Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Blood Circulation and Transport Module
Hochgeladen von
SENSOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Blood Circulation and Transport Module
Hochgeladen von
SENSCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
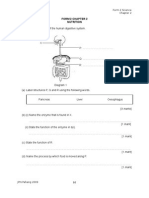
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE Chapter 2: . Blood Circulation and Transport 2.1 Understanding the transport system in human 1.
Label the diagram of the heart by using the words given below. Left ventricle Right ventricle Aorta Tricuspid valve Pulmonary artery Left atrium Vena cava Right atrium Semilunar valves Pulmonary vein Bicuspid valve
2. Three types of valve in the heart. Type of valve Tricuspid Function
Bicuspid
Semilunar
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE 3. Blood vessels are tube in the body that channel blood. Four blood vessels are connected to the heart. Type of blood vessel Vena cava Function
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary vein
Aorta
4. Complete the table below to shows the comparison between the atriums and the ventricle. Atriums Characteristics Function Ventricles
Wall Space
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE 1. Complete the flow chart below to show how blood circulates from the vena cava through the heart, to all parts of the body.
All parts of the body
Lungs
Key:
Blood vessel chamber
valve
Heart
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE 2 a) Compare the blood vessel in the human body Blood capillary Artery Vein
Structure
Function Type of blood carried Rate of blood flow
Thickness
of wall
Lumen size
Existence
of valve Blood pressure
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE 2 b) Name the type of blood vessel J,K and L and type of blood M and N in the following diagram.
3 Figure below shows the blood circulation.
a) Label the blood circulation T and U in the diagram. b) Name the blood vessel i) P : ii) Q : iii) R : iv) S :
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE
4. Comparison between oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood Oxygenated blood Deoxygenated blood
Difference
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
The concentration of digested food (like glucose and amino acid)
Waste products
Blood vessel that carries it
Deoxygenated blood has to be carried to the lungs to change it into oxygenated blood
2.2
HUMAN BLOOD 6
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE 1. Human blood consists of two components: (a) plasma (55%) (b) blood cells (45%) Nutrient Hormones Heat Inorganic ions Plasma (55%) Dissolved gases Waste products Blood cell (455%) Red blood cells (Erythrocytes) White blood cell (Leucocytes) Platelets (Thrombocytes)
2. Write the functions of blood in the following diagram.
FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD
3. Comparing red blood cells, white blood cells abd platelets
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE Characteristics Red blood cells White blood cell Platelets
Diagram
Shape
No fixed shape
Function
Help blood clot
Presence of nucleus
Place of production
Presence of heamoglobin
Presence of cytoplasm
Life span 4. Complate the chart below
Blood group A 1
Can donate blood to 8
Can receive blood from
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE
AB
AB
5. If the donors blood and the recipients blood are not compatible, what will happen to the blood and what are the effects? Donors blood Recipients blood
Are not compatible What will happen to the blood?
.............................. may take place
Cause
Can be ...........................................
2.3 Transport system in plants a. Complete the following chart. TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN PLANT
Stomata
Xylem
Phloem
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE
Function
Transpiration __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ _ The importance
Part
Monocotyledon plant
Dicotyledon plant
Affecting factors 1. 2. 3. 4.
ACTIVITY 1 The apparatus in figure 1 was used in a science activity.
10
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE
FIGURE 1 The following steps were carried out: Step 1 : Two similar hibiscus plants, about 25 cm tall, were selected. Step 2 : The plants were pulled out of the soil and the roots were washed to remove any remaining soil. Step 3 : The plants were trimmed until ten leaves were left on each plant. Step 4 : Each plant was placed in a measuring jug filled with water, and labelled F and G, as shown in the figure above. Step 5 : 10 ml of cooking oil was poured into each jug. Step 6 : A layer of grease was applied to the leaves in G. Step 7 : The plants were placed in the Sun for three hours. The initial and final water levels in both jugs were recorded in the table below. Plant F 75 ml 68 ml Plant G 75ml 75 ml
Initial water level Final water level
(a) Suggest a hypothesis for this experiment.
(b) What are the three variables that are kept constant in this experiment?
(c) Name the variable that (i) is manipulated : (ii) responds :
(d) Name two processes in plants that require the uptake of water from the roots. (e) What conclusion can you draw from this experiment?
11
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE
(f) How is water transported in plants?
(g) Describe the direction in which water is transported in plant
STRUCTURE QUESTIONS 1 Figure 4(a) shows two similar healthy plants in two different pots of the same
12
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE amount of soil and nutrients. The bark of one of the plants is removed, leaving a cut ring. Figure 4(b) shows the cut ring at the initial stage.
Figure 4(a)
Figure 4(b)
(a) Draw a diagram to show the final result of the experiment. Indicate the results on the diagram clearly.
(b) What is the hypothesis of this experiment?
(c) Name the variables stated below: i. constant variable: ii. manipulated variable: iii. responding variable: (d) State the inference for the observation. (e) Make a conclusion for this experiment. (f) Predict the condition of the plant when left uncared for two months. 2 Figure 5 shows the apparatus set up for an experiment
13
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE
(b) Figure 5 The experiment is set up with the following steps. 1. Set up the apparatus as shown in diagram 3 (a) 2. Weigh the apparatus and record its weight 3. Leave the apparatus on a table in a bright room. 4. Repeat step 1 but place the apparatus in a cupboard as shown in diagram 6 (b) in the same room. 5. The weights of the plants and the apparatus are taken hourly. The results of the experiment are shown in table 1 Time of the day 10 am 11 am 12 pm 1 pm 2 pm Weight of the plant and apparatus on a table in a bright room 600 g 590 g 580 g 570 g 560 g Table 1 a) What is the objective of the experiment? __________________________________________________________ Weight of the plant and apparatus place in a cupboard 600 g 595 g 590 g 585 g 580 g
b)
State the variables in the experiment i. ii. iii. Manipulated variable : ______________________________ Responding variable : ______________________________ Constant variable : ______________________________
14
FORM 3 : SCIENCE MODULE c) Based on the result, draw a bar chart to show the weight of the apparatus under different conditions.
d)
Calculate the rate of transpiration based on the result found in Table 1 What conclusion can be made from this experiment? _____________________________________________________________________
f)
State one hypothesis from the experiment. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________
g)
List two other factors which control the rate of transpiration. i. ii. ________________________________________ ________________________________________
15
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Blood Circulation and Transport Learning Objective: 2.1 Understanding The Transport System in HumansDokument14 SeitenBlood Circulation and Transport Learning Objective: 2.1 Understanding The Transport System in HumansJames WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Algebraaic ExpressionsDokument33 SeitenChapter 7 Algebraaic ExpressionsCik Yana100% (3)
- Science Module Form 3 Chapter 4Dokument23 SeitenScience Module Form 3 Chapter 4Hazira HaidzirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4Dokument11 SeitenLatihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4李友志67% (3)
- Additional Science 2010 SPMDokument15 SeitenAdditional Science 2010 SPMArthur JonnesNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Trial Paper 2Dokument21 SeitenSPM Trial Paper 2Tan Suk WanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Matematik Tahun 3 Penilaian 1Dokument5 SeitenSoalan Matematik Tahun 3 Penilaian 1norizan bt awang100% (2)
- Sce Form 2Dokument22 SeitenSce Form 2williamkong123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Form 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsDokument11 SeitenForm 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsCheah Foo Kit50% (2)
- Modul F2 Science C2Dokument14 SeitenModul F2 Science C2NorelyanaAli67% (3)
- Answers Math MF2 Chapter 2 (Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube Roots)Dokument2 SeitenAnswers Math MF2 Chapter 2 (Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube Roots)compeil100% (2)
- Chapter 3 MatterDokument8 SeitenChapter 3 Matternaza9775100% (2)
- Form 3 Chapter 8Dokument8 SeitenForm 3 Chapter 8naza9775100% (6)
- Topical Test (Integer) BiDokument1 SeiteTopical Test (Integer) BiRohasniRoslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Algebraic FormulaeDokument12 SeitenChapter 4 Algebraic FormulaeCik Yana50% (2)
- Pt3 Science Seminar ModuleDokument28 SeitenPt3 Science Seminar ModuleSuntharan Muniandy100% (5)
- Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions 1.Dokument2 SeitenChapter 7 Algebraic Expressions 1.cikguanuar89% (9)
- 2012 Math F2 (Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube Roots)Dokument1 Seite2012 Math F2 (Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube Roots)compeilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module Science Pt3Dokument11 SeitenModule Science Pt3lccjane8504Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz f3Dokument10 SeitenQuiz f3Hafizah PakahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gempur PT3 2020Dokument30 SeitenGempur PT3 2020Nur Aisy Raihanah Panicker100% (1)
- Sek Keb Taman Cuepacs Mathematics Year 5 Paper 2 (40 Minutes)Dokument6 SeitenSek Keb Taman Cuepacs Mathematics Year 5 Paper 2 (40 Minutes)Dzul HellmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 1 Chapter 3Dokument7 SeitenScience Form 1 Chapter 3huisinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 5 Science BDokument6 SeitenYear 5 Science Bnorzila adanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2.1 Angles and Lines II, PT3 Practice - PT3 MathematicsDokument9 Seiten1.2.1 Angles and Lines II, PT3 Practice - PT3 MathematicsPrince NeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Linear InequalitiesDokument8 SeitenChapter 7 Linear InequalitiesROSMAWATI BINTI MOHAMED -Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 1 Science Form 2Dokument4 SeitenChap 1 Science Form 2Yobal YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module Chapter 3Dokument31 SeitenModule Chapter 3Azween SabtuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers Math MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)Dokument2 SeitenAnswers Math MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)compeil100% (2)
- MODULE 14 Algebraic Exp Expand Factor Is at IonDokument6 SeitenMODULE 14 Algebraic Exp Expand Factor Is at IonNyai Blorong KetombeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enhancement GravitationDokument5 SeitenEnhancement GravitationCart KartikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module Chapter 1Dokument41 SeitenModule Chapter 1sakinahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 1 Sciences Light and OpticsDokument9 SeitenForm 1 Sciences Light and Opticschaiseng yongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Year 6 (Paper 1)Dokument6 SeitenMathematics Year 6 (Paper 1)s2166980Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Science Form 2Dokument36 SeitenModul Science Form 2Nur Atiah Daud94% (18)
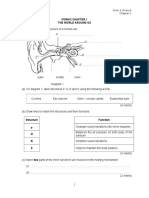
- Form 2 Chapter 1 The World Around UsDokument6 SeitenForm 2 Chapter 1 The World Around UsAnonymous o7B02XWOJpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1Dokument2 SeitenScience Form 3 Chapter 1Mazidah MokhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation PDFDokument4 SeitenScience Form 3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation PDFFarah Sofea Razali91% (11)
- Form 2 Chapter 10Dokument10 SeitenForm 2 Chapter 10naza9775100% (7)
- Science Exercise Year 2Dokument1 SeiteScience Exercise Year 2shahruddin Bin SubariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Sains Unit 2: Life Processes Tahun 4Dokument3 SeitenSoalan Sains Unit 2: Life Processes Tahun 4ika_nikan0% (1)
- KSSM Maths Form 1 Chapter 1Dokument11 SeitenKSSM Maths Form 1 Chapter 1mab3lNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Tuition April Exam (Mathematic Year 1) : Count The Objects and Write The NumbersDokument7 SeitenHome Tuition April Exam (Mathematic Year 1) : Count The Objects and Write The NumbersAnNourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 FractionsDokument2 SeitenChapter 3 Fractionscikguanuar75% (8)
- M012-Consumer Mathematics (Taxation)Dokument5 SeitenM012-Consumer Mathematics (Taxation)Tan Jun YouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 Chapter 2Dokument7 SeitenForm 2 Chapter 2naza977579% (19)
- Soalan Sains Tingkatan 1 Bab 1Dokument10 SeitenSoalan Sains Tingkatan 1 Bab 1Nurul Fairuz HusnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFDokument22 SeitenSoalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFIsmaliza Ishak0% (1)
- Science-Form 3-Chapter 3 Excretion by KelvinDokument10 SeitenScience-Form 3-Chapter 3 Excretion by KelvinKelvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 1 Chapter 3 MatterDokument6 SeitenForm 1 Chapter 3 Matterjj9821100% (1)
- Form 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 5Dokument4 SeitenForm 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 5KelvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul 1 - Form 1 STFDokument31 SeitenModul 1 - Form 1 STFmadrosli100% (3)
- Blood Circulation and Transport ModuleDokument15 SeitenBlood Circulation and Transport ModuleIella's Rashid100% (1)
- This Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsDokument12 SeitenThis Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsKhusyairy Daeng Sailendra0% (1)
- Exercise PDFDokument12 SeitenExercise PDFAmsyidi Asmida100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Cell Structur and Cell Organisation: Form 4Dokument10 SeitenChapter 2: Cell Structur and Cell Organisation: Form 4Siti Rohani Mohd KadriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Examination Paper 1: Photosynthesis. Below Is An Outline of The Procedure The Students UsedDokument4 SeitenSample Examination Paper 1: Photosynthesis. Below Is An Outline of The Procedure The Students UsedCarl Agape DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Junior Lyceum Annual Examinations 2000: Do Not Write in This MarginDokument4 SeitenJunior Lyceum Annual Examinations 2000: Do Not Write in This MarginPui Pui LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- TranspirationDokument4 SeitenTranspirationAini AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Paper 2Dokument13 SeitenBiology Paper 2Aniel DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of BloodDokument14 SeitenComponents of BloodSENS100% (1)
- Collection of TIMSS Released Items Based On KBSM Science Curriculum Themes Form ThreeDokument3 SeitenCollection of TIMSS Released Items Based On KBSM Science Curriculum Themes Form ThreeSENSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 1 Science-Know Your Words (1st Week Activity)Dokument2 SeitenForm 1 Science-Know Your Words (1st Week Activity)SENSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 4Dokument12 SeitenBiology Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 4Ezzad HamdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Livin Pay Plus 2Dokument12 SeitenLivin Pay Plus 2SENSNoch keine Bewertungen
- T3 Bab 8Dokument6 SeitenT3 Bab 8SENSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Had Mata Pelajaran 10 + 2 Mulai SPM 2010Dokument2 SeitenHad Mata Pelajaran 10 + 2 Mulai SPM 2010SENSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Vein Thrombosis Causes and Consequences.4Dokument4 SeitenDeep Vein Thrombosis Causes and Consequences.4zarozeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tinea Fungal Infections - Hoja 1Dokument3 SeitenTinea Fungal Infections - Hoja 1EVELYN MONSERRAT SAPIEN TOBONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public Health Group AssignmentDokument7 SeitenPublic Health Group AssignmentNANNYONGA OLGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Pleomorphic AdenomaDokument4 SeitenPleomorphic AdenomaRobins DhakalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Sadasivan S Iyer Consultant Anaesthesia and Pain ManagementDokument2 SeitenDR Sadasivan S Iyer Consultant Anaesthesia and Pain ManagementMayura D HorakerappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery Solved UHS SeqsDokument46 SeitenSurgery Solved UHS SeqsMuntaha Javed100% (3)
- PacemakerDokument39 SeitenPacemakerb7bkroroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monospot LatexDokument12 SeitenMonospot Latexlai cruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temazepam (Restoril)Dokument1 SeiteTemazepam (Restoril)E100% (2)
- Module 1 Am Activity On Prioritization v2Dokument5 SeitenModule 1 Am Activity On Prioritization v2KeanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCCN HCC For Patients 2020Dokument76 SeitenNCCN HCC For Patients 2020Dona LagurinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Essential Detox Rescue ProtocolDokument15 SeitenYour Essential Detox Rescue Protocolana braga100% (1)
- Spike Protein Detox GuideDokument3 SeitenSpike Protein Detox GuideMauro CabelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADA Glossary Edition 9 2010Dokument87 SeitenADA Glossary Edition 9 2010刘芳妤Noch keine Bewertungen
- Swine Flu InfoDokument20 SeitenSwine Flu InfoUdit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Item Deskription Stok Barang Tersedia 13Dokument12 SeitenItem Deskription Stok Barang Tersedia 13Muhamad Peransyah TasmawisesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dencover ClaimformDokument4 SeitenDencover Claimformd763106Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physiotherapy Management For THR and DHSDokument5 SeitenPhysiotherapy Management For THR and DHSHaris KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 SbarDokument11 Seiten6 Sbarsathish kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anxiety DisorderDokument56 SeitenAnxiety DisorderHafiiz ShafiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enteral and Parenteral RoutesDokument3 SeitenEnteral and Parenteral RoutesKarla Karina Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Report BALRAM SINGHDokument2 SeitenPatient Report BALRAM SINGHNeeraj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC 1-Circ 1598Dokument62 SeitenMSC 1-Circ 1598Lito VertziniNoch keine Bewertungen
- (B-0520) Operating UnitDokument48 Seiten(B-0520) Operating UnitAhmad Gamal Elden MAhanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Prescotts Microbiology 11th Edition Joanne Willey Kathleen Sandman Dorothy WoodDokument29 SeitenTest Bank For Prescotts Microbiology 11th Edition Joanne Willey Kathleen Sandman Dorothy WoodJesseFarrellqojgf100% (22)
- UntitledDokument2 SeitenUntitledAna AlbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- M M Rvaxpro ProspectDokument57 SeitenM M Rvaxpro ProspectNicoleta CiobotarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Update On MRI Safety in Patients With Stents, Prosthetic Heart Valves and Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic DevicesDokument7 SeitenUpdate On MRI Safety in Patients With Stents, Prosthetic Heart Valves and Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic DevicescornealenutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS Sysmex Hematology EIGHTCHECK-3WP - 30jun12-3Dokument4 SeitenMSDS Sysmex Hematology EIGHTCHECK-3WP - 30jun12-3Laboratorium RswkNoch keine Bewertungen