SeitenProcedure - Muscle Flexibility and StretchingShrutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Gambar Diagonsis Penyakit MulutDokument48 SeitenLatihan Gambar Diagonsis Penyakit MulutBefalia AisarahmadaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- B32C08 Lab Report ProformaDokument13 SeitenB32C08 Lab Report Proformajtoh22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research JournalDokument8 SeitenResearch Journalmarianne pudaderaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preprosthetic SurgeryDokument4 SeitenPreprosthetic SurgeryDentist HereNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADokument3 SeitenAtheanuuradha1993gmaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0009 Rheumatology Notes 2015 PDFDokument56 Seiten0009 Rheumatology Notes 2015 PDFMuhammad HaneefNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConstipationDokument11 SeitenConstipationAsma SikanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adverse Event TemplateDokument5 SeitenAdverse Event TemplateGocThuGianNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-PULMO - (LEE-TAN-CONSTANTINO) - Prelims (TD) B - Pulmo - (Lee-Tan-Constantino) - PrelimsDokument17 SeitenA-PULMO - (LEE-TAN-CONSTANTINO) - Prelims (TD) B - Pulmo - (Lee-Tan-Constantino) - PrelimsJohn Paulo CatacutanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Insallburstein Posterior Stabilized Condylar Knee ProsthesisDokument8 SeitenThe Insallburstein Posterior Stabilized Condylar Knee ProsthesisGERARDO TORRES RUIZNoch keine Bewertungen
- USPI-Zithromax - Azithromycin - IVDokument22 SeitenUSPI-Zithromax - Azithromycin - IVTufail AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slipped Capital Femoral EpiphysisDokument17 SeitenSlipped Capital Femoral EpiphysisElvisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btl-Physio Cat En202Dokument56 SeitenBtl-Physio Cat En202avaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glasgow-Lanarkshire-Scotland: The Future For Searl Technology LTD in Manufacturing Lies in Added Value and InnovatingDokument50 SeitenGlasgow-Lanarkshire-Scotland: The Future For Searl Technology LTD in Manufacturing Lies in Added Value and InnovatingSamuel KinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 201305283en Capsurefix 5076Dokument2 Seiten201305283en Capsurefix 5076Bian PurwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Product Information On IngredientsDokument6 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Product Information On IngredientsukalNoch keine Bewertungen